-
what is the axis of symmetry called?
the principal axis
-
what is the principal focus?
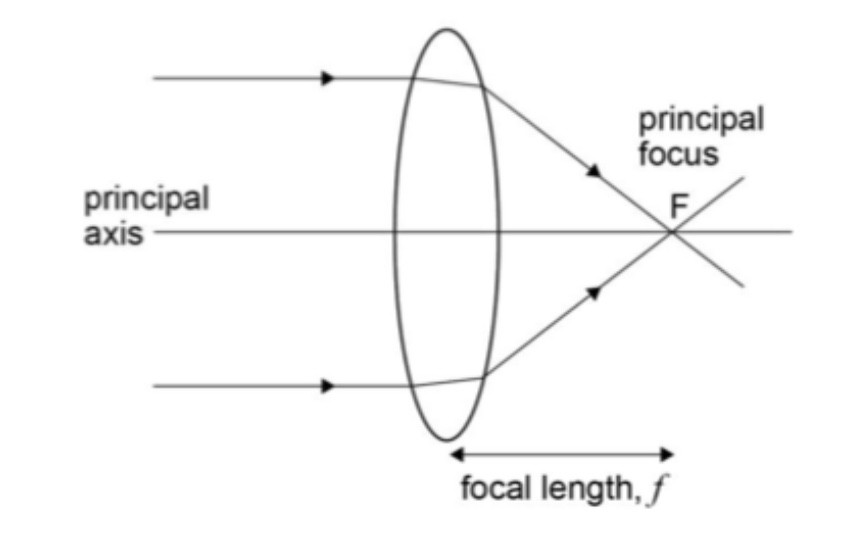
a point on the axis which is the same distance from the optical center as the focal length, this is where light rays travelling parallel to the principal axis prior to refraction converge
-
focal length
the distance between the center of the lens and the principle focus
-
u in lens diagram
the distance between the object and the center of the lens
-
v in lens diagram
The distance between the image and the center of the lens
v is positive for real images and negative for virtual images
-
