-
describe lateralization of cortical functioning
there is a division of labor between hemispheres
-
what is cerebral dominance?
designates the hemisphere dominant for language
-
explain the term ambidextrous
right cerebral dominant person that has a cerebral cortex that functions bilaterally
-
describe the structure and function of cerebral white matter
-myelinated fibers bundled into large tracts
-responsible for communication between cerebral areas and between the cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers
-
what are the three cerebral white matter types?
commissural fibers
association fibers
projection fibers
-
what is the function of commissural fibers?
connects corresponding areas of the two hemispheres
-
what is the function of association fibers?
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
-
what is the function of projection fibers?
ties the cortex to the rest of the nervous system and to the body's receptors and effectors
-
describe the structure and function of the basal nuclei
structure:
-deep within cerebral white matter
-caudate nucleus
-putamen
-globus pallidus
----
function:
-influence movements directed by primary motor cortex
-cognition and emotion
-filters out incorrect motor responses
-
describe the structure of the diencephalon, is it white or grey matter? what 3 structures compose it?
-forms the central core of the forebrain and is surrounded by the cerebral hemispheres
-grey mater area
-thalamus
-hypothalamus
-epithalamus
-
give three functions of the thalamus
-relay station for information coming into the cerebra cortex
-sorts and edits information from general sensory receptors
-mediates sensation
-cortical arousal
-learning
-memory
-
give three functions of the hypothalamus
-main visceral control center
-controls the autonomic nervous system
-initiate physical response to emotions
-regulate body temperature
-regulate food intake
-regulate water balance and thirst
-regulate sleep wake cycles
-control endocrine system function
-
what are the 2 functions of the epithalamus?
-secretes melatonin
-helps regulate sleep-wake cycles
-
what are the 3 regions of the brainstem?
-midbrain
-pons
-medulla oblongata
-
name the 5 structures of the midbrain
-periaqueductal gray matter
-superior colliculi
-inferior colliculi
-substantia nigra
-red nucleus
-
what are 2 functions of the periaqueductal grey matter?
-pain suppression
-links ANS pathways that control the fight or flight response
-
what is the function of the superior colliculi?
-visual reflex centers
-
what are the 2 functions of the inferior colliculi?
-reflexive responses to sound
-part of the auditory relay from our hearing receptors to the sensory cortex
-
what is the function of the substantia nigra?
-releases a precursor to dopamine
-
what is the function of the red nucleus?
-relay nuclei in descending motor pathways for limb flexion
-
name two functions of the pons
-relay conversations between the motor cortex and cerebellum
-helps the medulla oblongata maintain normal breathing rhythm
-
explain the reason why each cerebral hemisphere controls voluntary movements of the muscles on the opposite side of the body
-pyramids are pyramidal corticospinal tracts descending from the motor cortex
-they cross over before continuing to the spinal cord
-this is called the decussation of pyramids
-
describe the role of the medulla oblongata in homeostasis
-cardiac center that adjusts force and rate of heart contraction
-vasomotor center changes blood vessel diameter to regulate blood pressure
-respiratory centers generate respiratory rhythm
-
explain how the cerebellum participates in skeletal muscle contraction and cognitive function
-motor areas notify cerebellum of their intent for voluntary muscle contraction via relay nuclei in the brainstem
-at the same time, cerebellum receives information from proprioceptors
-cerebral cortex calculates the best way to coordinate force, direction, and extent of muscle contraction to maintain posture and produce smooth controlled movements
-via superior punducles, the cerebellum dispatches to the cerebellar motor cortex a blueprint for coordinating movement
-
what is a functional brain system?
-networks of neurons that work together, but span a relatively large distance in the brain
-limbic system and reticular formation
-
name three structures that compose the limbic system? what is the main function of the limbic system?
cingulate gyrus
amygdala
hippocampus
--
process and regulate emotion and memory
-
what is the function of the reticular formation?
maintains cerebral cortical alertness through the reticular activating system
-filters our repetitive stimuli
-helps regulate skeletal and visceral muscle activity
-
what are meninges?
