-
What do the ovaries produce?
Gametes (that will mature into ova).
-
What are the ovaries held up by?
- Broad ligament - part of the parietal peritoneum
- Ovarian ligament - anchors ovaries to uterus
- Suspensory ligament - attaches ovaries to pelvic wall
-
At puberty, what hormone is released to stimulate FSH?
Gonadotropin
-
What area does fertilization occur?
The ampulla of the uterine tube
-
What is an ova that was fertilized?
Zygote (2n)
-
When a zygote has implanted itself in the uterus, what is it called?
An embryo
-
What are the three layers of the uterus from the most superficial to deep?
- perimetrium (serosa)
- Myometrium (three layers of smooth muscle)
- Endometrium (its stratum functionalis is shed every month)
-
Why is the muscle of the uterus so thick?
For contractions to push the baby out.
-
What does a mature follicle produce?
A secondary oocyte through ovulation.
-
After a mature follicle has produced a secondary oocyte, what does it leave behind and what does it secrete?
Leaves behind a corpus luteum which will degenerate. It produces progesterone, estrogen, relaxin and inhibin.
-
While oogenesis is occurring, the follicle cells surrounding the oocyte also undergo developmental changes. True or false?
True.
-
What is the sequence of follicular cell changes?
Primordial > primary > secondary > mature follicles > corpus luteum > corpus albican (dies due to apoptosis)
-
What hormones stimulate the development of primordial follicles each month after puberty?
FSH and LH
-
What event determines when the secondary follicle matures?
When the granulosa cells secrete follicular fluid which builds up the antrum. The antrum then expands to be the corona radiata. Once the corona appears that's when it becomes a mature follicle.
-
What is a polar body?
A package of discarded nuclear material.
-
When does meiosis II occur?
When the secondary oocyte (ovum) has been fertilized.
-
To reach the ovum, what structure does the sperm cell have to penetrate?
The corona radiata
-
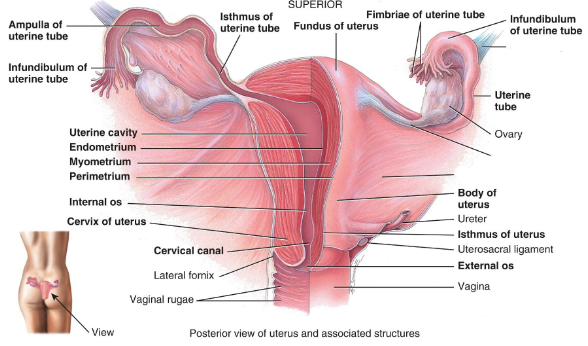
Label this diagram.
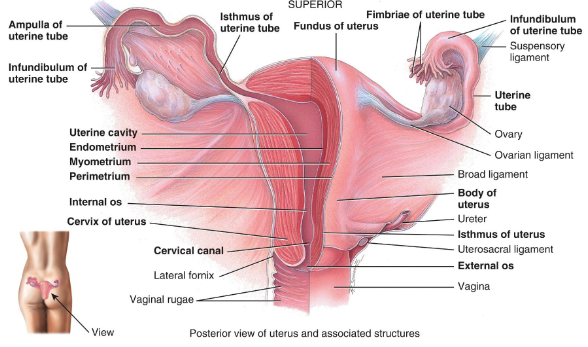
-
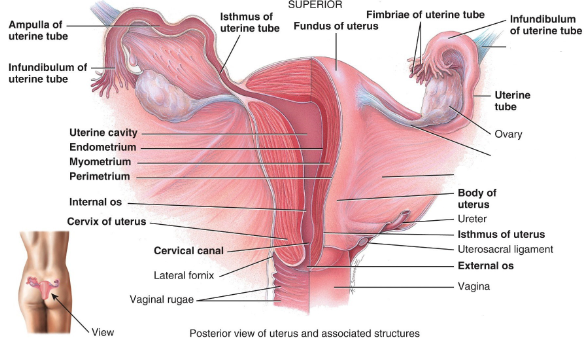
Label this diagram.
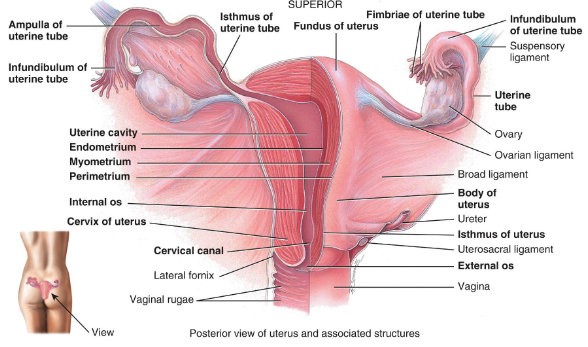
-
The ___ is the site of implantation of the zygote.
The uterus
-
What is the interior of the cervix?
Cervical canal
-
What are the muscular protrusion in the cervix called?
The fornix
-
Is the cervix innervated?
No
-
What is the opening of the canal into uterus called?
The internal os
-
What is the environment of the vagina, and why is it built like that?
Acidic; to kill off bacteria

