-
Conductor resistance causes a(n) ? between the voltage source and the connected
load.
a.
decrease in current
b.
power loss
c.
voltage drop
d.
all of the above
The correct answer is: all of the above
-
The NEC recommends that voltage drops on branch circuits not exceeding ? at the
farthest outlet of power, for heating or lighting loads, will provide for reasonable
efficiency of operation.
a.
2%
b.
3%
c.
4%
d.
5%
The correct answer is: 3%
-
Loads are normally connected in ? with the source, and the resistance of the line is in
? with the source.
a.
parallel / parallel
b.
parallel / series
c.
series / parallel
d.
series / series
The correct answer is: parallel / series
-
If a generator voltage is 240 volts, and the load voltage is 235 volts, how much voltage
is dropped on the line?
Answer:
The correct answer is: 5 V
-
What is the percentage of voltage drop if you have 235 volts at a load fed from a 240-
volt source? (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal place.)
Answer:
%
The correct answer is: 2.1
-
Two rows of fluorescent lamps are installed in an office on the same branch circuit, with
each row drawing 12.5 amperes. The source voltage is 277 volts, and the total line
resistance of the circuit conductors is 0.5 Ω. The wire used has a constant (k) of 12.6.
What is the voltage at the load? (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal place.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 264.5 V
-
Two rows of fluorescent lamps are installed in an office on the same branch circuit, with
each row drawing 12.5 amperes. The source voltage is 277 volts, and the total line
resistance of the circuit conductors is 0.5 Ω. The wire used has a constant (k) of 12.6.
What is the percentage of voltage drop? (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal place.)
Answer:
%
The correct answer is: 4.5
-
Two rows of fluorescent lamps are installed in an office on the same branch circuit, with
each row drawing 12.5 amperes. The source voltage is 277 volts, and the line resistance
is 0.5 Ω. The wire used has a constant (k) of 12.6. The voltage drop will be within the
recommendation of the NEC.
Select one:
True
False
The correct answer is 'False'.
-
How could you correct a voltage drop problem involving two rows of fluorescent fixtures
fed from the same circuit in a practical manner?
I. Change the fluorescent fixtures to incandescent light fixtures.
II. Install a lighting panel closer to the fixtures.
III. Install larger wire.
IV. Put each row of fixtures on a separate circuit.
a.
I. or II.
b.
I. or III.
c.
II. or III.
d.
III. or IV.
The correct answer is: III. or IV.
-
Two rows of fluorescent lamps are installed in an office on the same branch circuit, with
each row drawing 12.5 amperes. The source voltage is 277 volts, and the line resistance
is 0.5 Ω. The wire used has a constant (k) of 12.6. If the load is 129 feet from the source,
what is the specific wire size used in this installation? (Assume 75°C wire.)
Wire size = ____ AWG
Answer:
The correct answer is: 12
-
Two rows of fluorescent lamps are installed in an office on the same branch circuit, with
each row drawing 12.5 amperes. The source voltage is 277 volts, and the line resistance
is 0.5 Ω. The wire used has a constant (k) of 12.6. If the load is 130 feet from the source,
what size wire would you need to install for this circuit to meet the recommendations of
the NEC for acceptable voltage drop on a branch circuit? (Assume 75°C wire)
Wire size = ____ AWG
Answer:
The correct answer is: 10
-
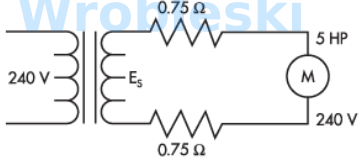
A motor was overheating because of low voltage at its terminals. A transformer was
installed to correct the problem. What is the secondary voltage of the transformer
required to be in order to supply 240 volts to the motor? (Round the FINAL answer to one
decimal place.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 263.3 V
-
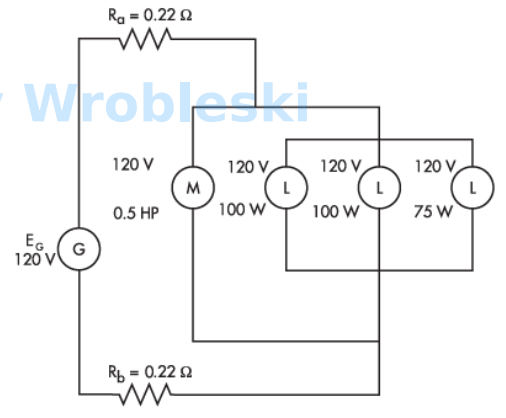
Use the diagram to determine total resistance. (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal
place.) Note: Use the rated voltage and wattage to determine resistance.
