Capillaries II (Physiology)
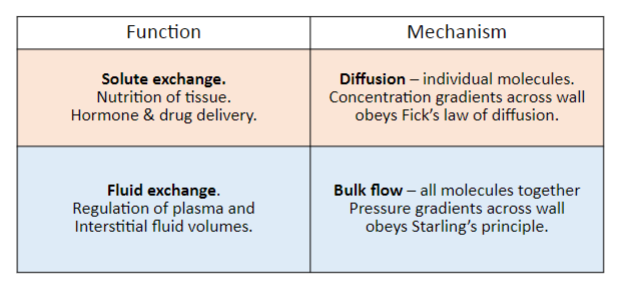
Session summary DO NOT CONFUSE STARLINGS LAW WITH STARLINGS FORCES This lecture deals with why we need fluids and fluid transport. Starling’s principle of fluid exchange and the 4 main forces affecting fluid exchange will be discussed. The idea of capillary permeability will be introduced, along with reflection coefficients, in a description of how filtration occurs. Approximately 8 litres of fluid gets filtered from the blood into the interstitial fluid every day, and the lecture will discuss why that occurs. This will bring us on to the lymphatic system itself and the control of interstitial fluid. Finally some of the causes of oedema will be explored including what happens when the whole process goes wrong and a there is a build-up of fluid in