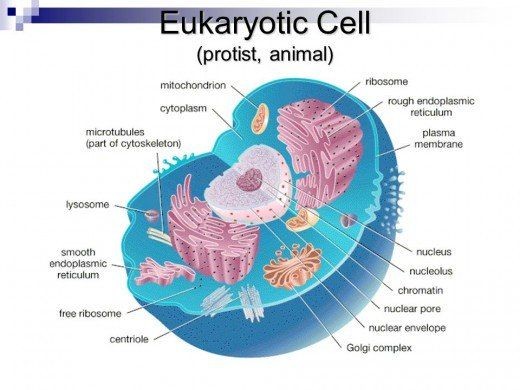
-
all cells are surrounded by
a cell membrane
-
function of the cell membrane
controls the exchange of materials between the internal cell environment and the external environment
-
definition of a cell membrane
a partially permeable membrane which surrounds a cell
-
cell membrane is formed from
a phospholipid bilayer
-
diameter of the phospholipid bilayer
10nm
-
location of the cell wall
outside the cell membrane
-
function of the cell wall
structural support
-
structural support of the cell wall is provided by
the polysaccharide cellulose in plants
peptidoglycan in most bacterial cells
-
definition of plasmodesmata
narrow threads of cytoplasm
-
function of plasmodesmata
connect the cytoplasm of neighbouring plant cells
-
what is present in all eukaryotic cells
a nucleus
-
size of a nucleus
relatively large
-
a nucleus is surrounded by
a nuclear envelope
-
definition of a nuclear envelope
a double membrane which has many pores
-
importance of nuclear pores
channels for allowing mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus
allowing enzymes and signalling molecules to travel in
-
the nucleus contains
chromatin
-
definition of chromatin
the genetic material from which chromosomes are made
-
definition of nucleolus
one or more darkly stained regions in the nucleus
-
function of nucleolus
sites of ribosome production
-
function of the mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells
-
mitochondria are surrounded by
a double membrane
-
the inner membrane of mitochondria are folded to form
cristae
-
the matrix formed by cristae contains
enzymes needed for aerobic respiration producing ATP
small circular pieces of DNA
ribosomes
-
where are chloroplasts found
in the green parts of a plant
-
chloroplasts are larger than
mitochondria
-
chloroplasts are surrounded by
a double membrane
-
in chloroplasts, what structure contains chlorophyll
thylakoids
-
in chloroplasts, what are grana
stacks of thylakoids
-
what is chlorophyll
photosynthetic pigment
-
grana are joined together by
lamellae
-
what are lamellae
thin and flat thylakoid membranes
-
the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis takes place in
the thylakoids
-
the light-independent stage of photosynthesis takes place in
the stroma
-
what is the Calvin Cycle
the light -independent stage of photosynthesis
-
chloroplasts also contain
small circular DNA
ribosomes
-
what are ribosomes in chloroplasts used for
to synthesize proteins needed in chloroplast replication and photosynthesis
-
what are ribosomes composed of
almost equal amounts of ribosomal RNA and protein
-
where are ribosomes formed
in the nucleolus
-
where are ribosomes found in all cells
freely in the cytoplasm
-
where are ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells
part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
-
what type of ribosomes are found in eukaryotic cells
80s
-
where are 70s ribosomes found
prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts
-
what are 80s ribosomes composed of
60 s and 40s
-
what are 70s ribosomes composed of
50s and 30s
-
ribosomes role in protein synthesis
site of translation
-
distinguishing factor of rough endoplasmic reticulum
surface covered in ribosomes
-
how is rough endoplasmic reticulum formed
from continuous folds of membrane continuous with the nuclear envelope
-
function of rough endoplasmic reticulum
processes proteins made by the ribosomes
-
distinguishing factor of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
does not have ribosomes on the surface
-
function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
involved in the production, processing and storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
-
structure of the golgi apparatus
cisternae
-
which two structures have similar flattened sacs of membrane in their structure
smooth endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus
-
function of golgi apparatus
modifies proteins and packages them into vesicles or lysosomes
-
definition of a large permanent vacuole
a sac in plant cells that is selectively permeable
-
vacuoles are surrounded by the
tonoplast
-
which vacuoles are small and temporary
animal cell vacuoles
-
a vesicle is surrounded by a
bilayer
-
definition & function of a vesicle
membrane-bound sac for transport and storage
-
definition of a lysosome
specialist form of vesicles which contain hydrolytic enzymes
-
definition of hydrolytic enzymes
enzymes that break biological molecules down
-
function of lysosomes
break down waste materials
-
examples of materials lysosomes break down
worn out organelles
-
definition of microtubules
hollow fibres made of microtubules
-
definition of a centrosome
two centrioles at right angles to each other
-
function of a centrosome
organises the spindle fibres during cell division
-
in which organisms are centrosomes absent
flowering plants and fungi
-
function of microtubules
make up the cytoskeleton of the cell
-
size of a microtubule
about 25 nm in diameter
-
formation of a microtubule
made of alpha and beta tubulin combined to form dimers
dimers are then joined to form protofilaments
13 protofilaments in a cylinder make a micrtubule
-
how many protofilaments in a cylinder make a microtubule
13
-
function of the cytoskeleton
used to provide support and movement of the cell
-
what are microvilli
cell membrane projections
-
function of microvilli
to increase surface area for absorption
-
what are cilia
hair-like projections
-
what are cilia made from
microtubules
-
function of cilia
allows movement of substances over the cell surface
-
cilia have a similar structure to
flagella
-
difference in structure of cilia and flagella
flagella are made from longer microtubules
-
function of flagella
contract to provide cell movement
-
an example of an animal cell with flagella
sperm cell