-
What does the hypothalamus do?
Maintains homeostasis in the body and controls the body's neg. feedback loop.
-
Which are the 3 parts of the brainstem?
Superior > inferior
- midbrain
- pons
- medulla oblongata
-
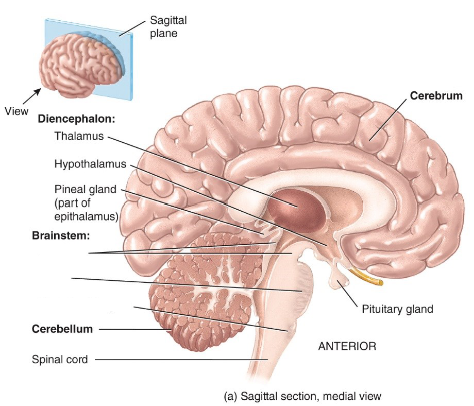
Label the diagram.

-
What does the cerebellum do?
Maintains our posture.
-
What does the corpus callosum do?
Connects the left and right hemispheres; the bridge that allows signals to travel between the two.
-
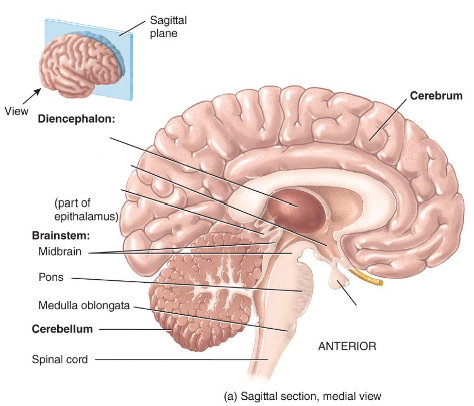
Label the diagram.

-
What bone is the the pituitary gland located in?
The sella turcica
-
What is the largest structure of our brain?
The cerebrum
-
The brain is protected by the:
- cranial bones
- cranial meninges
- CSF (in the subarachnoid space)
-
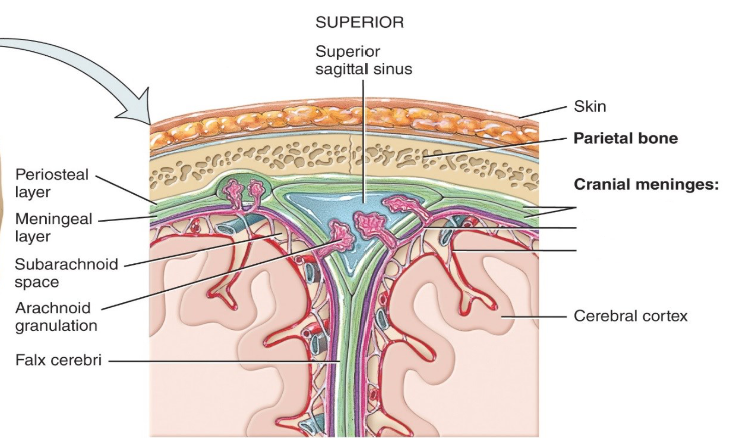
Label the diagram.
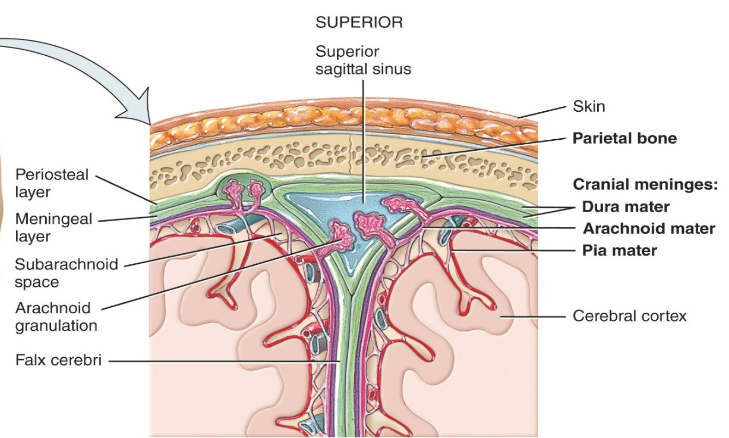
-
What is the dura mater made of?
