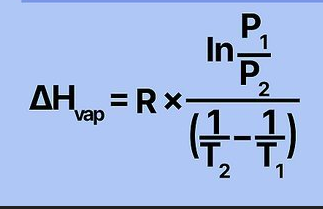-
Ion - dipole forces
Occurs between a (+) ion and the (-) end of a polar molecule
-
Dipole - dipole forces
Occurs between two polar molecules
-
Hydrogen bonding
Occurs between an H atom directly bonded to an O/N/F atom and the (-) region of an O/N/F atom on a separate molecule
-
Dispersion forces
Occurs between the electron clouds of all molecules but mostly between nonpolar molecules
-
Which intermolecular forces are noncovalent
Hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces (no electrons shared)
-
Intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest
Dispersion < dipole-dipole < hydrogen < ion-dipole
-
What are 2 things that affect the strength of dispersion forces (explain them)
Molecular size: larger molar mass/size = greater dispersion forces
Molecular shape: Larger surface area/chained = greater dispersion forces
-
Definite vs indefinite property
Definite = keeps shape in container
Indefinite = takes the shape of the container
-
5 Properties of solids
- high density
- definite shape
- definite volume
- strong intermolecular forces
- particles close together/in-compressible
-
5 properties of liquids
- high density
- indefinite shape
- definite volume
- moderate intermolecular forces
- particles close together/in-compressible
-
5 properties of gases
- low density
- indefinite shape
- indefinite volume
- weak intermolecular forces
- particles far apart/compressible
-
definition of boiling point in relation to intermolecular forces
The amount of thermal energy needed (added) to break the intermolecular forces between particles in a liquid and turn it into a gas (vapor)
-
Definition of freezing point in relation to intermolecular forces
The loss (removed) of thermal energy needed for particles in a liquid to slow down and turn into a solid
-
Higher boiling and freezing point (temp-wise) equals ___
stronger intermolecular forces (more energy to boil/less heat needs to be removed)
-
Lower boiling and freezing point (temp-wise) equals ___
weaker intermolecular forces (less energy to boil/more heat needs to be removed)
-
What is surface tension and why does it occur
the tendency of liquids to minimize their surface area and resist external penetration
- Molecules on the surface of a liquid have stronger IMF with their neighbors and are more densely packed, minimizing their surface area
-
What is viscosity and what are 3 things that effect the viscosity of a substance
A liquid's resistance to flow
- Intermolecular forces = stronger attractions makes molecules more resistant to flow
- longer molecular shape = more likely to tangle and resist free flow
- Temperature = almost all liquids became less viscous as temp increases
-
What is capillary action and what are the 2 forces behind it
The ability of a liquid to flow upward against gravity in a narrow tube
- Cohesive: attraction between molecules that keep them together
- Adhesive: attraction between molecules and the surface of the tube
-
Capillary action only occurs if ___ and the liquid will have a ___ meniscus
- The adhesive forces are greater than the cohesive forces
- concave (bulging upward)
-
Vaporization
Liquid phase to gas phase
-
Condensation
Gas phase to liquid phase
-
What are 2 things that increase rate of vaporization
1) temperature increases
2) surface area increases
-
Liquids that evaporate quickly are ___
Liquids that evaporate slowly are ___
1 - volatile (think alcohols)
2 - nonvolatile (think oils)
-
Heat (enthalpy) of vaporization (how is it related to condensation)
Amount of heat energy needed to vaporize 1 mole of a liquid
- The amount of heat added to vaporize a liquid is equal to the amount of heat removed for it to condense (H condensation = - H evaporation)
-
Brief explanation of vapor pressure (4 points)
- A dynamic equilibrium is when a liquids rate of evaporation = its rate of condensation in a container
- The pressure exerted by the vapor is the vapor pressure
- vapor pressure depends on the particular IMF in a liquid and its temp
- Weaker IMF = higher V.P / Stronger IMF = lower V.P
-
REAL definition of boiling
When the air pressure above a liquid equals its vapor pressure at that temperature
-
Relationship between temperature and vapor pressure (3 points)
- As temperature increases vapor pressure increases
- Even small temp increases have a big impact on vapor pressure
- higher altitude/lower atm. pressure lowers the boiling point of many liquids
-
The 2 point form of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation can tell you what 3 things
1 - The heat of vaporization if given 2 measures of vapor pressure and temperature
2 - The vapor pressure at any temperature if given the heat of vaporization and normal boiling point
3 - The normal boiling point if given heat of vaporization and 1 measure of vapor pressure and temperature
-
Melting
Solid phase to liquid phase
-
Heat (enthalpy) of fusion (how is it related to freezing)
Amount of heat energy needed to change 1 mole of a solid to a liquid
- The amount of heat added to melt a solid is equal to the amount of heat released for it to freeze (H freezing = - H melting)
-
In the heating curve of a solid, at what points does the temperature increase
1 - at the beginning until it reaches its melting point
(temp is steady)
2 - after the solid is completely melted (and begins liquefying)
-
Int he heating curve of a liquid, at what points does the temperature increase
1 - at the beginning until it reaches its boiling point
(temp is steady)
2 - after the liquid completely boils (and begins turning into a gas)
-
Sublimation
Solid phase directly to gas phase
-
Deposition
Gas phase directly to solid phase
-
Which 2 phase changes are endothermic and which 2 phase changes are exothermic
vaporization and melting = endothermic (added)
freezing and condensation = exothermic (released)
-
If hydrogen bonding is present it becomes the ___ force
- It becomes the strongest molecular force
-
Find final pressure using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation
1) Plug in values and convert C to K
2) Convert R to 0.00831 KJ/mol
3) Solve equation(s) on right side
4) Raise both sides to e^ to cancel ln
5) Times both sides by P2 to cancel P2 on left side
6) Isolate P2 on the right side by dividing both sides by the attached value
-
Conduction
Direct transfer of heat through a solid
-
Convection
heat transfer through fluid motion (Liquid or gas)
-
Radiation
Transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves without a medium
-
Find ΔHvap using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation