-
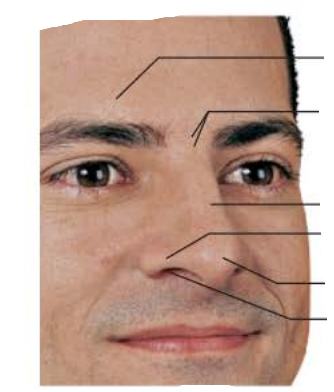
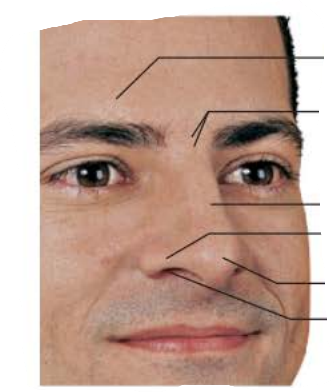
_________ ______
Thin epithelial layer and covered with many sebaceous glands
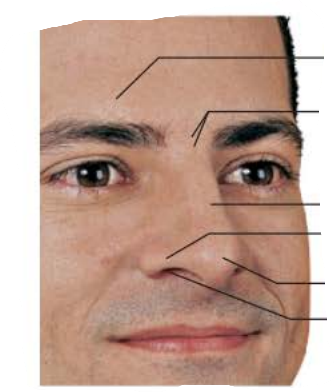
external nose
-
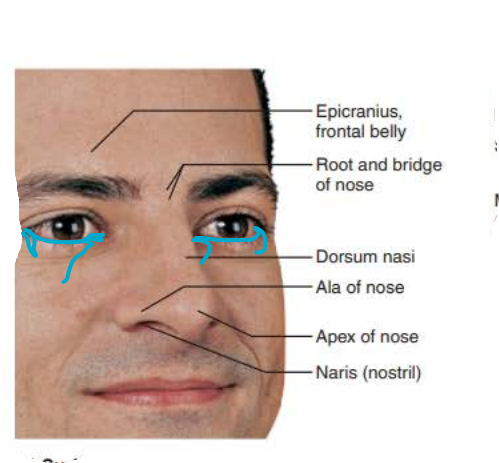
external nose
______
Area between eyebrows
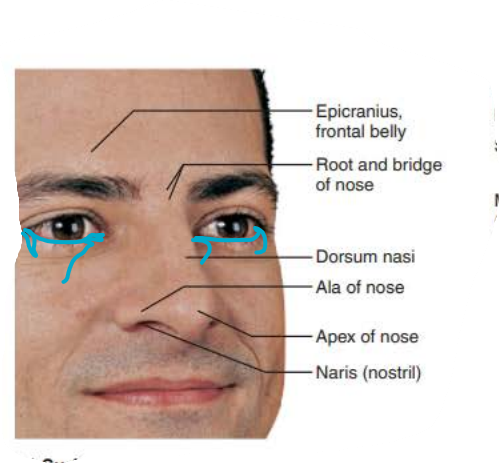
root
-
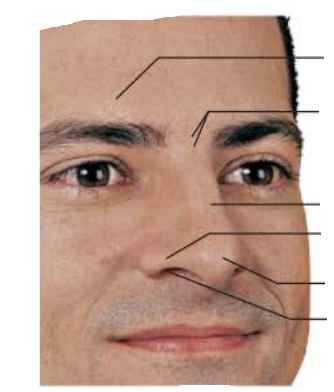
external nose
______
tip of nose
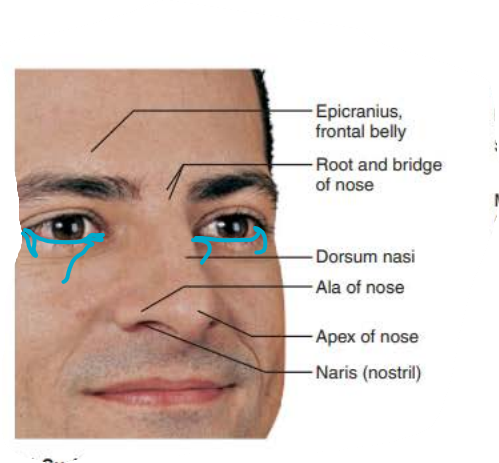
apex
-
external nose
_________
allows air into nasal cavity
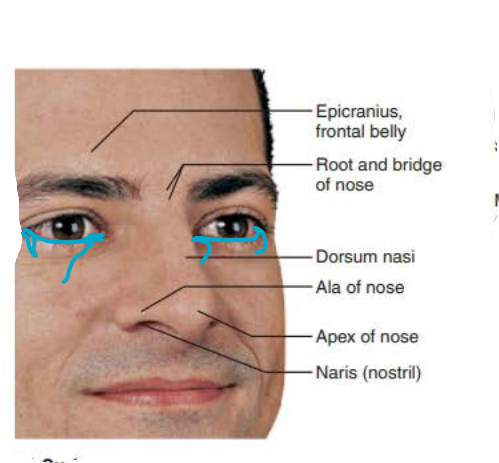
nostrils
-
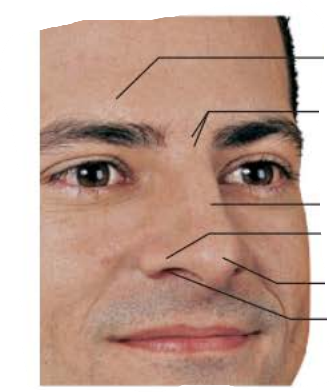
external nose
_____
lateral extensions of nostrils
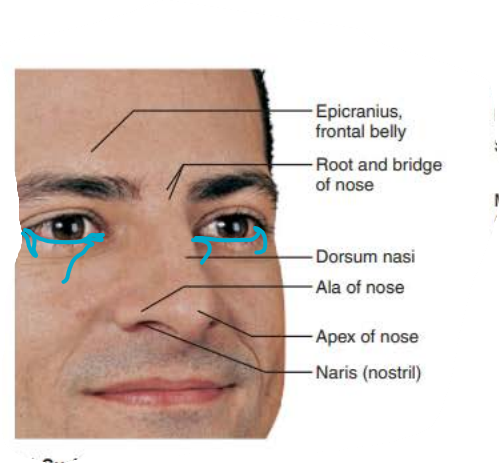
alae
-
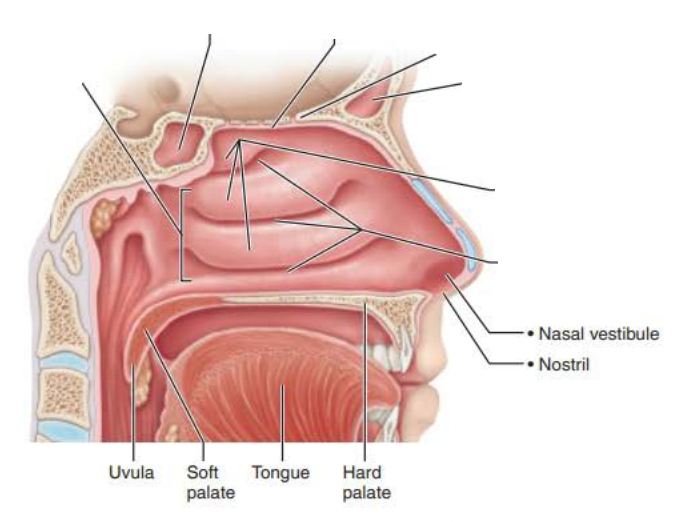
_______ ________
Lies posterior to the external nose
Roof is formed by ______ and ___________ bones
Floor is formed by the _______ that separates the ______ and ____ cavities
nasal cavity
ethmoid
sphenoid
palate
nasal
oral
-
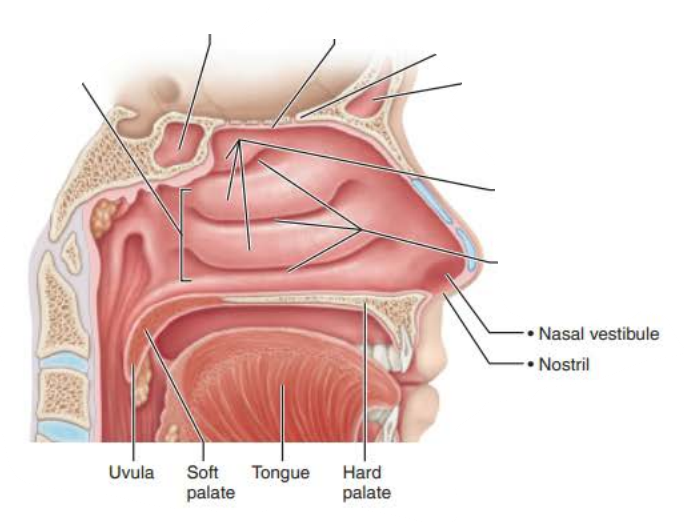
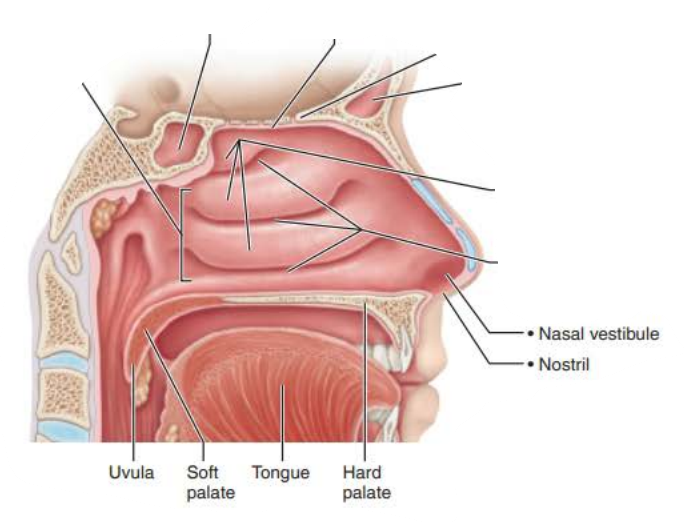
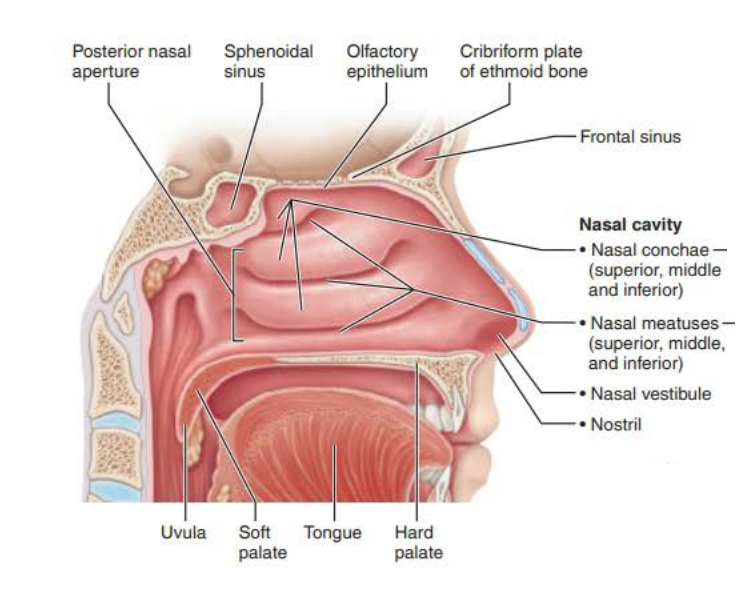
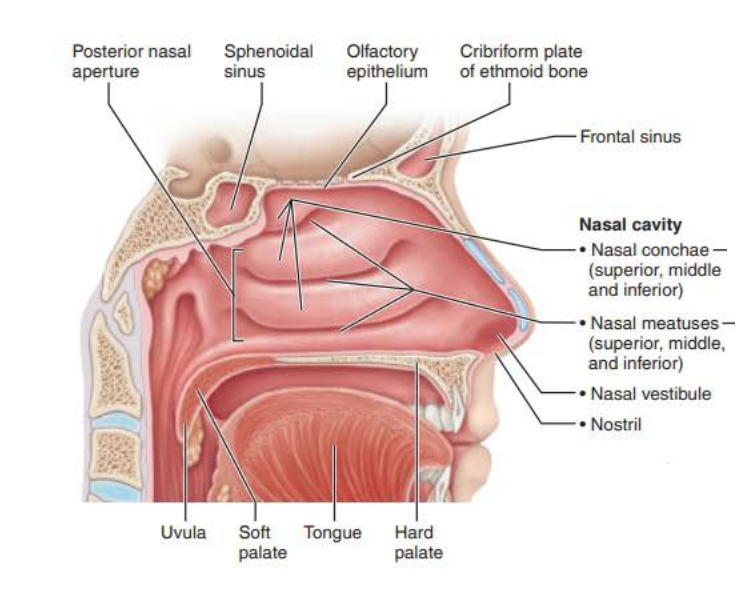
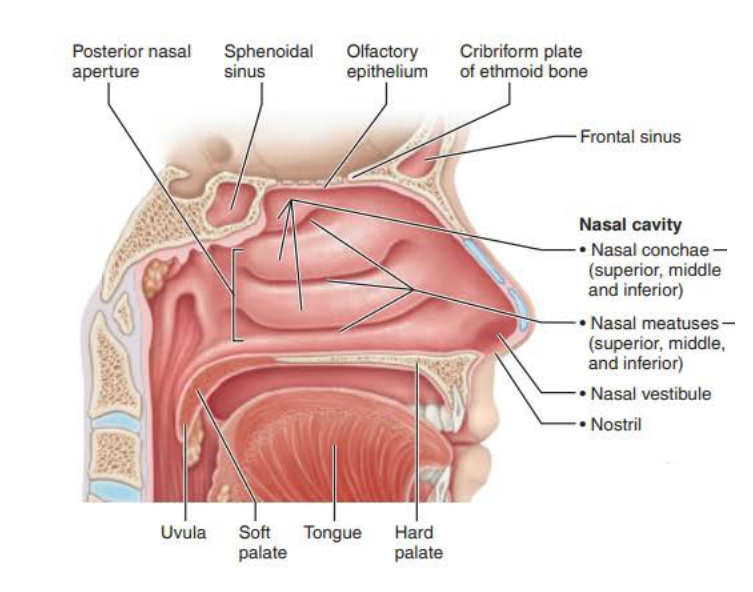
Nasal Cavity
the __________ anteriorly is _______ ________ and posteriorly ______ _______ and ____________ ________, it divides the _____ ________
nasal septum
septal cartilage
vomer bone
perpendicular plate
nasal cavity
-
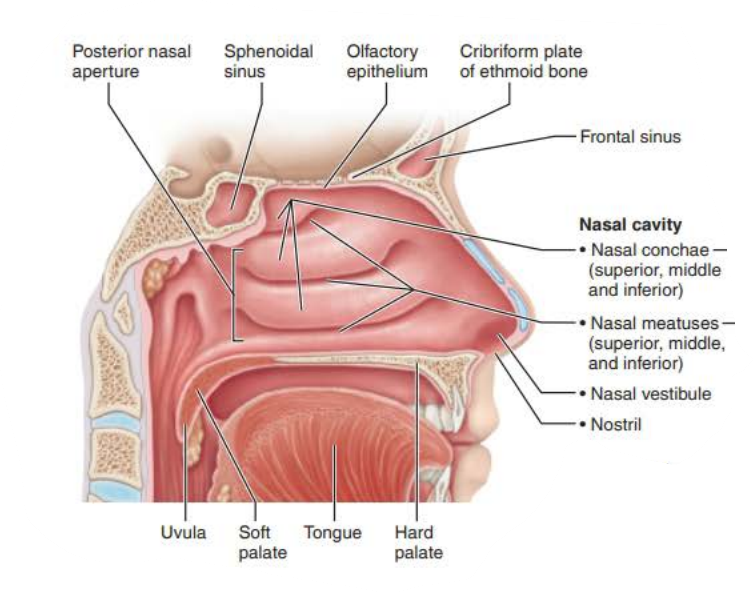
Nasal Cavity
________ ______ ___________
Posterior nasal cavity where it meets pharynx
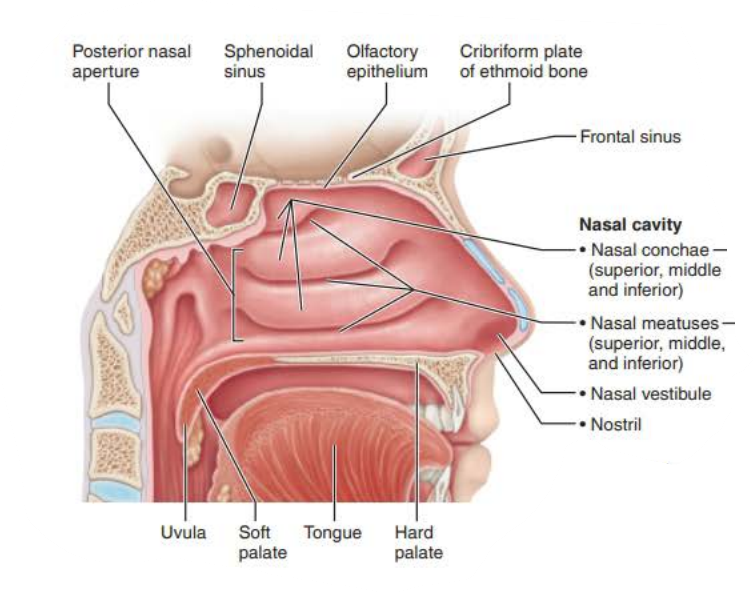
posterior nasal apertures
-
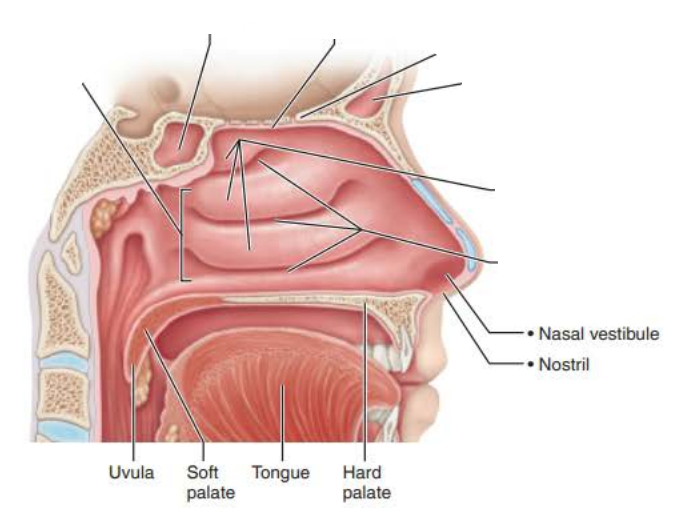
Nasal Cavity
the _________ ___________ is part of nasal cavity superior to each nostril, lined with skin containing _____ glands, _________ glands, and __________
nasal vestibule
sweat
sebaceous
vibrissae