2 layers of DICT.
-
There is no epidural space around the spinal cord, only in the brain. True or false.
False; we only have that space in the spinal cord.
-
What space separates the dura and arachnoid mater and what is it normally filled with?
Subdural space; covered with a thin layer of serous fluid.
-
What space separates the arachnoid and pia mater and what is the space filled with?
Subarachnoid space; filled with CSF.
-
What are the arteries that bring blood to the brain?
Vertebral and carotid
-
What does brain use as a fuel?
Only glucose
-
What can occur in a person with glucose deficiency?
Mental confusion, dizziness, unconsciousness; the proteins won't be able to cross the BBB.
-
What does the BBB do?
Serves as a selective barrier to the brain which prevents the brain from harmful substances and pathogens.
-
What substances can cross the BBB?
Lipid-soluble, alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, and water molecules.
-
What does the CSF do?
- Protection from chemical and physical injuries
- Carries oxygen, glucose and other important substances towards the brain from the blood.
-
Describe the creation and storage of CSF in the brain.
Created in the choroid plexuses > stored in the left ventricles > travels down the interventricular foramen > goes down the third ventricle >down the aqueduct of the midbrain (cerebral aqueduct) > down the fourth ventricle and then all the way down the spinal cord
-
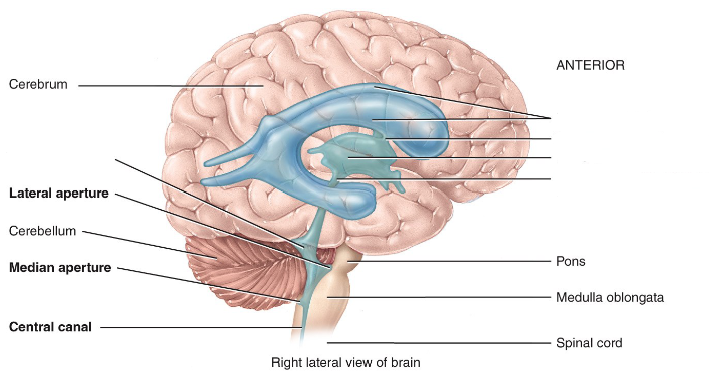
Label the diagram.

-
What are the choroid plexuses?
Networks of capillaries
-
Where are we extracting the CSF from?
The blood in the choroid plexuses, which are in the lateral ventricles.
-
CSF absorbed by the arachnoid villi goes to the ___.
venus blood.
-
The absorption of CSF by the arachnoid fluid is constant to the maintenance of the volume of CSF. True or false.
True.
-
What are the 3 function of the CSF?
- Mechanical protection: shock absorption and protection of the delicate tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
- Chemical protection: provides optimal composition for accurate neural signals (Na+ and K+).
- Circulation: exchanges nutrients and waste products between the blood and nerve tissue.
-
90% of the axons ___ in the medulla.
decussate; moving to the opposite side (movements using the right side of the body will be controlled by the left hemisphere).
-
The medulla oblongata has ___ and ___ tracts.
sensory and motor tracts
-
What are pyramids responsible for?
The decussation of neurons in the left cerebral cortex controlling the skeletal muscles on the right side and vice versa.
-
Where do cranial nerves originate from?
VIII through XII
-
What do the inferior olivary nuclei do?
Relay impulses from proprioceptors (receptors in joints of skeletal muscles to convey the position of the body) to adjust muscle activity.
-
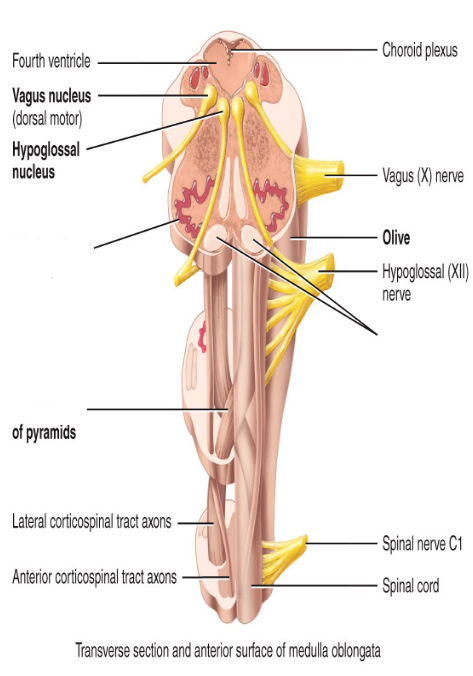
Label the diagram.
