-
sulfinyl sulfur
Omeprazole contains a:
triazole
thiazole
phenyl ring
sulfinyl sulfur
-
racemate
Omeprazole is a :
racemate
prodrug
active
-
proton pump inhibitor; Gastroesophageal disease
Esomeprazole MOA & indication.
-
esomeprazole; omeprazole
_____________ is twice as effective as ___________.
-
Amphiphilic
- local anesthetics that interact hydrophobically and electrostatically with lipid bilayers; directly inhibiting membrane functions and inhibition of channel functions.
-
Amphotecerin B MOA/indication
antifungal; forms barrel-like structure w hydrophilic environment that allows for ions to flow into cell damaging it and leading to cell death
-
50-150 kcal/mol
What is the strength of covalent interactions?
-
5-10 kcal/mol
What is the strength of electrostatic interactions?
-
2-5 kcal/mol
What is the strength of hydrogen bond interactions?
-
0.5-1 kcal/mol
What is the strength of hydrophobic interactions?
-
aspirin, penicilin, omeprazole, clopidogrel, neratinib
What are our covalent inhibitors?
-
cyclooxygenase inhibitor; prevents the conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A(2).
Aspirin class & MOA?
-
B-lactamase inhibitor; inhibits transpeptidase that catalyzes the final step in cell wall formation; the cross-linking of peptidoglycan
Penicillin class & MOA?
-
anticancer drug; inhibits EGFR
Neratinib indication & MOA
-
CYP2C19
Clopidogrel is metabolized by ______
-
omeprazole, esomeprazole
CYP219 inhibitors such as, __________ & ___________ can decrease the antiplatelet effect of clopidogrel.
-
covalent
Which bonds are the strongest in drug-receptor interactions?
-
irreversible; destruction; resynthesize new receptors
Covalent bonds will result in ________binding. This leads to _________ of the receptor. Cells must ____________
-
decreases the strength
How does distance affect the strength of electrostatic bonds?
-
b
Strongest Electrostatic interactions occur where?
a)Hydrophilic environments
b)hydrophobic environments
c)Neutral environments
d)none of the above
-
true
Ionic bonds are the most important initial interactions as a drug enters the binding site. T/F
-
hydrogen bond acceptor
-electron rich heteroatom
-
hydrogen bond donor
-electron deficient hydrogen
-
carboxylate ion, phosphate ion, tertiary amine
What are our strong hydrogen bond acceptors?
-
carboxylic acid, amide oxygen, ketone, ester, ethyl, alcohol
What are our moderate hydrogen bond acceptors
-
sulfur, fluorine, chlorine, aromatic ring, amide nitrogen, aromatic amine
What are our poor hydrogen bond acceptors
-
-nib
What suffix helps indicate it is an anti-cancer drug?
-
increased binding to enzyme/receptor & absorption through membrane
What are the benefits of a high LogP?
-
decreased aqueous solubility; increased binding to P450, blood proteins, hERG heart ion channel
What are potential downsides to high LogP?
-
logP <=5, MW < =500, HBD <=5, HBA <=10
What are Lipinski's guidelines?
-
Rotatable bonds <= 10, Polar surface area <= 140, total HA + HB <= 12
What are Veber's rules?
-
Amide C-N
Which type of bonds don't apply to Veber's rotatable bond rule?
-
benzodiazepine; privileged structure; CCK antagonist
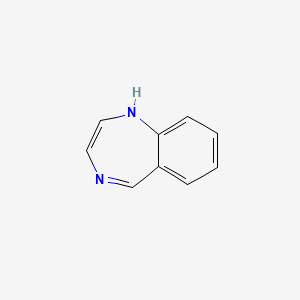
What is the name of this structure?
What is special about it?
-
Privileged structure
- common structures or molecular fragments that can be found regularly among active sets of molecules.
- have the universal ability to bind to several protein targets
-
indole; privileged structure; CCK antagonist
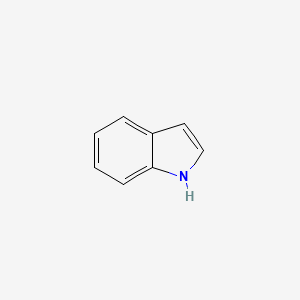
What is the name of this structure?
What is special about it?
What is its class?