-
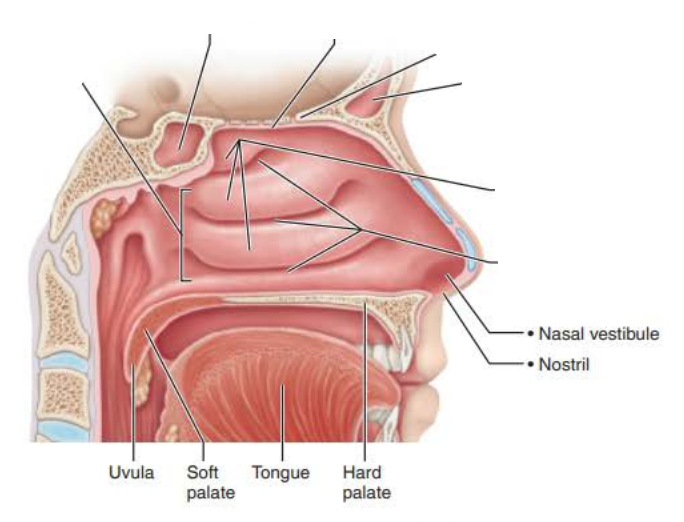
Nasal Cavity
_____________ are found in the ______ __________
and _______ ________ ___________ like dust and pollen from the _________ ___
vibrissae
nasal vestibule
filters coarse particles
inspired air
-
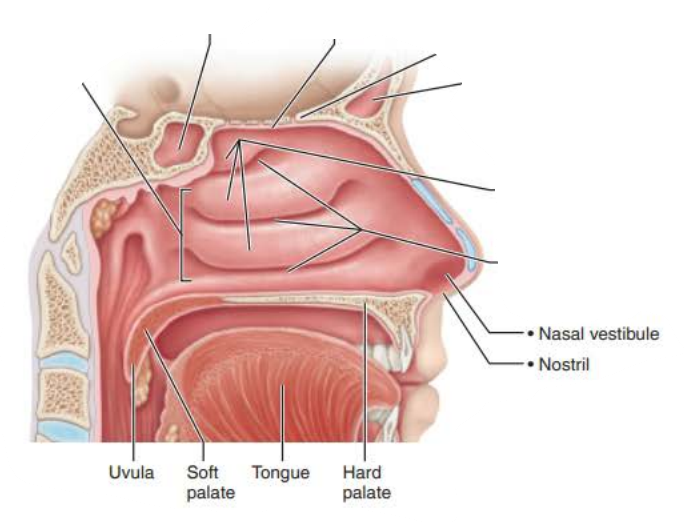
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: __________ _________
Structure
Lines the superior nasal cavity and contains ___________ ___________ which has _________ _________ ________
Olfactory Mucosa
olfactory epithelium
olfactory sensory neurons
-
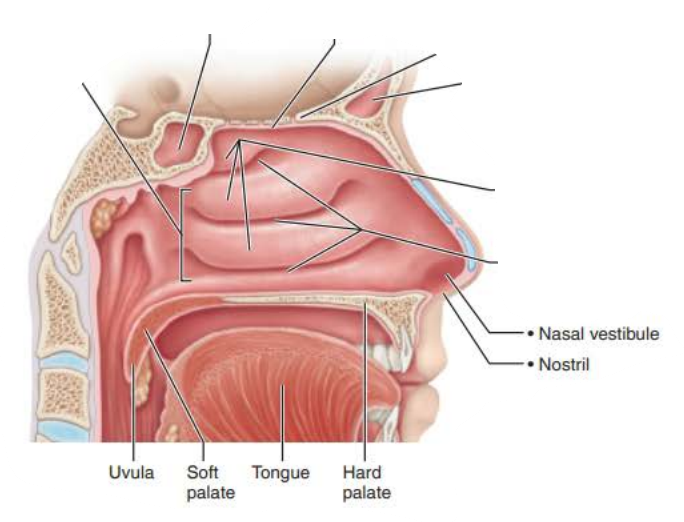
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: ___________ __________
Function:
the Olfactory sensory neurons form the ________ ______ that send _____ _______ towards the ________ ________
olfactory mucosa
olfactory nerve
smell afferents
olfactory cortex
-
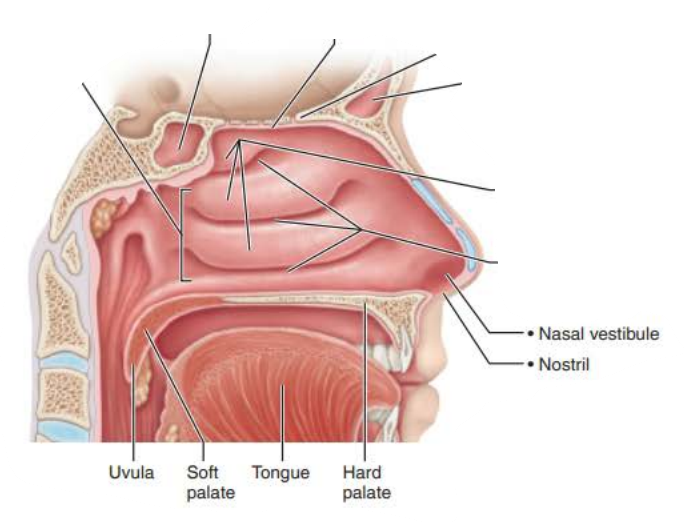
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name :_____________ _________
Structure:
Lines most of the nasal cavity
Tissue type: ________________ _________ _________ ___________ which contains _________ ______ and _____________ ______ ________
respiratory mucosa
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
goblet cells
seromucous nasal glands
-
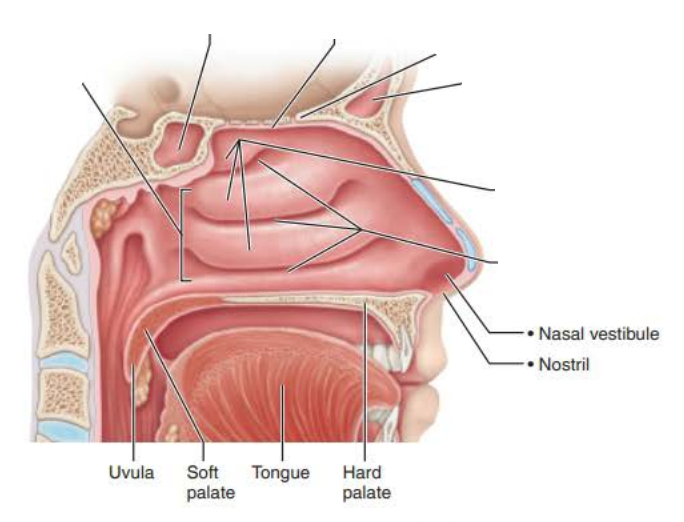
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Respiratory Mucosa
Function 1/2
The ___________ ___________ contains ________ ______ that creates a _______ that _____ ___ _______ __ ___________ _____ __________ toward the _________ to be _______
their ___________ secrete ________ which are natural antibiotics
Seromucous nasal glands
Secrete mucus containing lysozyme
Mucous
traps dust, bacteria and debris
High water content humidifies air
Lysosome works as an antibacterial enzyme
respiratory mucosa
ciliated cells
current