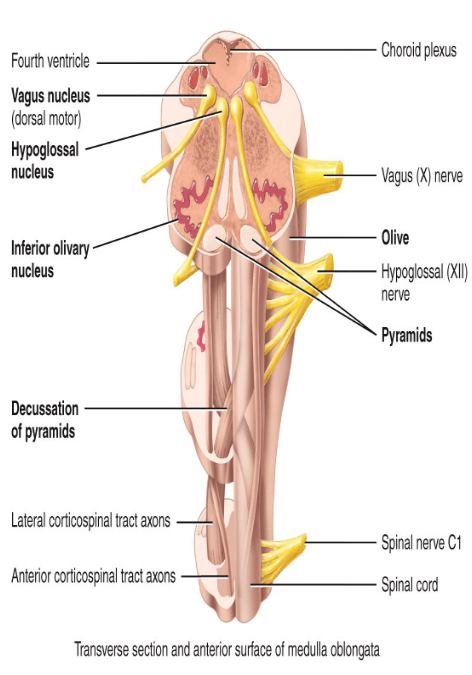
-
Why is the medulla oblongata the vital center of the brain?
Because it has the cardiovascular center which regulates heart rate and the medullary center which regulates the respiratory rate (also the pons).
-
The reticular formation is in the MO, which ___.
keeps us conscious and aware of our surroundings and awakening from sleep.
-
The pons along with the MO controls the ___.
rate of respiration
-
What do the cerebral peduncles contain?
Motor tracts from the cerebrum which goes towards the spinal cord, medulla and pons.
-
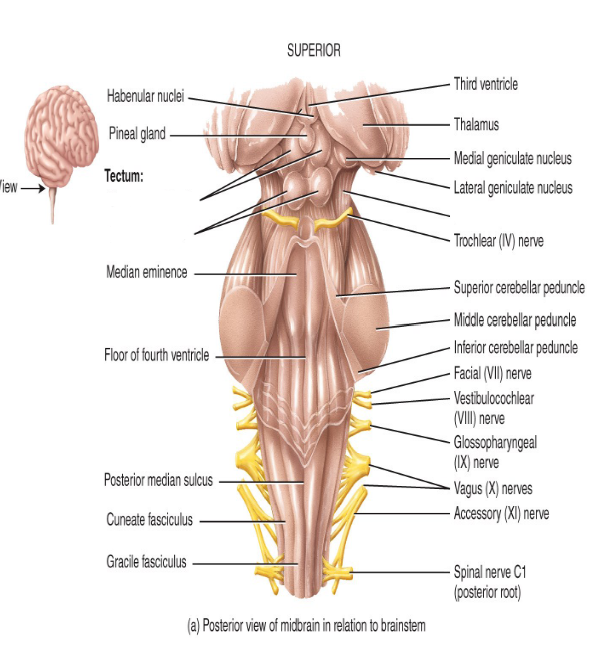
Label this diagram.
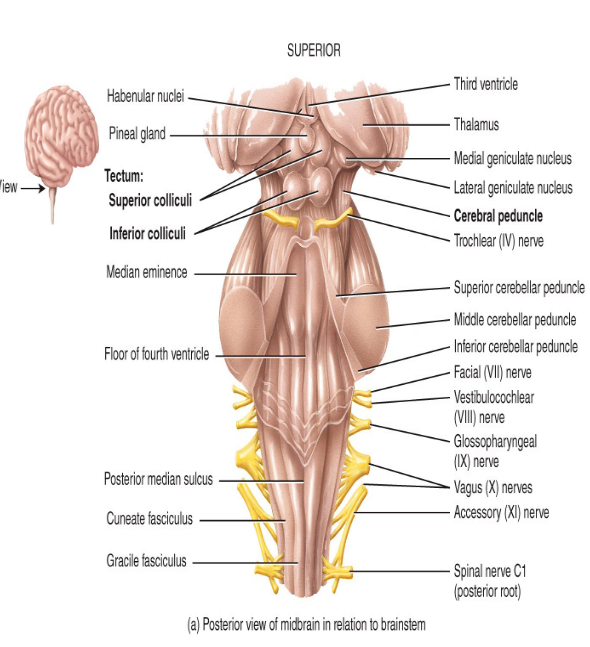
-
What do the superior colliculi respond to and what do the inferior colliculi respond to?