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 22.7 Ω
-
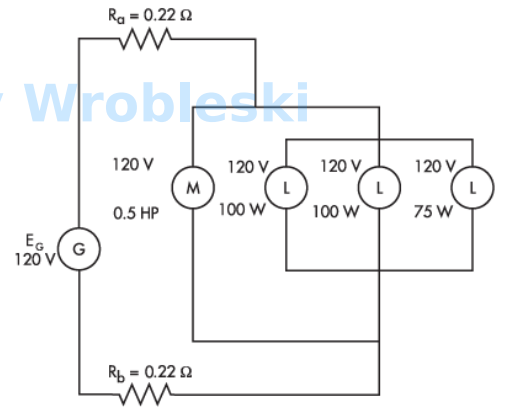
Use the diagram to determine total current. (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal
place.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 5.3 A
-
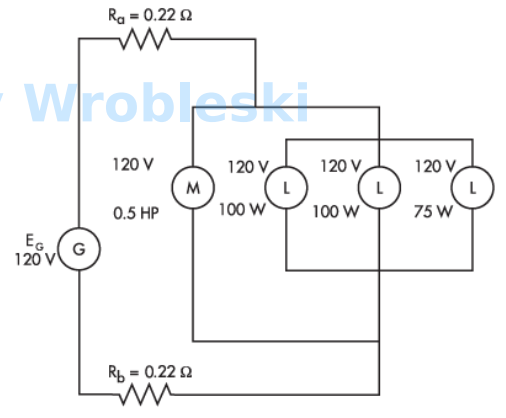
Use the diagram to determine the voltage drop of the conductors. (Round the FINAL
answer to two decimal places.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 2.33 V
-
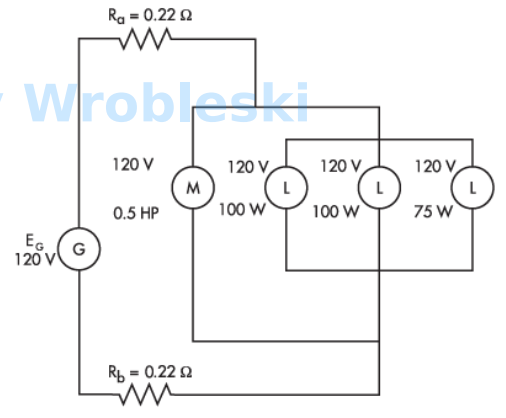
Use the diagram to determine the voltage at the load after calculating the voltage drop
of the wire.
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
a.
115.34 V
b.
117.67 V
c.
120 V
d.
122.33 V
The correct answer is: 117.67 V
-
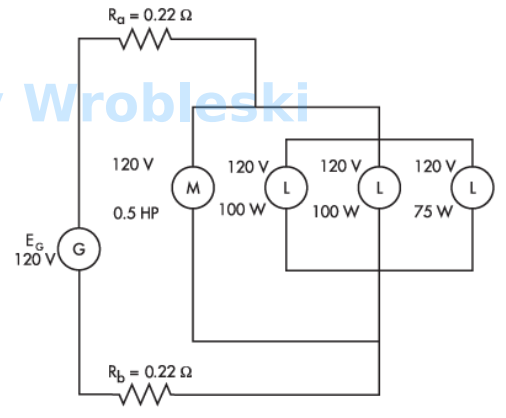
Use the diagram to determine the power loss in the conductors. (Round the FINAL
answer to two decimal places.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 12.36 W
-
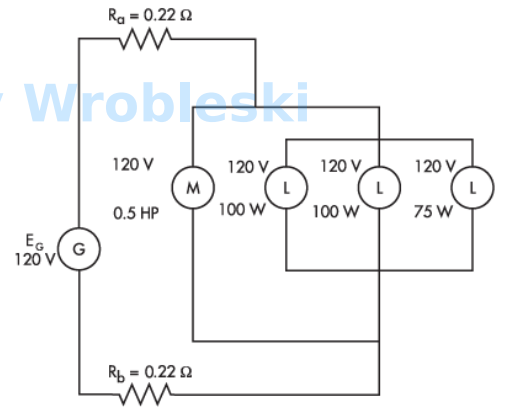