moves the sheet of contaminated mucus posteriorly
esophagus
digested
epithelial cells
defensins
-
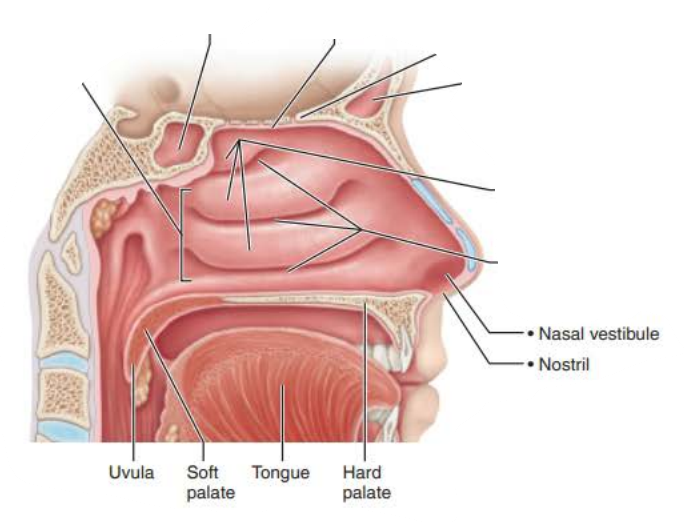
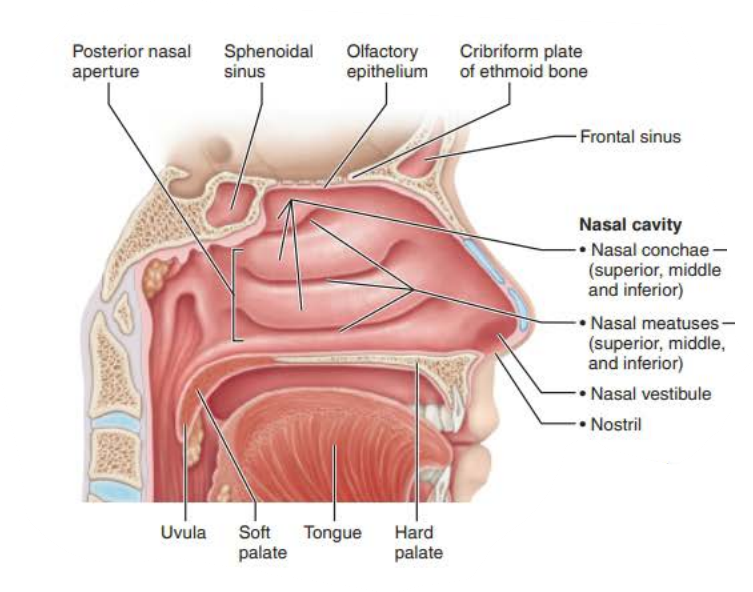
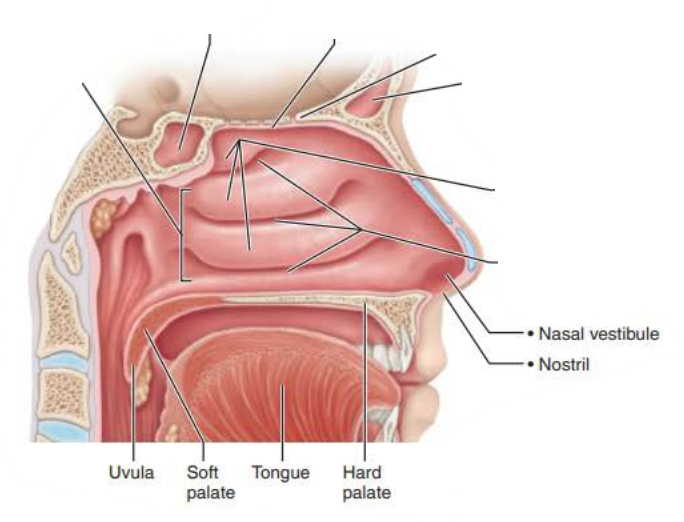
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Respiratory Mucosa
Function 2/2
Respiratory mucosa
Ciliated Cells
Creates a current that moves the sheet of contaminated mucus posteriorly toward the esophagus to be digested
Epithelial cells secrete defensins
Natural antibiotics
The ___________ _______ contains ___________ _____ _____ that secretes mucus containing ________ that works as an ____________ ________
The secreted ______traps dust, bacteria, and debris
High _______ content ________ air
respiratory mucosa
seromucous nasal glands
lysozyme
antibacterial enzyme
mucus
water
humidifies
-
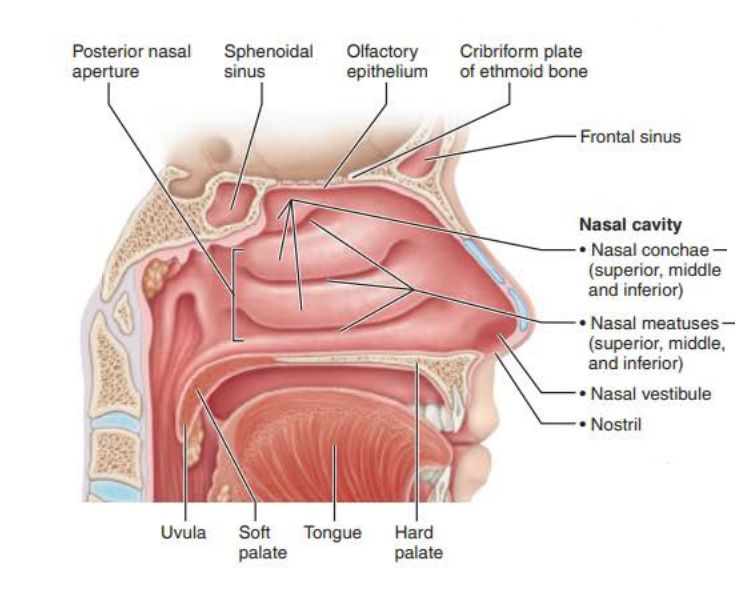
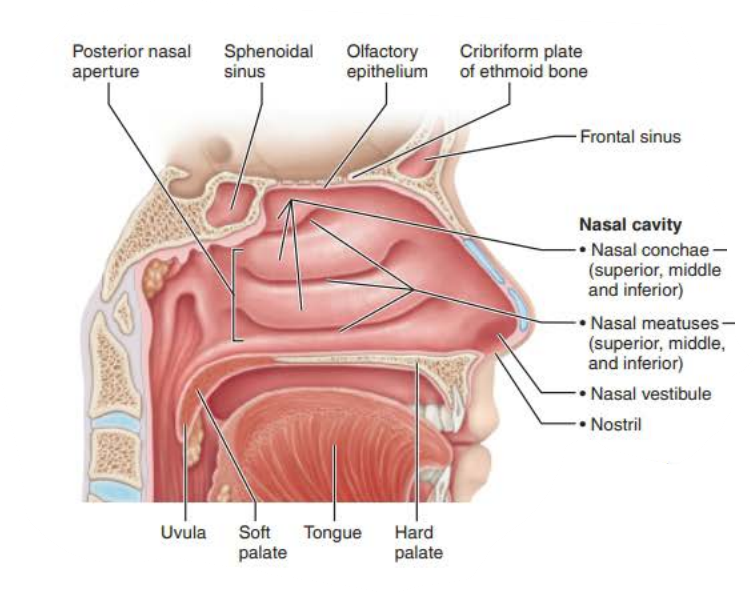
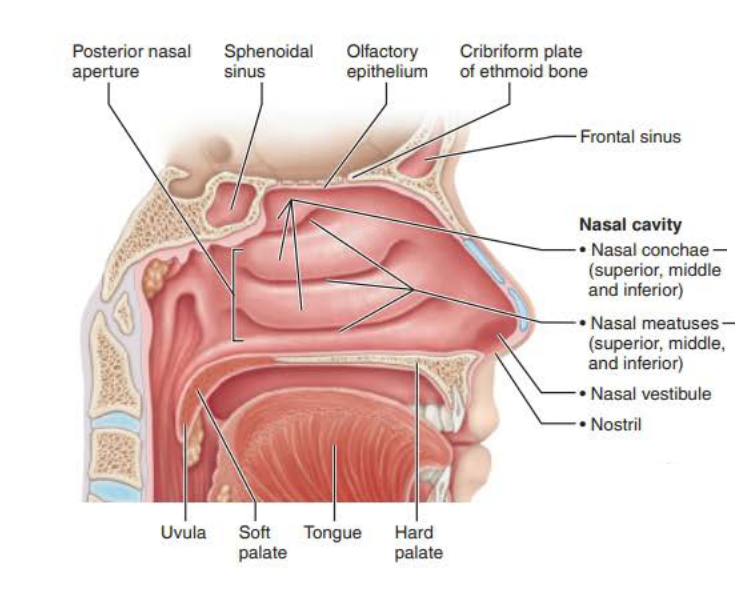
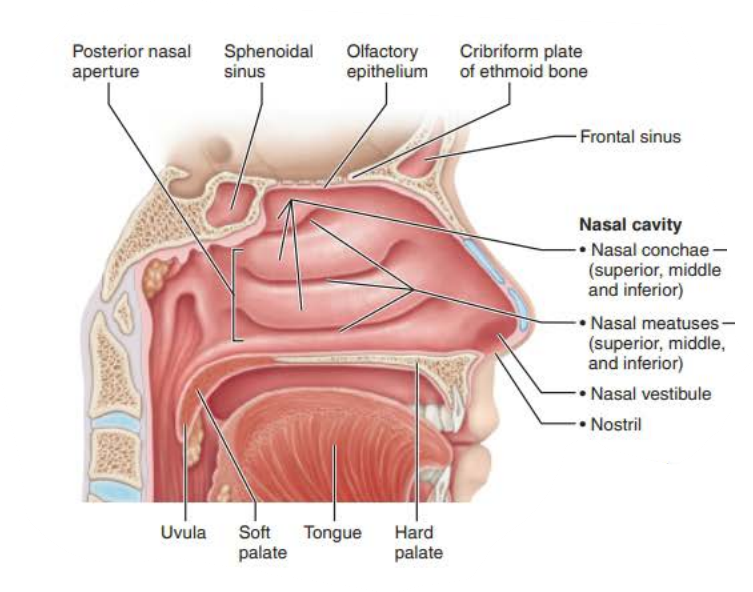
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: ________ _________
Structure:
Three scroll-like _______ covered projections
Inferior grooves called _______ _________
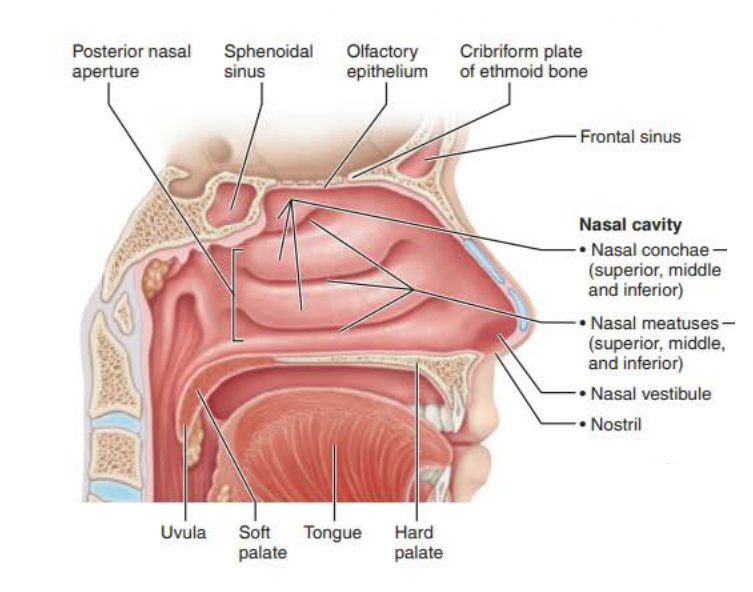
nasal conchae
mucosa
nasal meatus
-
Lysozyme
____________ _______
antibacterial enzyme
-
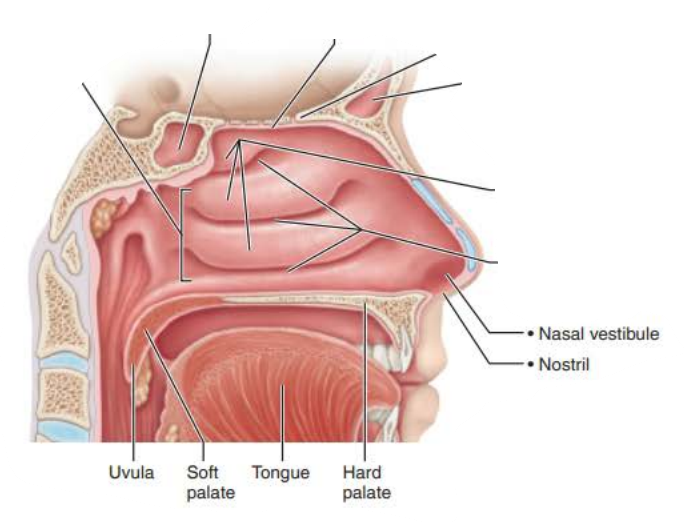
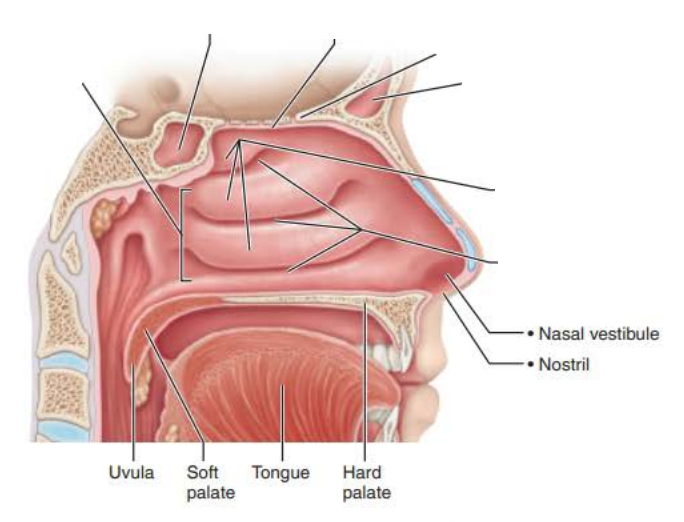
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name :_____________
Function:
_________ _________ ________ ____ exposed to air and enhances ____ _________ in the cavity
_____ larger particles
Minimizes the amount of ________ ____ ____ ____ from the body through breathing
________ air _______ conchae
________ air _______ conchae
Nasal Conchae
increases mucosal surface area
air turbulence
traps
moisture and heat lost
inspired
cools
exhaled
warms
-
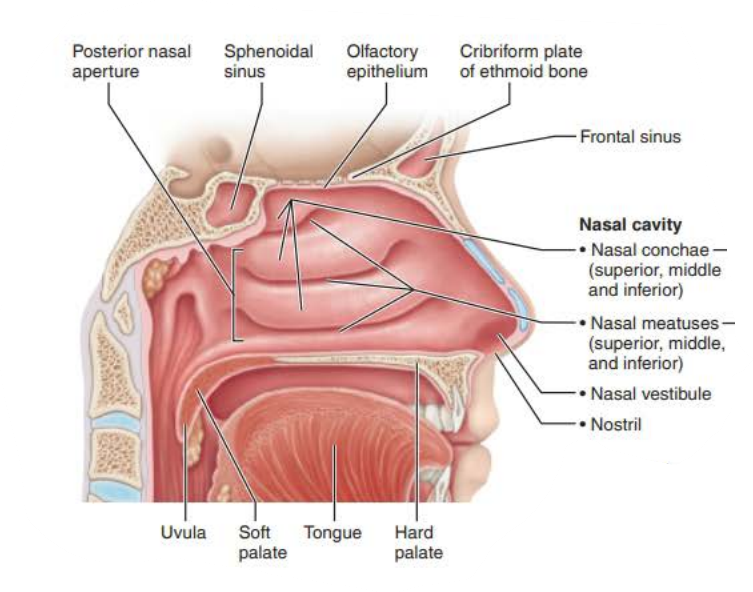
