
Carbohydrate Metabolism (The Living Cell)
Explain why glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle Describe the important steps in the synthesis and degradation of glycogen Describe the role and importance of glucose-6-phosphate as a key metabolic intermediate Describe the role of the pentose phosphate pathway in the synthesis of fatty acids Describe the role and importance of gluconeogenesis in the maintenance of blood glucose
-
Outline of what this flashcard set covers (in red)
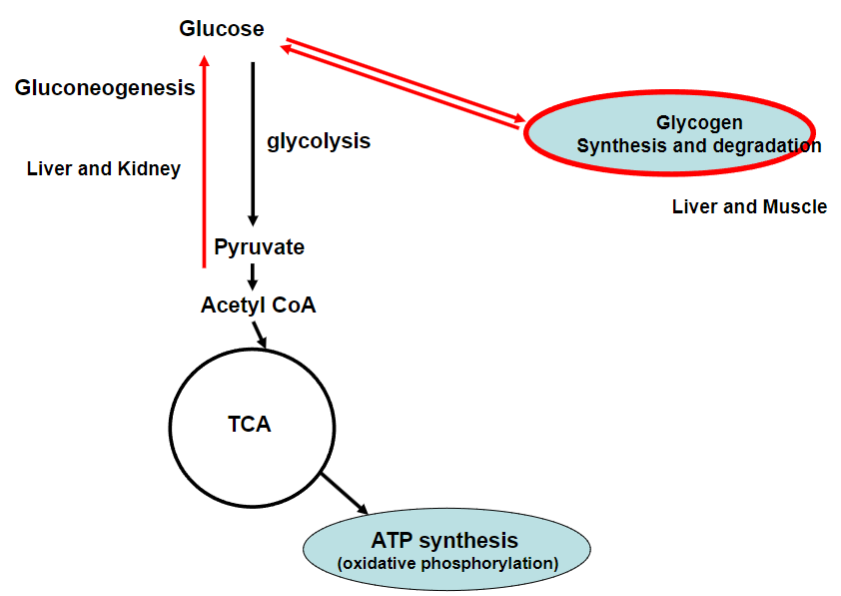
-
What is Hypoglycaemia?
Low blood glucose levels
-
What is Hyperglycaemia?
High blood glucose levels
-
What are the symptoms of Hypoglycaemia? (8)
Shakiness or tremors
Sweating
Irritability or mood changes
Loss of coordination
Rapid heartbeat
Blurred vision
Weakness or fatigue
Severe cases may lead to Hypoglycaemic coma and death
-
What are the symptoms of Hyperglycaemia? (8)
Increased thirst (polydipsia)
Frequent urination (polyuria)
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow wound healing
Increased hunger (polyphagia)
Non-enzymatic modification of proteins
Severe cases may lead to Hyperosmolar coma
-
What is the value when blood glucose is considered critical?
2.5mM
-
Picture overview of the processes that occur in the Liver
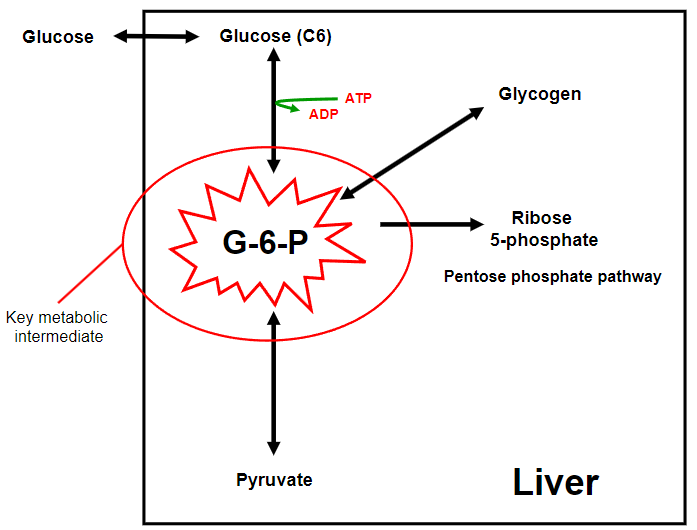
-
Where does glycogenesis take place?
-Liver (100g)
-skeletal muscle (300-400g)
-
When does glycogenesis take place?
When blood glucose levels are high
-
Why does glycogenesis take place?
Glycogen is a safe way to store glucose
-
What regulates glycogen synthesis?
Insulin
-
What bonds does glycogen have?
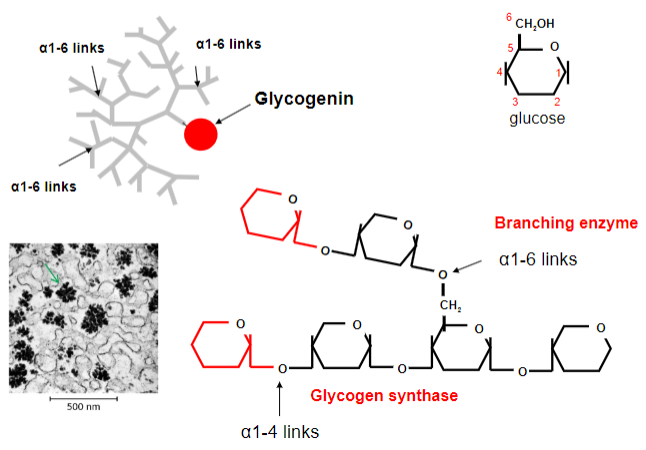
-alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds
-alpha-1,6-glycosidic bonds
-
Outline the steps of glycogen synthesis:
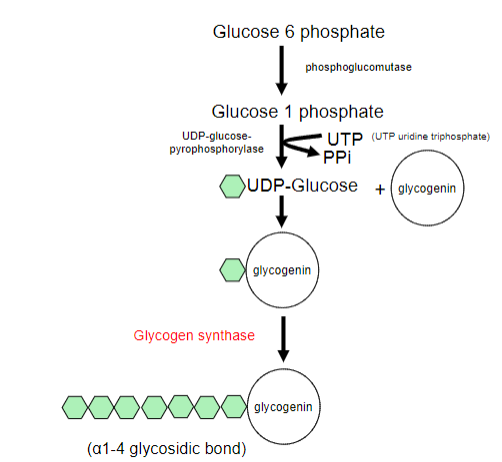
-
What does the branching enzyme do in glycogen synthesis?
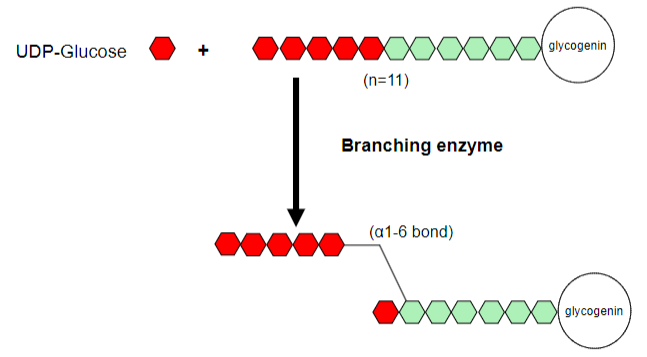
-The branching enzyme transfers a segment of the growing chain and attaches it to an earlier part of the chain
-Forming an alpha-1,6-glycosidic bond
-
Why does the body store glucose in the form of glycogen? (3)
• Cannot store glucose as it is osmotically active• 400mM glucose is stored as 0.01μM glycogen, so storage efficient• The branched structure of glycogen means it can berapidly mobilised