-Three connective tissue membranes that lie external to the CNS organs
-cover and protect the CNS
-protect blood vessels and enclose venous sinuses
-contain cerebrospinal fluid
-form partitions in the skull
-include dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
-
describe the structure of the Dura Mater
-strongest layer
-two-layered sheet of fibrous connective tissue
-periosteal layer attaches to periosteum of skull
-meningeal layer forms the true external covering of the brain
-
describe the structure of the Arachnoid Mater
-forms loose brain covering
-separted from dura mater by a narrow serous cavity, subdural space
-beneath, contains subarachnoid space
-filled with cerebrospinal fluid
-contains largest blood vessels in the brain, poorly protected
-arachnoid granulations that protrude superiorly
-
describe the structure of the Pia Mater
-delicate connective tissue
-contains tiny blood vessels
-only layer that clings tightly to the brain
-
describe the structure and function of dural sinuses
structure:
-seperated by the periosteal and meningeal layer of the dura mater
-includes the falx cerebri, falx cereblli, and tentorium cerebelli
---
function:
-collect venous blood from the brain and direct it to the internal jugular veins of the neck
-
what are falx cerebri?
dural sinus
-large sickle shaped fold that dips into the longitudinal fissure between cerebral hemispheres
-anteriorlly attached to crista galli of ethmoid bone
-
what are falx cerebelli
-continues inferiorly from the posterior falx cerebri
-runs along the vermis of the cerebellum
-
Tentorium cerebelli
-resembles a tent over the cerebellum
-extends into the transverse fissure between the cerebral hemispheres