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: ___________ ________
Function:
_________ the skull
________ and ________ ___
Produces _______ that ____ into the _______ _______
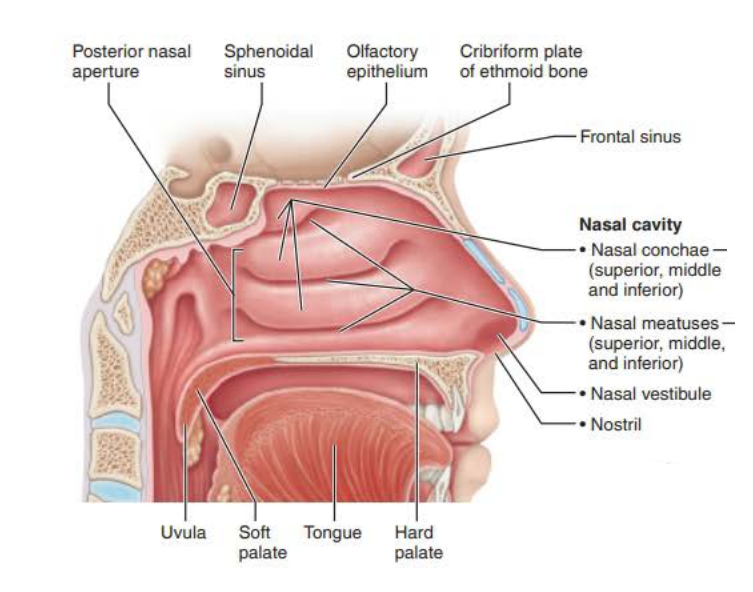
paranasal sinuses
lightens
warms
moistens air
mucus
flows
nasal cavity
-
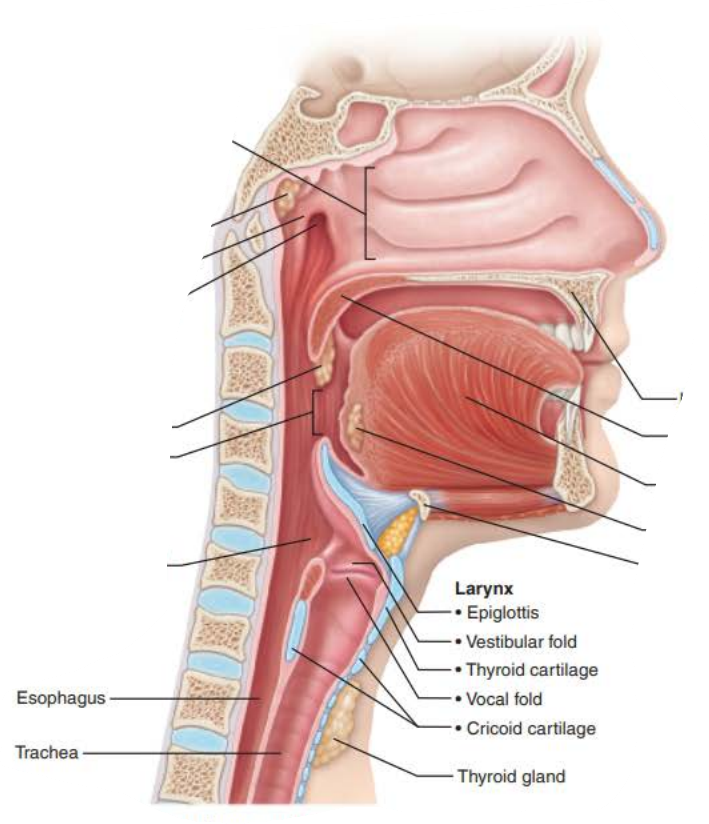
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: ________
Structure:
_______ shaped
________ muscle
Extends for 5 inches
From base of skull to ___
Divided into three regions
__________
___________
______________
pharynx
funnel
skeletal
C6
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
-
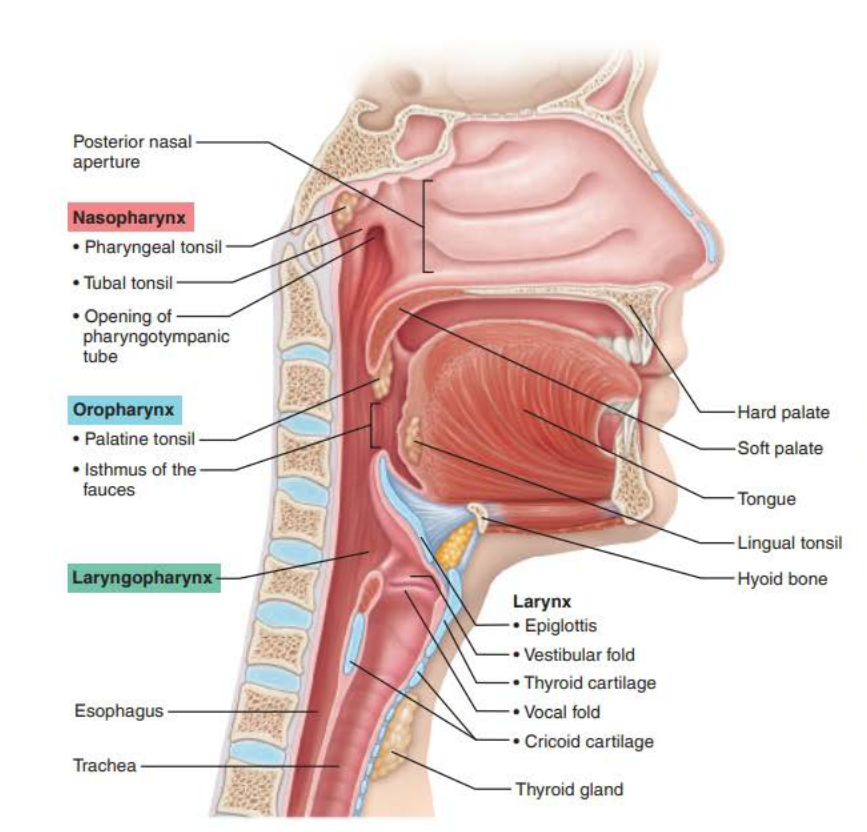
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Function:
Connects the ______ _______ and _______ superiorly to the ________ and __________ inferiorly
connects
nasal cavity
mouth
larynx
esophagus
-
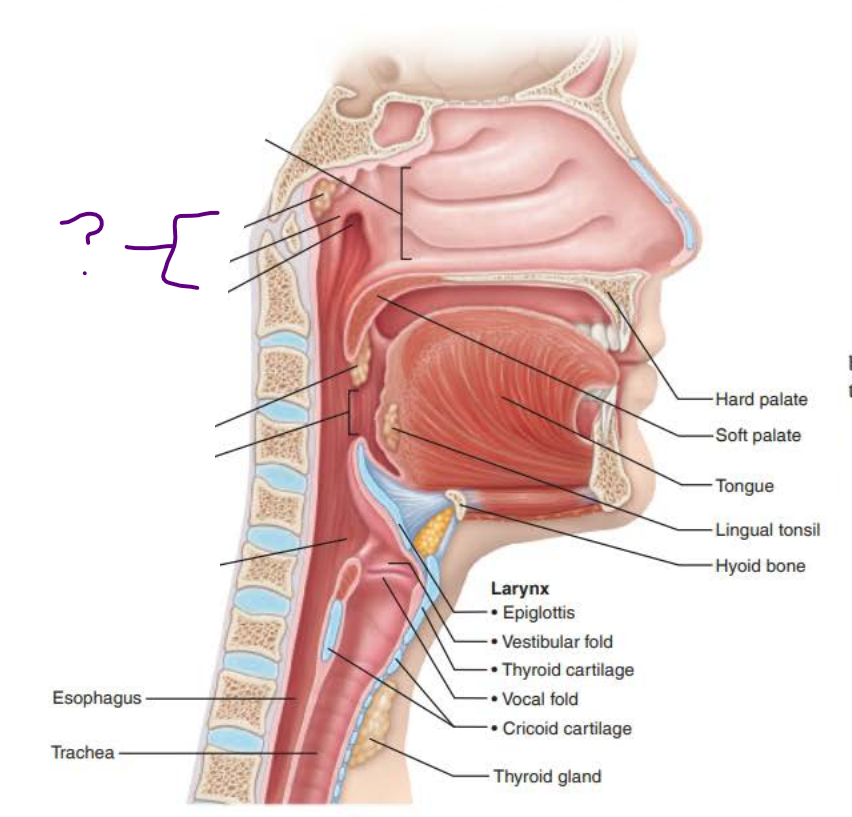
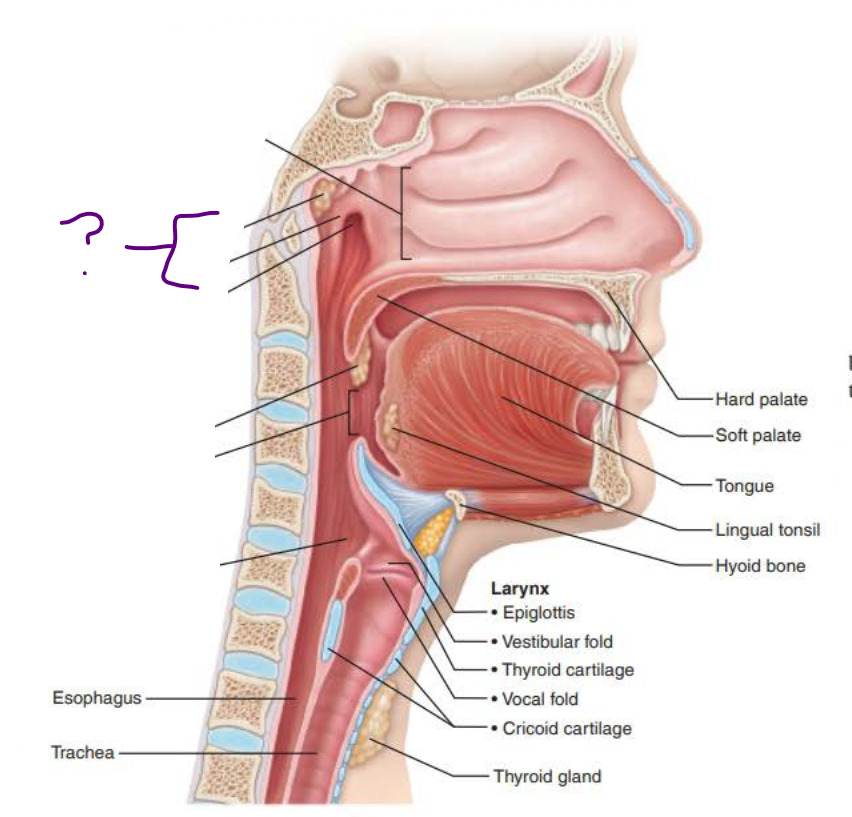
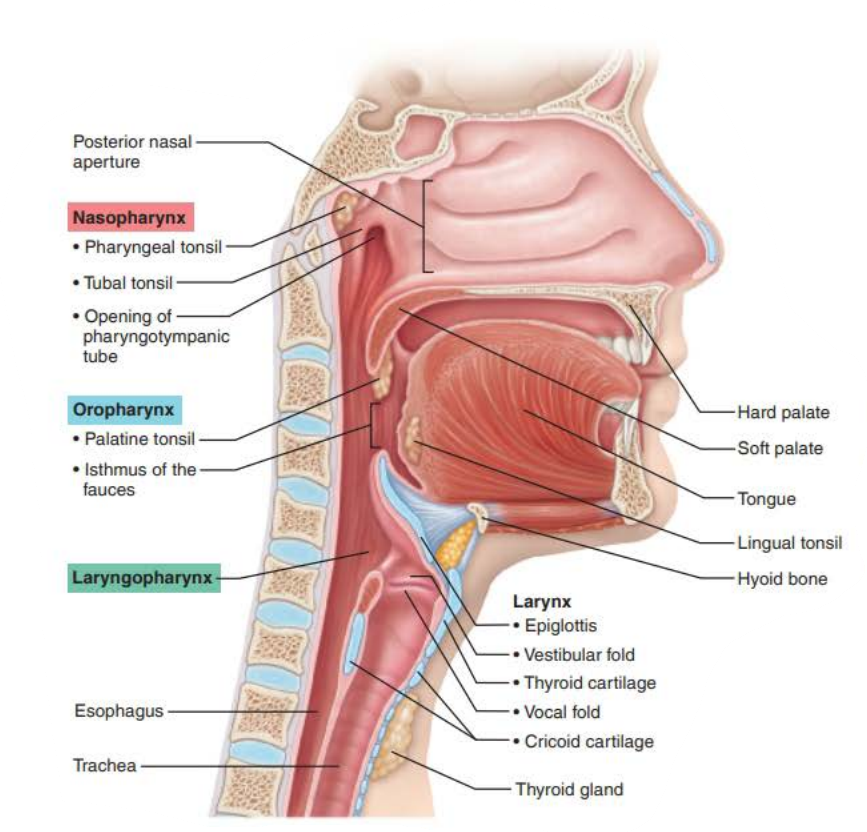
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: _____________
Structure:
Posterior to nasal cavity
Inferior to sphenoid bone
Superior to soft palate
Continuous with the _________ _____ _________
composed of _______________ ________ ___________
Contains the ___________ and ______ tonsils
Contains the __________ _____
nasopharynx
posterior nasal cavity
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
pharyngeal
tubal
eustachian tube
-
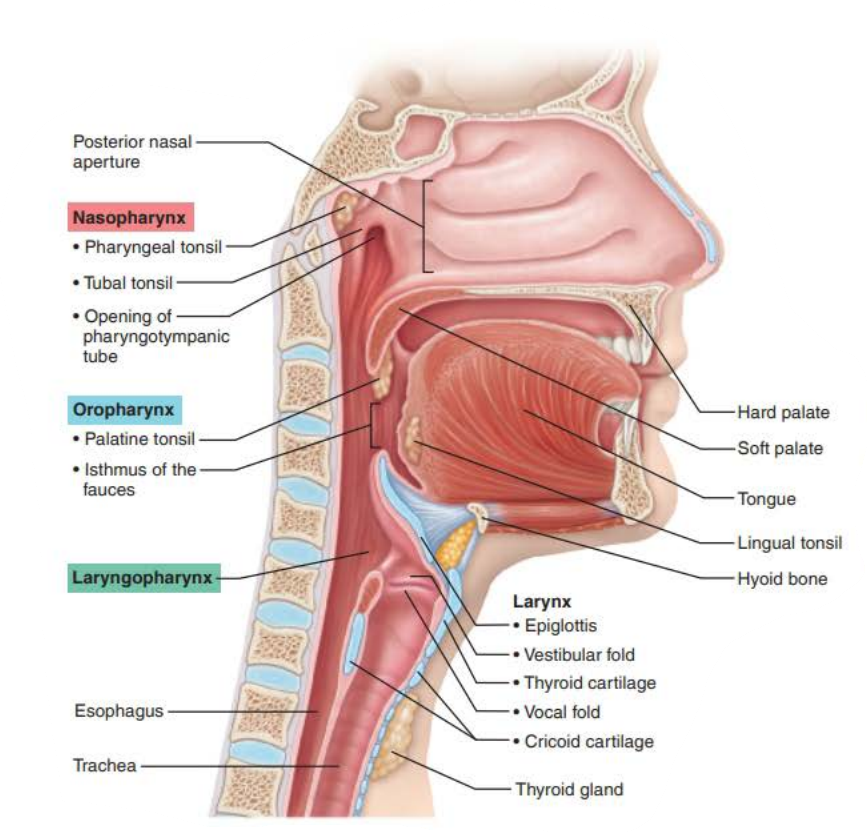
Mucous membranes of the Nasal Cavity
Name: _______________
Function: ___ _____________ that _______ during _____________ to prevent food from entering the ______ ______
the _______________ ______ __________ ___________ propels ______
__________ and ______ tonsils destroy pathogens entering the nasopharynx
the____________ ____ equalizes middle ear pressure allowing tympanic membrane to ring freely