superior - visual stimuli
inferior - auditory stimuli
-
What does the midbrain do?
- conveys motor impulses from the cerebrum > cerebellum > spinal cord
- sends sensory impulses from the spinal cord > thalamus
- regulates auditory and visual reflexes (superior and inferior colliculi)
-
The cerebellum consists of two hemispheres and a ___.
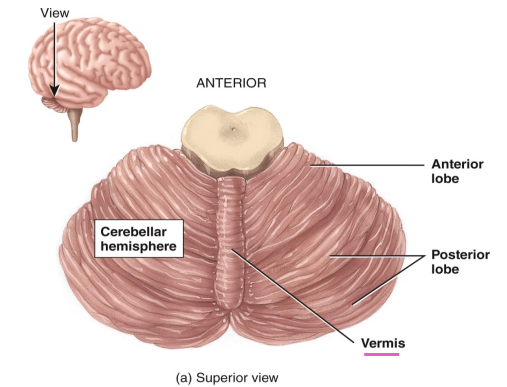
vermis
-
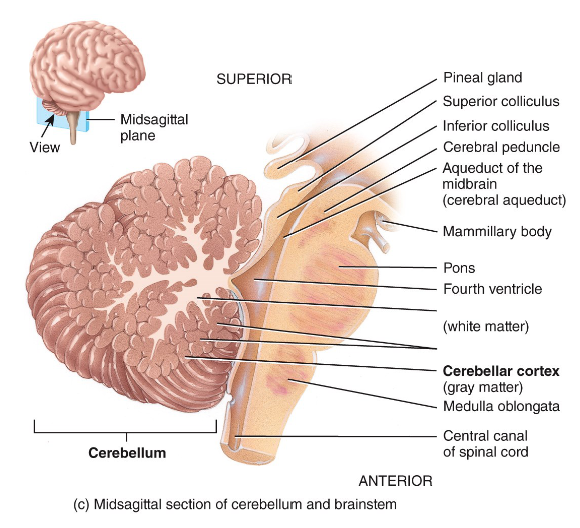
Label the diagram.

-
What is the diencephalon composed of?
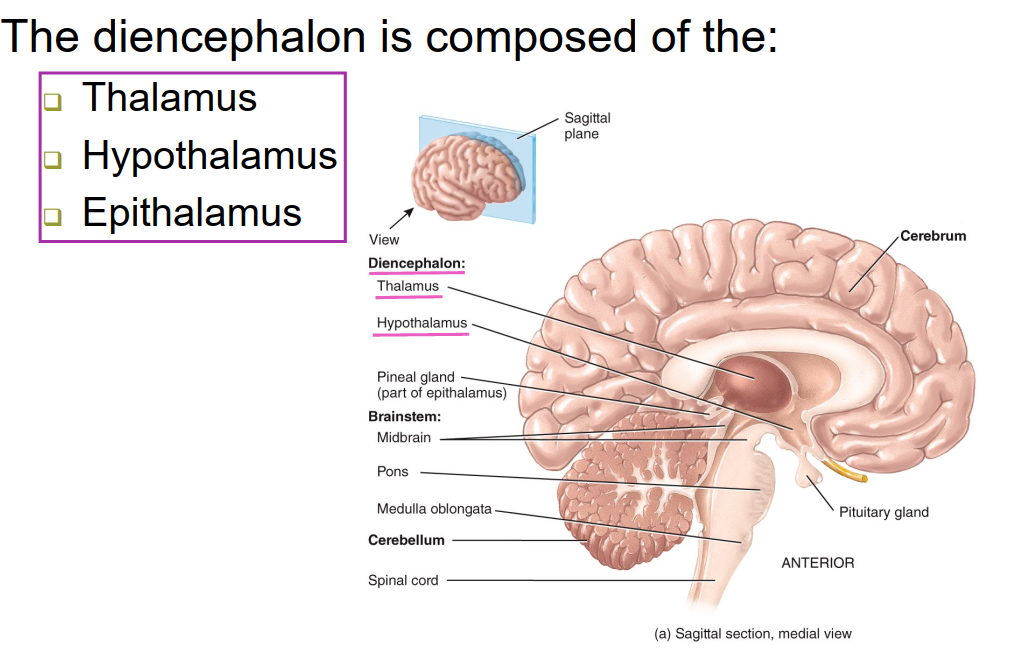
-
Thalamus contains nuclei that relays sensory impulses (except ___) to the cerebral cortex.
