-
What is extracellular matrix?
Specialized material outside of the cell
-
What are the two types of protein sorting?
1. Post-Translational Process
Fully synthesised in cytosol before sorting
Unfolded: mitochondria, plastids
Folded: nucleus, peroxisomes
2. Co-Translational Process
During translation you sort it
-
What are the three types of Protein Sorting mechanisms?
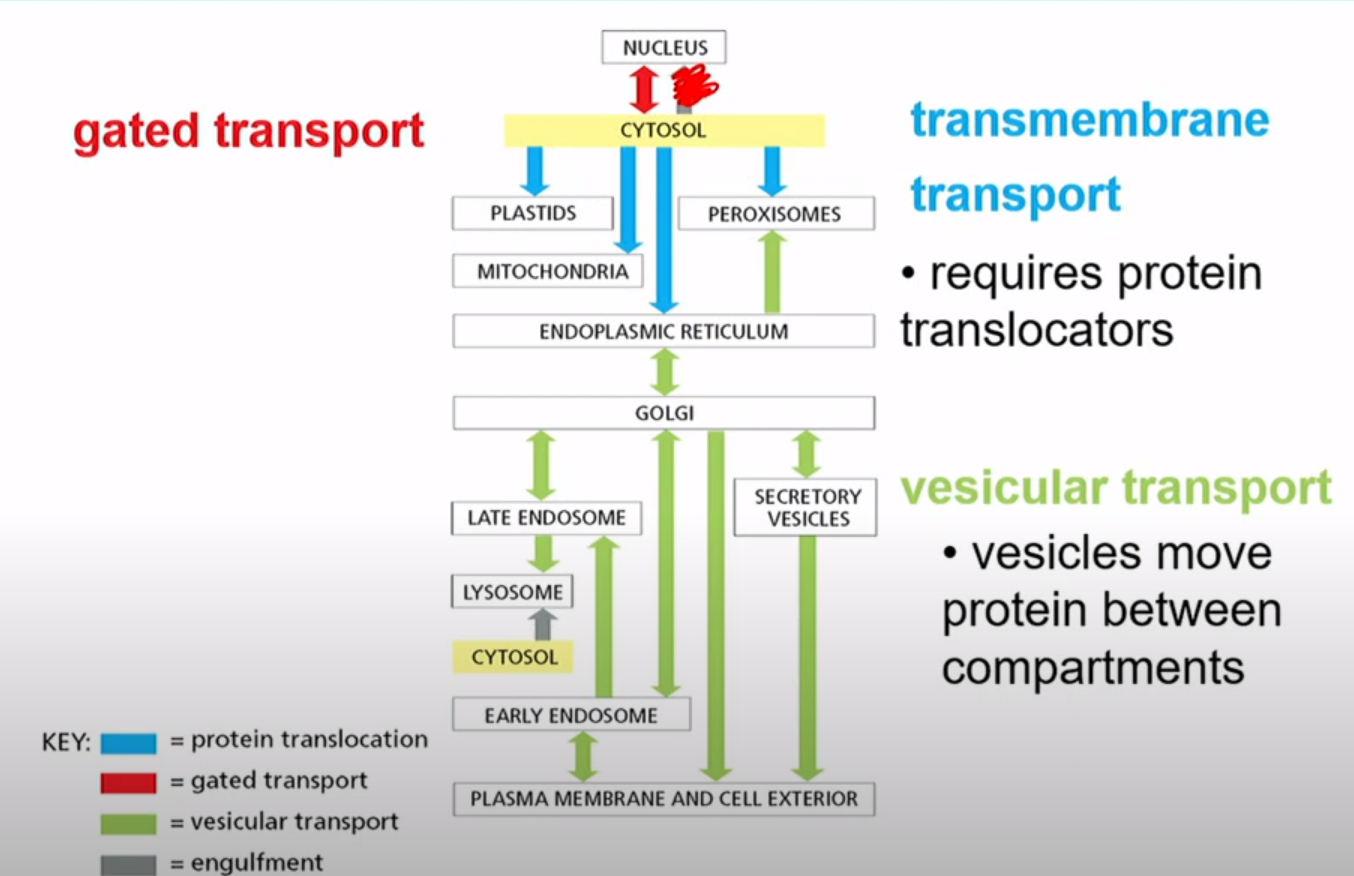
Gated Transport
Transmembrane Transport
Vesicular Transport
-
What is Gated Transport?