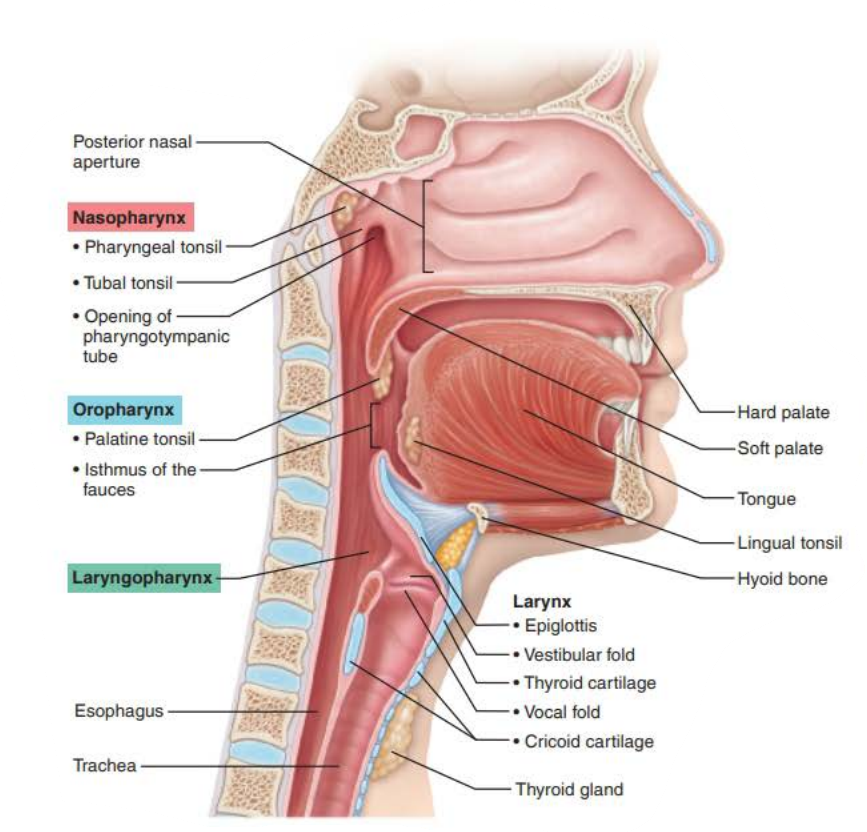
Nasopharynx
air passageway
closes
swallowing
nasal cavity
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
mucus
pharyngeal
tubal
eustachian tube
-
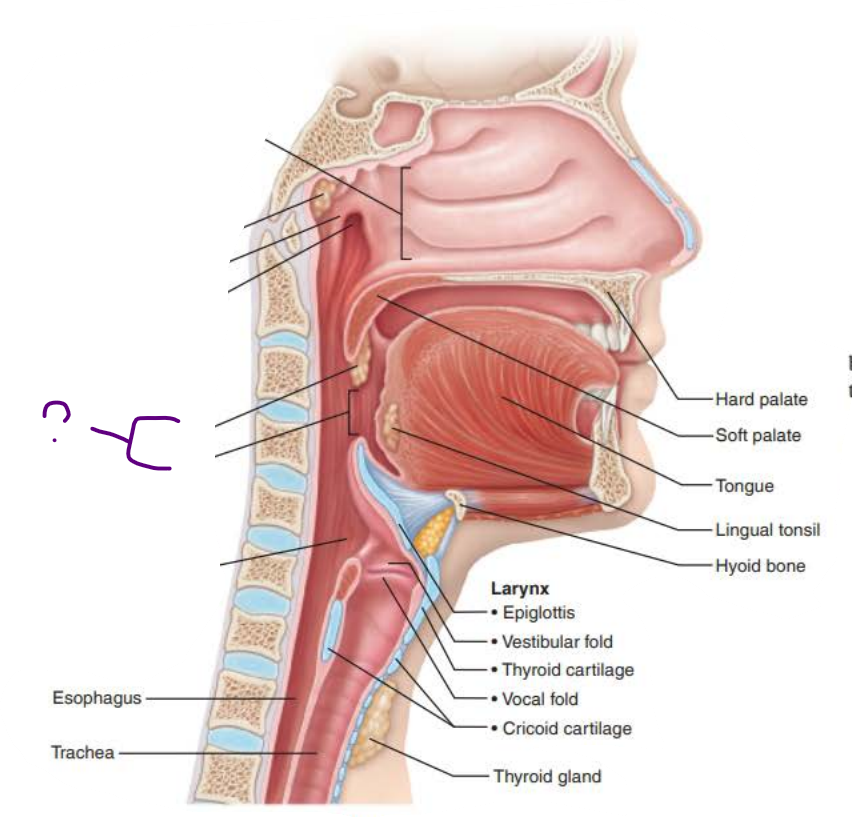
Name: ____________
Structure:
Lies posterior to the oral cavity and is continuous through archway called the _________ ___ _________
it is composed of _________ _________ __________ and contains the _________ and _______ tonsils
Oropharynx
Isthmus of fauces
stratified squamous epithelium
palatine
lingual
-
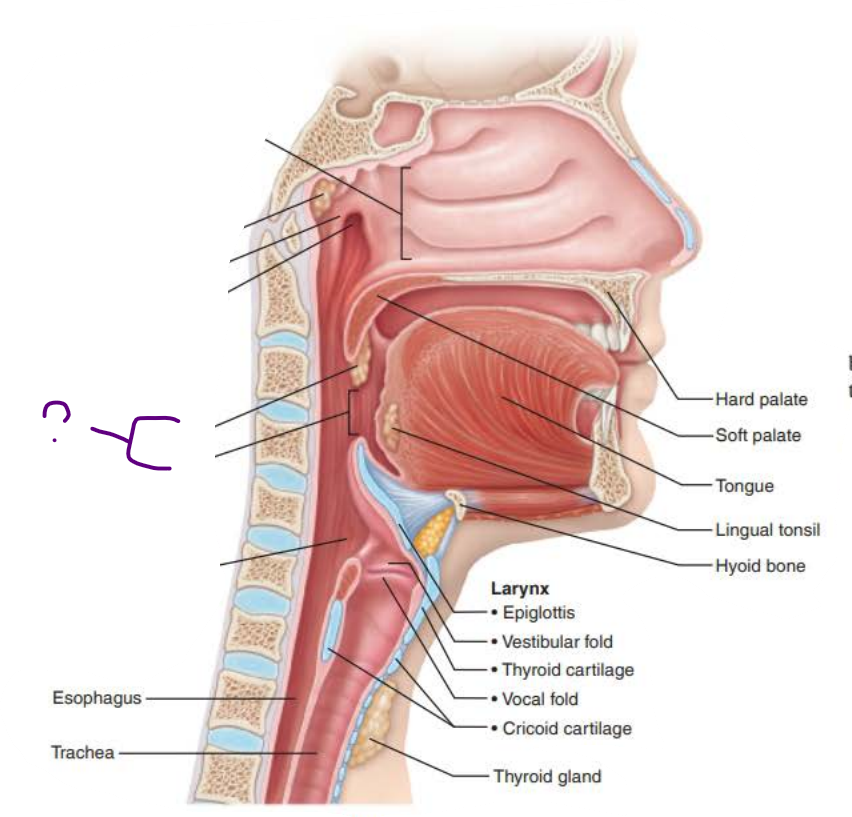
Name: _______________
Function:
_________ swallowed ____ and ____
its tissue the, _________ ____________ ___________ protects against ________ ________ and _________ _______
oropharynx
transmits
food
air
stratified squamous epithelium
increased friction
chemical trauma
-
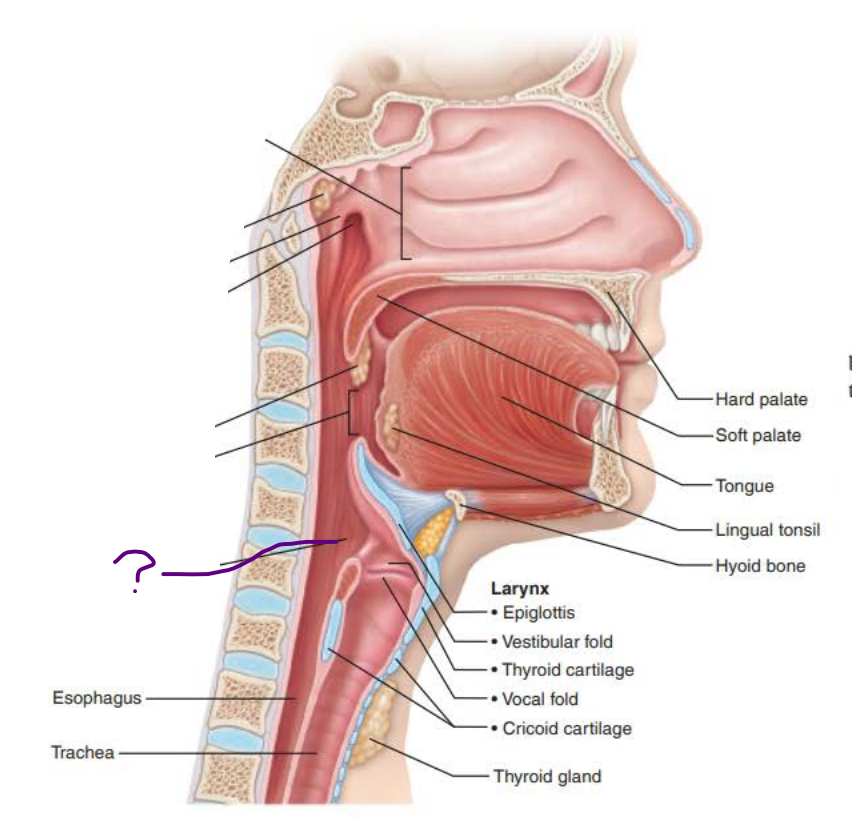
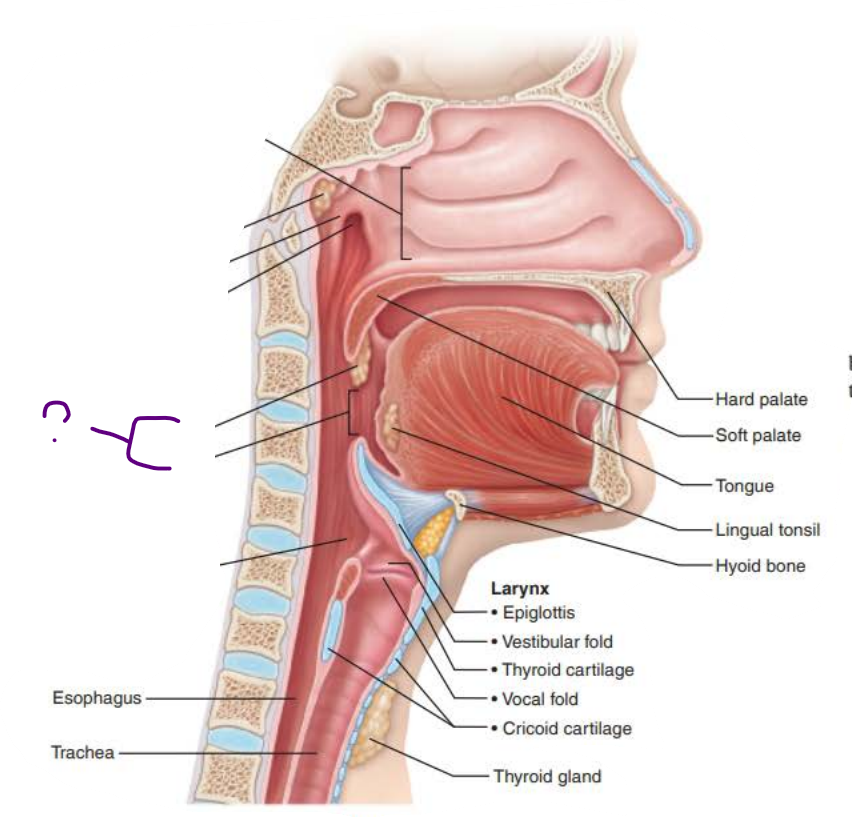
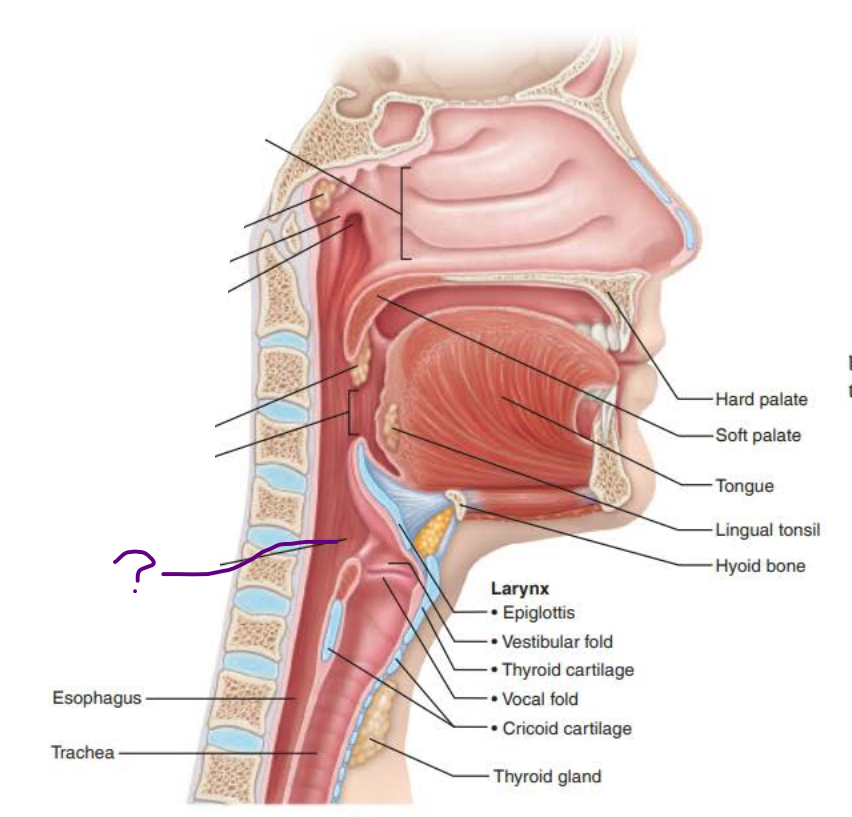
Name: _________________
Structure:
its tissue the, ____________ _________ ___________ is posterior to _______
Continuous with the ____________ posteriorly
laryngopharynx
stratified squamous epithelium
larynx
esophagus
-
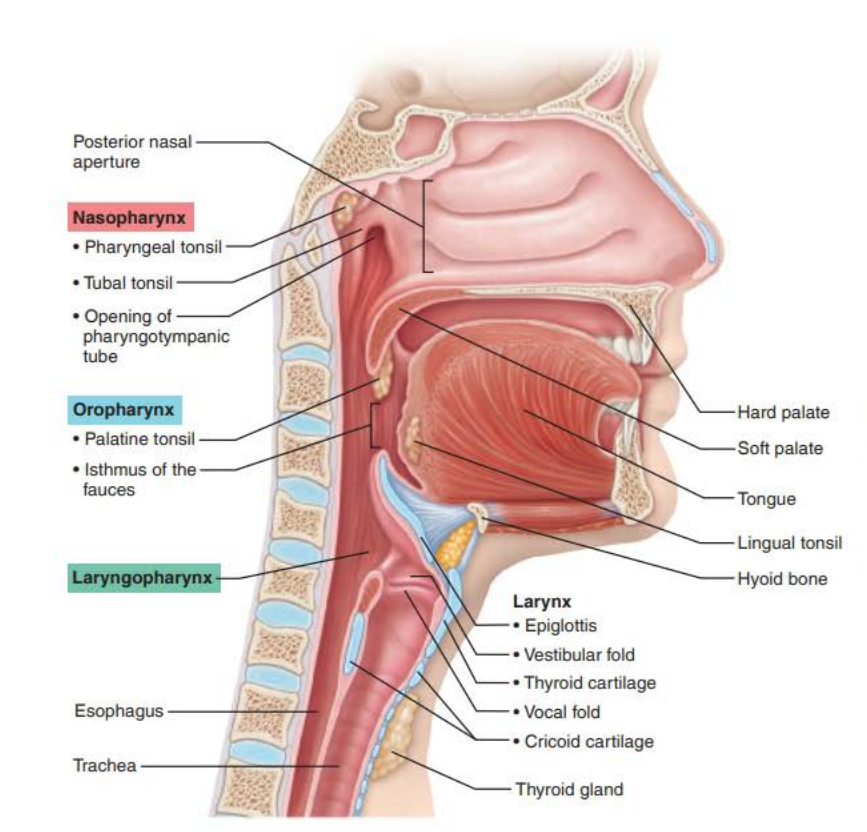
Name: Laryngopharynx
Function:
___________ for ____ and ___
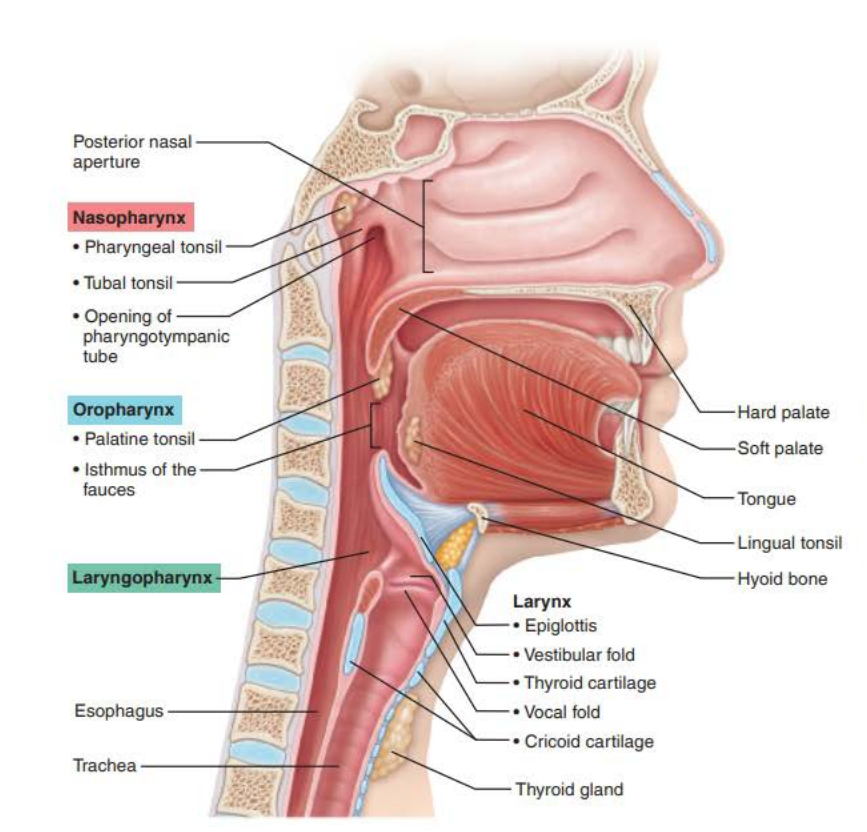
passageway
food
air
-
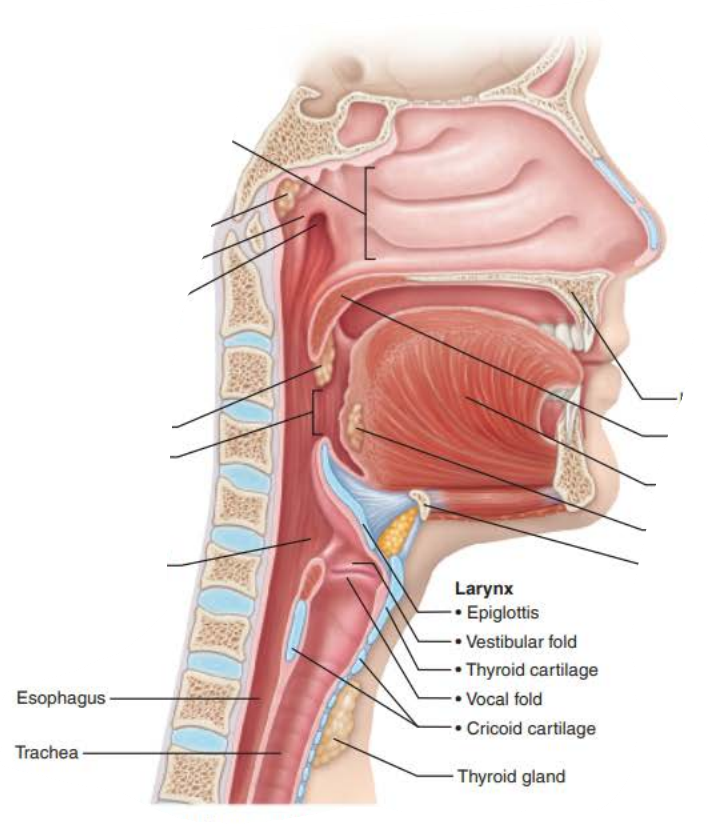
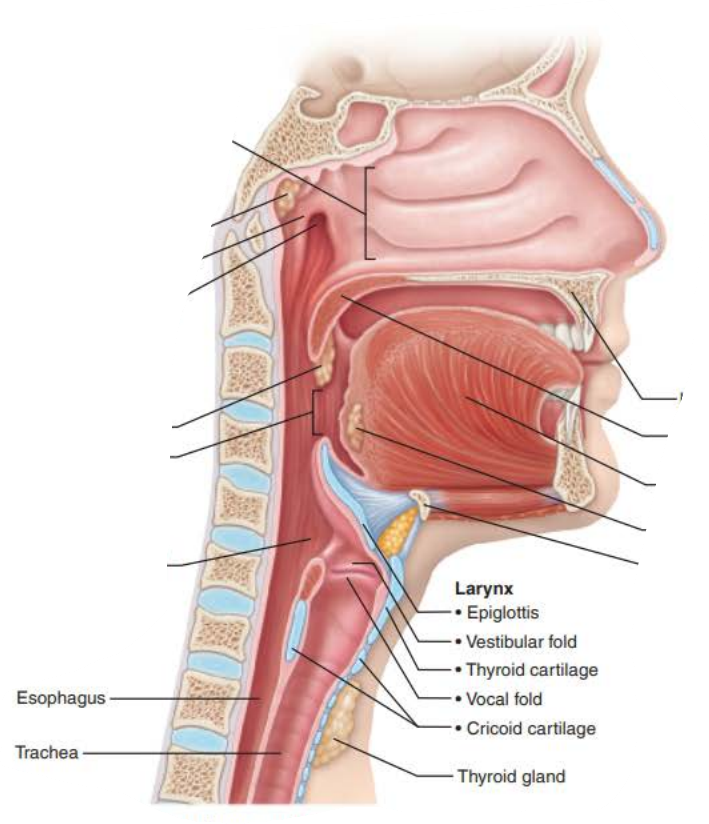
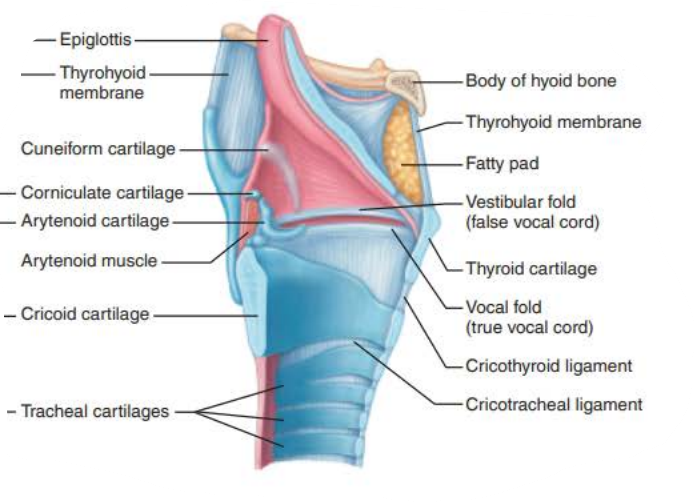
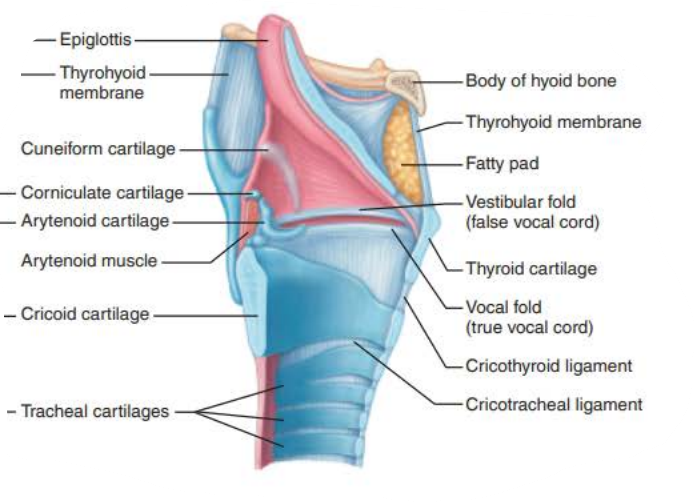
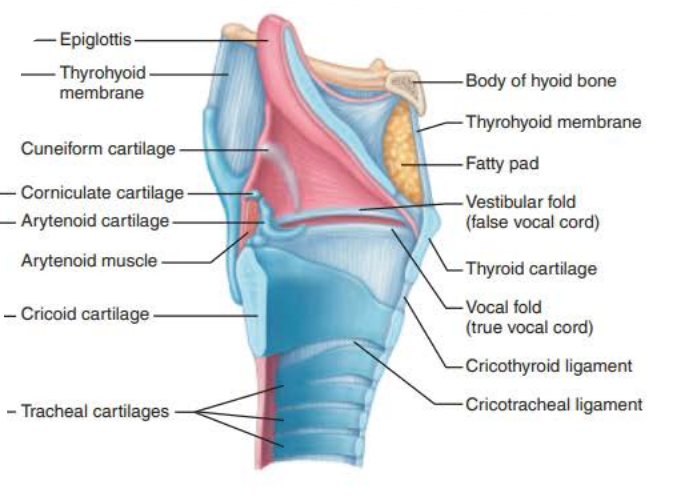
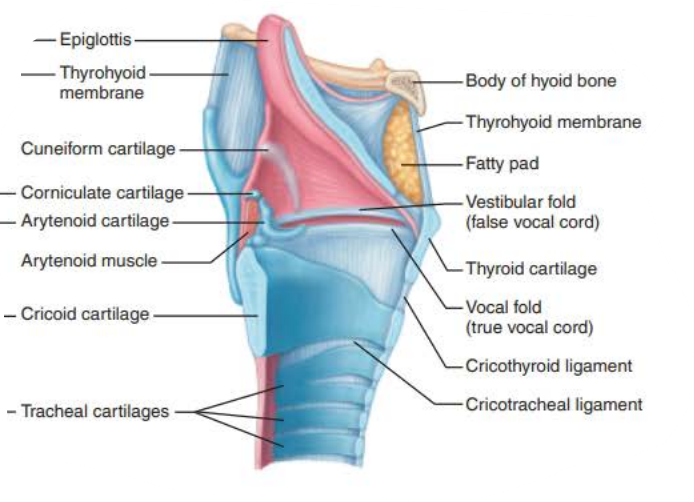
Name: ________
Structure:
composed of __________ __________ _________ superiorly
_______________ _______ _________ ________ below vocal folds
Extends for 2 inches from C3 to C7