the interstitial space. Learning outcomes Describe four pressures of Starling’s principle of fluid exchange Describe capillary permeability and reflection coefficients Describe filtration along capillaries Role of the lymphatic system in the control of interstitial fluid Explain causes of oedema
-
Abnormalities in fluid exchange can lead to oedema/tissue swelling. What is another name for this?
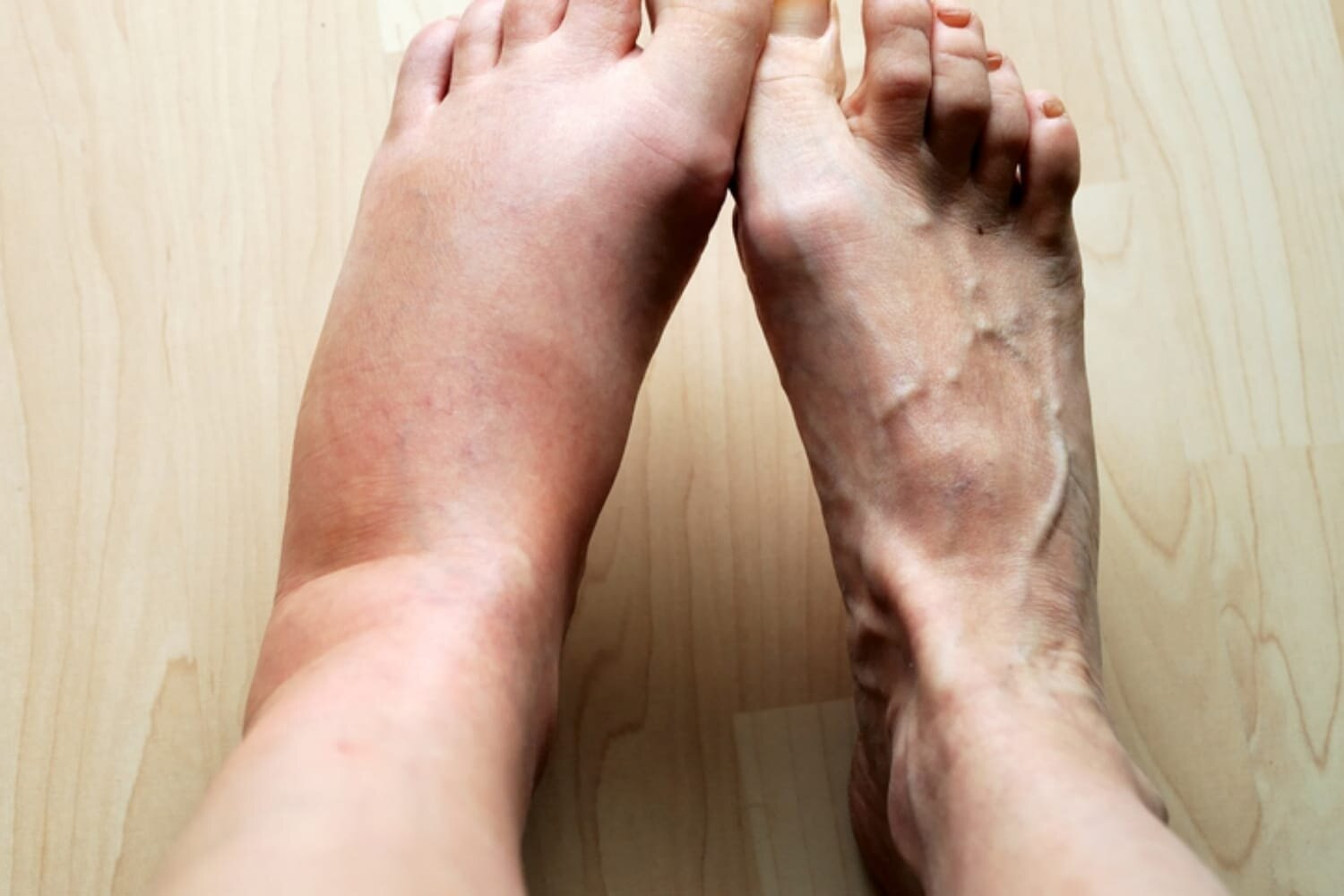
Odema/Edema
-
Fluid moves across membrane into interstitial space due to blood flow, which exerts what kind of pressure?
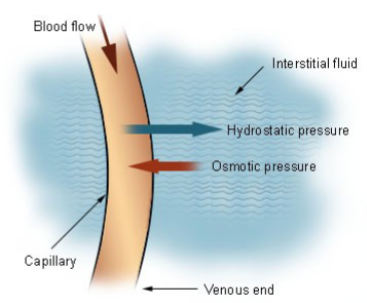
Hydraulic pressure
-
Large molecules (eg. plasma proteins) cannot pass through the membrane so they exert an osmotic pressure termed ________ __________ which creates suction force to move fluid intocapillary
What is the missing term?
