-
Mitosis
(asexual)
one 2n cell divides into two 2n cells
(form of cellular reproduction for growth and repair)
-
Meiosis
(sexual)
2n cells produce 1n cells(used to reduce the chromosome number during the development of sperm and egg).
-
Sister Chromatids
Direct, identical copies of a particular chromosome.
-
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes of the same type of chromosome, but from a different parent (non-identical)
-
Centromere
A chromosomal region where chromosomes of a particular type join for cell division
-
Phases of mitosis
Premiotic
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
-
Interphase
Prior to mitosis
Cell duplicates contents of cytoplasm
DNA replicates in nucleus
Chromosomes not visible
Centromes outside nucleus
-
Prophase
First stage of mitosis
Chromosomes start to condense
Spindle begins to assemble btw centrosomes
Nucleolus and Nuclear envelope breaks down
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
chromosome first moves towards poles
-
Metaphase
Second stage of mitosis
Chromosomes are aligned at the spindle equator
Spindle fibers on either side extend to opposite poles of the spindle
-
Anaphase
Third stage of mitosis
Sister chromatids separate and become daughter chromosomes
spindle fibers attached to chromosomes disassemble
-
Telophase
Fourth stage of mitosis
Spindle disappears as new nuclear envelope forms around daughter chromosomes
each nucleus contains the same number ad kinds of chromosomes as the original parent cell
Remnants of spindle fibers are still visible btw the two nuclei
-
Phases of meiosis
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
-
Prophase I
Tetrads form
Crossing over occurs
Chromosomes condense
Nuclear envelope fragments
-
Metaphase I
Tetrads align at spindle equator
Either homologue can face either pole
-
Anaphase I
Homologues separate
Diads move to poles
-
Telophase I
Daughter nuclei are haploid (received one duplicated chromosome from each homologous pair)
-
Prophase II
Chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope fragments
-
Metaphase II
dyads align at the spindle equator
-
Anaphase II
sister chromatids separate becoming daughter chromosomes that move to poles
-
Telophase II
four haploid daughter cells are genetically different from each other and the parent cell
-
recombination
homologous chromosomes cross over and exchange parts.
allows diverse gametes to be made
-
Results of meiosis
production of a nucleus with just one genome that is unique combination of both parents
produces much genetic variety
-
comparison of mitosis and meiosis
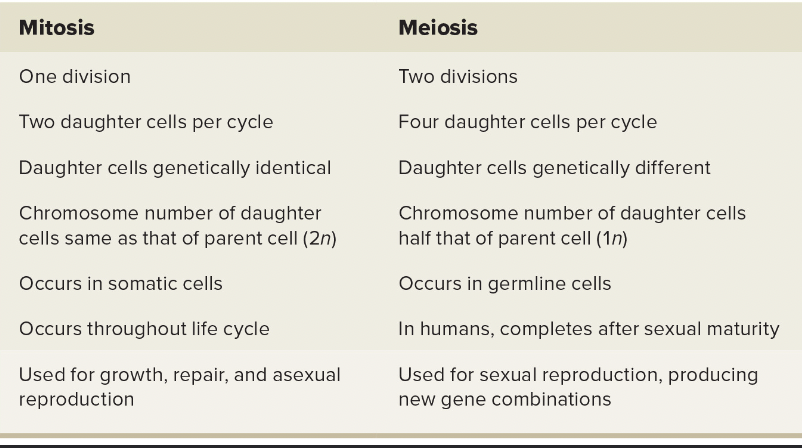
-
nondisjunction
chromatids/chromosomes fail to separate
generally lethal
-
effects of nondisjunction in meiosis I & II
Meiosis I—both members of a pair go into the same daughter cellMeiosis II—sister chromatids fail to separate
-
Trisomy—three copies of a chromosome
—three copies of a chromosome
-
Monosomy
single copy of a chromosome

