-
_____-_______ _________ ________ __________ _______
_________________________
______________________
Oxidative enzymes
___ ___________ __________ and motor unit strength
_________ __________ ________ and myosin ATPase
Small ________ ________ ________
_____sarcoplasmic reticulum development
Slow-twitch Type 1 slow oxidative fibers
high aerobic capacity
high fatigue resistance
oxidative enzymes
Low anaerobic capacity
slow contractile speed
motor neuron size
low
-
_____-_______ ________ ____ _____ ___________ ________
__________ _________ _________
____________ __________ __________
____________ ___ __________ ________
________ __________ ____________ and motor unit strength
_____ _______________ _______ and myosin ATPase
______ sarcoplasmic reticulum development
Fast-twitch Type IIa fast oxidative glycolytic fibers
moderate aerobic capacity
moderate fatigue resistance
glycolytic and oxidative enzymes
high anaerobic capacity
fast contractile speed
high
-
_____-_____ _______ ___ ___ __________ ______
_________ __________ _________
____ ______ __________
__________ ___________
________ ___________ _________ and motor unit strength
________ _________ __________ and myosin ATPase
____ sarcoplasmic reticulum development
fast-twitch type 2x fast glycolytic fibers
lowest aerobic capacity
low fatigue resistance
glycolytic enzymes
highest anaerobic capacity
fast contractile speed
high
-

force is developed while the muscle is shortening
-


force is generated but the length of the muscle is unchanged
-


force is generated while the muscle is lengthening
