-

What bird are these feathers from? What are the notable features / what does this suggest about the bird?
Kiwi, feathers lack barbules and aftershafts, and are fine and hair-like. This suggests these are not flight feathers, and kiwi are flightless.
-

What does this bill suggest about the diet of this bird?
Kiwi bird, eats small invertebrates, seeds, grubs, worms. nostrils are located at the end of the long beak, kiwi can locate insects and worms underground using their keen sense of smell, without actually seeing or feeling them
-
Describe two differences between Cassowaries and Emus

Cassowaries (can) have a casque and wattle, are black-bodied; emus are brown and do not have these.
-

What order of bird are these feet from? What is it used for?
Casuariiformes (emus and cassowaries), the long sharp toenails are used defensively
-
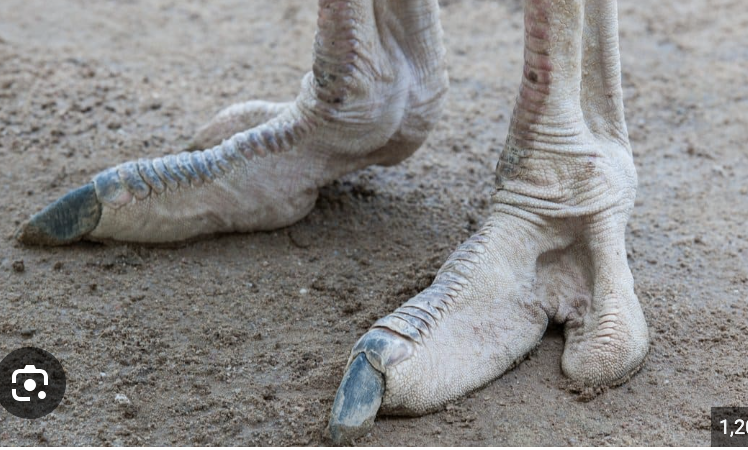
What order of bird are these feet from?
Struthioniformes (Ostriches), run very fast
-
What birds are Ratites
Struthioniformes (ostriches)
Rheiformes (rheas)
Casuariiformes (cassowaries and emus)
Apterygiformes (kiwi)
All Ratites are flightless but not all flightless birds are ratites
-
skeletal differences of ratites vs flying birds
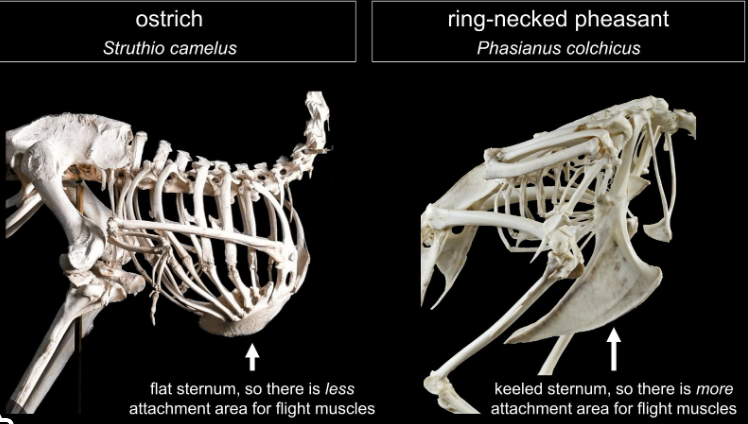
ratites/tinamous : reduced wing bones and reduced or absent keel.
-
What is the name of the feather attached at the superior umbilicus
Aftershaft
-
what is the purpose of the keel bone
Anchor/ attachment point for flight muscles
-
What feature do paleognathae have in common?
Paleo=old; gnath=jaw. Morphological characteristics of the bones of the skull's palate.
-
what orders of birds are in the infraclass paleognathae?
Apterygiformes (kiwi)
Casuariiformes (cassowaries and emu)
Rheiformes (rhea)
Struthioniformes(ostriches)
Tinamiformes(tinamou)
-
How do these attach to each other: barbule, barb, hooklet, rachis
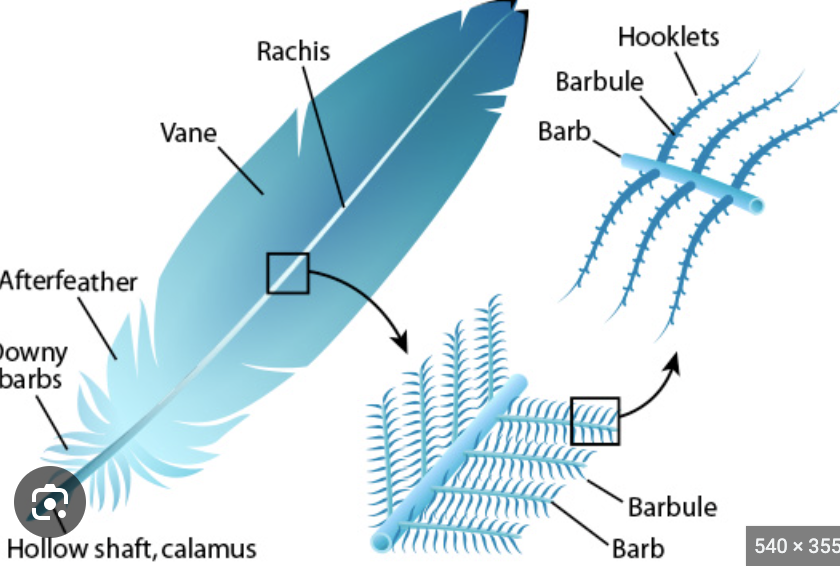
rachis->barb->barbule->hooklet
-
(types of feathers) Vaned feathers of body, and tail including flight feathers of the wings
contour feather
-
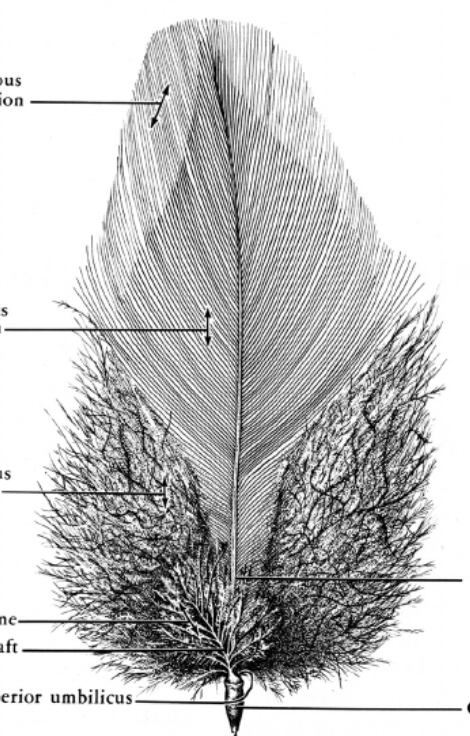
What portion of the feather are the top two lines pointing to?
Open pennaceous and normal pennaceous portion of the vane
-
(types of feathers) name of the flight feathers of the wing
Remiges
-
(types of feathers) name of the flight feathers of the tail