smell
-
The thalamus is responsible for ___ and ___.
awareness and cognition
-
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
- regulation of emotional and behavioral patterns
- eating and drinking through their appropriate centers
- controls temp.
- circadian rhythm (sleep) and consciousness, produces hormones
- controls and integrates activities of the ANS
-
What is the epithalamus responsible for?
Contains the pineal gland, which secretes melatonin; controls circadian rhythm.
-
Why do we have gyri?
To fit the bran in the skull (it increases the SA and when it's opened up it's bigger).
-
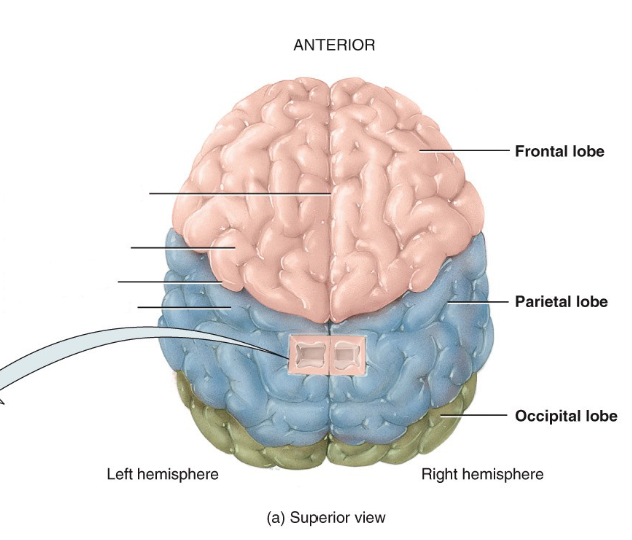
Label the diagram.
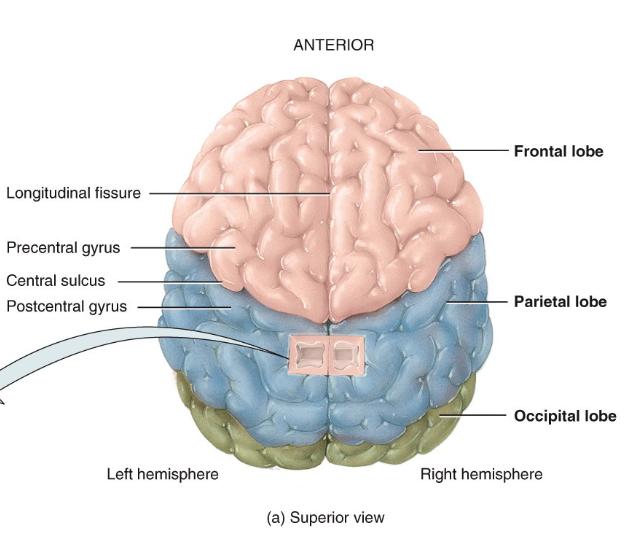
-
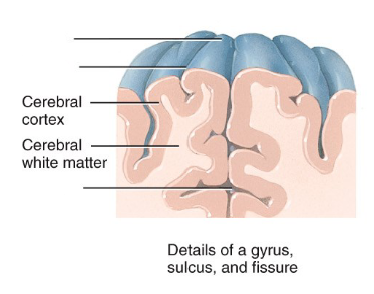
Label the diagram.