ray diagram for an object long way from the lens and describe the image's appearance beyond 2f
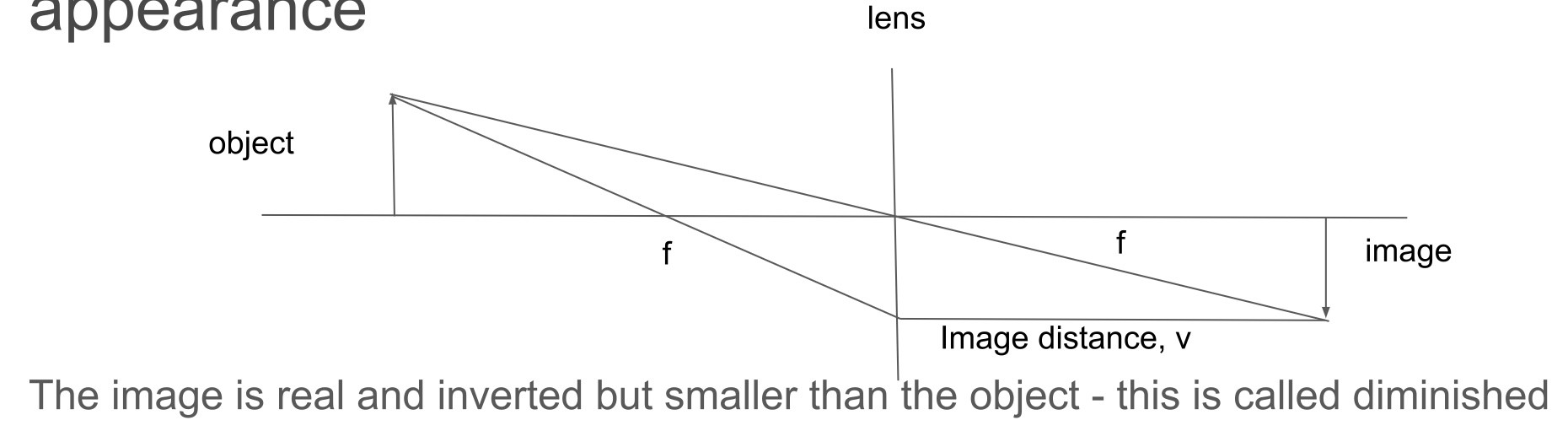
-
ray diagram for an object really close to the lens and describe the image's appearance
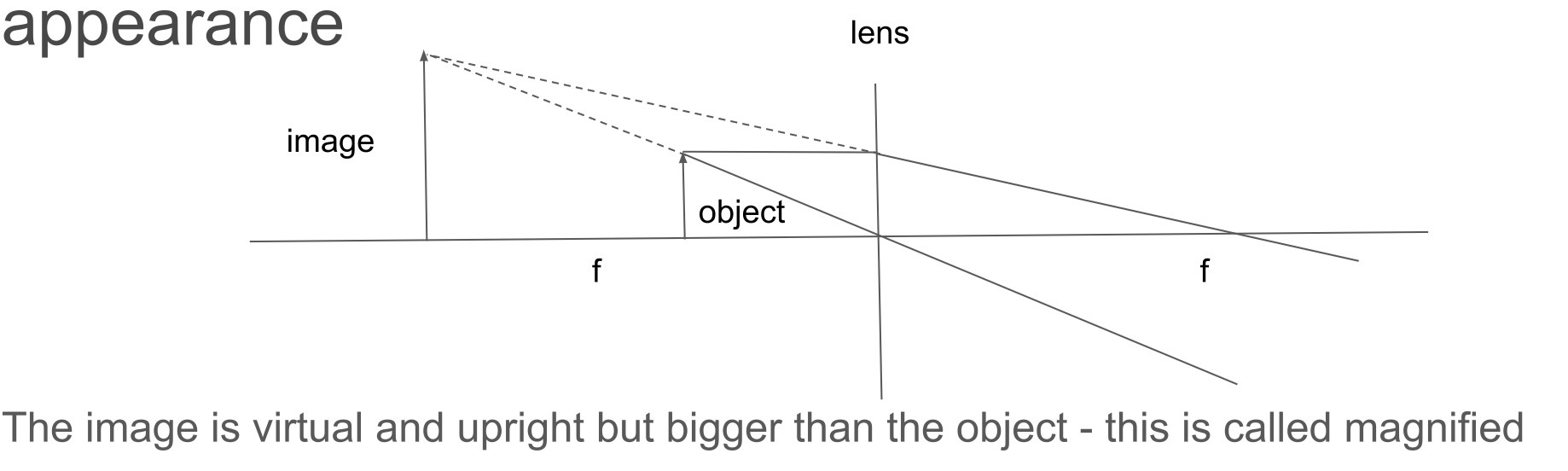
-
ray diagram for an object at fairly close to the lens , f and 2f, and describe the image's appearance
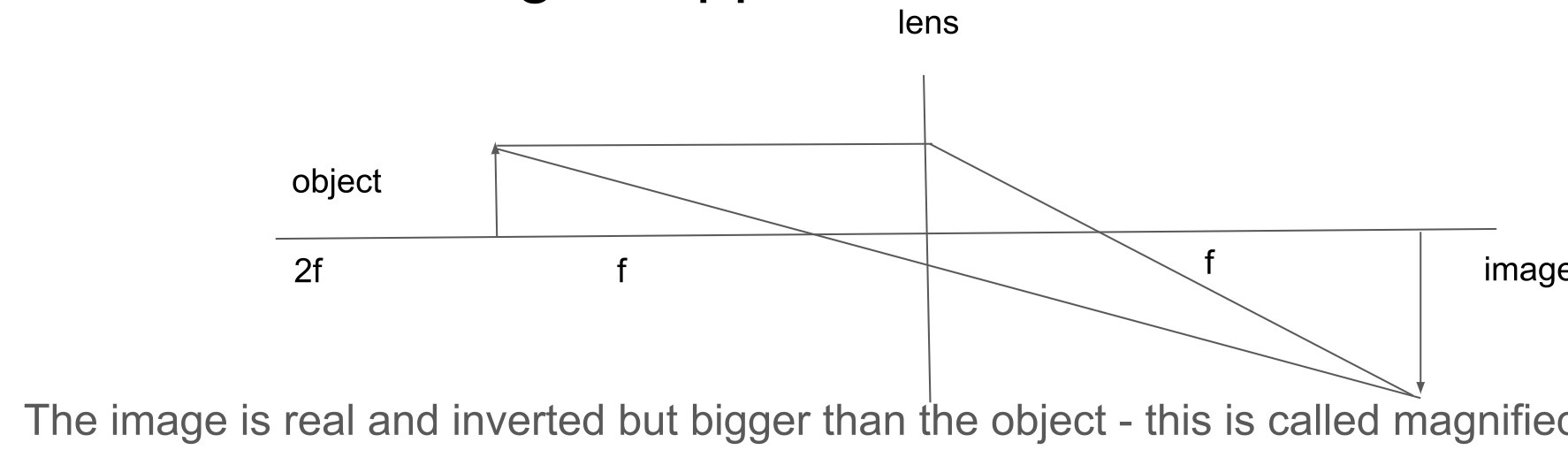
-
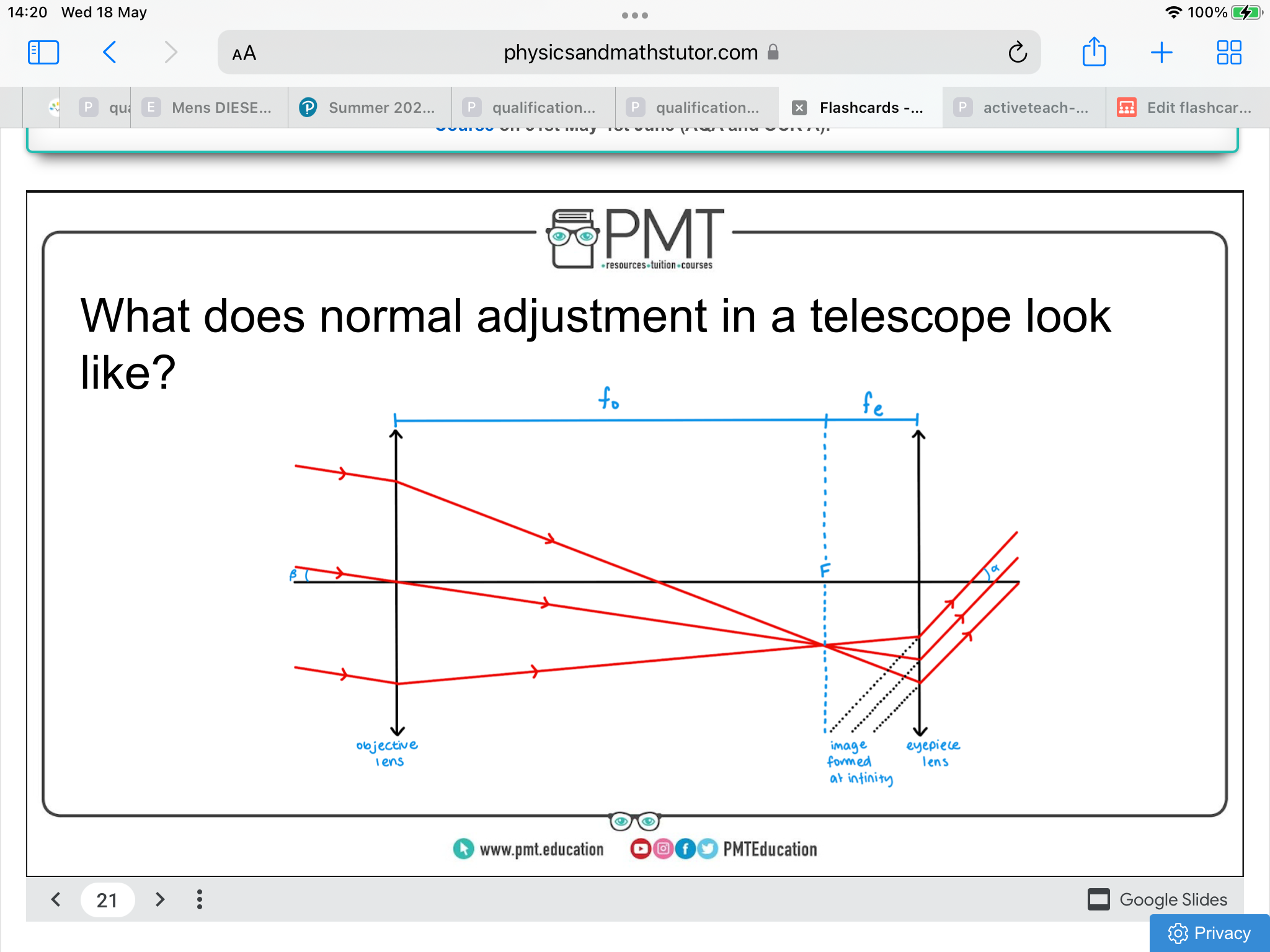
what normal adjustment in a telescope looks like
-
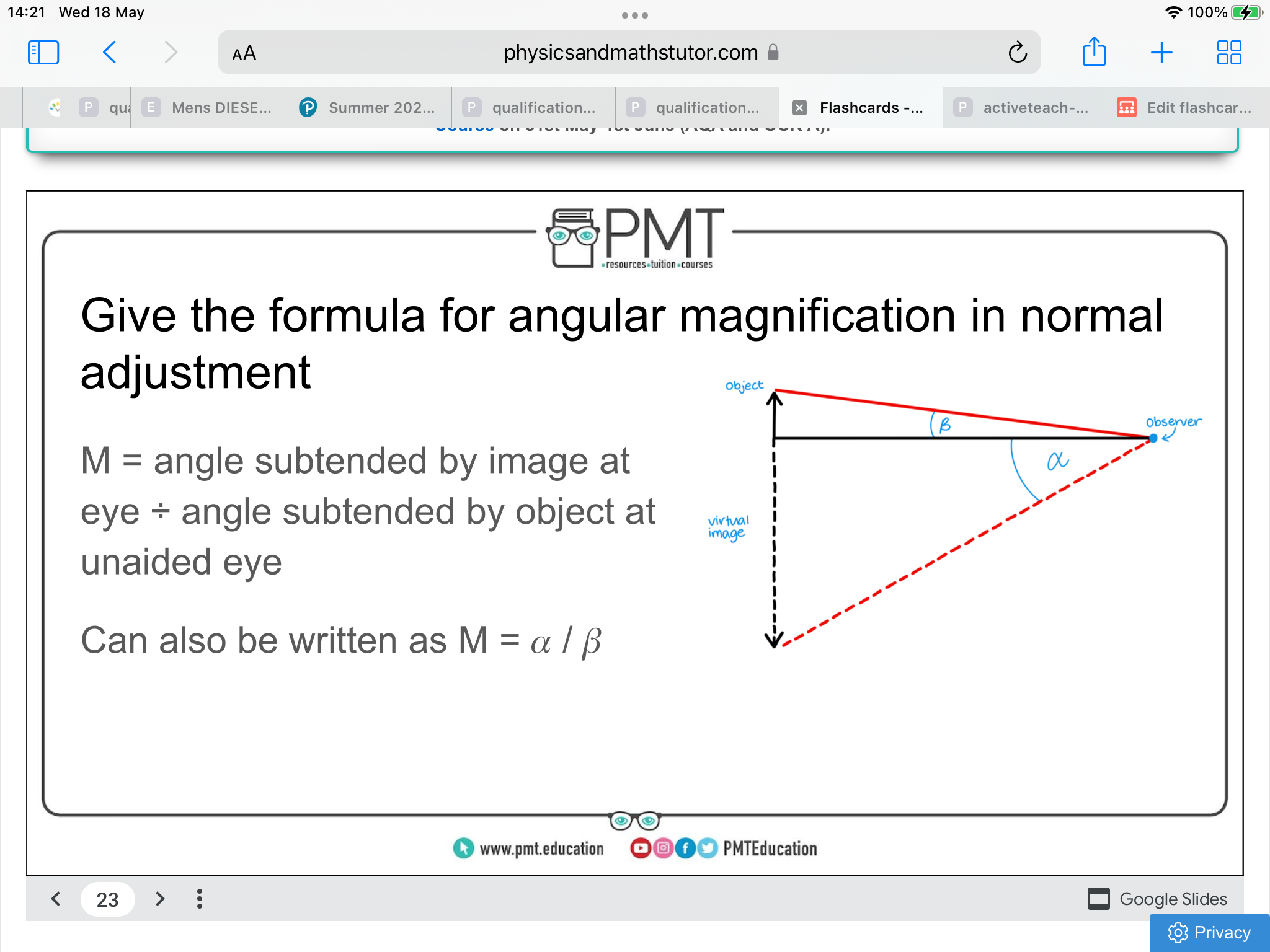
formula for angular magnification in normal adjustment
-
state the equation that relates M to the focal length for objective eyepiece lenses
M = fo/fe