Superiorly attaches to hyoid bone
Opens into laryngopharynx
Inferiorly continuous with the ________
contains __ _________ connected by membranes and ligaments
_____ ______ (true vocal cords)
Pearly white
No blood vessels
Vocal ligaments
Elastic fibers
contains the ________, the medial opening between vocal folds
__________ _____ (False vocal cords)
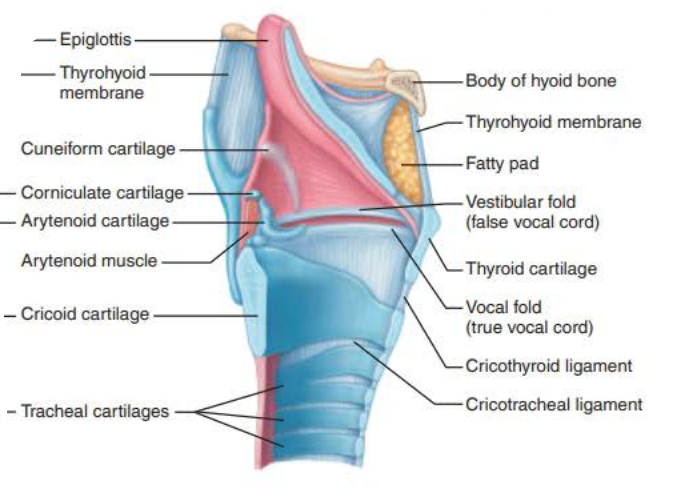
larynx
Stratified squamous epithelium
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
trachea
9 cartilages
vocal folds
glottis
vestibular folds
-
Larynx
True or False and WHY
every one of the 9 cartilages in the larynx is hyaline cartilage
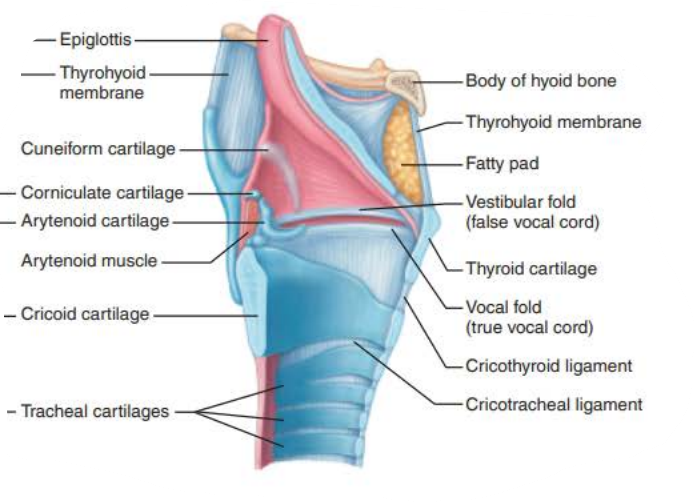
false the epiglottis is elastic cartilage
-
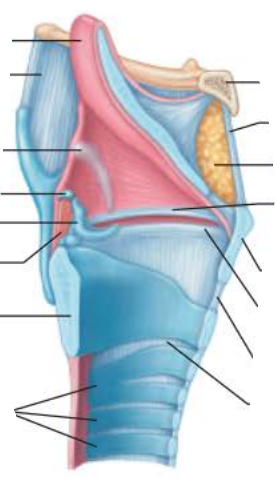
Larynx
__________ cartilages ______ the ______________
arytenoid
anchor
vocal folds
-
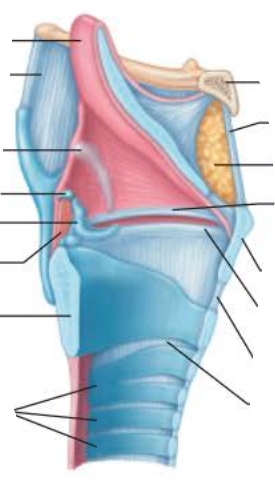
Larynx
___________
Posterior aspect of the tongue
Anchors on thyroid cartilage
Ninth cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Covered by taste-bud containing mucosa
epiglottis
-
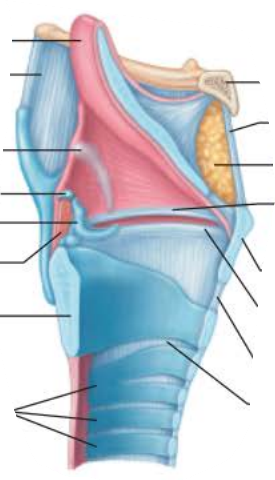
Larynx
the ___________ during ____________ projects upwards to _______ ____ flowing into _______
epiglottis
inhalation
allow air
larynx
-
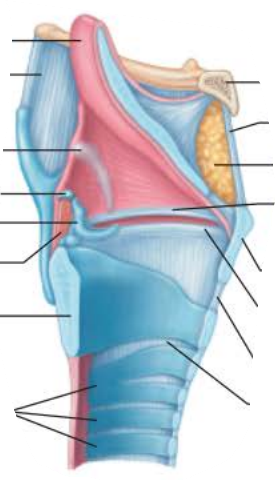
Larynx
the _______________ during ____________ is pulled superiorly and ______ the __________ ______
epiglottis
swallowing
covers
laryngeal inlet
-
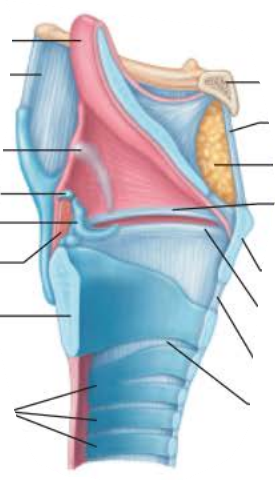
Larynx
the medial opening or _______ is a __ ____________
glottis
air passageway
-
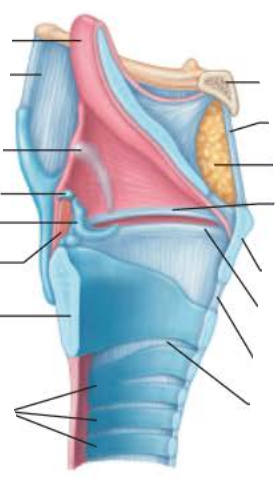
Larynx
to produce sound, the _________ ________ ________ as ___ rushes from _______
vocal folds vibrate
air
lungs
-
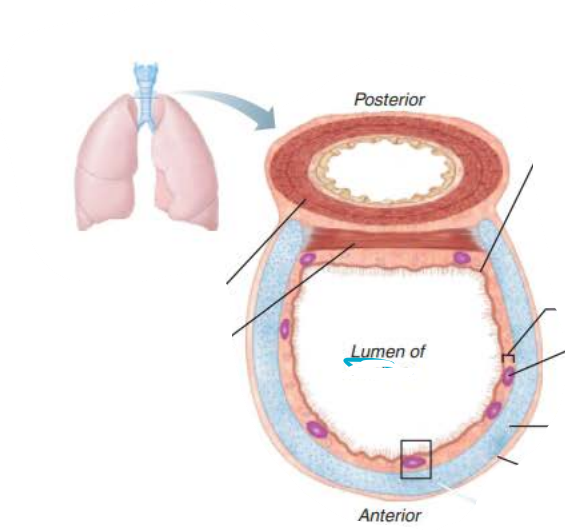
__________
Structure:
Descends from the larynx through the neck into the mediastinum
