-
How are proteins sorted to the ER?
Transmembrane transport then further sorted by vesicular transport to other compartments or to cell surface.
-
What are the 2 major functions of the ER?
Synthesis and modifications of proteins (rough)
Synthesis of lipids (smooth)
-
How do proteins know they should go to the ER?
They have an ER signal sequence. These proteins include soluble proteins, transmembrane proteins, proteins destined for Golgi, secretion and lysosomes
-
What are the steps in how proteins are sorted into the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
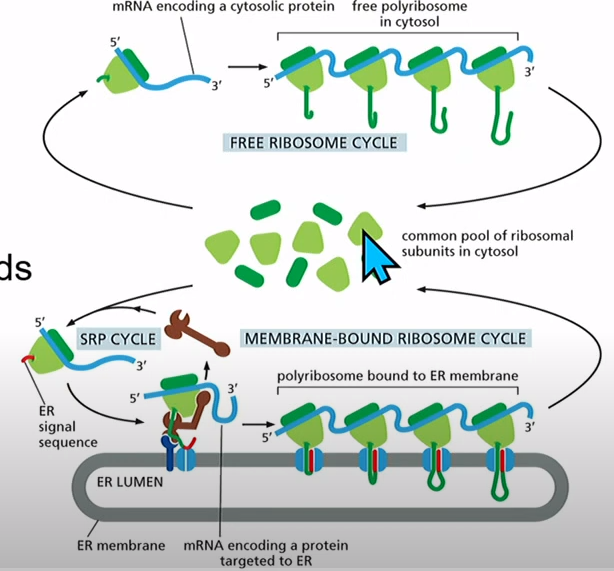
1. mRNA + Ribosomes
2. Translation starts but there's an ER signal sequence (emerges first at N-terminus hydrophobic)
3. Ribosomes directed to ER membrane (SRP)
4.Co-Translational translocation
-
What is SRP, what does it do?
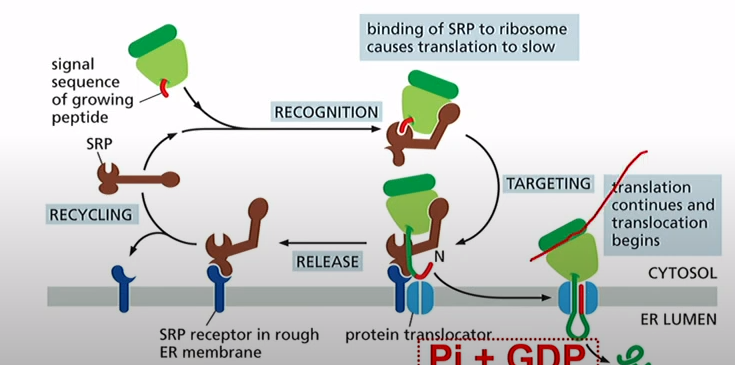
Signal Recognition Particle and SRP receptor have GTPase domains that bind GTP.
SRP + Ribosome=Low affinity
SRP + ribosome + ER signal sequence = high affinity and binds to SRP receptor
Binding of SRP causes translation to pause
-
What is the ER signal sequence also called?
N-Terminal start-transfer sequence
-
How does the protein actually get made from the ribosomes straight into the cell?
ER signal sequence is bound to the translocator
Protein is fed through translocator
signal peptidase cleaves signal
Protein is in ER
-

D
-
What are the three types of single-pass transmembrane proteins?
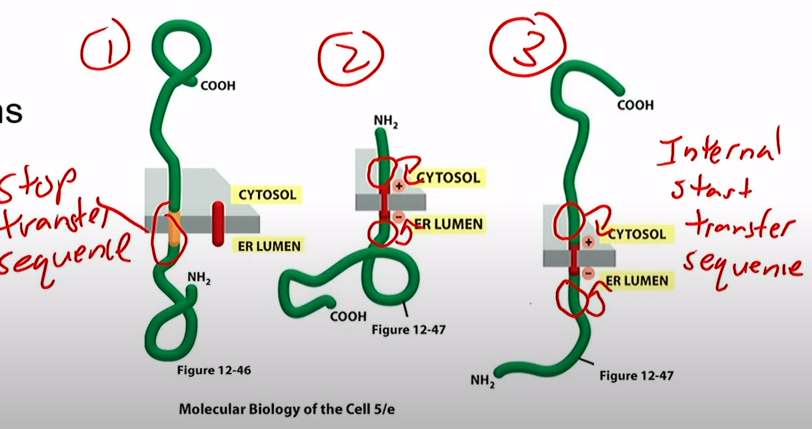
1.Stop Transfer sequence
2/3.Internal start transfer sequence
-
How does the stop transfer intermembrane protein get imbedded?
N terminal signal sequence goes through translocator like normal. Translocator reaches a stop transfer sequence. Rest of protein gets made in cytosol. Signal peptidase cleaves signal sequence. COOH in cytosol
-
How do the other two intermembrane proteins get imbedded?
