-
Taste is a chemical sense, and has 5 primary tastes. Name the 5.
- sour
- sweet
- bitter
- salt
- umami (meaty, savory)
-
What are the 3 cranial nerves involved in taste?
- Facial (VII) > anterior 2/3 of tongue
- Glossopharyngeal (IX) > posterior 1/3 of tongue
- Vagus (X)
-
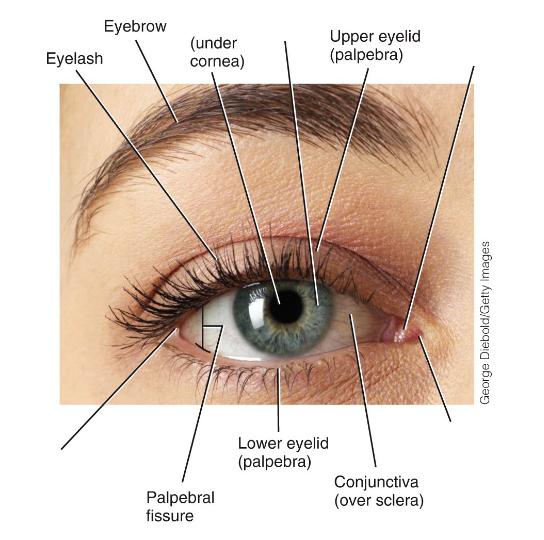
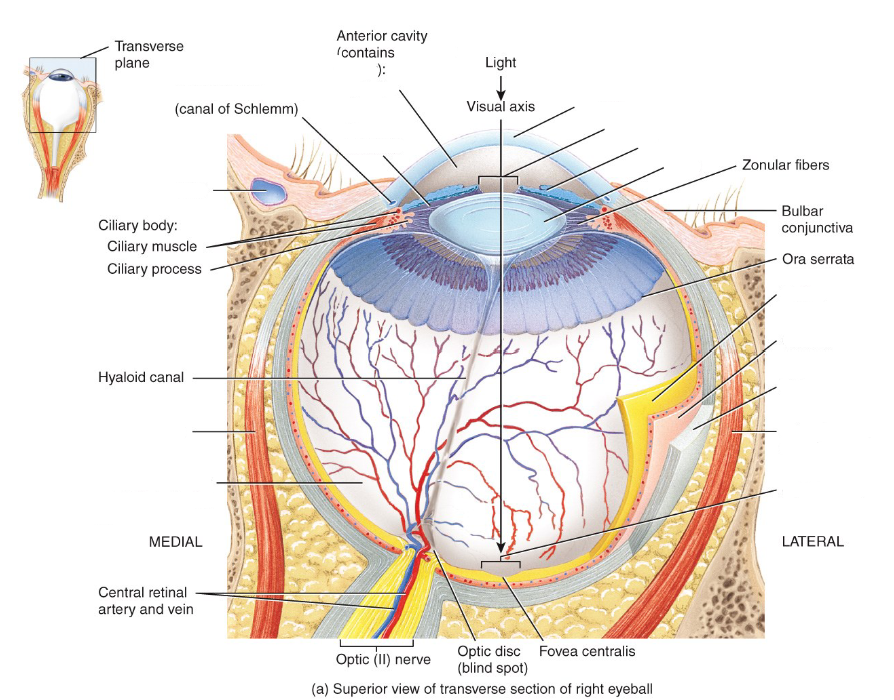
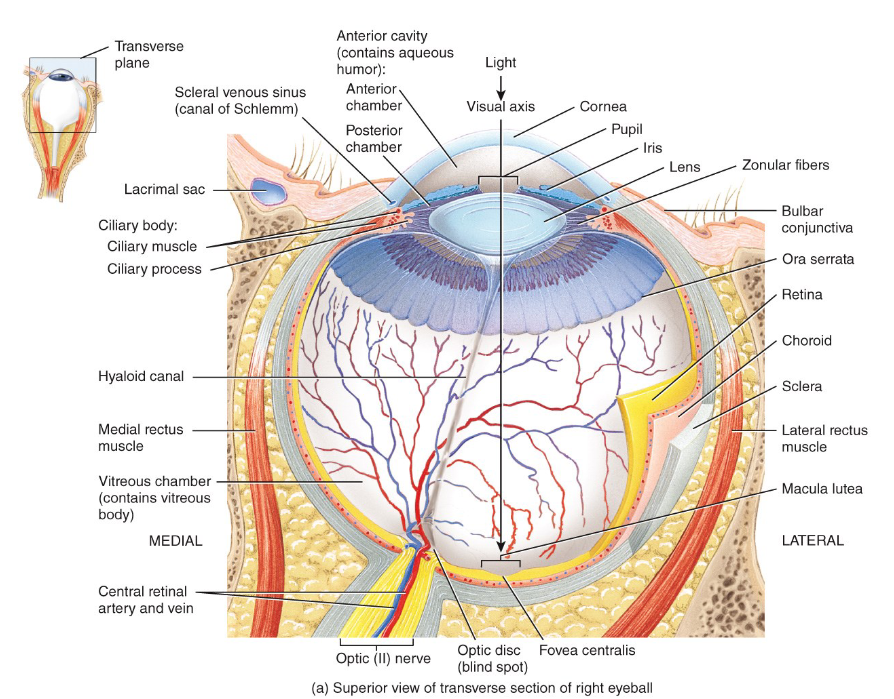
Label the diagram.