4 inches long, ¾ inch in diameter
Flexible
Several layers
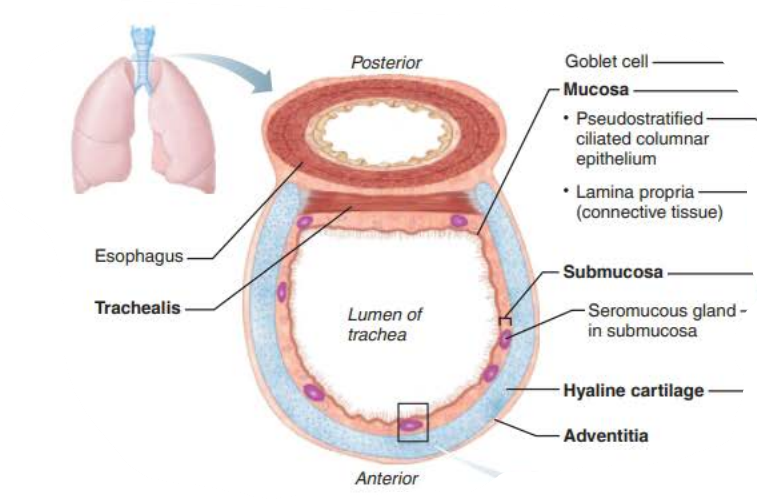
trachea
-
Name: _______
Function:
When incoming air reaches end of the passageway at the _______ air is _____ and ________ of most impurities
Saturated with ______ _______
the _______ elements allow for _______ during ___________ and _______ during ___________
Trachea
carina
warm
cleansed
water vapor
elastic
flexibility
inspiration
recoil
expiration
-
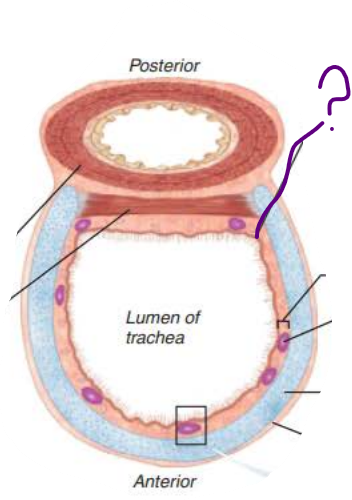
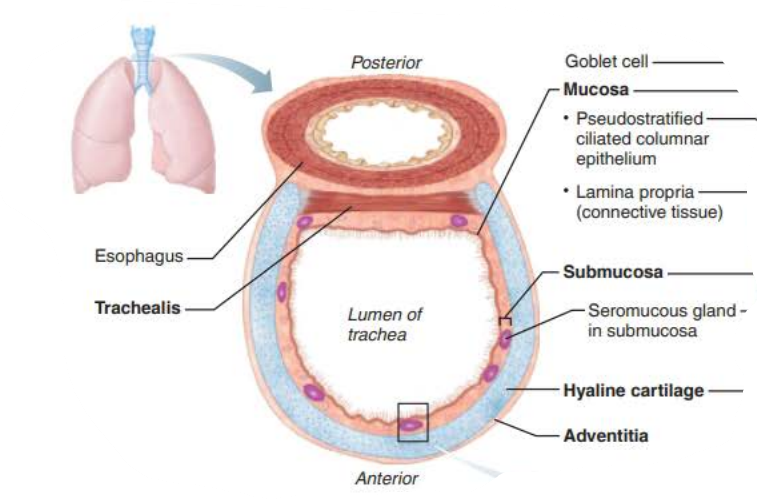
in the trachea, _______ lined with ____ propel _______ containing _____ upwards toward the _______
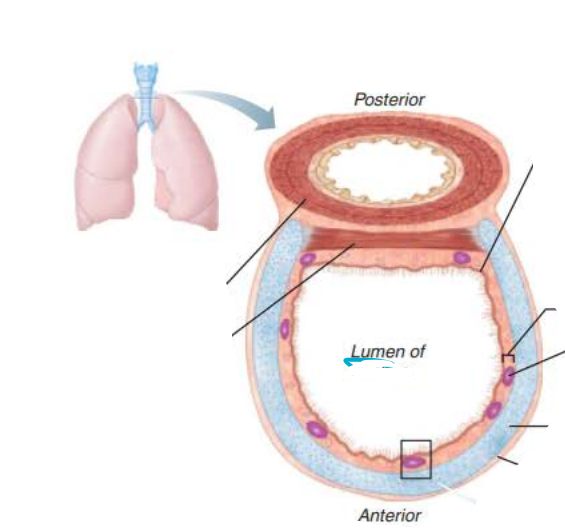
mucosa
cilia
mucus
debris
pharynx
-
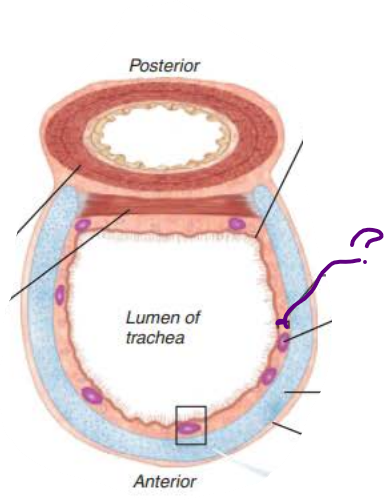
in the trachea, the ____________ contains ___________ ______
that produce _______ ______
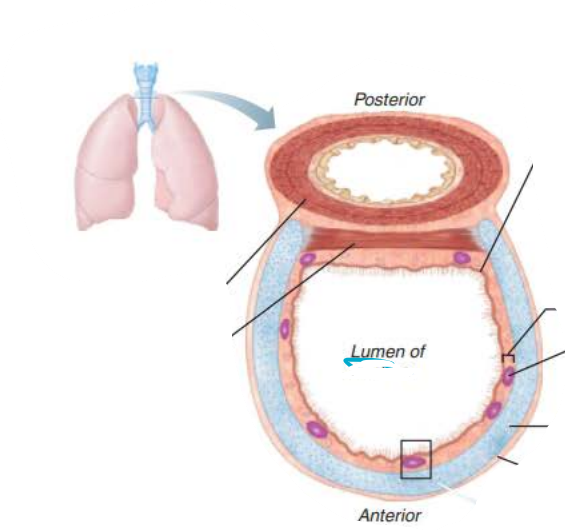
submucosa
seromucous glands
mucus sheets
-
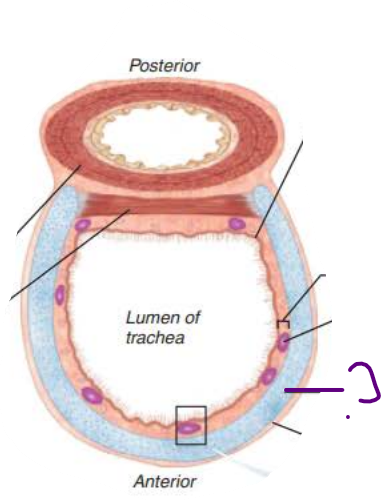
in the trachea, the _____ __ _________ ________ prevent the trachea from ___________ and keeps the _______ _____ despite ___________ _________
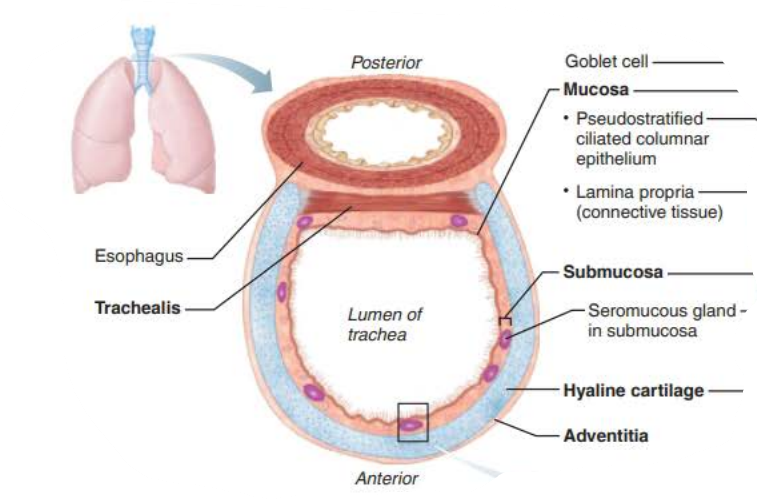
rings of hyaline cartilage
collapsing
airway open
pressure changes
-
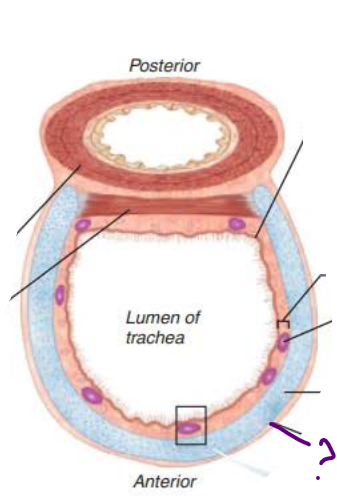
In the Trachea, the _________ is the __________ layer of _________ ______ that encases the ____ __ ______ ________
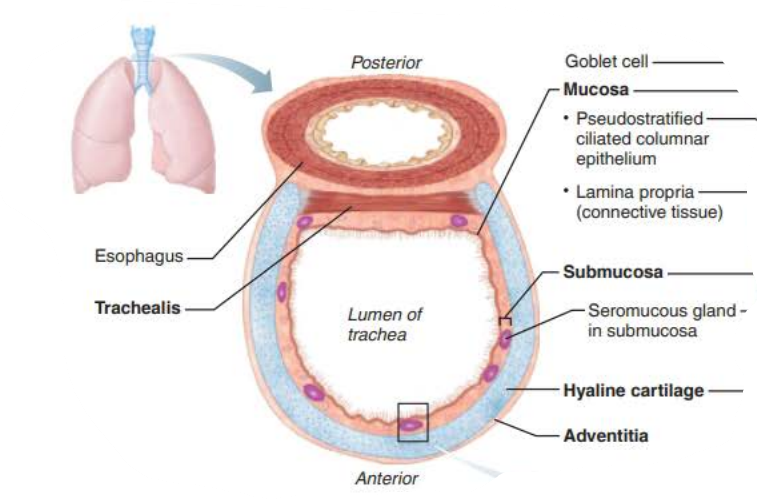
adventitia
protective
connective tissue
rings of hyaline cartilage
-
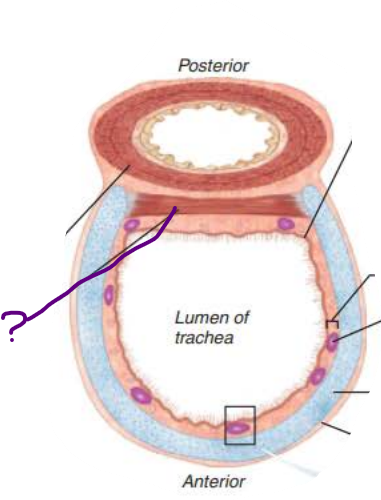
In the Trachea, the ___________ contracts to ________ ______ ___________ so ________ air rushes from lungs with ______ _____ expelling ______ when we ______
trachealis
decrease trachea diameter
greater force
expired
mucus
cough
-
In the Trachea, the _______ contains ________ ________ that triggers __________ when _______ _______come in contact