only used if both angles from M = alpha/beta is less than 10
-
How does an astronomical refracting telescope work?
There are two converging lenses, the objective lens and the eyepiece lens. The role of the objective lens is to collect light and create a real image of a distant object. This image is magnified by the eyepiece lens which produces a virtual image - formed at infinity to reduce eyestrain when looking between the object and the telescope image
-
What is apparent magnitude
m how bright the star appears from Earth
-
What is absolute magnitude
M how bright the star appears 10 parsecs from Earth
-
equation relating absolute and apparent magnitude
m – M = 5 log (d/10)
-
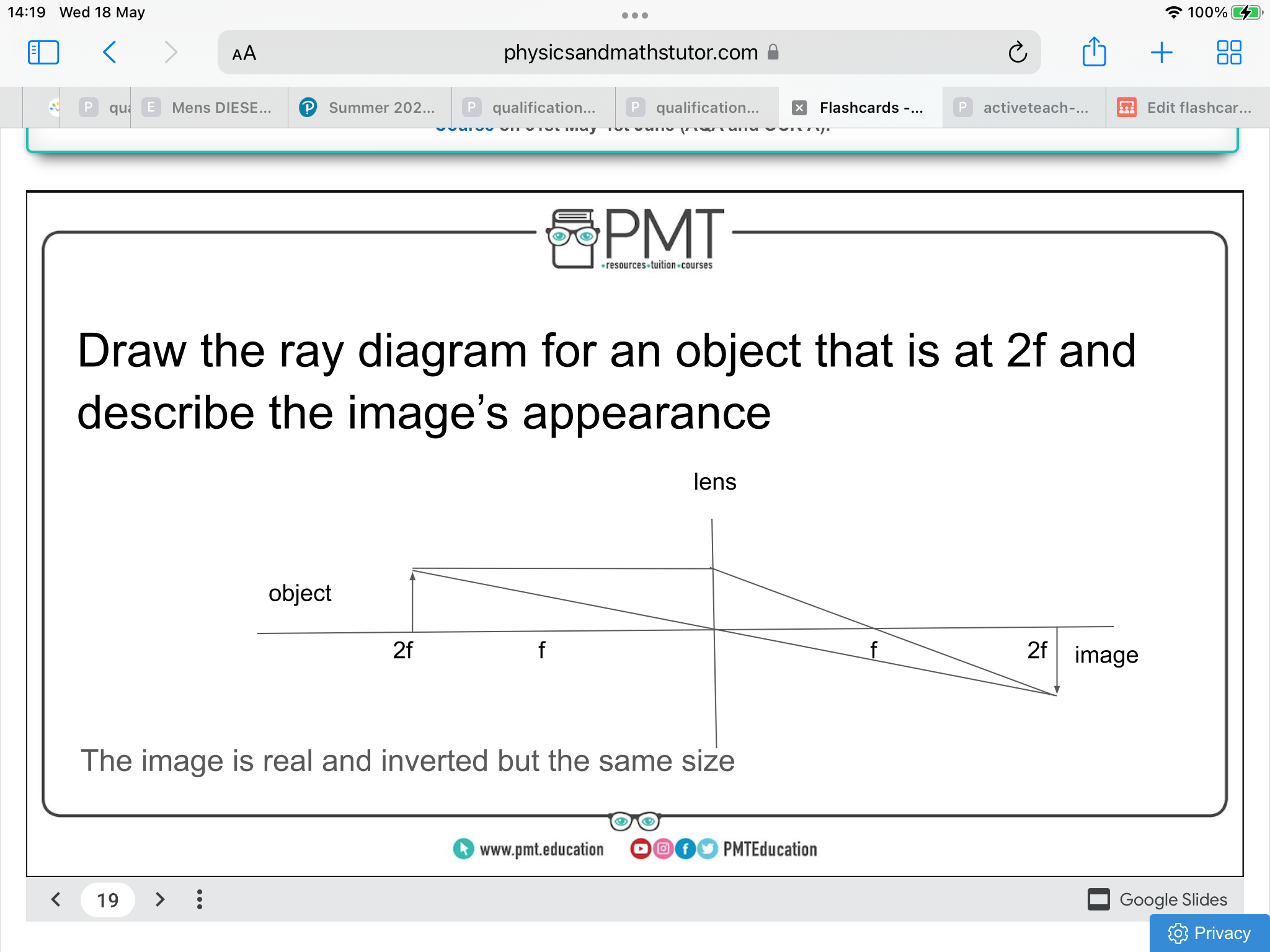
ray diagram for an object at 2f, and describe the image's appearance
-
What is the unit of distance in inverse square law for power of star
au
-
Unit for distance in m -M = 5log(d/10)
pc
-
Unit for distance in hubble law
Mpc
-
A smaller angular resolution
Better at resolving images of close together object
-
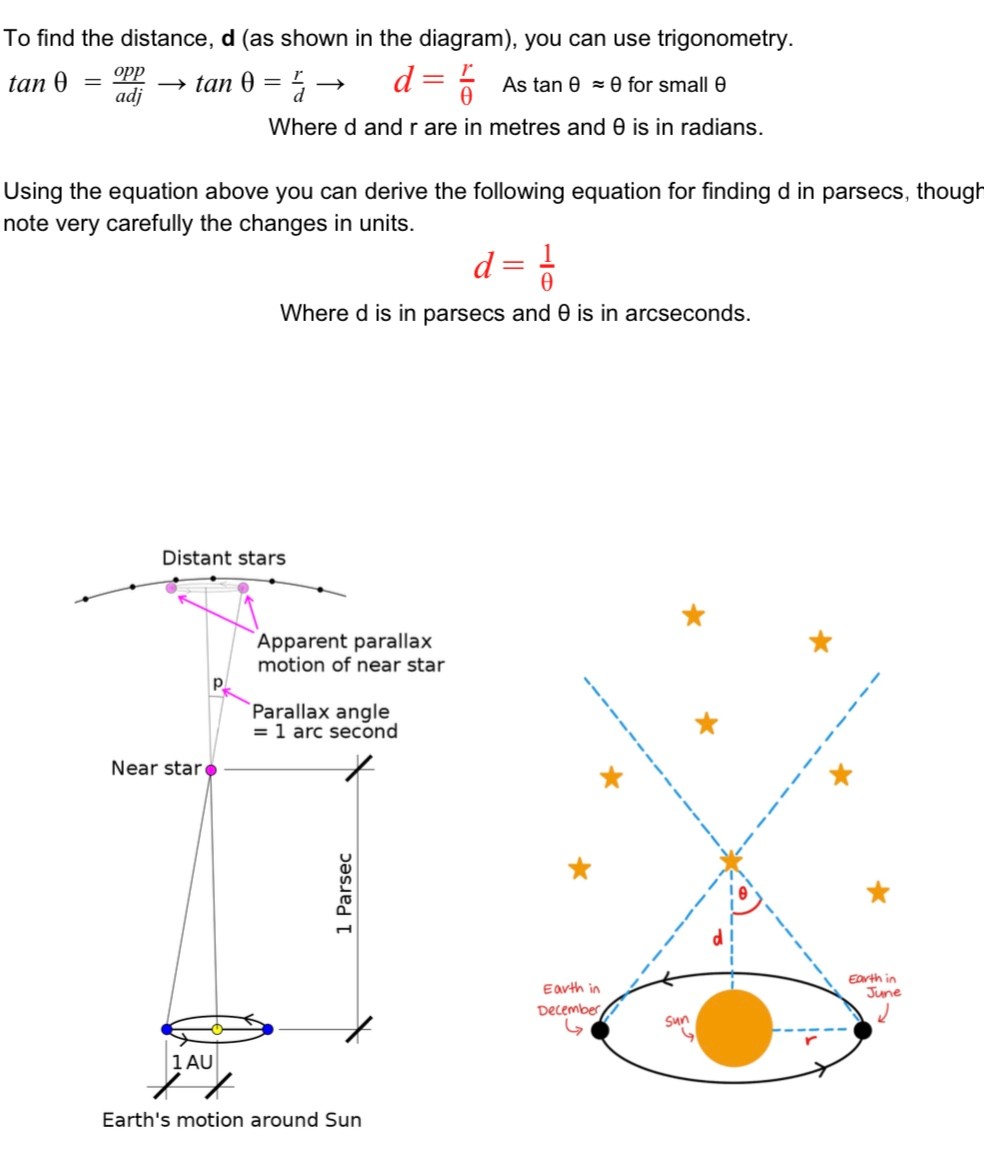
Parsec
Distance at which the 1 au subtends an angle of 1/3600th degree
-
Power of a lens
1/u + 1/v = 1/focal length
A measure of how closely a lens can focus a beam
-
Parallax
Apparent change of position of a nearer star in comparison to distant stars in the background due to the orbit of the Earth around the sun