-
describe the function of cerebrospinal fluid
-found in and around the brain and spinal cord
-forms a liquid cushion that gives buoyancy to the CNS structures
-by floating the brain, effectively reduces the brain weight by 97%
-prevents the delicate brain from crushing under its own weight
-protects brain and spinal cord from blows and other trauma
-in addition to the blood supply, helps nourish the brain
-
describe the flow of cerebrospinal fluid
-Choroid plexus of each ventricle produces CSF
-CSF flows through the third and fourth ventricles and into the subarachnoid space
-flows into central canal
-CSF flows through the subarachnoid space
-CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via arachnoid granulations
-
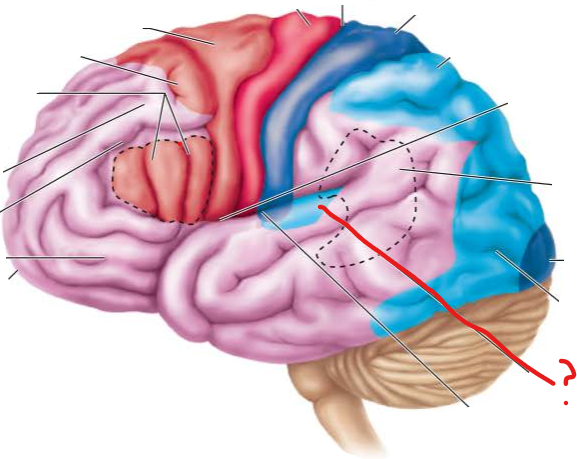
auditory association area
-
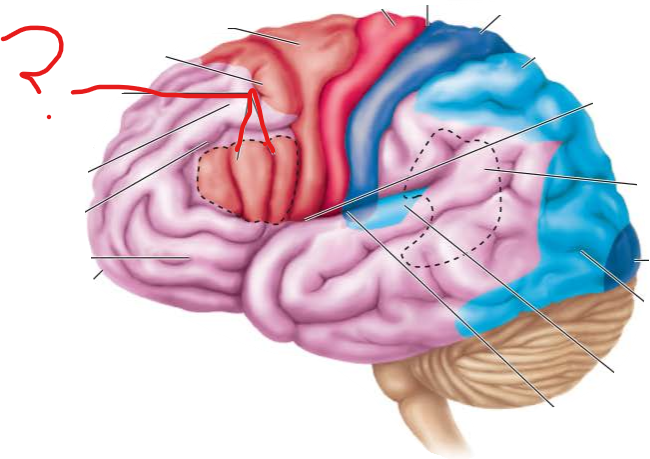
broca's area
-
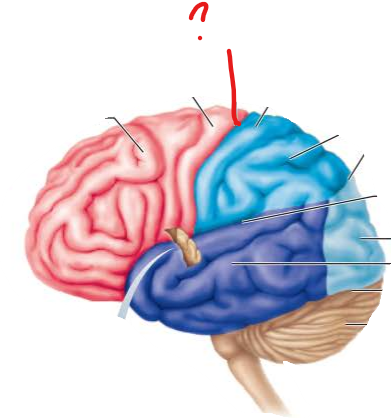
name the broddman's area
central sulcus
-
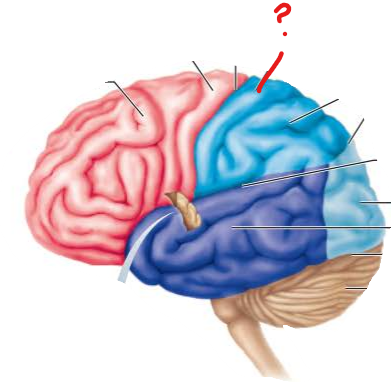
name the broddman's area and the functional brain region that sits on it
post central gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
-
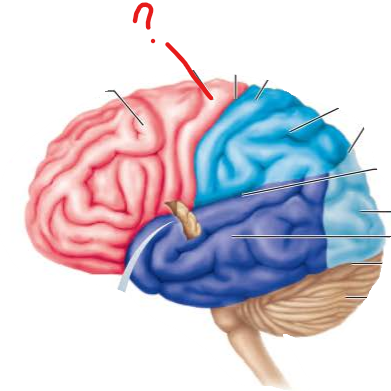
name the broddman's area and the functional brain region that sits on it
pre central gyrus
primary motor cortex
-
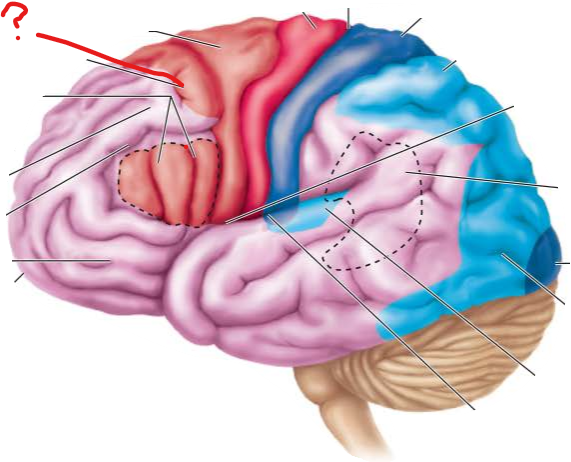
frontal eye fields
-
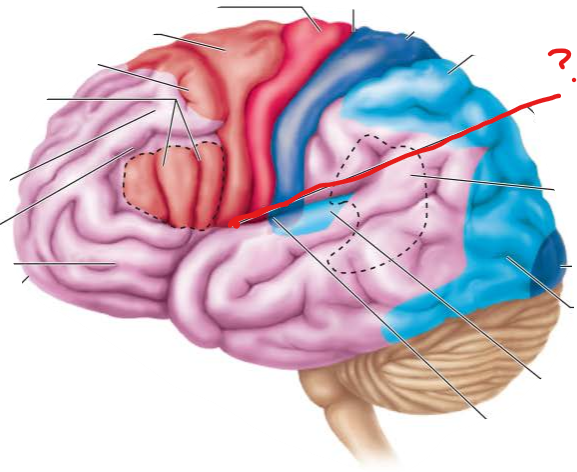
gustatory cortex in insula
-
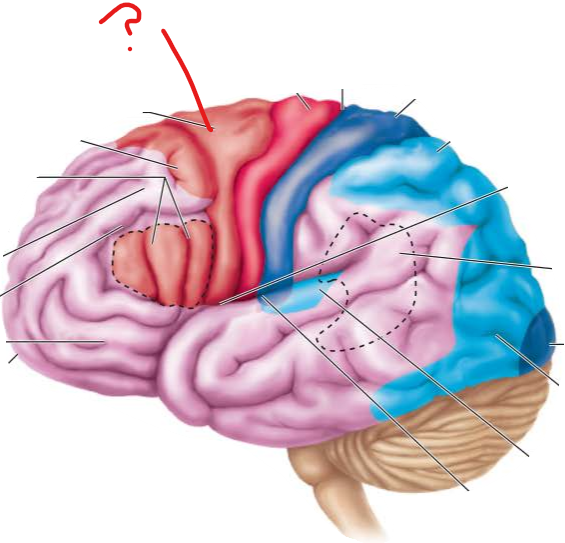
premotor cortex
-
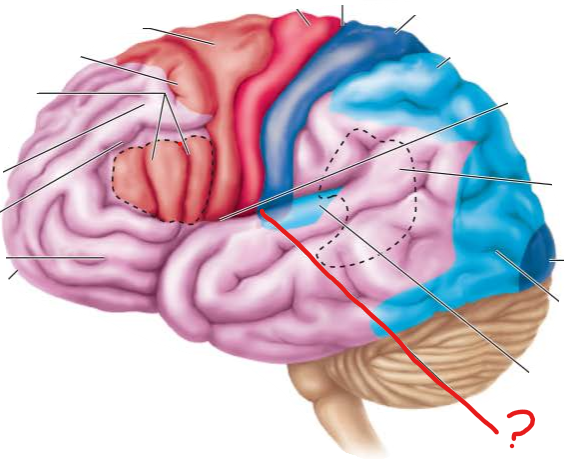
primary auditory cortex
-
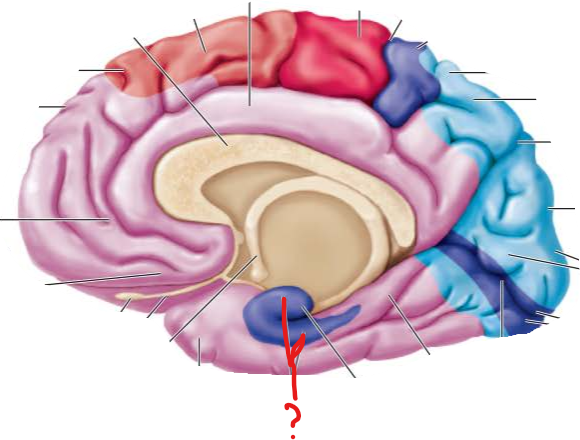
primary olfactory cortex
-
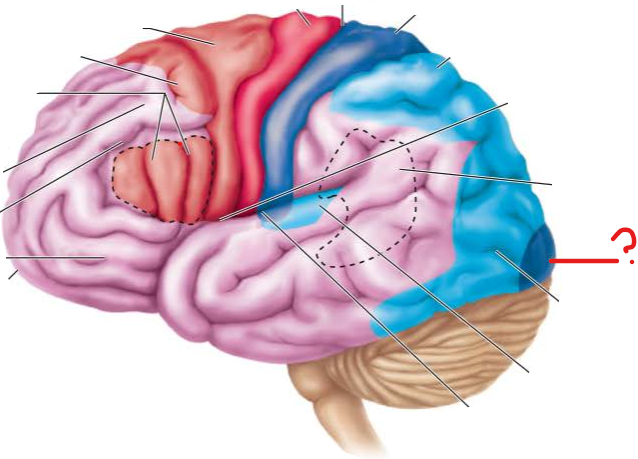