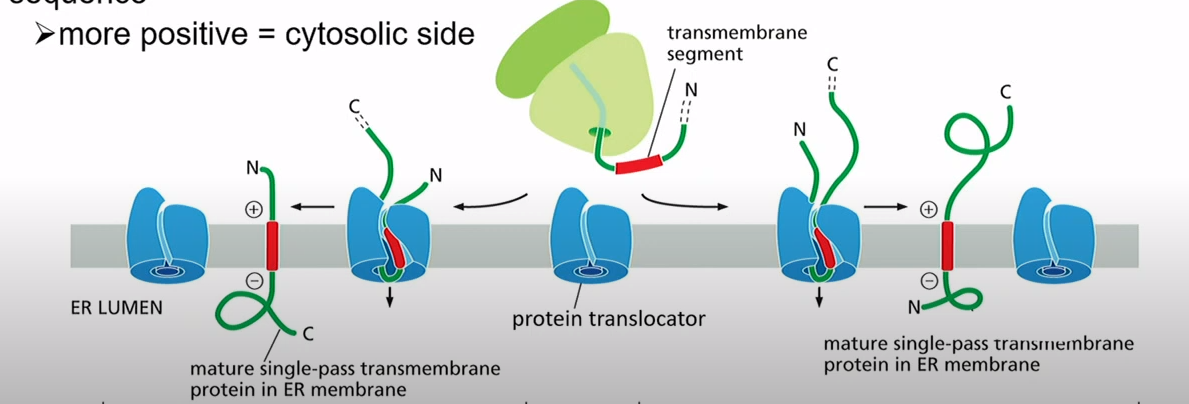
Ribosome makes it, there's an internal start transfer sequence. the more positive side of each end of the sequence ends up in the cytosol
-
How does multipass transmembrane protein get embedded if N terminus is more positive?
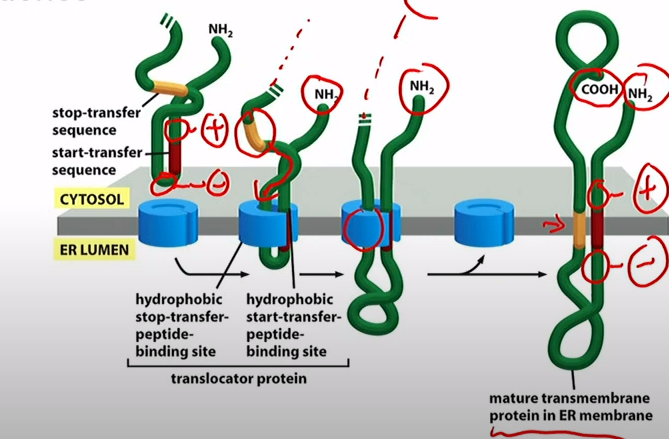
Translocator finds more positive side that one goes to cytosol. Translocator reaches stop-transfer sequence. You get a multipass. Both N-terminus and C-terminus in cytosol.
-
How does multipass transmembrane protein get embedded if C terminus is more positive?
