-
what is the function of the nervous system?
it is the master control and communication center for the body
-
what is sensory input?
sensory receptors monitor changes inside and outside body
-
what is integration?
the nervous system processes and interprets sensory input and determines what to do
-
what is motor output?
the nervous system activates effector organs to cause a response
-
what is the CNS consist of? what is its function?
brain and spinal cord
integrating and control center
-
how does the CNS dictate motor output?
-reflexes
-current condition
-past experience
-
what does the PNS consist of? what is its function?
-spinal nerves
-cranial nerves
-ganglia
communication lines that link all parts of the body to the CNS
-
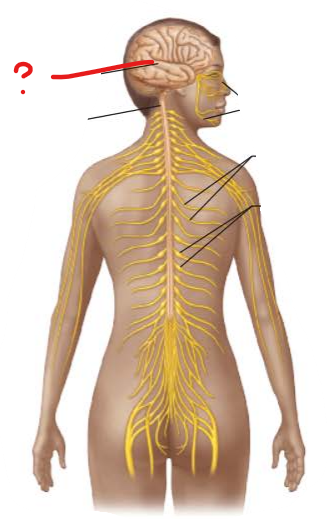
what is this and is it PNS or CNS?
Brain
CNS
-
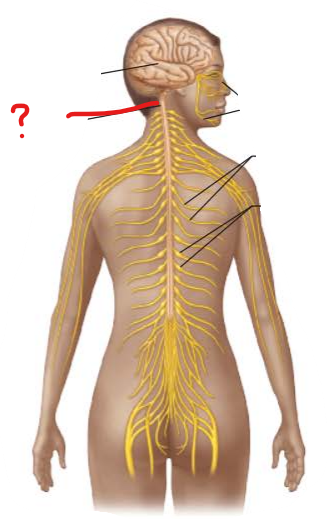
identify and is it PNS or CNS?
Spinal Cord
CNS
-
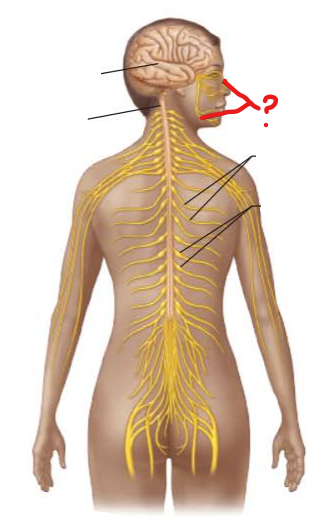
identify and is it PNS or CNS?
Cranial Nerves
PNS
-
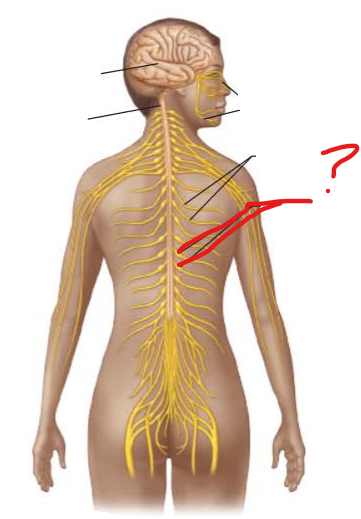
identify and is it PNS or CNS?
Ganglia
PNS
-
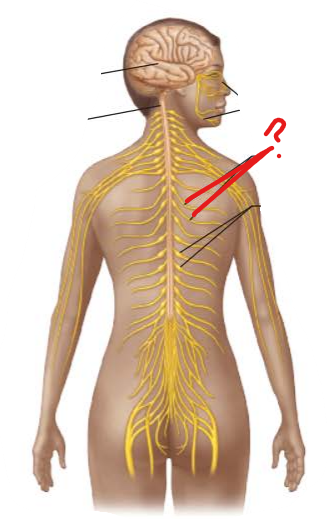
identify and is it PNS or CNS?
PNS
Spinal Nerves
-
what does the sensory division consist of? what is its role?
-somatic sensory fibers convey impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints
-visceral sensory fibers transmit impulses from the visceral organs
-
what does the motor division consist of? what is its role?
-motor nerve fibers that make up the somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
-conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors?
-
what are effectors?
-muscle and glands
-
what does the somatic nervous system consist of? what is its function?
-voluntary motor nerve fibers
-conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
-
what does the autonomic nervous system consist of? is its function?
-involuntary motor nerve fibers that make up the sympathetic and parasympathetic division
-conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
-
what is the function of the sympathetic division?
-mobilizes body systems during an activity
-
what is the function of the parasympathetic division?
-conserves energy
-promotes housekeeping functions during rest
-
what is a Glial Cell?
Supporting cells that surround and wrap around the more delicate neurons
-
what are Astrocytes?
CNS glial cell
-anchors neurons to capillaries
-resorbs leaked potassium ions
-recycles released neurotransmitters
-participates in information processing
-
what are Microglial cells?
CNS glial cell
-monitor the health of neurons
-specialized macrophage that engulfs debris or microorganisms, important because immune cells cannot enter the CNS
-
what are Ependymal Cells?
CNS glial cell
-line the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord
-cilia helps circulate the cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the brain and spinal cord
-
what are Oligodendrocytes?
CNS glial cell
-line up along the thicker nerve fibers in the CNS
-myelin sheathe of some nerve fibers in the CNS
-
what are Satellite Cells?
PNS glial cell
function unknown, but thought to have many of the same functions of astrocytes
-
what are Schwann cells?
PNS glial cell
-forms myelin sheathes around thicker nerve fibers
-vital to the regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers
-
What are the three characteristics of a neuron?
High Metabolic Rate
Amitotic
Extreme Longevity
-
what are nuclei?
Collection of neuron cell bodies in the CNS
-
what is a tract?
Bundle of Axons in the CNS
-
what is a ganglia?
Collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
-
what is a nerve?
A bundle of Axons in the PNS
-
regions in the nervous system with short, non-myelinated neurons
Grey Matter
-
regions in the nervous system with mostly myelinated neurons
White Matter
-
what is the ability for a neuron to detect and respond to stimuli
Irritability
-
what is an Action Potential?
what voltage does it start at and go to?
where is it generated?
does it decay with distance?
-brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100mV (-70mV to +30mV)
-typically only generated in Axons when adequately stimulated
-Does not decay with distance.
-
why is the human body electrically neutral overall?