The greater the angle of parallax the closer the stars to Earth
-
Angle of parallax
-
Why can red shift formula only be used when v <<< c
The formula is derived without any relativistic effect
-
Spectroscopic binaries
Binary star systems which are too close to be resolved by a telescope so can only identified by using doppler shifts of each star
-
As binary stars eclipse one another
They are travelling perpendicular to the line of sight from the observer and so there is no doppler shift in their emitted radiation
-
Eclipsing binaries
When the plane of the orbit of star in the line of sight of Earth to the system means that the stars cross between behind and infront as they orbit
-
The big bang theory
The universe started from an infinitely small hot singularity then a huge explosion occurred this high energy radiation was everywhere then as the universe cooled lost energy so red shifted the remains of thus radiation is CMBR
-
Angular magnification equation
Min angular resolution / the angle the object subtends the unaided eye
-
What is meant by a supernoavae
An object that produces a rapid increase in apparent magnitude
-
Properties of a neutron star
Veey dense and made of neutrons
-
Consequences for the Earth of a supernovae in a nearby galaxy
A lot of energy is released in a supernova equivalent to the power output of a star in gamma rays these rays are highly collimated so cause mass extinction for earth
-
The discovery of the star was made by measuring the variation in the apparent magnitude of the star over a period of time
Explain how an orbiting planet causes a change in the apparent magnitude of a star
Curve of a planet crossing a binary star straight line then curve then straight line
When planet passes in front of star (as seen from Earth), some of the light from star is absorbed and therefore the amount of light reaching Earth reduced
Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light reaching Earth from the star