Use the diagram to determine the current of the motor. (Round the FINAL answer to two
decimal places.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 3.05 A
-
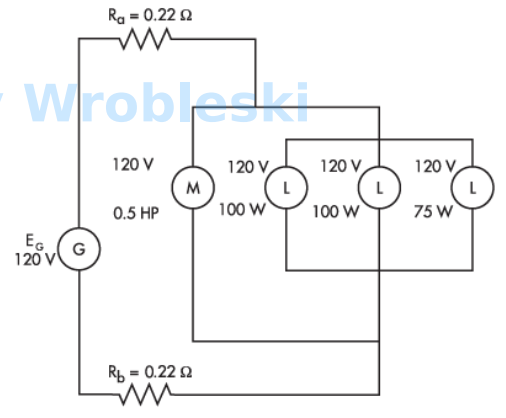
Use the diagram to determine the current of each 100 W lamp. (Round the FINAL answer
to three decimal places.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 0.817 A
-
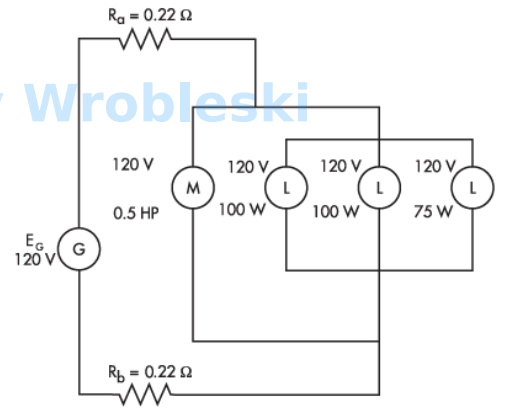
Use the diagram to determine the current of the 75 W lamp. (Round the FINAL answer to
three decimal places.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 0.613 A
-
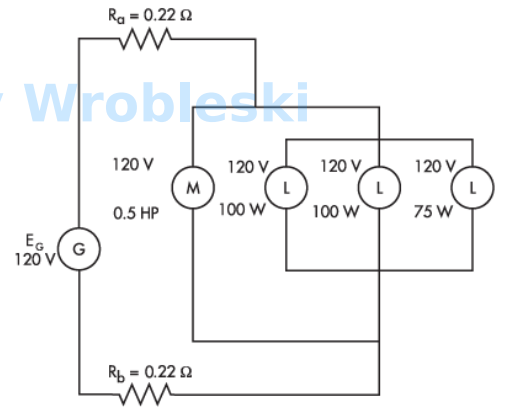
Use the diagram to determine the total current of the loads. (Round the FINAL answer to
one decimal place.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 5.3 A
-
In a parallel circuit, the total current equals the sum of the current of the loads.
Select one:
True
False
The correct answer is 'True'.
-
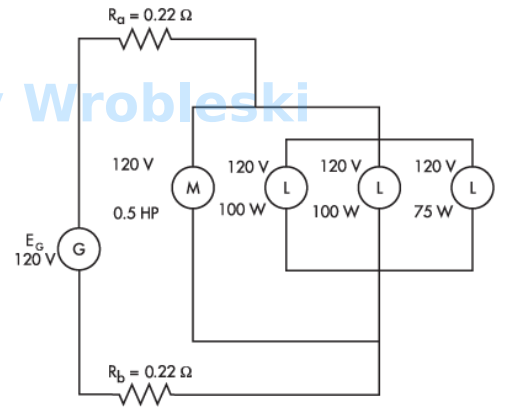
Use the diagram to determine the total power consumed by the circuit.