primary visual cortex
-
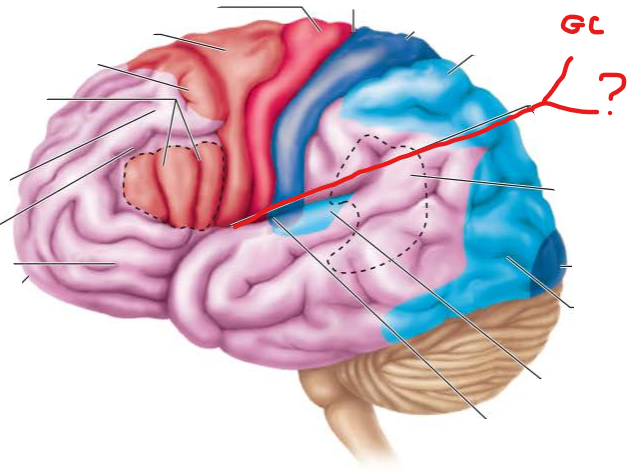
vestibular cortex in insula
-
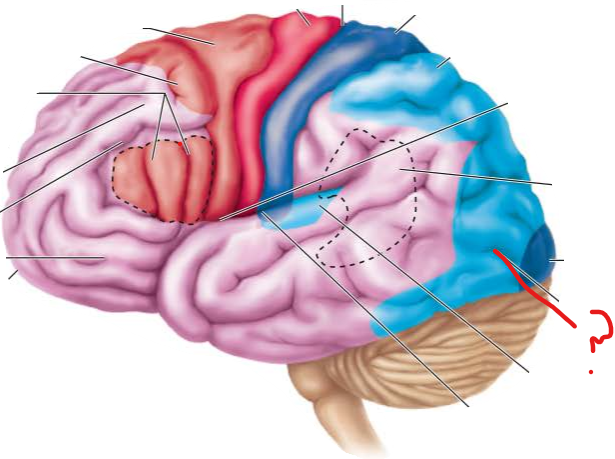
visual association area
-
which lobes compose the posterior association area? what role does this association area play?
parietal
occipital
temporal
-recognizes patterns and faces
-localizes us and our surroundings in space
-binding sensory inputs into a coherent whole
-
what composes the limbic association area?
what functional brain system is it part of?
what role does this association area play?
-hippocampus
parahippocampal gyrus
cingulate gyrus
-part of the limbic system
-provides the emotional impact that makes a scene important to us
-
what does the ventral horn carry?
motor fibers
-
what does the dorsal horn carry?
sensory fibers
-
dorsal roots fuse to form what?
spinal nerve
-
what is the blood-brain barrier?
where is it absent
-selectively permeable barrier created by capillary endothelial cells joined by tight junctions, maintains a stable environment for the brain
-absent from the hypothalamus
-
what is a psychosomatic illness?
how does the hypothalamus contribute to psychosomatic illness?
disorders with physical symptoms that originate from emotional causes
most of the limbic system goes through the hypothalamus
-
what gland is located in the epithalamus?
what does it secrete?
pineal gland
melatonin, sleep-inducing signal and antioxidant
-
what is the mapping of the human body in the CNS called?
somatotopy
-
what is the cartoon-like image used in somatotopy?
what does it mean if a section of this image is larger?
sensory homunculus
areas of the body with more sensory and motor connections
-
what is the groove that separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres?
median longitudinal fissure
-
what is the groove that separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum?
transverse cerebral fissure
-
what is the groove that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe?
central sulcus
-
what is the groove that separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes
lateral sulcus
-
what are spaces in the brain? where do originate from?
ventricles
central cavity of the neural tube
-
what is the term used to describe the elaborate development of the anterior aspect of the CNS through evolution?
cephalization
-
what is the flat embryonic structure present at 19 days of gestation that eventually develops into the CNS?
neural plate
-
what is the hollow, tube-like embryonic structure formed at 26 days of gestation that will eventually develop into the CNS?
what nutrient is required for its proper development?
what birth defect arises from the incomplete development of this structure?
neural tube
folic acid
anencephaly, cerebrum and part of brain does not develop
-
what is the flat embryonic structure present at 19 days of gestation that eventually develops into the CNS?
neural plate
-
what is the function of association areas?
Integrates current stimulation in the context of past experience
-
Distinguish between pre and primary motor cortex homeostasis imbalance
primary motor cortex homeostasis imbalance means
-
name 2 cognitive functions of the cerebellum
Recognize and predict sequence of events
word association
puzzle solving
-
function of ependymal cells
ciliated action aid flow of cerebrospinal fluid