Proteins moving between cytosol and nucleus
For example the selective transport of macromolecules and free diffusion of small molecules
-
How do proteins move into the nucleus?
Through a Nuclear Import Receptor. The nuclear import receptor binds to the nuclear import localization signal (NLS, rich in Arg and Lys specific)
-
How do proteins move out of the nucleus?
Through Nuclear Export Receptor, which Cargo proteins bind to using their Nuclear Export Signal (NES)
-
What is required for nuclear import and export?
Ran GTPase
-
How is GTPase regulated?
Ran-GAP (GTPase-activating protein)- stimulates GTP hydrolysis by Ran
Ran-GEF(Guanine nucleotide exchange factor)- Promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP
-
Where are Ran-GAP and Ran-GEF found in the nucleus and cytosol?
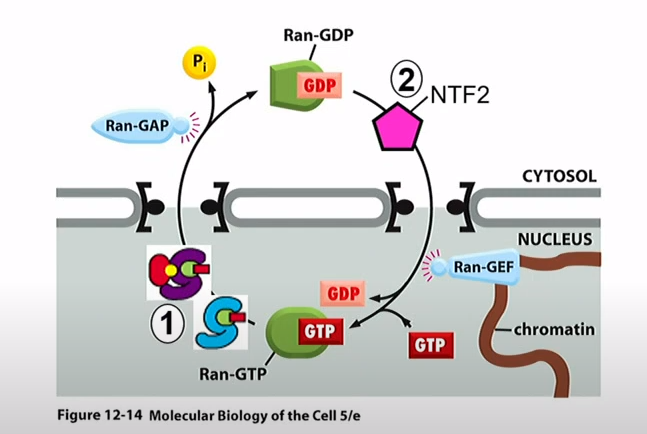
Ran-GAP is in the cytosol and Ran-GEF is in the nucleus
-
What are the concentrations of Ran-GTP in the nucleus and cytosol
High Ran-GTP in nucleus and low Ran-GTP in cytosol
-
How is Ran-GDP transported back to the nucleus?
Using a protein called NTF2 (Nuclear Transport Factor 2)
-
What are the steps for nuclear import?
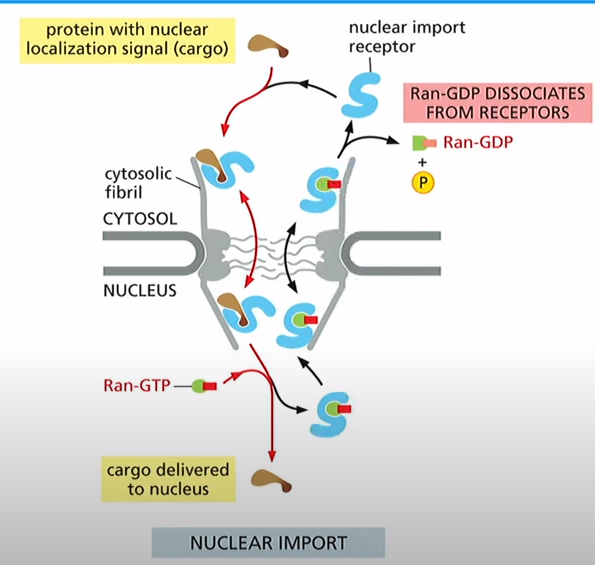
1. Nuclear import receptor binds to cargo in cytosol
2. Receptor and cargo move into nucleus
3. Ran-GTP binding cause release of cargo
4. Now you have import receptor and Ran-GTP move into cytosol
5. Ran Binding Protein and Ran-GAP promote GTP hydrolysis and release of import receptor
-
What are the steps for nuclear export?
