-
to get more active, potent, and safer agents
What is the main aim of structure-activity relationships (SARs)?
-
Homologation
-lengthen alkyl chain in chemical structure by CH2
-
9; low water solubility, low bioavailability
What is the maximum chain length?
What happens when you exceed this number?
-
Homologation
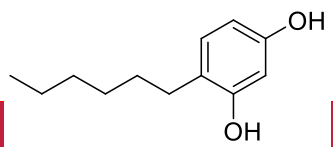
What SAR is this?
-
chain branching; lower lipophilicity, weaker binding with target

What SAR is this? What kind of implications are associated with it?
-
ring chain transformation; affects lipophilicity and metabolism
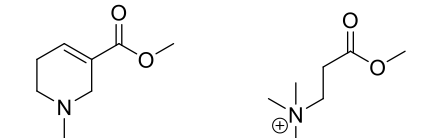
What SAR is this? What kind of implications are associated with it?
-
Phenylalanine (PEA)
-especially high or low concentrations of it is associated with specific psych disorders like ADHD
-
catecholamine-releasing properties; competes with dopamine and norepinephrine
What structure of Amphetamine is responsible for its psychostimulant effects?
-
serotonin 5-HT, SERT, MAO
What are the targets for Amphetamine?
-
sulfa, antimicrobial agent, p-amino group, amides; can be converted to prodrugs
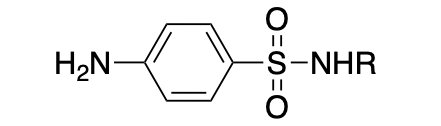
Drug class?
Indication?
What is essential to its activity?
Any exceptions?
-
competitive inhibitors of DHPS; enzyme essential for folate synthesis
MOA for Sulfonamide antibacterials?
-
Sulfmethoxazole
-used for the treatment of infections such as
- chronic bronchitis
-UTI and ear infections
-enteric infections, shigellosis, and traveler's diarrhea
-Pneumocystis pneumonia
-
6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Primaquine, an anti-malarial drug, is toxic for individuals who are deficient in
_______.