Oncotic pressure
-
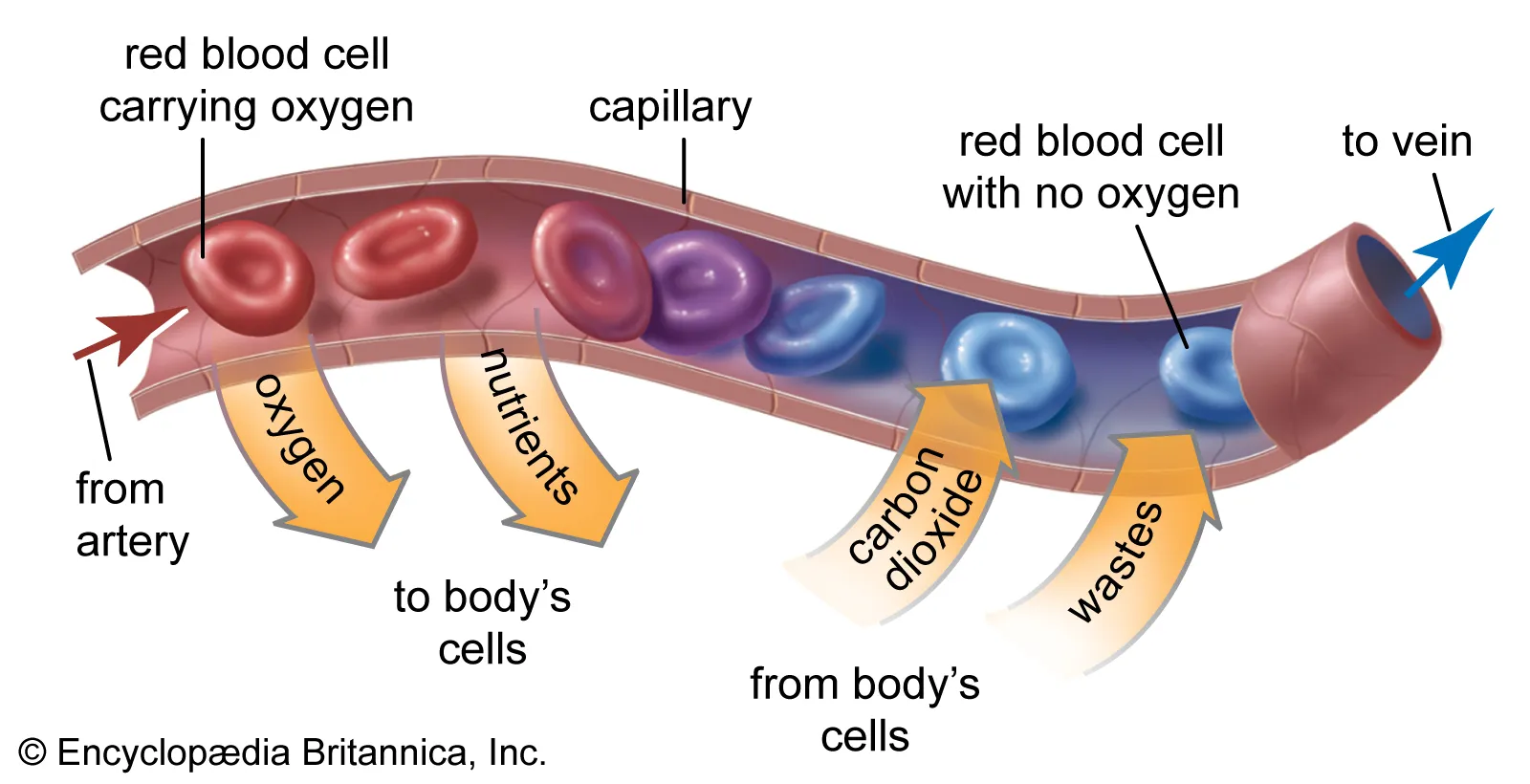
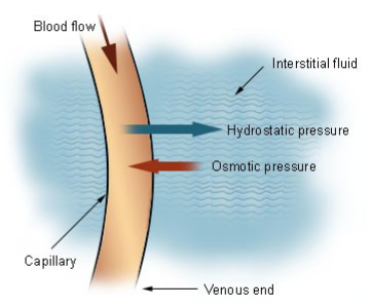
What does fluid movement across the capillary walls depend on?
The balance between hydraulic and oncotic pressures across the capillary wall
-
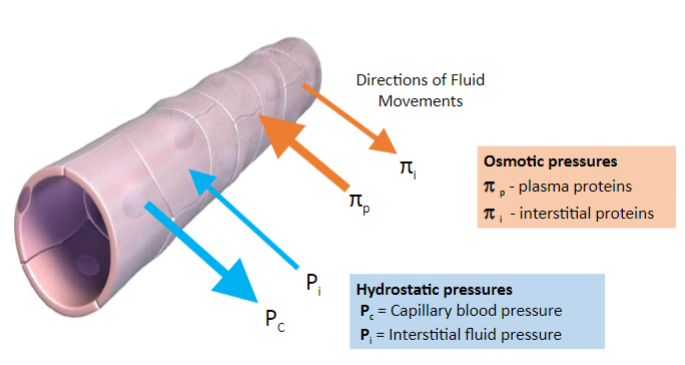
Four pressures determine filtration rates of the capillaries.
What are these four pressures?
-
State starling's principle of fluid exchange (formula)
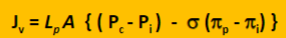
-
What do the constants in starlings principle of fluid exchange mean?

-

What is a formula for reflection coefficient σ
Effective osmotic pressure = σ x potential osmotic pressure
-
What is the reflection coefficient value (σ) for plasma protein?
0.9
-
Regarding starlings forces (the principles) what remains constant in normal conditions?