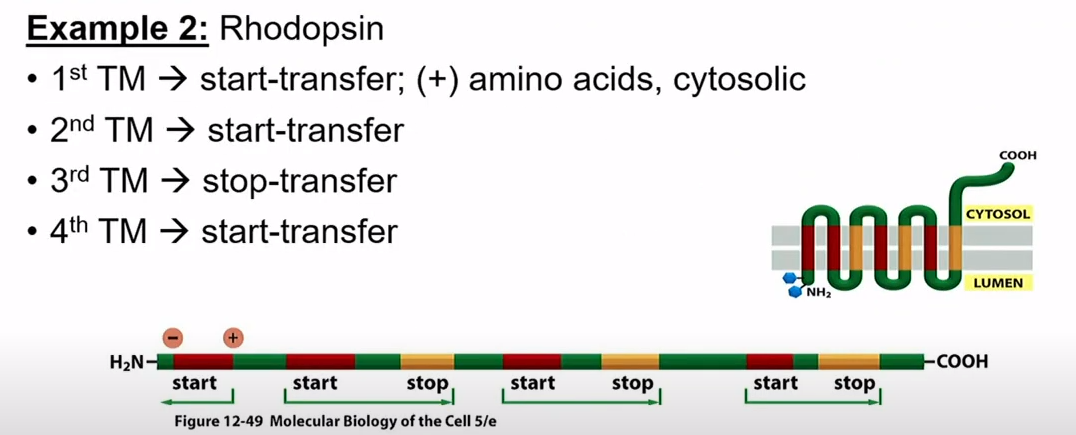
-
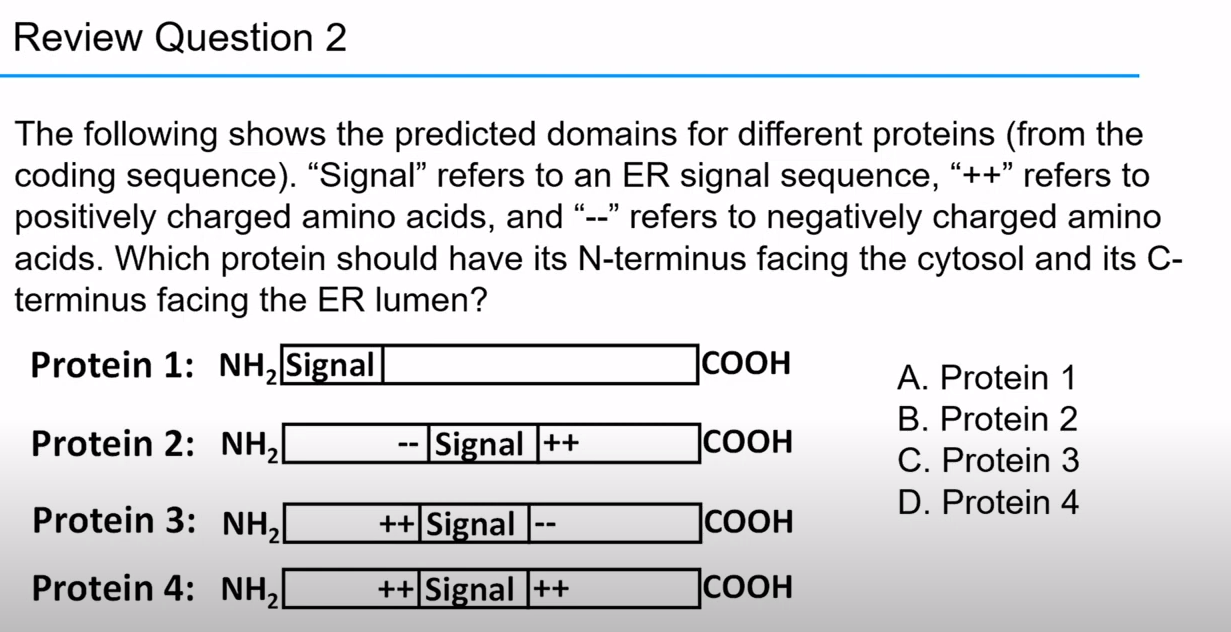
C
-
What are the 3 membrane protein types?
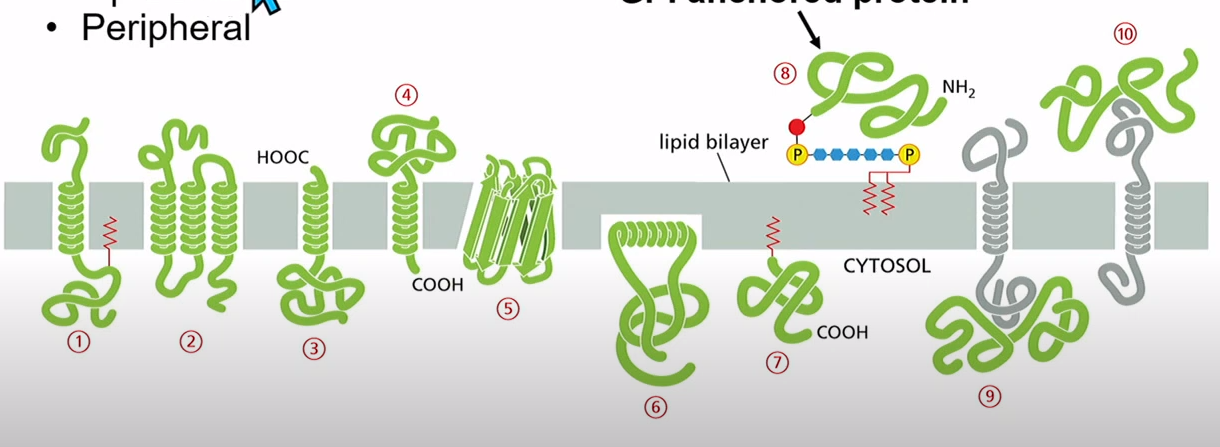
Integral
Lipid anchored
Peripheral
-
How to anchor protein onto GPI anchor?
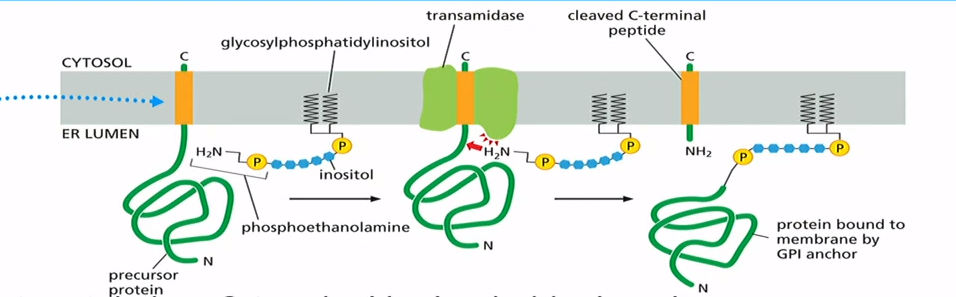
Target protein has C terminal in cytosol. Transamidase comes in and takes pre formed GPI anchor, mediate a cut at ER lumen side of protein and attach it to GPI anchor. GPI anchored protein ends up on ER lumen side and can go to cell exterior surface

