-
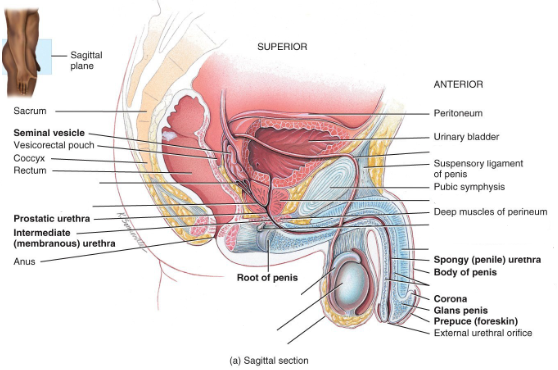
Label the diagram.
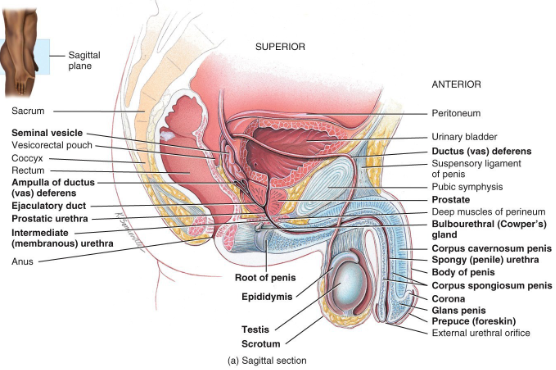
-
The scrotum is separated into two compartments, by what muscle?
The dartos muscle.
-
What us the temperature required for spermatozoa to survive?
2-3 degrees
-
What is the temperature of the testes controlled by?
Cremaster muscle
-
When the dartos muscle contracts what happens to the scrotum?
The scrotum becomes tight to reduce heat loss.
-
What is the condition called when the testes fail to descend through the inguinal canals?
Cryptochidism
-
What is the outermost layer of the testes?
Tunica vaginalis
-
Where are sperm cells made (spermatogenesis)?
In the testes, particularly inside the seminiferous tubules in the tunica albunigea.
-
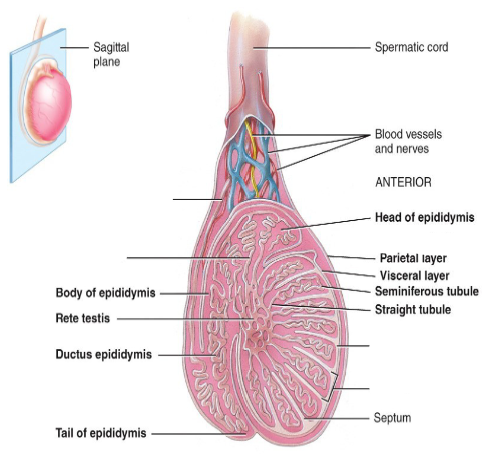
Label this diagram.

-
Where does sperm mature?
The epididymis.
-
What do sustentacular cells do?
- Nourish spermatocytes, spermatids and spermatozoa
- Mediate the effects of testosterone and FSH
- Secrete fluid for sperm transport (semen)
- Breaks down cytoplasm of spermatids to turn into sperm cells
-
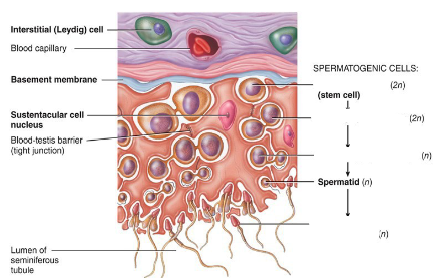
Label this diagram.

-
What does luteinizing hormone (LH) do?
Stimulates cells in the testes to produce testosterone.
-
How does testosterone affect spermatogenesis?
The more testosterone the more sperm is produce, therefore it stimulates spermatogenesis.
-
Describe the pathway of sperm.
Seminiferous tubules (created) > straight tubules > rete testis > efferent ducts > epididymis > ductus deferens
-
What do the seminal vesicles secrete?
An alkaline, viscous fluid called semen.
-
What is the purpose of semen?
- To transport spermatozoa
- Provides nutrients and ATP
- Neutralizes the acidity in the female vagina
-
An erection is a ___ reflex.
parasympathetic
-
Ejaculation is a ___ reflex.
sympathetic
-
What are the accessory sex glands and what do they do?
- seminal vesicles
- prostate
- bulbourethral glands
Produce semen