-
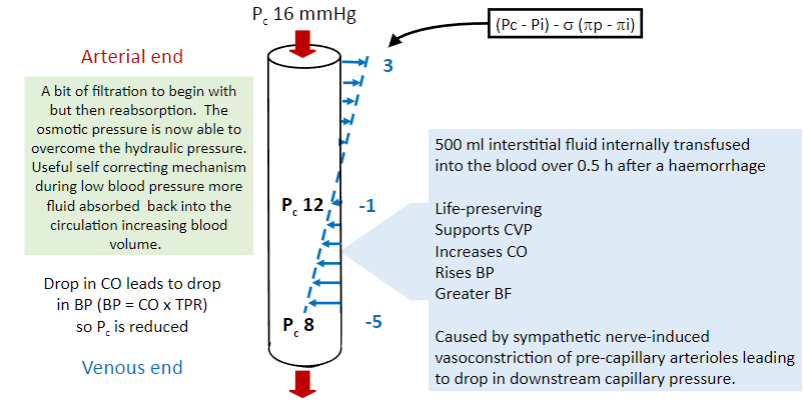
What is the equation for net filtration?
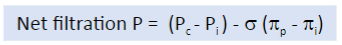
-
Picture that demonstrates the net filtration calculation in an example:
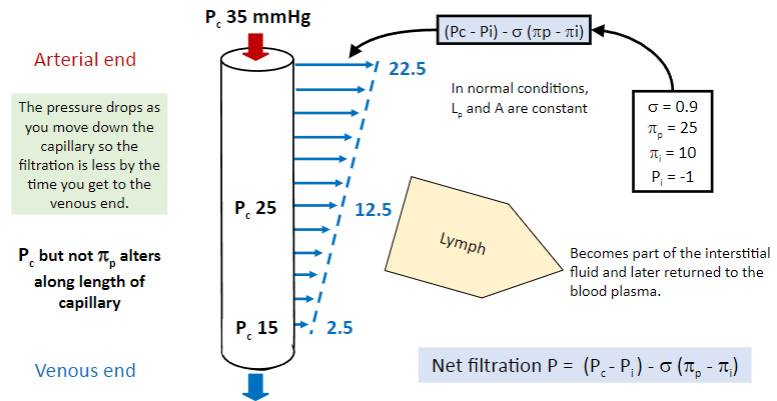
-
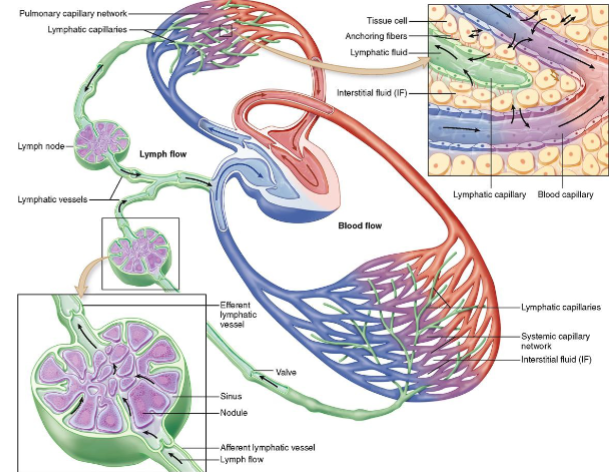
What is the function of lymphatic circulation?
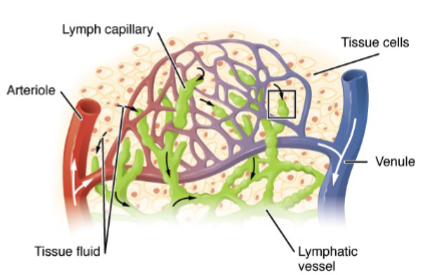
Lymphatic circulation returns excess tissue fluid/solutes back to the cardiovascular system
-
How much fluid is filtered by the lymphatic circulation per day?
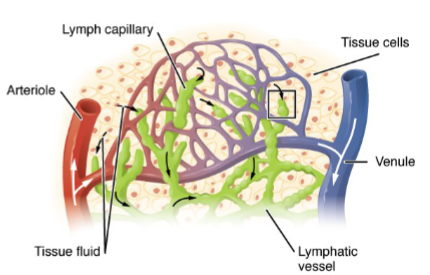
About 8 litres per day are filtered
-
What are some features of lymph vessels?
