-
what is the amount of substance formed at an electrode during electrolysis proportional to
amount of time where a constant current passes
the amount of electricity in Coulombs
relationship between current and time
-
formula to Charge
Q = I x t
Q = charge (coulombs, C)
I = current (amperes, A)
t = time, (seconds, s)
-
what can the amount or quantity of electricity be expressed by
the faraday (F) unit
-
what is one faraday
the amount of electric charge carried by 1 mole of electrons or 1 mole of singly charged ions
-
what is the equivalent of 96500 C mol-1
1 faraday
-
equation to express the relationship between the faraday constant and the Avogadro constant
F = L x e
F = Faraday’s constant (96 500 C mol-1)
L = Avogadro’s constant (6.022 x 1023 mol-1)
e = charge on an electron
-
what is the Avogadro's constant
the number of entities in one mole
L = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
-
the value of the Avogadro's constant can be experimentally determined by
electrolysis
-
formula for determination of the avogadro's constant from electrolysis
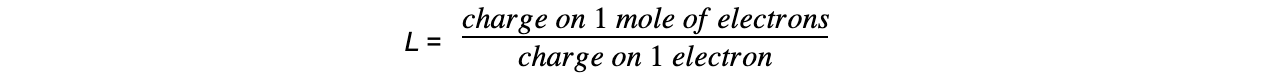
-
before the start of electrolysis the electrodes are
weighed
-
what kind of resistor and current is used during electrolysis to determine the Avogadros constant
variable resistor and about 0.17 A
-
after electrolysis, what is done to the electrodes
removed, washed with distilled water, dried with propanone and reweighed
-
the mass of which electrode is used to calculate the Avogadro's constant and why
the decreased mass of the anode, because the deposited metal does not always stick to the cathode
-
true/false:
the experimentally determined value for L should be very close to the theoretical value of L
True