-The human body has an equal amount of positive and negative charges, but there are regions where one type of charge predominates.
-
what is Potential Energy?
-any situation in which there are separated electrical charges of the opposite sign
-
what is voltage?
-Measure of potential energy generated by separated electrical charges
-
what is a current?
-flow of electrical charge from one point to another
-used to do work
-amount relies of voltage and resistance
-
What is resistance?
-hindrance to charge flow provided by
substances through which a current must pass
-
insulators have what property?
-high electrical resistance
-
conductors have what property?
-low electrical resistance
-
what is a Concentration gradient?
-Ions move along chemical concentration gradients from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
-
what is an Electrical Gradient?
-Ions move toward an area of opposite electrical charge
-
what is the Electrochemical Gradient?
-The direction an ion moves, in or out of a cell, depends on the greater of either the concentration gradient or electrical gradient
-
are leakage channels always open?
yes
-
how do voltage-gated channels open and close?
-changes in membrane potential
-
how do chemically-gated channels open?
-when the appropriate chemical binds
-
what is the resting membrane potential?
-measured potential difference between two points in a resting neuron
-
what is depolarization?
-decrease in membrane potential
-inside of the membrane becomes less negative than the resting potential
-increases probability of producing nerve impulses
-
what is hyperpolarization?
-increase in membrane potential
-inside of the membrane becomes more negative
-reduces probability of producing nerve impulses
-
what is a graded potential?
-brief, localized changes in membrane potential
-degrade with distance
-initiates action potentials
-
what is the threshold?
-when depolarization reaches a critical level between -55 and -50mV
-causes depolarization to become self-generating
-
What is the absolute refractory period?
-when a patch of neuron membrane is generating an AP it cannot respond to another stimulus
-ensures that each AP is a separate all or nothing event
-
what is the relative refractory period?
-follows the absolute refractory period
-happens when repolarization is occurring
-elevates threshold for AP generation
-requires exceptionally strong stimulus to reopen sodium channels
-
what is conduction velocity? what two variables affect it?
-how fast APs travel
-positive relationship with axon diameter
-positive relationship with the degree of myelination
-
what is Continuous Conduction?
-occurs in nonmyelinated axons
-voltage-gated channels in the membrane are adjacent to each other
-slow conduction velocity
-
what is Saltatory Conduction?
-occurs in myelinated axons
-myelin blocks sodium and potassium channels
-AP current is maintained and skips to the next myelin sheathe gap where it triggers another AP
-30x faster than continuous conduction
-
describe the basis of the resting membrane potential
-high intracellular potassium
-many potassium leakage channels allow for it to diffuse outside the cell
-high extracellular sodium
-few sodium leakage channels
-concentration gradient of both sodium and potassium leaves the membrane potential around -70mV
-sodium and potassium pump compensates for leaking ions and transports 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in against the concentration gradient
-this keeps the membrane potential at -70mV
-
explain the function behind dendrites
the soma can synapse on its own, but the addition of the dendrite processes increases the surface area allowing the neuron to receive more sensory information
-
Brain and Spinal Cord
integrative and control centers
-
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Nerves
Communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
-

Motor Nerve Fibers
Conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors
-

Somatic sensory nerve fibers
Visceral sensory nerve fibers
Conducts impulses from receptors to the CNS
-
Somatic motor Nerve fibers
Conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
-
Visceral motor nerve fibers
Conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
-

mobilizes body system during an activity
-

conserves energy
promotes housekeeping functions during rest


