-
Chemical change
When atoms rearrange and the original substance transforms into a different substance (change in composition)
-
Physical change
When atoms in a molecule do not change composition even though they transform from one physical state to another
-
Types of chemical properties (4)
- Corrosiveness
- Flammability
- Acidity
- Toxicity
-
Types of physical properties (6)
- Odor
- Taste
- Color
- Appearance
- Melting/boiling point
- Density
-
Chemical changes occur via ____
Chemical reactions
-
In a balanced equation, the number of each atom/element must be the ___
- Same on both sides
-
When balancing an equation, you change the ____ of the molecules
- Coefficients in front
-
Steps for balancing an equation
1) Balance the atoms/elements that occur the least on either side of the reaction
2) Balance the next atoms/elements that occur the least, and continue with this step
3) Balance compounds first and free elements last
4) If your answer contains fractions, multiply the entire equation by the denominator to clear it
-
Mole-to-mole conversion formula

-
When do you use a mole-to-mole conversion
1) if you're given the moles of 1 reactant and asked to find how many moles of the 2nd reactant is needed to completely react
2) If you're given the moles of 1 reactant and asked to find how many moles of the product will form
-
Gram-to-gram conversion formula
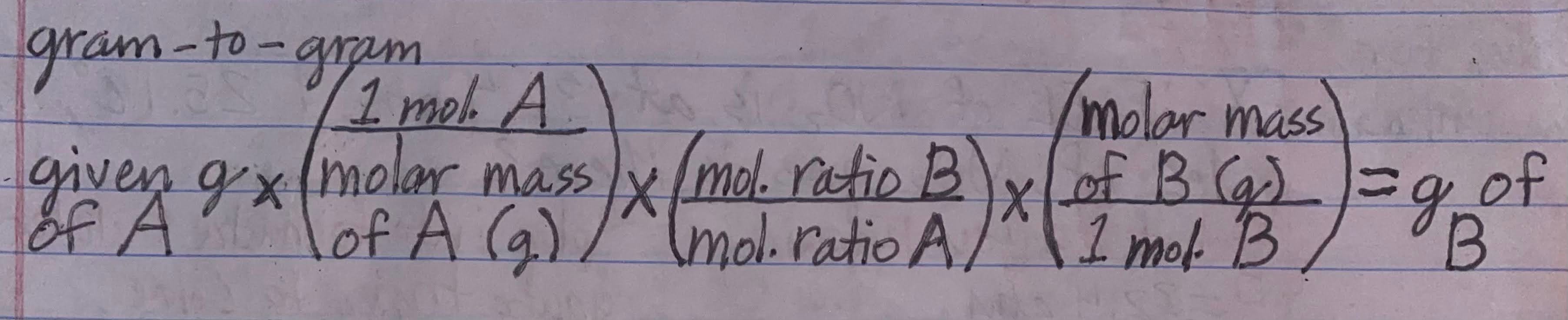
-
When do you use a gram-to-gram conversion
1)If you're given the g of 1 reactant and asked to find how many g of the 2nd reactant are needed to completely react
2) If you're given g of 1 reactant and asked to find how many g of product will form
-
Limiting reactant
The reactant that's completely consumed in a chemical reaction
-
Excess reactant
The reactant with a quantity greater than is needed to completely react with the limiting reactant
-
Theoretical yield
The amount of product that could theoretically be made based on the amount of the limiting reactant
-
Steps (formula used) for determining which reactant is limiting

-
What are the steps (equation used) for determining how much product can be formed from a limiting reactant

1) find/use limiting reactant
2) Use mole to mole or gram to gram conversion of limiting reactant and product to find the product yield
-
Formula for % yield of a reaction
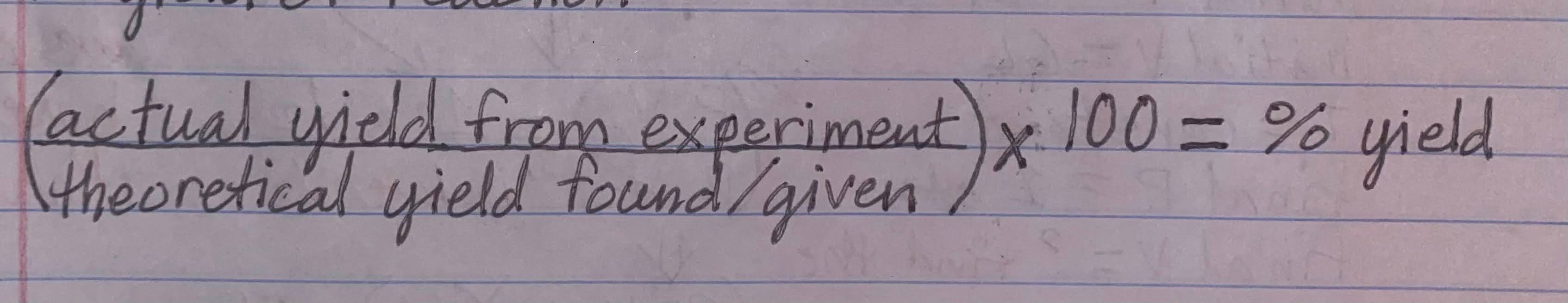
-
Mole-to-gram conversion factor (and vice versa)
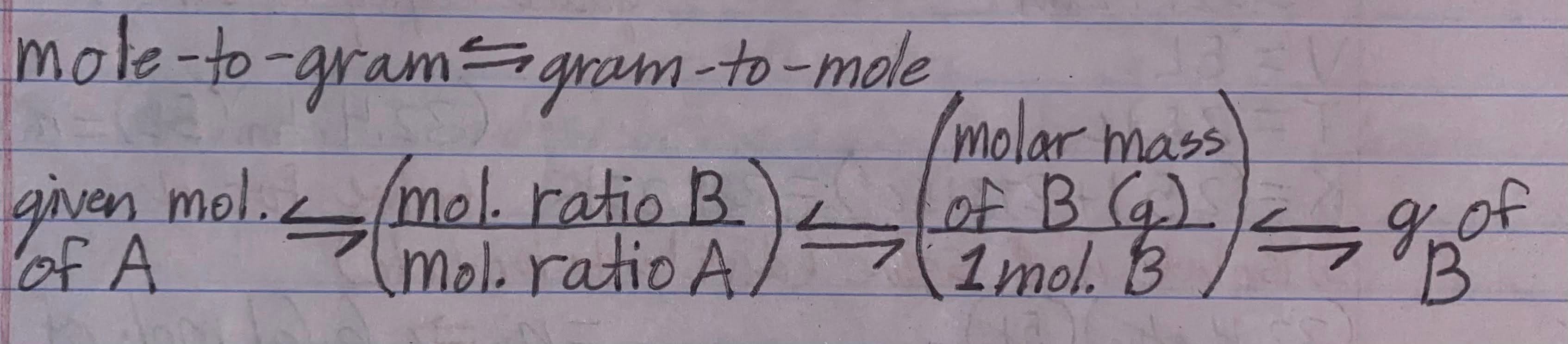
-
When do you use a mole-to-gram conversion
1) If you're given the mole of 1 reactant and asked to find out many g of the 2nd reactant is needed to react completely
2) If you're given the mole of 1 reactant and asked to find how many grams of product will form