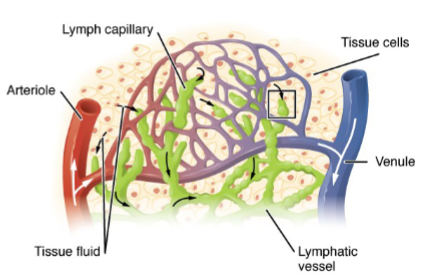
Lymph vessels have valves and smooth muscle
-
What contributes to the flow of lymph within lymph vessels
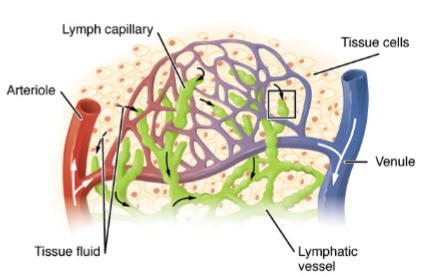
Spontaneous contractions of the smooth muscle and surrounding skeletal muscle contractions & relaxation contribute to lymph flow
-
What is found in lymph besides excess fluid and solutes
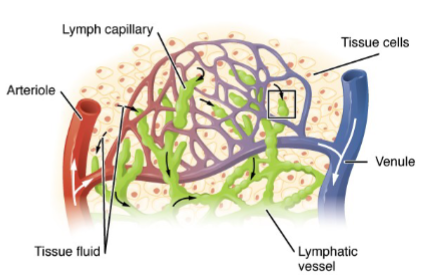
Lymph also contains immune cells, especially at the lymph nodes
-
Overall control of extracellular fluid balance depends on 3 things
State them:
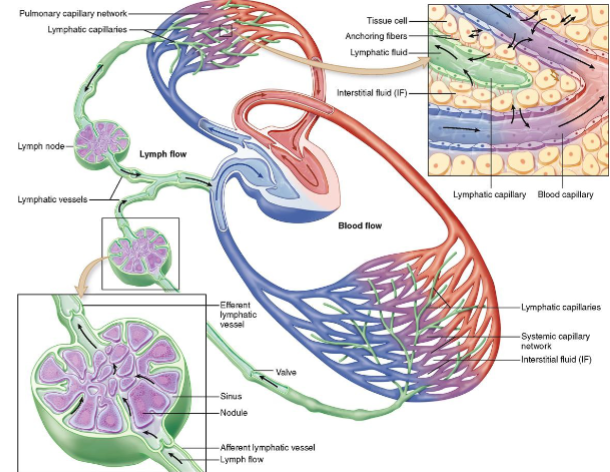
-Capillary filtration-Capillary reabsorption-Lymphatic system
-
Starling’s factors determine changes in fluid balance of 3 things
State them:
-Circulation-Interstitial fluid-Lymphatic system
-
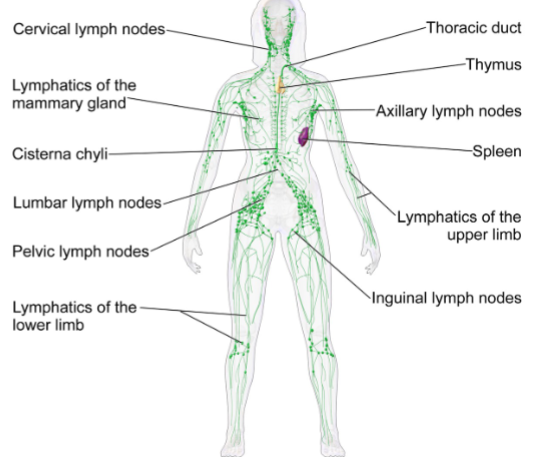
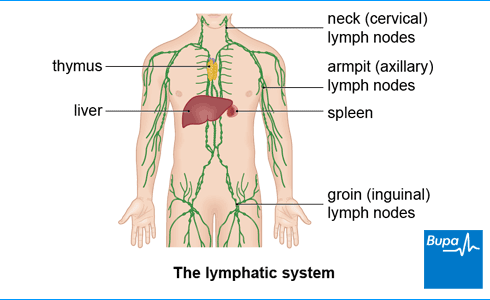
Name these parts of the lymphatic system
-
Picture demonstrating Low capillary pressure (Pc) - hypovolemia
-
Picture demonstrating how uncreased Pc gives oedema (as in DVT):
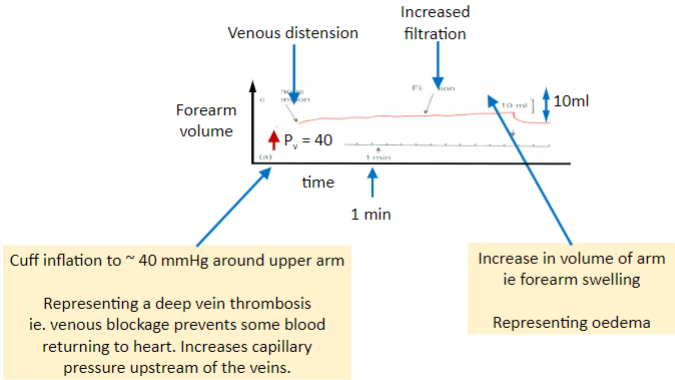
-
What are 4 causes of oedema?