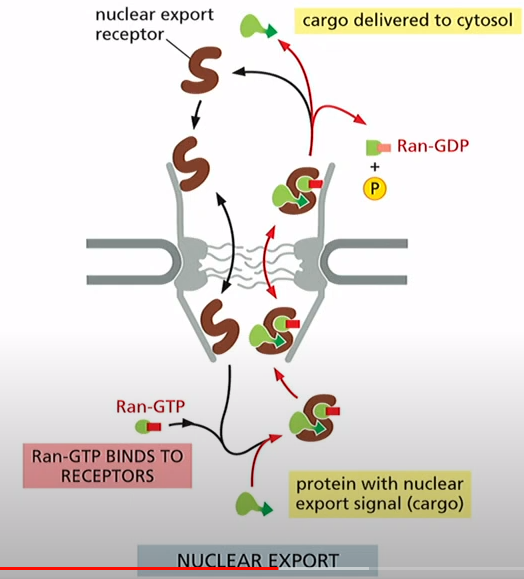
1. Nuclear export receptor binds to cargo and Ran-GTP
2. Receptor + Cargo + Ran-GTP move to cytosol
3. Ran Binding Protein and Ran-GAP promote GTP hydrolysis, release of cargo and receptor
4. Empty export receptor returns to nucleus
-
What is NFAT in its role in nuclear export and import?
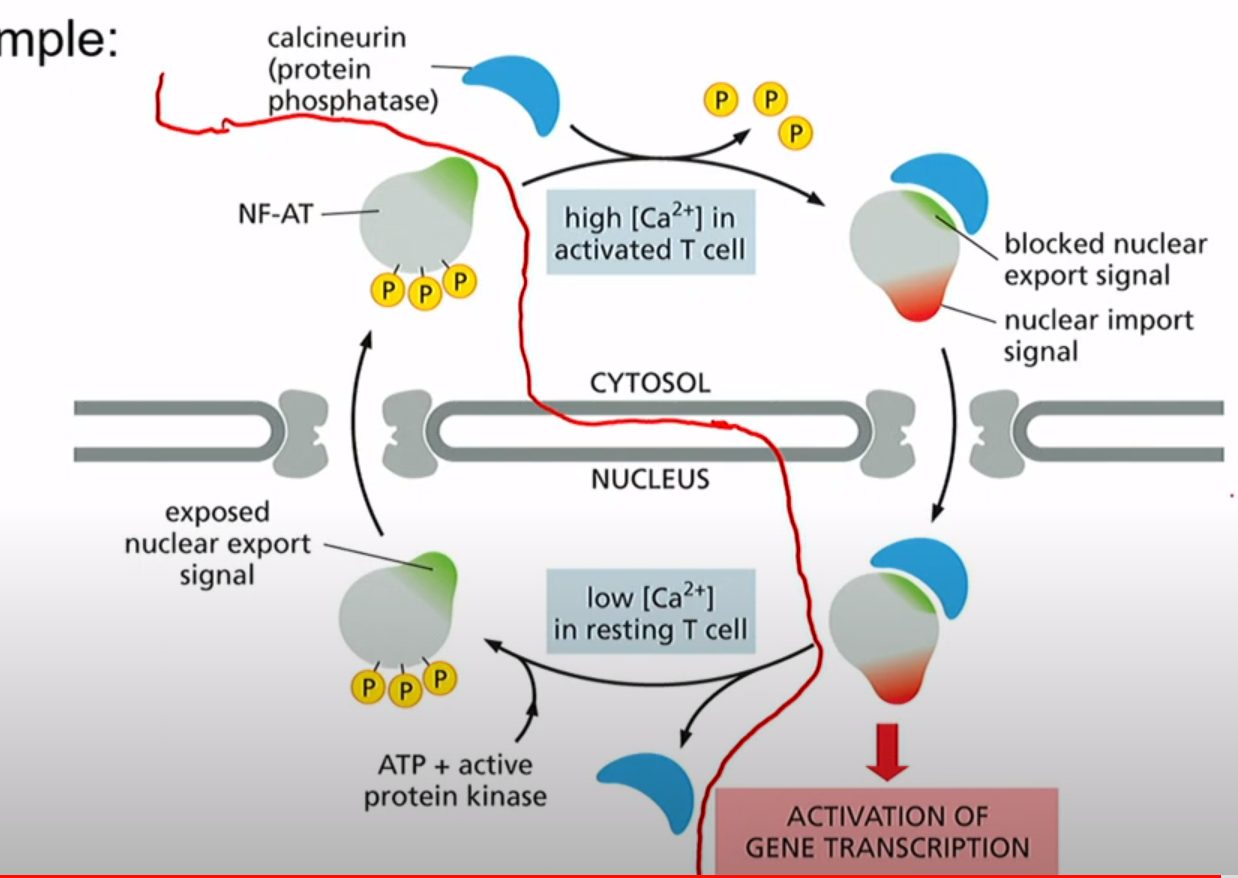
high Ca2+ = nuclear import
low Ca2+= nuclear export
-
How do you sort proteins to the mitochondria?
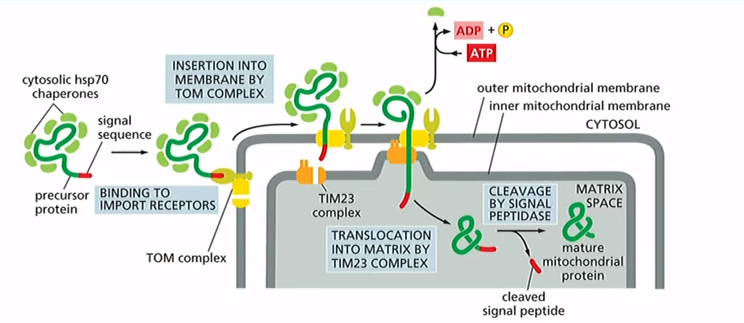
Cytosolic chaperone proteins with protein that has signal sequence(N-terminal amphipathic a-helix) bind to import receptors of TOM and TIM23 complexes. Signal sequence is then cleaved