Retrices - in some groups like woodpeckers these are adapted and strengthened to act as props and helps them to stabilize and remain vertical as they forage on tree trunks
-

(types of feathers) rachis is distinct and always longer than any of the barbs
Semiplume lies under surface contour feathers, purpose is to insulate and form smooth aerodynamic body contours
-
(types of feathers) Highly plumulaceous, layer of insulation under contour feathers, very short rachis
Adult down
-
(types of feathers) covers hatchlings, like adult down but no rachis
natal down
-
(types of feathers) disintegrate into fine powder when groomed to clean off mites/debris and add waterproofing.
powder down
-

(types of feathers) Contour feather without vane, found around the nostrils and rictus of the mouth
Bristles
-

(types of feathers) monitors position and movement of wings and tail feathers
filoplumes
-
What order are ostriches in?
Struthioniformes
-
What order are rheas in?
Rheiformes
-
What order are cassowaries and emus in?
Casuariiformes
-
What order are Kiwis in?
Apterygiformes
-

What order is this bird in?
Apterygiformes (kiwi)
-

What order is this bird in?
Casuariiformes (cassowary)
-

What order are these birds in?
Casuariiformes (emu)
-

What order does this bird belong to?
Struthioniformes (ostrich)
-

What order are these birds in?
Tinamiformes (tinamous)