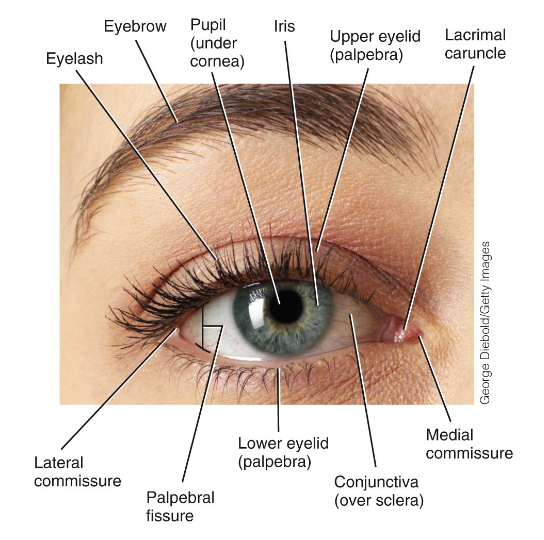
-
Name some accessory structures of the eyes.
- eyelids
- eyelashes
- eyebrows
- lacrimal glands
-
What do the eyelids (palpebrae) do?
Protects eyes from excessive light and foreign objects.
-
What do the meibomian (tarsal) glands do?
Spreads lubricant when blinking to prevent drying of the eyes.
-
What are extrinsic eye muscles?
Skeletal muscles that attach to the outside of the eyeball, and controls its movement.
-
Describe the flow of tears.

-
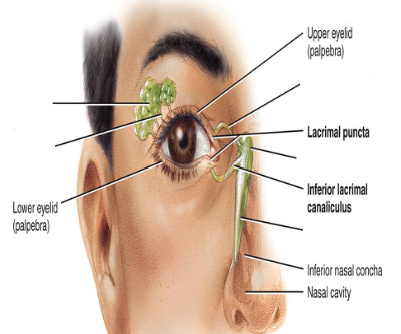
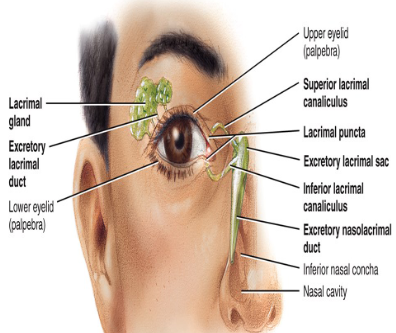
-
What is the function of tears?
- cleanses eyeballs, produces lysozyme and anti-bacterial enzyme
- moistens
- lubrication
-
What are the 3 layers of they eyeball?
- Fibrous tunic (sclera and cornea)
- Vascular tunic (choroid and pigments)
- Retina (nervous/sensory tunic)
-
Where does the excess fluid from the sclera go?
It is drained through the scleral venous sinus.
-
-
What does the sclera do?
Give shape to the eye because of the fluid inside.
-
What is the shape of the cornea and what is it's function?
Convex; it allows light to pass through it and plays a major role is the refraction of light.
-
What is the first eyeball structure that light passes through on its way to the retina?
The cornea
-
What does the vascular tunic do?
Nourishes avascular structures (sclera, cornea, etc.) through vascularization and absorbs light rays so they are not scattered.
-
What is the function of the ciliary processes?
Secretes aqueous humour, which is extracted from blood.
-
What is the function of the ciliary muscle?
Accommodates and is anchored to the lens through the suspensory ligaments.
-
What are the 2 layers of smooth muscle in the iris?
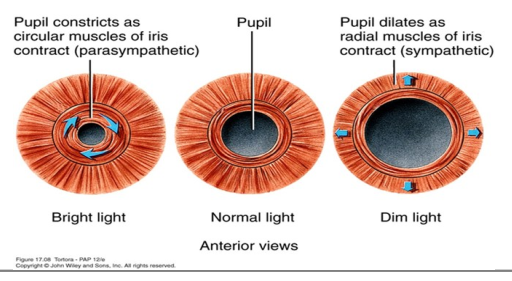
circular - allows constriction of the pupil; PNS
radial - allows dilation of the pupils; SNS
-
The innermost layer of the eyeball is the ___ and is held in place by ___.
retina; IOP
-
Why is the optic disc often referred to as the blind spot?
Because there are no photoreceptors.
-
What are the divisions of the retina?
- pigmented; absorbs excess light rays
- nervous tissue layer
-
What are rods for?
To see in dim light.
-
What are cones for?
For colour vision.
-
Where is the central fovea (fovea centralis)?
Macula lutea, which is the exact center of the visual axis of the eye
-
What structures of the eye are avascular?
- cornea
- lens
- sclera
-
Which structure in the visual axis does most of the light refraction?
the cornea
-
What keeps the eyeball and retina firmly in place?
The vitreous humor
-
Where does the optic nerve exit at?
The optic disc; is the reason why it's the blind spot and also because there are no cones present.
-
What are the 4 steps needed to produce an image in the retina?
1. Refraction of light
2. Accommodation of the lens
3. Control of the pupil size
4. Convergence of the eyeballs
-
What is the visual axis of the eye?
1. Cornea - major light refractor due to its convex shape.
2. Aqueous humour
3. Lens - able to change shape (accommodation), thus changing the amount of light refracted.
4. Vitreous humour
5. Retina
-
What does refraction mean?
Bending of light as it travels through different transparent media.
-
What is visual acuity?
The production of a clear, colour image due to refraction of light into the fovea centralis.
-
What does convergence mean and what does it do?
The movement of eyeballs inwards when looking at an object. Allows us to see one clear object from binocular vision and prevents diplopia.
-
What are the cranial nerves that control convergence?
Oculomotor, Trochlear and Abducens
-
What are the 3 photopigments of cones?
Red
Green
Blue
-
Which is faster: light or dark adaptation?
Light
-
What is the neural pathway for vision?
CN III > optic chiasm > optic tract > thalamus > optic radiation > primary visual area