-
How do you sort proteins to the thylakoid?
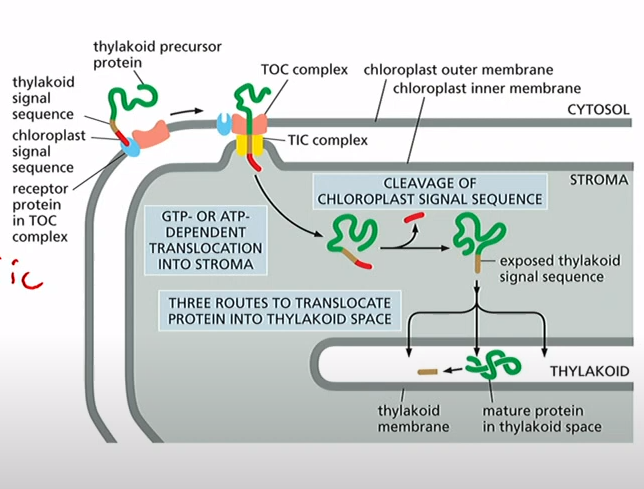
Protein that has signal sequence(N-terminal amphipathic a-helix) bind to import receptors of TOC and TIC complexes. Signal sequence is then cleaved inside chloroplast and thylakoid signal sequence revealed goes into thylakoid.
-
How do you sort proteins to the peroxisome?
Receptor binds to 3 amino acid at C-terminus(SKL) and it attaches to docking protein. Docking protein moves it to translocator where it goes into peroxisome

