-
What is glycosylation?
Adding sugar chains to proteins, most soluble and transmembrane proteins in ER are glycosylated
-
What are the two types of glycosylation
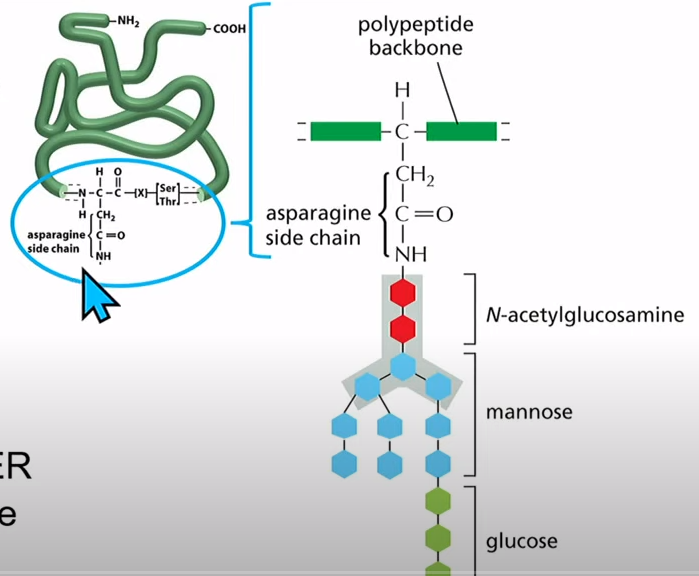
O-Linked - adding sugar to oxygen, oxygen is on side chain (10%)
N-Linked - adding sugar to nitrogen, nitrogen on asparagine (Asn) side chain (90%)
-
How is the the N-linked sugar added?
It is transferred by an oligosaccharyl transferase to an Asn on a protein being synthesized. The transferase looks for Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr where X is any amino acid besides proline. Proteins are only glycosylated on the ER lumen side.
-
What happens after the transfer of the N-linked sugar?
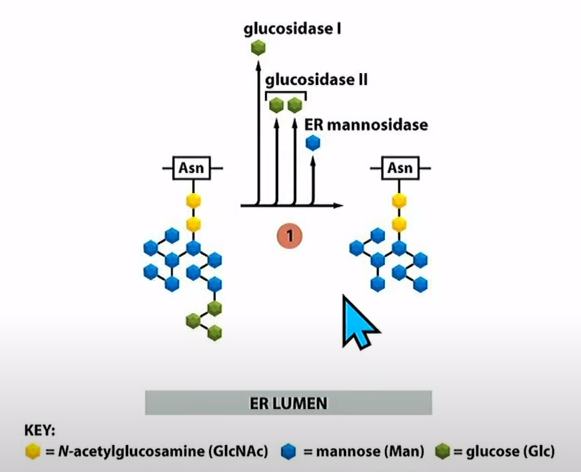
1. 3 glucoses are removed (linked to proper folding of protein)
2. 1 Mannose is removed
3. Glycosylated protein is transported via vesicles to the Golgi
4. That glycosylated protein is further modified in Golgi sacs
-
What are the three different Golgi sacs/cisternae?
Cis, Medial, and Trans
-
Why do we have glycosylation?
Tag to mark the state of protein folding
Protect proteins on cell surface from proteases
Play a role in cell adhesion
Allow proteins to form correct structures

