-
What does equilibrium allow us to do?
Maintains our balance and be aware of our orientation in the space around us.
-

-
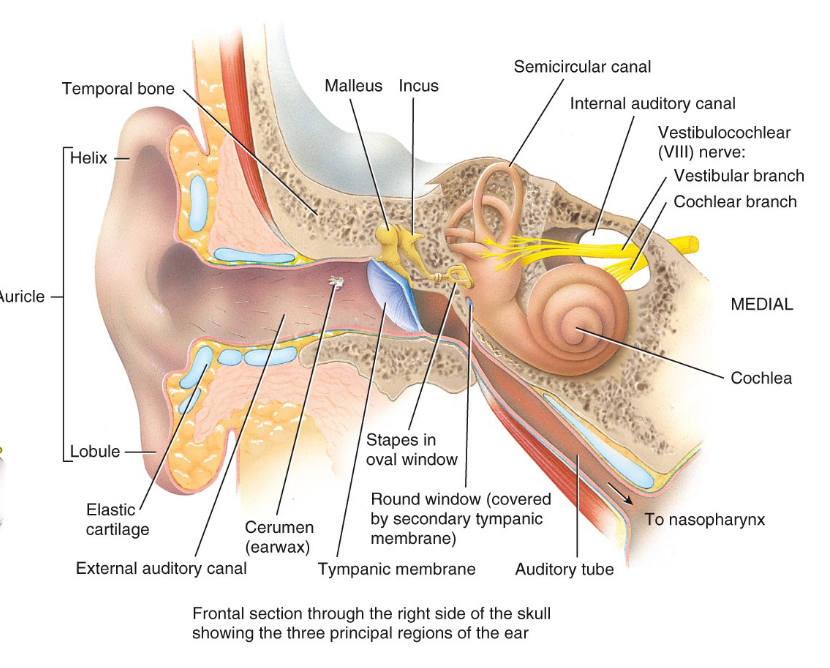
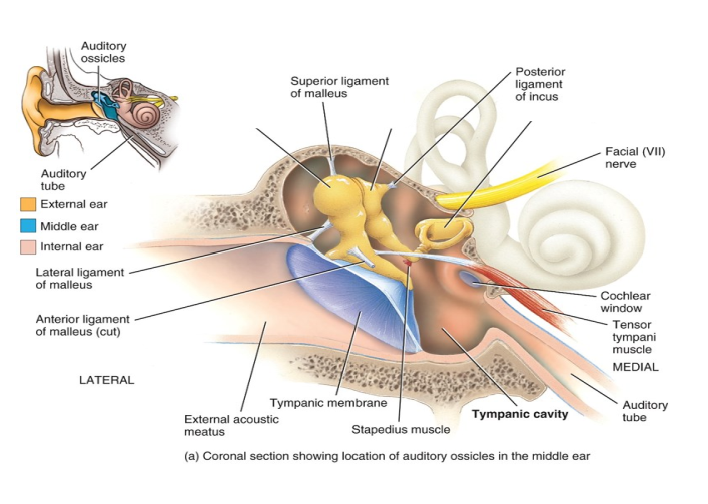
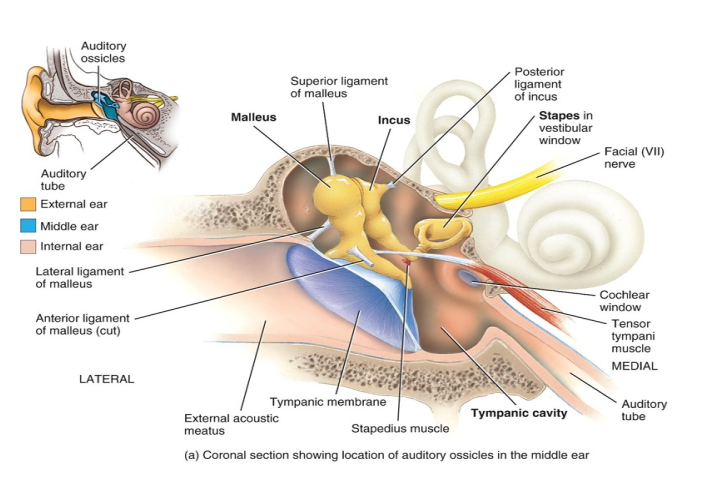
What ear structure separates the external and middle ear.
The tympanic membrane (ear drum)
-
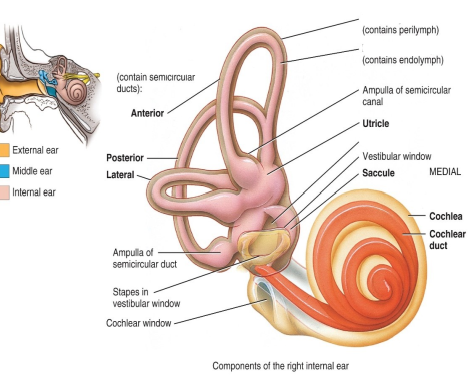
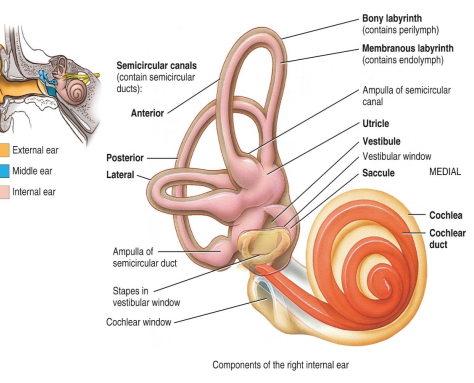
What structures are in the inner ear?
- cochlea
- vestibule
- semicircular canals
-
What is the external ear made of?
Elastic cartilage
-
What does the external ear do?
Collects sound waves and channels them into the typanic membrane.
-
What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
Vibrates as sound waves hit it which allows the middle ear ossicles to transfer the waves to the middle ear.
-
What is the function of the auditory tube?
Equalize air pressure.
-
What are the differences between adult and infant auditory tubes?
Adults - long and angled; opens only during swallowing and yawning
Infants - short and straight; always open
-
-
What are the 2 divisions of the inner ear?
- Bony labyrinth
- Membranous labyrinth
-
-
What do the semicircular canals have?
Receptors for dynamic equilibrium.
-
What receptors does the cochlea have?
Hearing
-
What receptors does the membranous labyrinth have?
Hearing and equilibrium
-
What receptors does the vestibule have?
Static equilibrium
-
What structures of the semicircular canals contain receptors for dynamic equilibrium?
Ampulla > crista ampullaris
-
Describe the pathway of equilibrium.
Equilibrium receptors > vestibular branch of CN VIII > cerebellum (for balance) > up the brainstem > cerebral cortex

