-
What is an Action potential?
- large change in membrane potential that propagates along an axon with no change in intensity and initiates at trigger zone
-
Where is the trigger zone that APs initiate?
- axon hillock of multipolar and bipolar neurons
- just past dendrites of unipolar neurons
-
What are the events that take place for/in an action potential?
- GP reaches threshold
- Action potential phases (depolarization, repolarization, after-hyperpolarization)
- repolarization
-
What happens in the depolarization phase of an AP?
- voltage-gated Na+ channels respond to MP change (GP) and open, increasing Na+ permeability
- increased Na+(pos MP change) in cell stimulates more Na+ channels to open (positive feedback mechanism) until +30mV
-
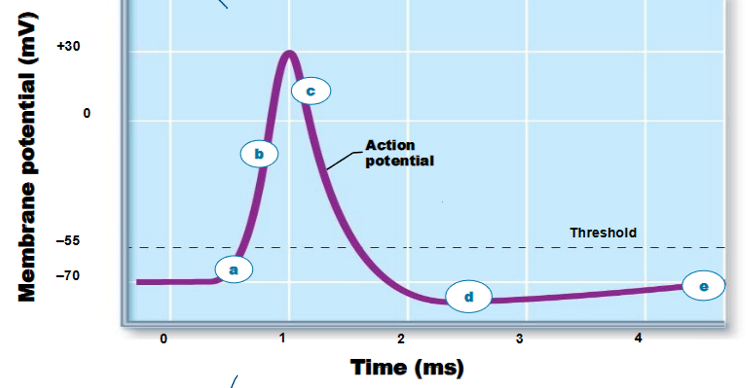
A. GP to threshold
B. depolarization
C. Repolarization
D. After-hyperpolarization
E. return to rest
-
What happens in the repolarization phase of AP?
- Na+ channels close/inactivate, Na+ movement returns to resting levels
- voltage-gated K+ channels open so K+ diffuses out (positive charges (K+) move out – decreases MP)
-
What increases and decreases permeability of an ion in a cell?
- channels of that ion type opening (increasing permeability) or closing (decreasing)
-
What happens during the after-hyperpolarization phase in AP?
- K+ channels are slow to close and remain open longer than necessary
- Na+ channels are reactivated – can respond to stimuli at this point
-
When does the MP return to RMP after AP?
When K+ channels close
-
How many APs does it take to cause measurable change in charge in the cell?
10 000 *
-
What is the all-or-none principle of APs?
- if threshold is reached, AP is produced (one level of intensity, same every time)
- if not reached, then no action potential
- means no change in size really, AP or no AP
-
What are the refractory periods of an AP?
- absolute refractory periods (prevents AP summation) and relative refractory period (can only be generated by greater than normal stimulus)
-
When is the absolute refractory period?
- when all Na+ channels are open (i.e. depolarization)
- all Na+ channels being inactivated (i.e. repolarization), cant open until MP reaches RMP
-
When is the relative refractory period?
- after-hyperpolarization phase
- larger stimulus needed because it is further reach threshold
- Na+ channels are closed but can be reopened if threshold is reached
- K+ channels are open and membrane hyperpolarized