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 636 W
-
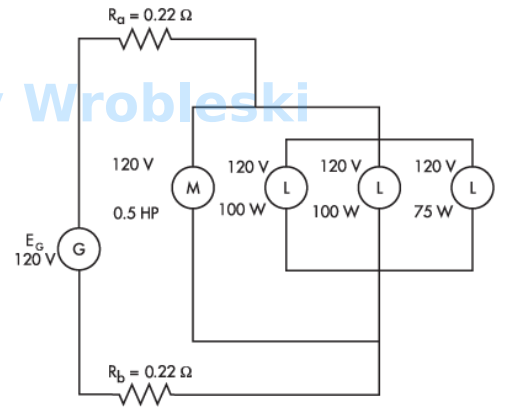
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor. (Round the FINAL
answer to one decimal place.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 358.9 W
-
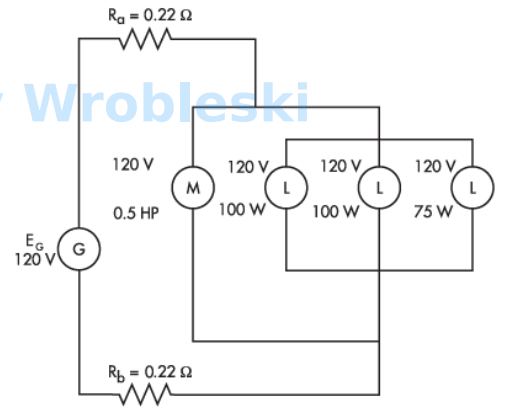
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by each of the 100 W lamps. (Round
the FINAL answer to the nearest whole number.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 96 W
-
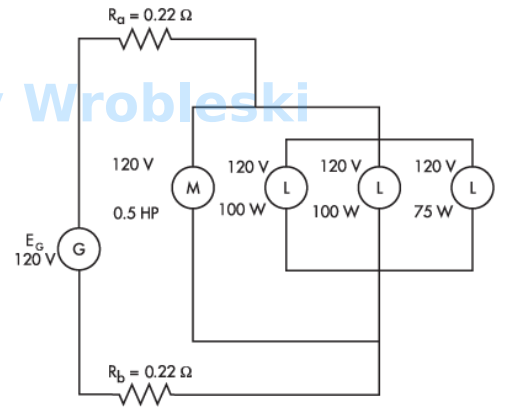
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the 75 W lamp. (Round the FINAL
answer to one decimal place.)
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 72.1 W
-
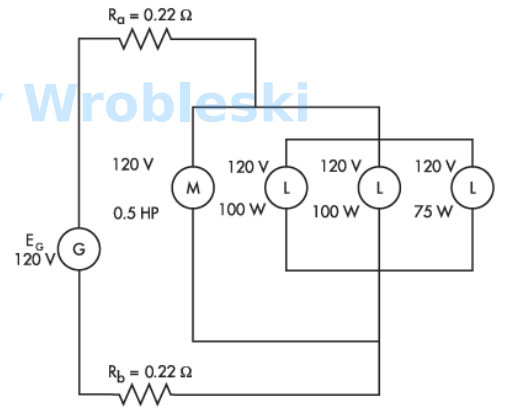
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the loads.
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 623 W
-
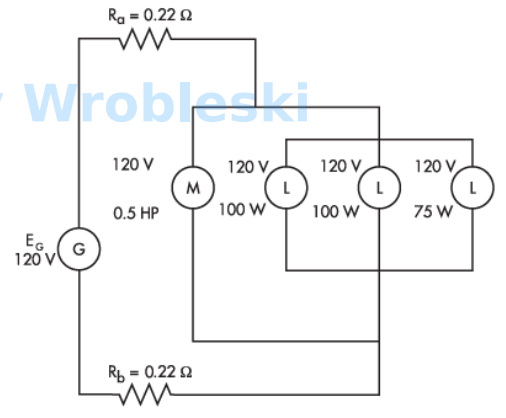
The total power consumed by the circuit is equal to the power consumed by the loads.
Note: Ra and Rb represent the resistance of the wire. The 120 volts of the motor and
lamps is their rated voltage and not the actual voltage.
Select one:
True
False
The correct answer is 'False'.
-
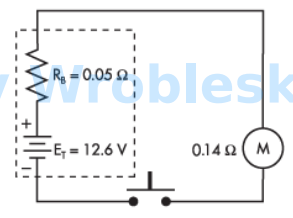
Use the diagram to determine the voltage across the load when the push button is
depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal place.)
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 9.3 V
-
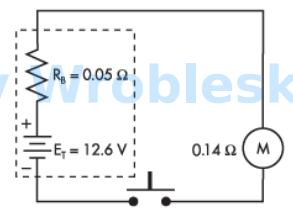
What would the current flow be if a short circuit is put across the battery's terminals?
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 252 A
-
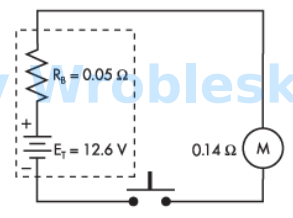
How much power is consumed by the load under short-circuit conditions?