-
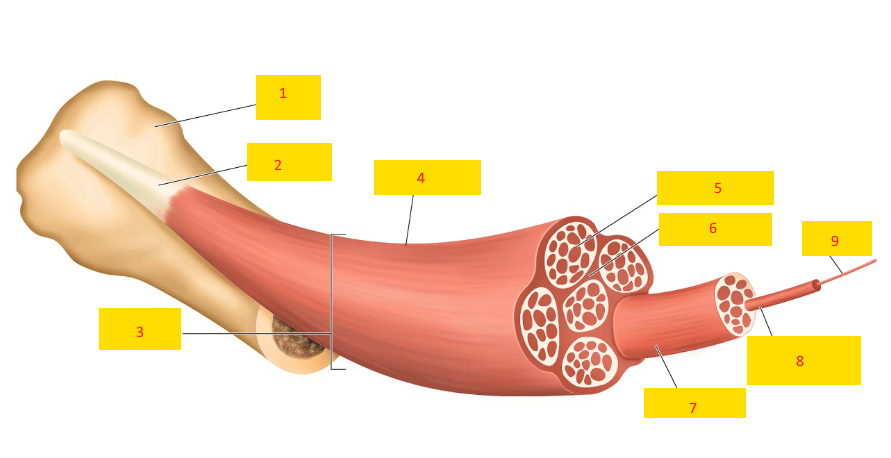
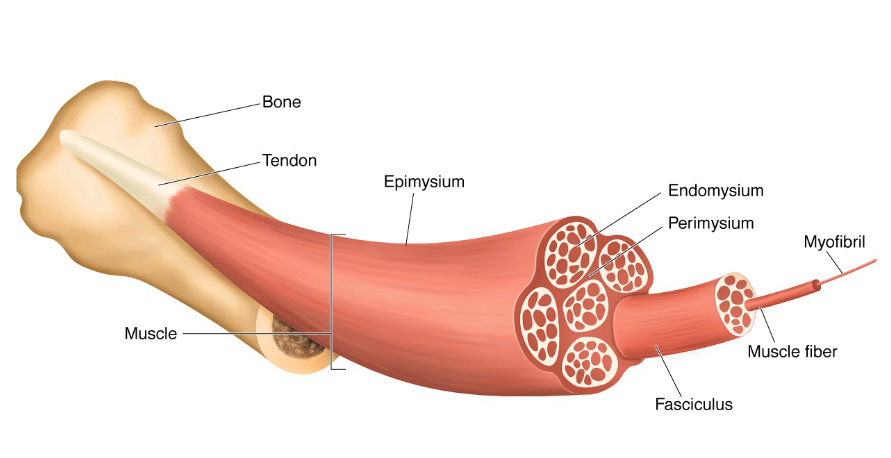
bone
tendon
muscle
epimysium
endomysium
perimysium
fasciculus
muscle fiber
myofibril
-
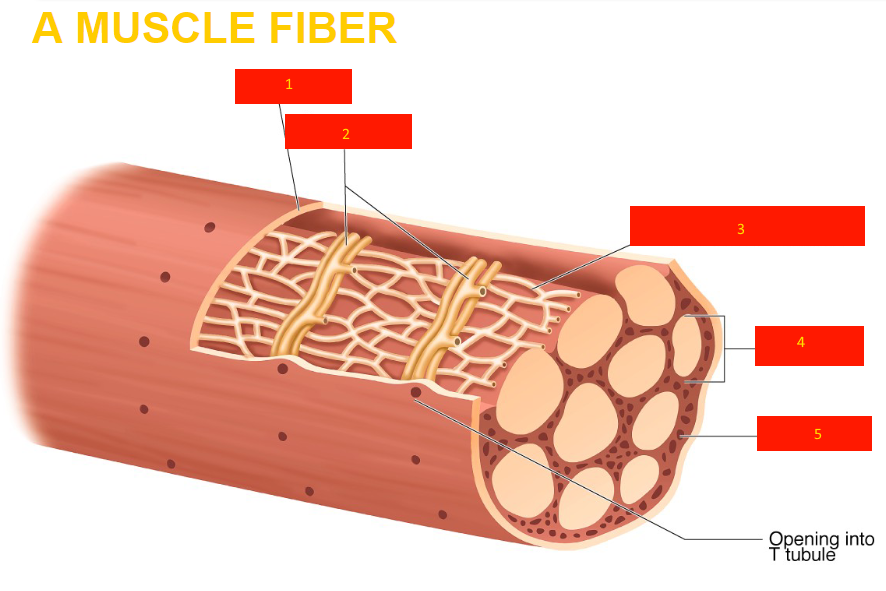
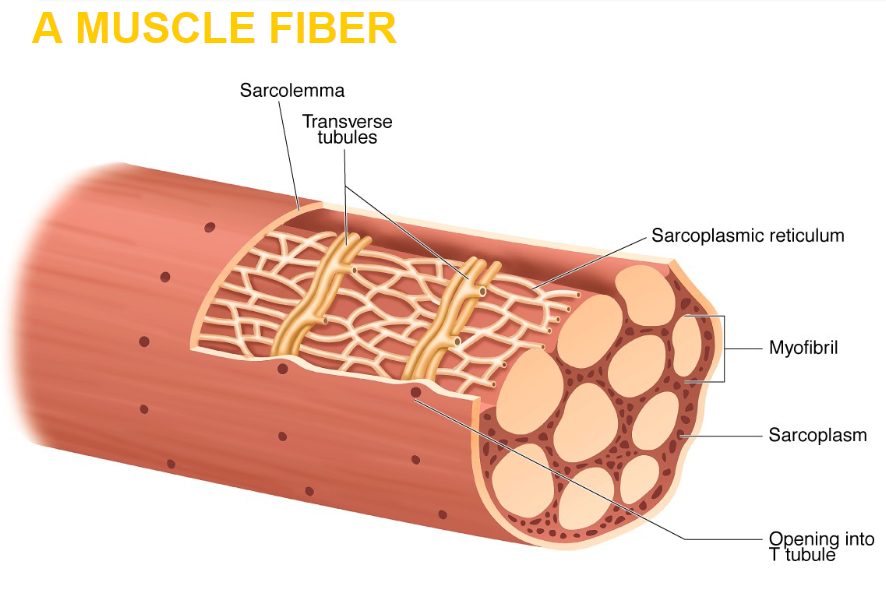
sarcolemma
transverse tubules
sarcoplasmic reticulum
myofibril
sarcoplasm
-
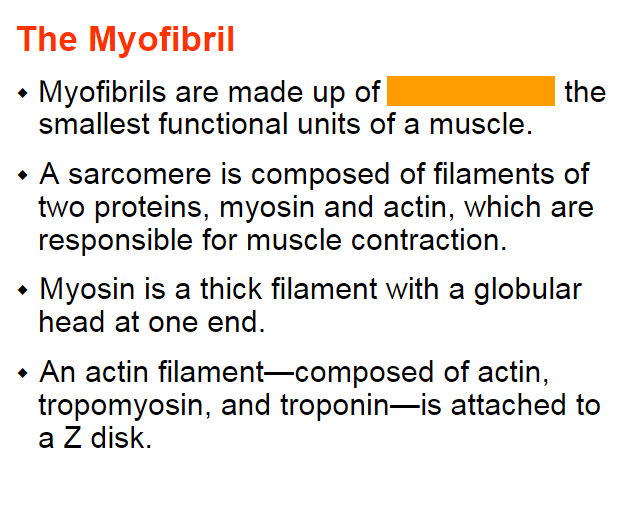
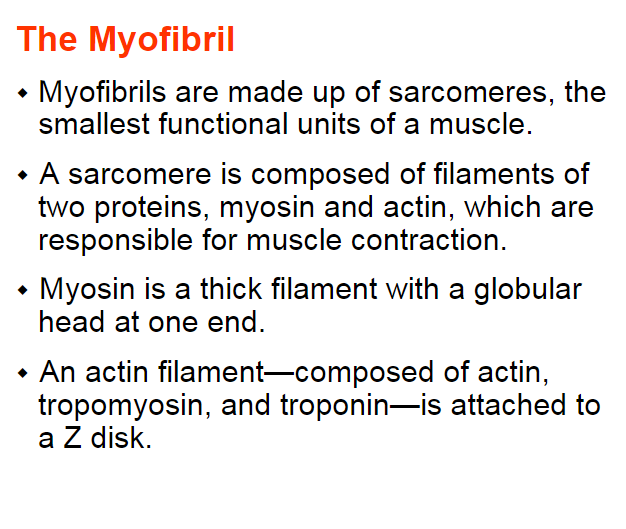
sarcomeres
-
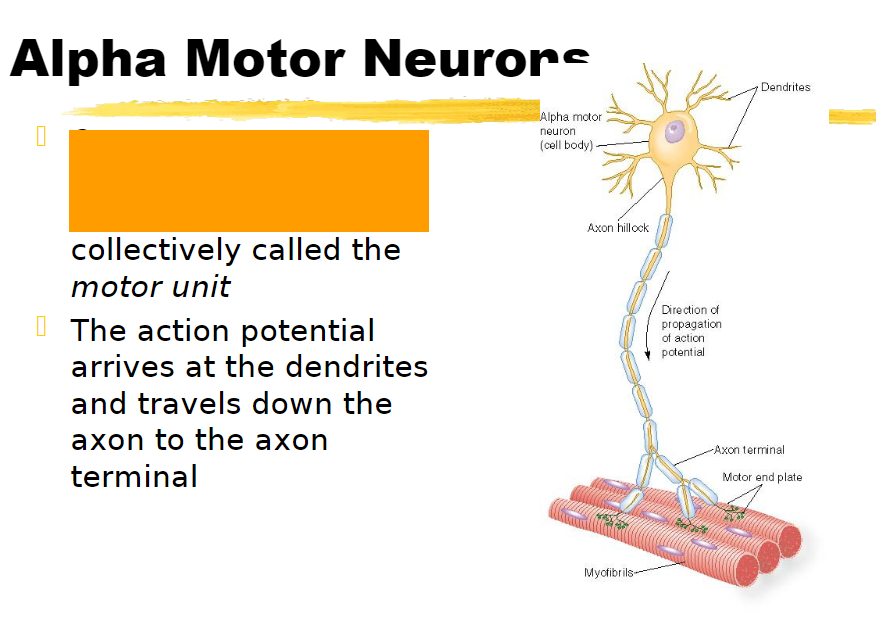
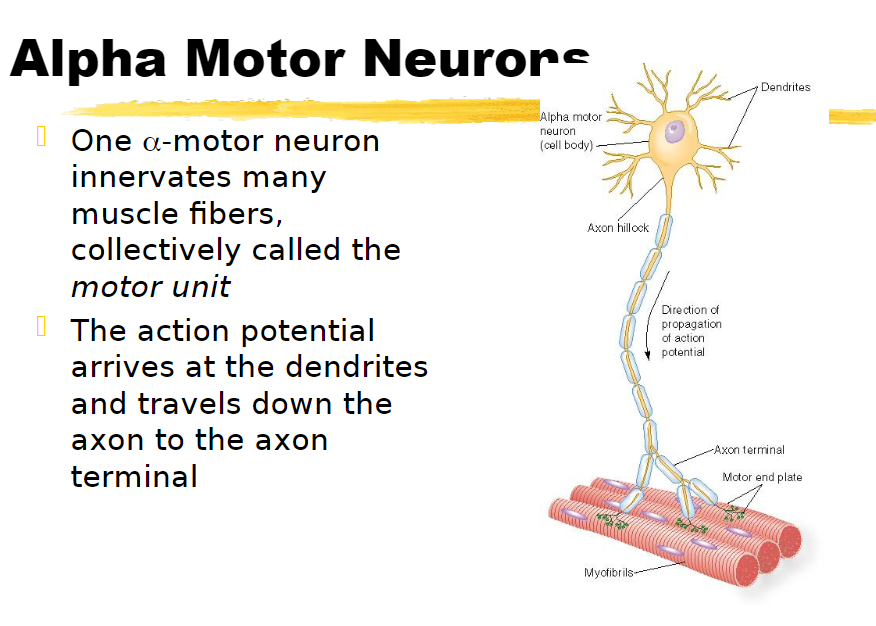