-
diphenylmethane; privelged structure; benadryl
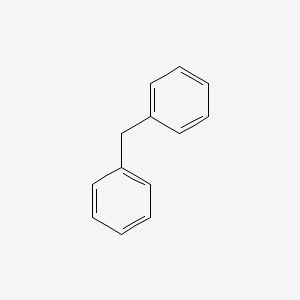
What is the name of this structure?
What is special about it?
What drug is it found in?
-
can bind to multiple targets causing side effects; hard to develop patens
What are some negatives associated with privileged structures?
-
<=30
How many nonhydrogen atoms can be on a drug for it to be included in the drug space?
-
Atenolol
beta blocker, blocks binding of catecholamines to beta-1 receptors; beta-1 selective, hypertension, abrupt discontinuation can lead to myocardial infarction
-
Amitryptiline
TCA, increases noradrenergic or serotonergic neurotransmission by blocking the ne or serotonin transporter, depression
-
b
When Amitriptyline is metabolized by _______ it results in an active metabolite known as Nortriptyline.
a) CYP2D6
b) CYP2C19
c) CYP3A4
d) CYP2C9
-
Benadryl
antihistamine, inverse agonist of H1 receptor, allergies
-
CYP2D6, CYP1A2; CYP2C9, CYP2C19; CYP2D6
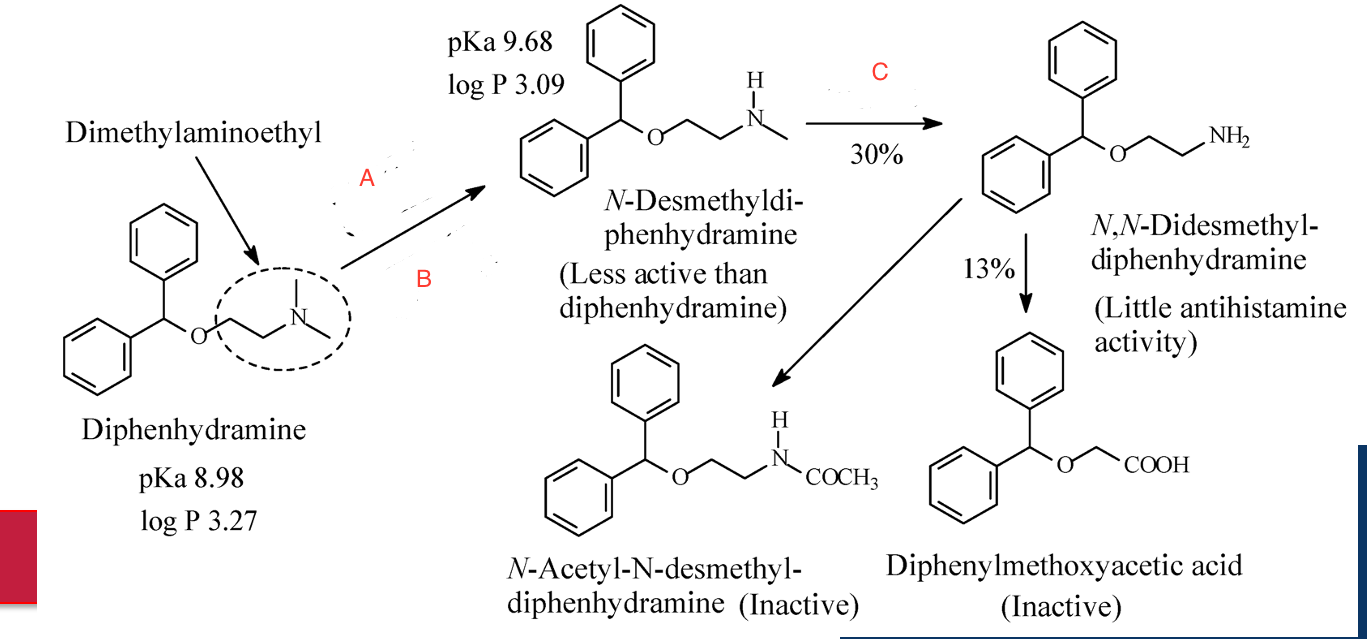
Enzymes at A, B, and C.
-
warfarin or vitamin k antagonist; fenofibrate can enhance anticoagulant effect
What drugs should be avoided when taking Fenofibrate? Why?