-Increased capillary pressure (Pc)-Decreased plasma protein oncotic pressure (πP)-Inflammatory response-Lymphatic problems
-
What can cause low protein oedema?
Caused by malnutrition/malabsorption, nephrotic syndrome, and liver disease
-
How does malnutrition/malabsorption contribute to low protein oedema?
Leads to not enough protein intake to make plasma proteins, resulting in low protein oedema
-
What happens in nephrotic syndrome regarding protein loss and production?
There is urinary protein loss, which is replaced by liver production, contributing to low protein oedema
-
How does liver disease contribute to low protein oedema?
There is not enough endogenous albumin produced, which can lead to low protein oedema
-
What does reduced plasma protein concentration lead to?
Reduced plasma protein concentration leads to reduced plasma oncotic pressure
-
What are the consequences of greater influence of Pc and πi?
Greater influence of Pc and πi leads to fluid efflux from capillaries into the interstitial fluid
-
What is the result of fluid efflux from capillaries into the interstitial fluid?
Fluid efflux from capillaries into the interstitial fluid leads to oedema
-
What triggers swelling according to the text?
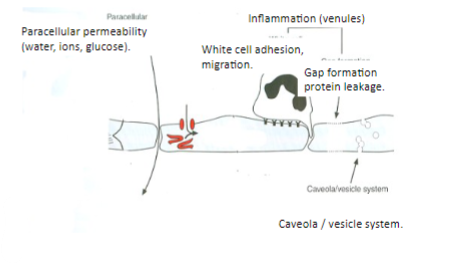
Swelling is triggered by local chemical mediators of inflammation
-
What physiological changes occur in capillaries during inflammation
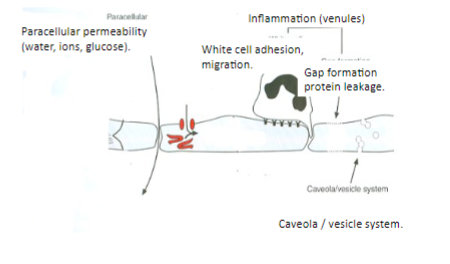
During inflammation, there is a large increase in capillary permeability, increased Lp, increased protein permeability (increased πi), and decreased σ
-
What are some factors that can induce inflammation?
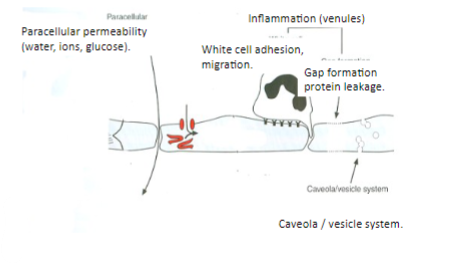
Factors that can induce inflammation include exposure to chemicals, insect bites, nettle stings, infections, physical trauma, and autoimmune diseases
-
What are some causes of lymphatic problems?
Lymphatic problems can arise from lymphatic obstruction and lymphatic removal
-
What is a specific example of lymphatic obstruction mentioned in the text?
An example of lymphatic obstruction is filariasis/elephantiasis, which is caused by nematode infestation. Larvae migrate to the lymphatic system, grow, mate, and form nests, leading to the blockage of lymph drainage.
-
How can lymphatic removal contribute to lymphatic problems?
Lymphatic removal, such as in surgery to treat testicular cancer, can cause lymphoedema by removing lymphatics, disrupting normal lymphatic drainage
-
A summary of this lecture