-
What are the two parts of the ECF compartment?
- Plasma (fluid of the blood)
- Interstitial fluid (IF)
-
What does hydrostatic pressure do?
Causes the movement of fluid between compartments.
-
Solute movement between compartments is an ___ process, thus needing ATP.
active transport
-
Active transport does what?
Moves substances against its concentration gradient through a membrane protein, which is why it requires energy.
-
What is osmolality?
The ratio of solutes in a solution to its solvent.
-
What are the two barriers that separate ICF, IF and blood plasma?
- Plasma membrane (selectively permeable barrier) of cells, separates ICF from IF.
- Blood vessel walls, divide IF from blood plasma. Only in capillaries can exchange occur between the two.
-
What physiological response do we experience when the blood gets more concentrated?
Thirst, so that our water intake is regulated.
-
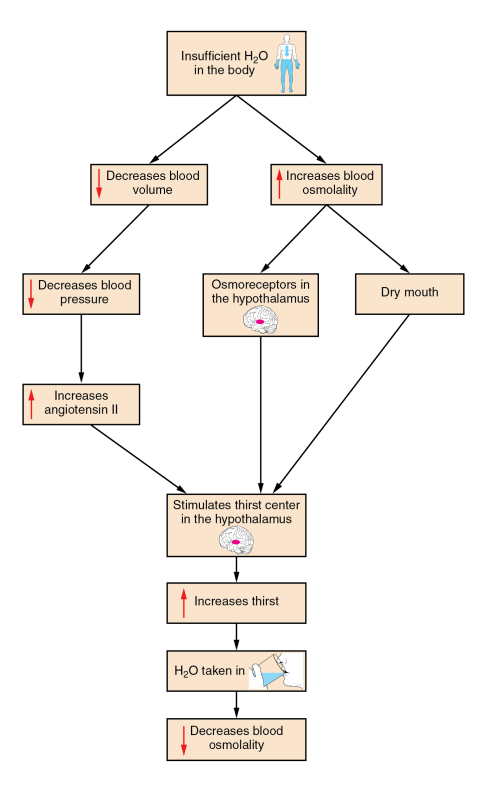
What is this diagram showing?
The thirst response
-
The antidiuretic hormone (ADH), or vasopressin controls what?
The amount of water reabsorbed from the collects ducts in the kidney.
-
What does ADH do?
Retains water in the kidneys and constricts arterioles in the peripheral circulation (reduces blood flow to extremities).
-
What are the six most important electrolytes?
- sodium
- potassium
- chloride
- bicarbonate
- calcium
- phosphate
Aid in nerve excitability, endocrine secretion, membrane permeability and controlling movement of fluids between compartments.
-
If the body needs more calcium and phosphate, what part of the body might be broken down to obtain them?
Bone tissue

