-
Oxygen inhaled into the lungs must pass through both ________ and _________ _____ before it reaches the intracellular fluid of tissue cells
plasma
interstitial fluid
-
Nutrients absorbed from the GI tract must pass through both __________ and __________ _____ before they reach the intracellular fluid of tissue cells
plasma
interstitial fluid
-
Ions reabsorbed and secreted by the kidney tubules must pass through both _______ and _________ _____ before they reach the intracellular fluid of tissue cells
plasma
interstitial fluid
-
Because _______ moves freely between body compartments, osmolalities of all body fluids are equal except immediately following a change in one of the fluids
water
-
The _________ _________ is the force compelling water intake, increasing plasma osmolality from 2% to 3% excites the thirst center in the _______________
thirst mechanism
hypothalamus
-
_____ of sodium is reabsorbed in the PCT. _____ of sodium is reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle. The presence of the hormone ___________ results in reabsorption of the remaining sodium at the DCT and collecting ducts.
65%
25%
aldosterone
-
What part of the nephron is primarily responsible for maintaining potassium homeostasis? _______ _______
This is accomplished by altering the amount of potassium _________into the filtrate.
The most important factor impacting potassium secretion is potassium concentration in the ____________ ______
Aldosterone also impacts potassium secretion into the renal filtrate because when aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of sodium, potassium is simultaneously _________
renal tubules
secreted
extracellular fluid
secreted
-
The normal pH of arterial blood is _____
7.4
-
Four sources of acids in the body
1. breakdown of phosphorus-containing proteins releasing __________ ____ into the ECF
2. Anaerobic respiration of glucose producing ______ ____
3. fat metabolism yielding _______ ____such as _________ ____ and __________ ______
4. loading and transport of carbon dioxide in the blood as HCO3¯ liberates _________ _____
phosphoric acid
lactic acid
organic acids
fatty acids
ketone bodies
hydrogen ions
-
A ______ ____ dissociates completely in water and liberates all its hydrogen ions. A _____ ______ dissociates only partially thus having a lesser impact on pH.
strong acid
weak acid
-
A ________ ___ dissociates quickly in water and ties up hydrogen ions. A ______ ____ is slower to accept protons.
strong base
weak base
-
Anything that impairs the respiratory system will cause acid-base ___________
imbalances
-
The ultimate responsibility for acid-base regulation belongs to what organs? __________
kidneys
-
The lungs can dispose of carbonic acid by eliminating carbon dioxide, but only the kidneys can eliminate other acids such as __________ ____, _________ ____, ____ ____, and _________ _______
phosphoric acid
lactic acid
uric acid
ketone bodies
-
Only the kidney can regulate blood levels of ___________ substances and renew _________ _________ that are consumed while regulating hydrogen ion levels in the ECF.
alkaline
chemical buffers
-
Name three actions the kidney can take when handling bicarbonate ions (HCO3-):
1.
2.
3.
reabsorb bicarbonate ions
generate new bicarbonate ions
excrete bicarbonate ions
-
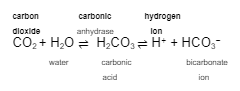
Excreting one bicarbonate ion is the same as gaining one __________ ____ because it pushes the equation to the ______ and ________ the hydrogen ion level.
hydrogen ion
right
increases
-
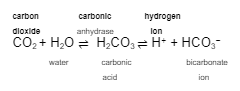
Generating or reabsorbing one bicarbonate ion is the same as losing one _____________ ___ because it pushes the equation to the ____ and __________ the hydrogen ion level.
hydrogen ion
left
decreases
-
When reabsorbing bicarbonate, the kidney ________ hydrogen and when it excretes excess bicarbonate, hydrogen is _________.
secretes
retained
-
Acid-base balance depends on hydrogen ion secretion into the ________
filtrate
-
The rate of hydrogen ion secretion rises and falls with _____ levels in the ECF. The more carbon dioxide in the peritubular capillary blood, the _______ the rate of hydrogen ion secretion.
CO2
faster
-
The kidney is also responsible for ____________ depleted levels of bicarbonate ion. The kidney has a mechanism to conserve filtered bicarbonate ions.
replenishing
-
The kidney can generate new bicarbonate ions via two mechanisms:
-secretion and excretion of ___________
-secretion and excretion of ____________ ___
hydrogen
ammonium ions
-
When a person breathes shallowly or when gas exchange is disrupted by disease, _________ ________ accumulates. This is called _____________ _________
carbon dioxide
respiratory acidosis
-
When a person hyperventilates, they eliminate ___________ _______ faster than it is produced. This is often caused by ______ or _______. This is called _____________ ________
carbon dioxide
stress
pain
respiratory alkalosis
-
__________ pH imbalances include all abnormalities of acid-base except those caused by too much or too little carbon dioxide.
metabolic
-
If pH and bicarbonate are too low, this is called metabolic acidosis.
Causes include excessive alcohol consumption which is metabolized to acetic acid, excessive loss of bicarbonate ions from persistent diarrhea, excess lactic acid accumulation during exercise or shock, ketosis from diabetic crisis or starvation, kidney failure
metabolic acidosis
-
If pH and bicarbonate are too high, this is called metabolic alkalosis.
metabolic alkalosis
-
Causes include excessive alcohol consumption which is metabolized to acetic acid
excessive loss of bicarbonate ions from persistent diarrhea
excess lactic acid accumulation during
exercise or shock
ketosis from diabetic crisis or starvation
kidney failure
metabolic acidosis
-
Causes include vomiting the acidic contents of the stomach
intake of excess base like antiacids
metabolic alkalosis
-
The absolute limits of blood pH compatible with life are a low of ____ and a high of ____
6.8
7.8
-
When an acid-base imbalance is caused by dysfunction by one of the physiologic buffer systems (either respiratory or renal), the other system tries to ____________
The respiratory system will alter respiratory _____________ to compensate for metabolic imbalances
The renal system will alter ___________ levels to compensate for respiratory imbalances.
compensate
ventilation
bicarbonate