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 0 W
-
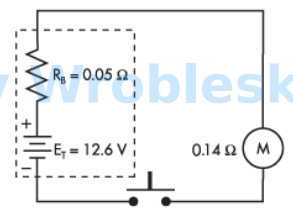
When the battery terminals are open, how much power is consumed by the load?
Answer:
The correct answer is: 0 W
-
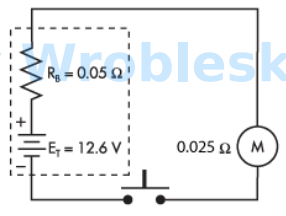
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor when the push button
is depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to the nearest whole number.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 706 W
-
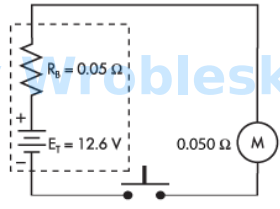
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor when the push button
is depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to the nearest whole number.)
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 794 W
-
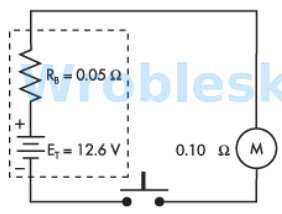
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor when the push button
is depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to the nearest whole number.)
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 706 W
-
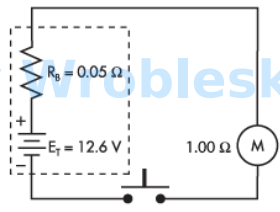
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor when the push button
is depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to the nearest whole number.)
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 144 W
-
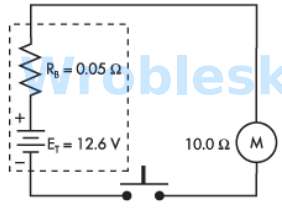
Use the diagram to determine the power consumed by the motor when the push button
is depressed. (Round the FINAL answer to one decimal place.)
Note: All voltage sources contain internal resistance that is usually ignored in
calculations because the resistive value of the load is so much greater than the
resistance of the source. This is not always the case. (Rb represents the battery's internal
resistance.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 15.7 W
-
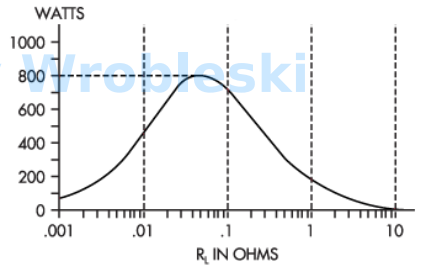
What is the value of RL when the wattage is at peak?
a.
0.01 Ω
b.
0.25 Ω
c.
0.05 Ω
d.
1.00 Ω
The correct answer is: 0.05 Ω
-
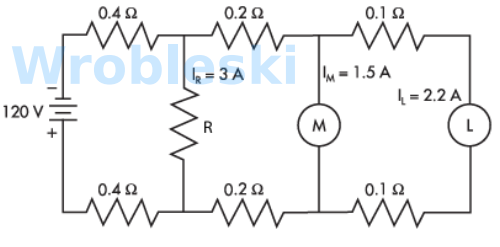
Use the diagram to determine the voltage drop across the resistor R. (Round the FINAL
answer to two decimal places.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 114.64 V
-
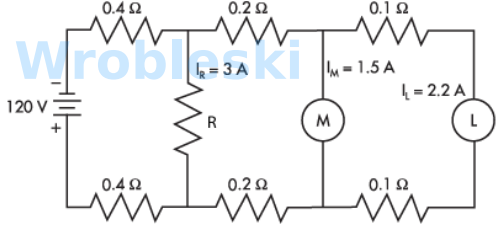
Use the diagram to determine the voltage drop across load M. (Round the FINAL answer
to two decimal places.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 113.16 V
-
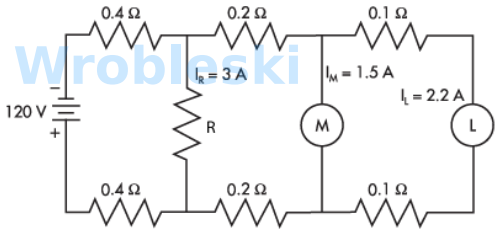
Use the diagram to determine the voltage drop across load L. (Round the FINAL answer
to two decimal places.)
Answer:
The correct answer is: 112.72 V