one alpha motor neuron innervates many muscle fibers
-
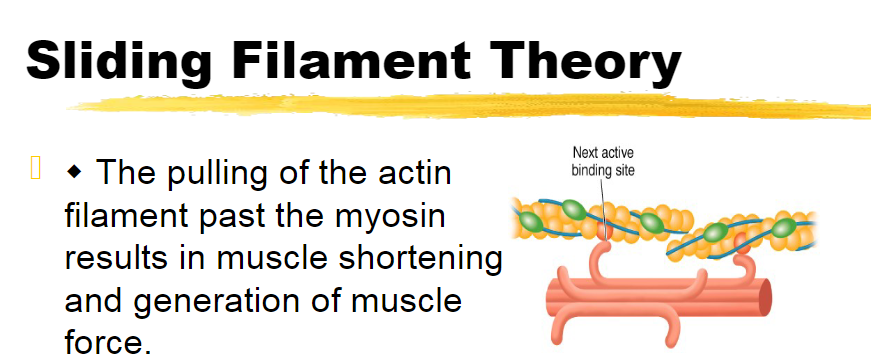
the pulling of the actin filament past the myosin results in muscle shortening and the generation of muscle force
-


myosin head
ATPase
powerstroke
-


calcium must be pumped back into the SR
-


type 1 -> type IIa -> type IIx
-
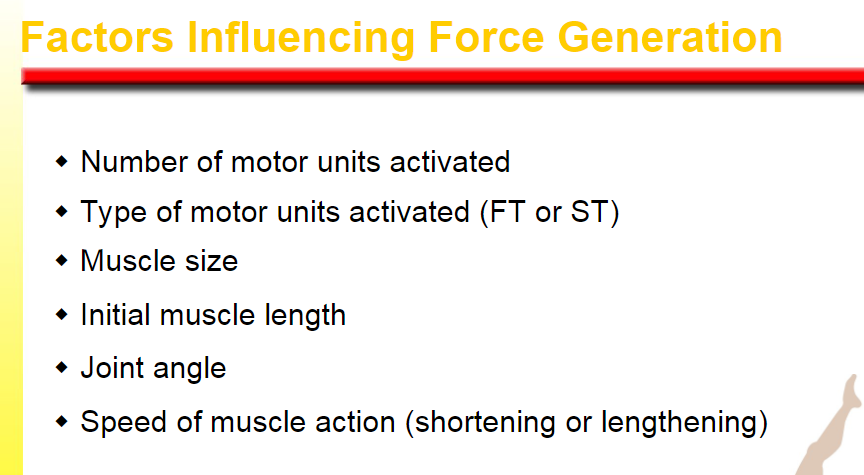
motor units activated
type of motor units
muscle size
-
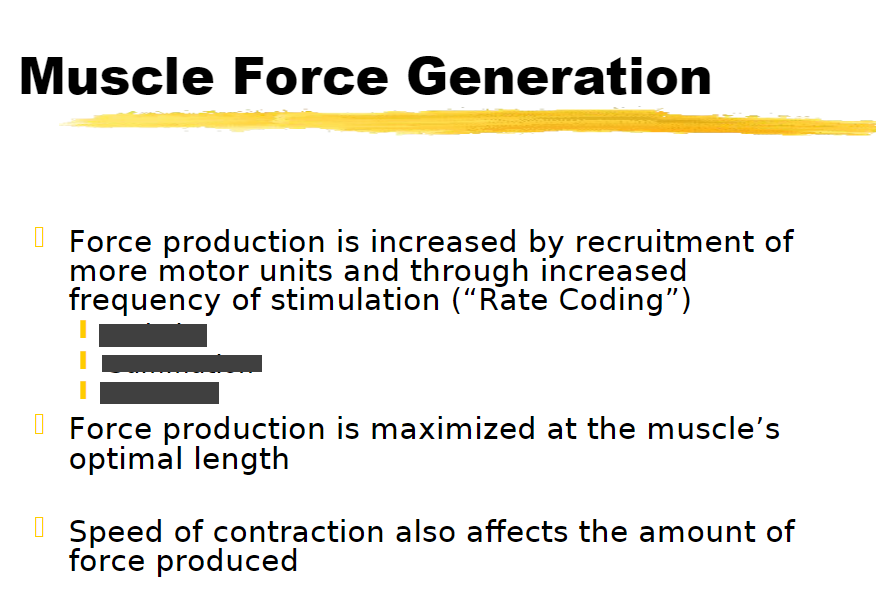
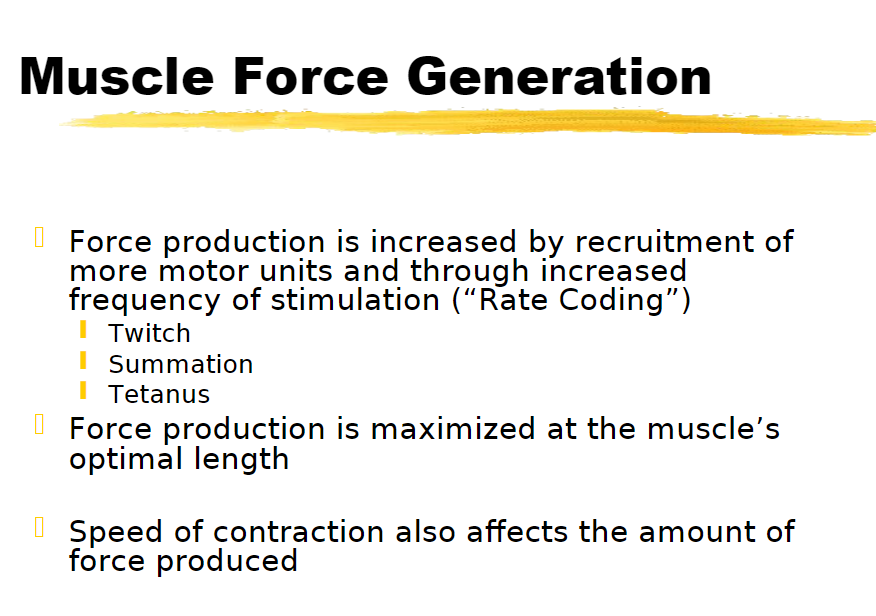
muscle twitch
summation
tetanus