carina
sensitive mucosa
coughing
foreign objects
-
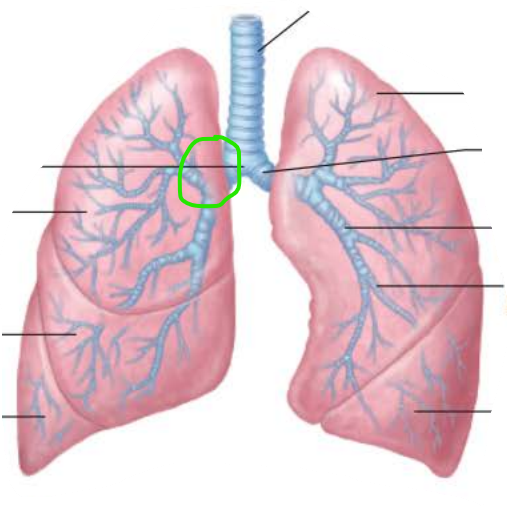
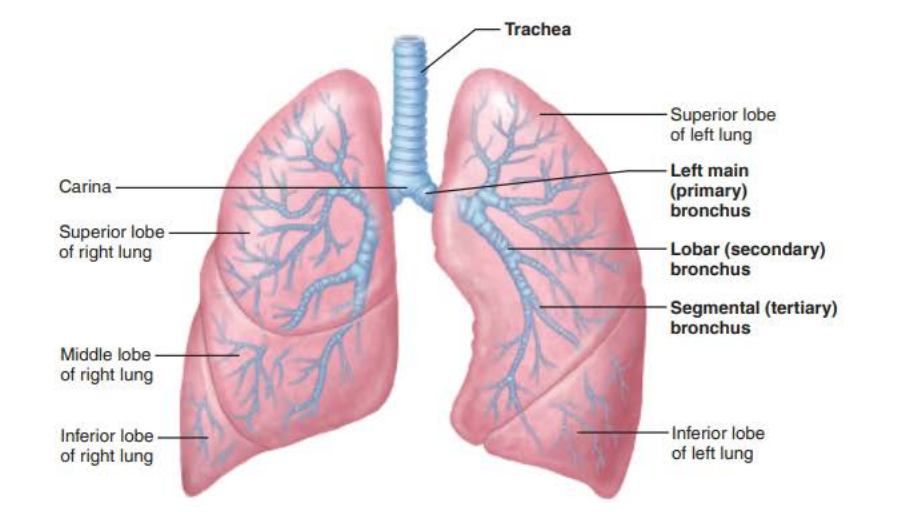
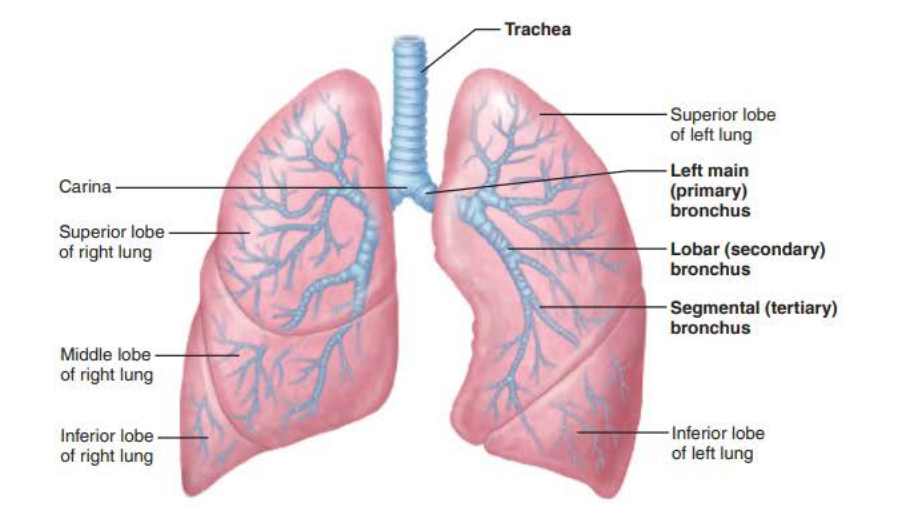
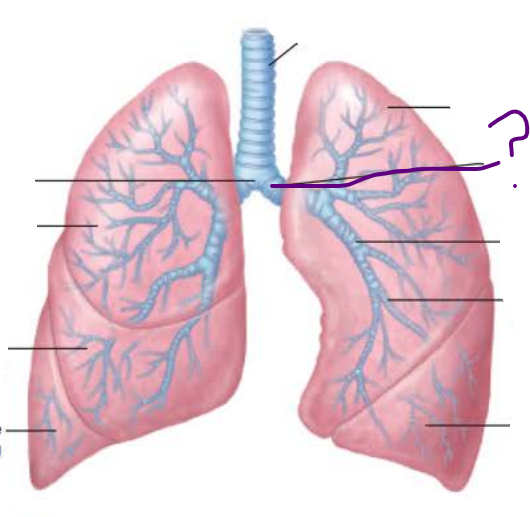
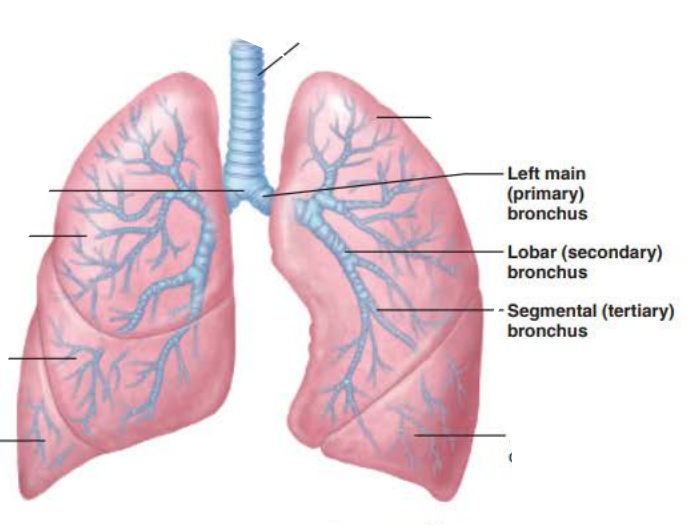
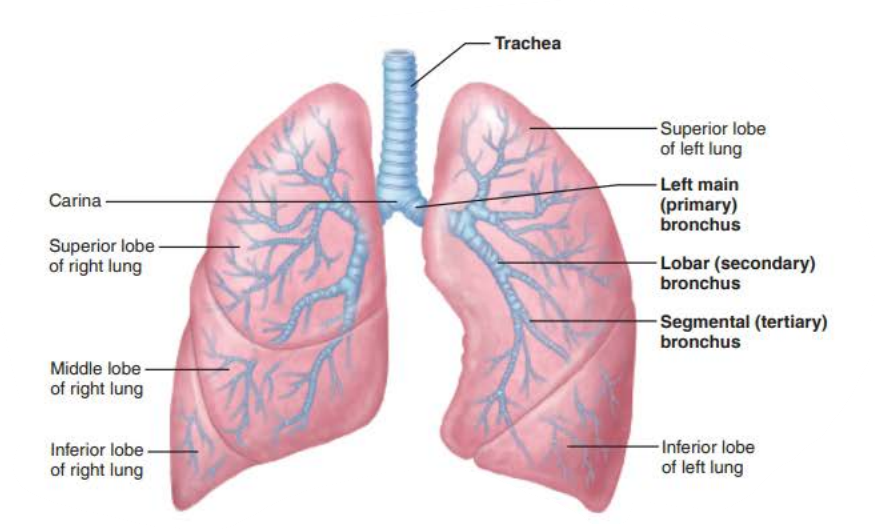
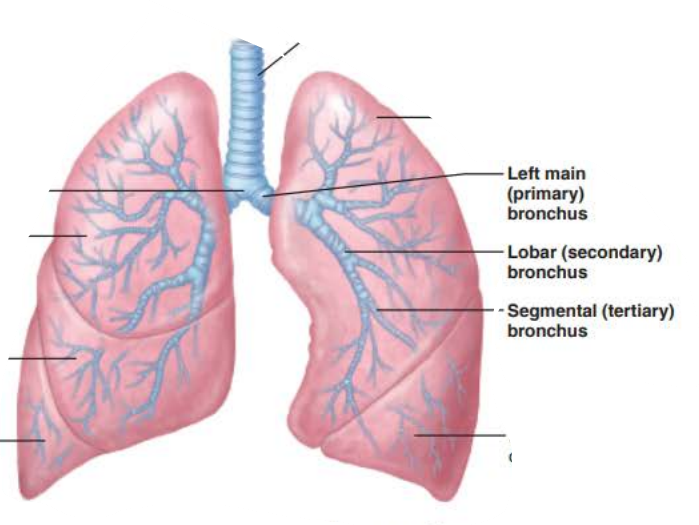
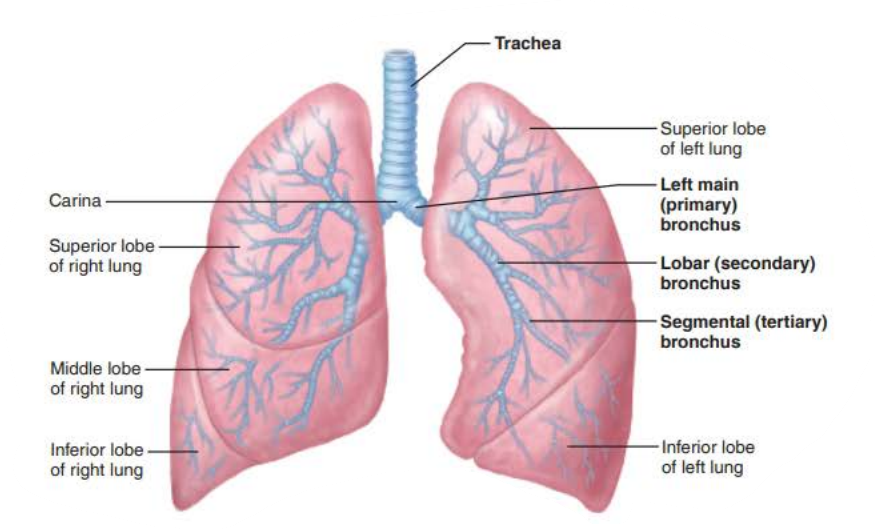
True or false
Right main bronchi is wider, shorter, and more vertical than left
true
-
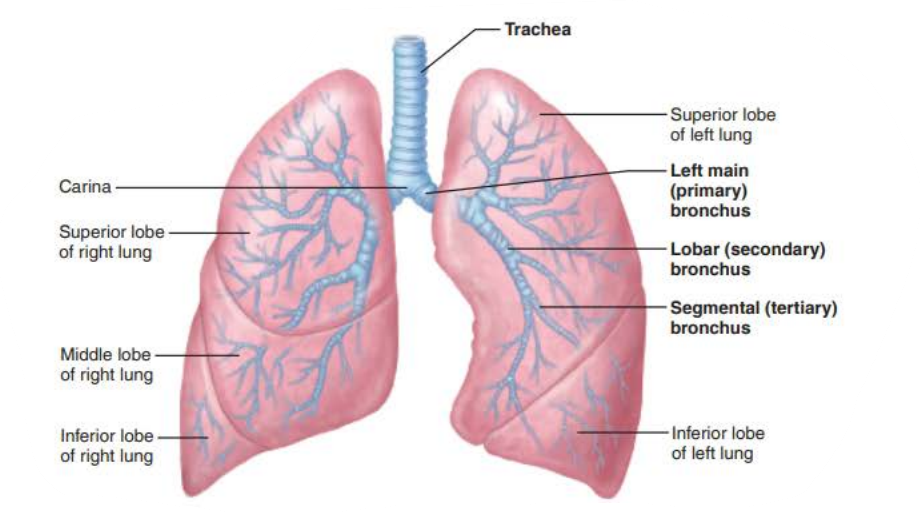
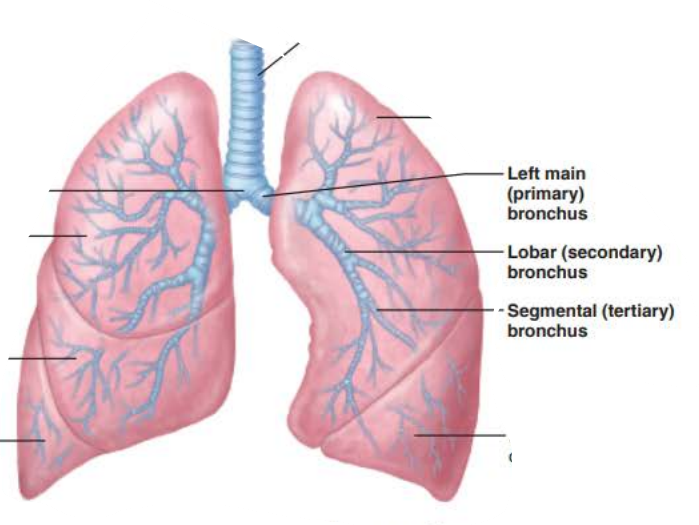
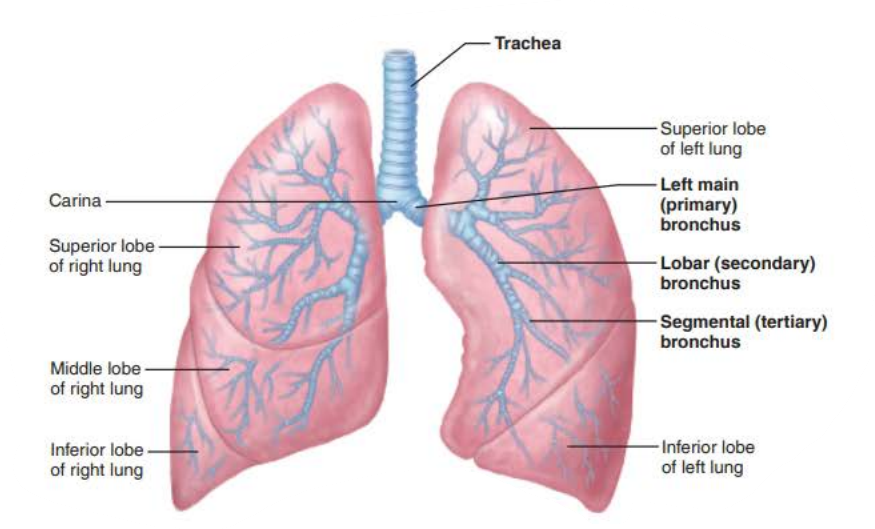
the _______ are ___ _____________ connecting the _______ with ______
Cleans, warms, and moistens air
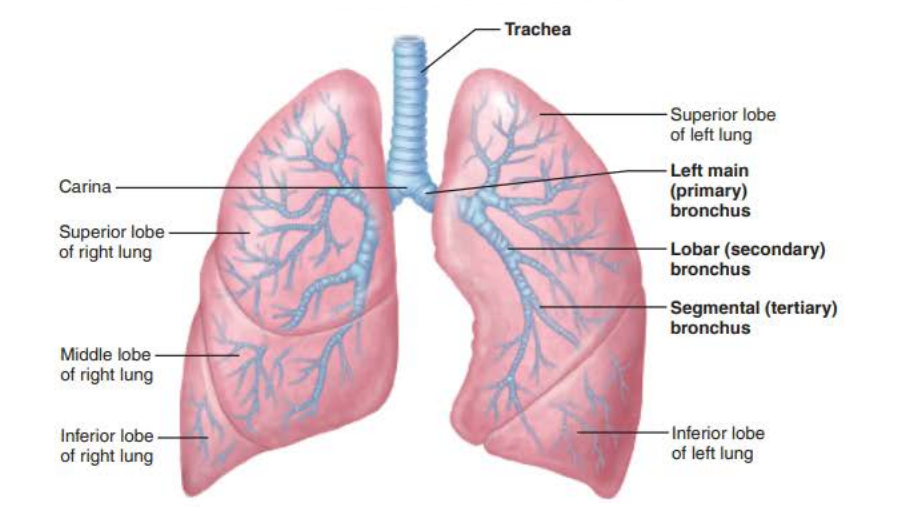
bronchi
air passageways
trachea
alveoli
-
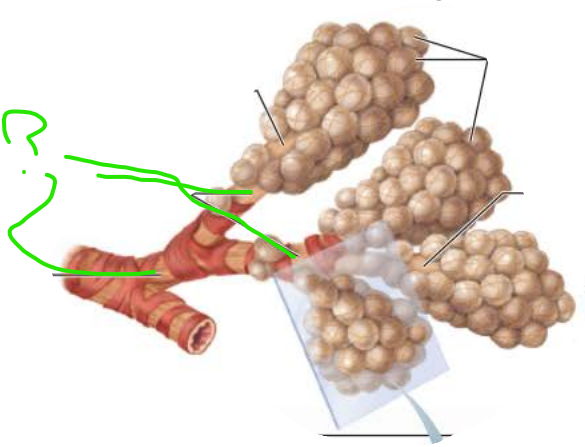
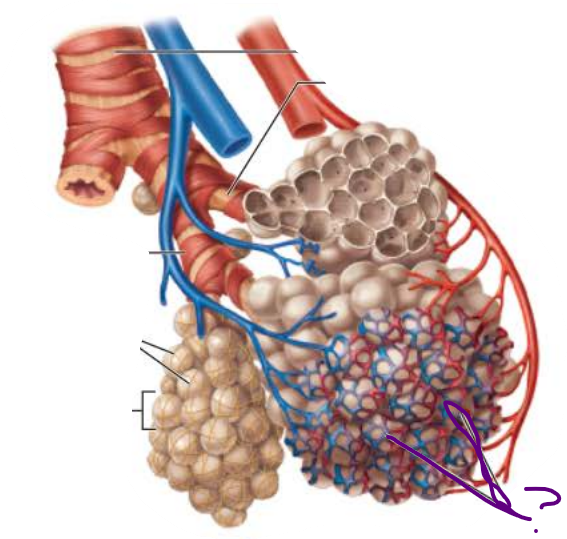
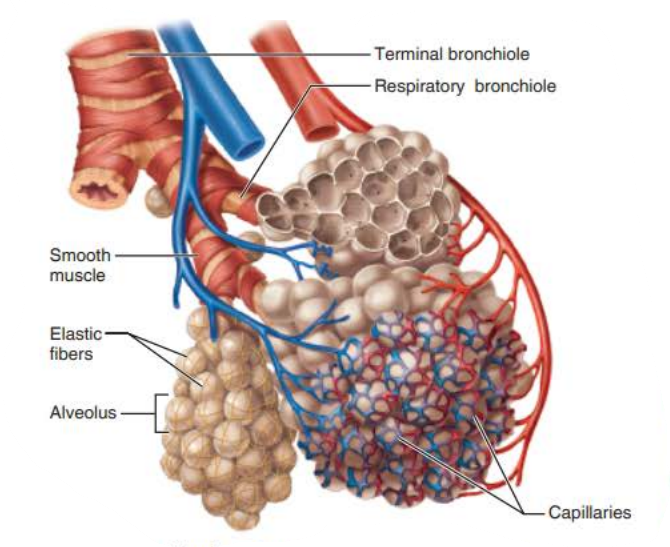
______________
Passages smaller than ____ in diameter
Bronchioles
1mm
-
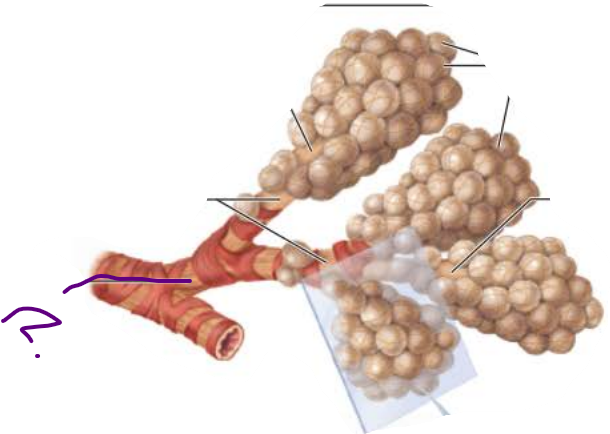
__________ _____________
Passages less than _____ in diameter
terminal bronchioles
0.5mm
-
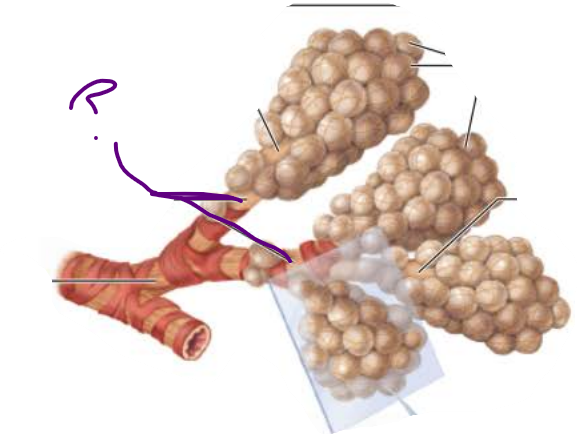
___________ ____________
Contains _______
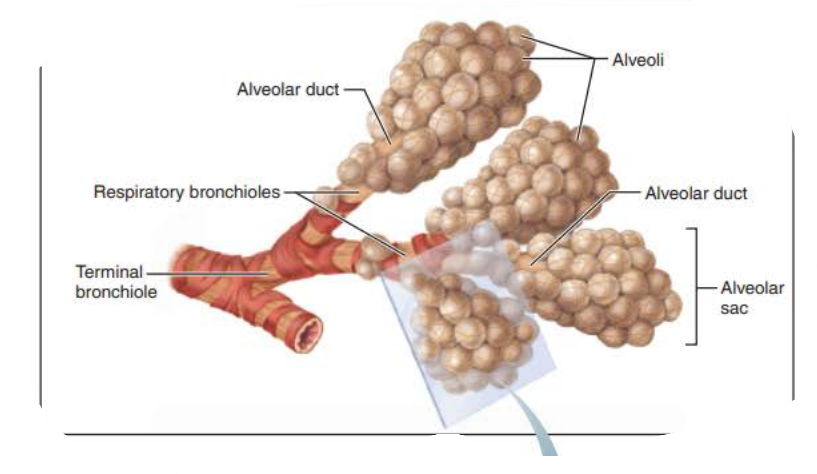
respiratory bronciholes
alveoli
-
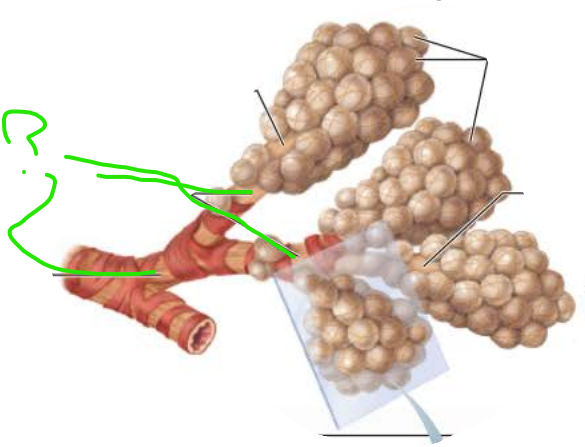
the _____________ contains ________ ______ that provides __________ to the ___ ___________under certain conditions
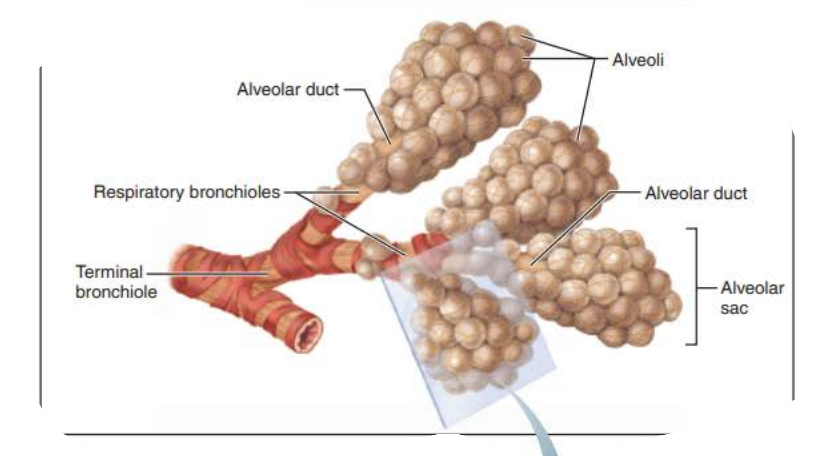
bronchioles
smooth muscle
resistance
air passage
-
the main _______ have the same tissue composition as trachea , but as conducting tubes get smaller (1/3)
____________ _______ of ________ replace the _________ _____
No cartilage in ____________
bronchi
irregular plates
cartilage
cartilage rings
bronchioles
-
Main ________ have same tissue composition as trachea , but as conducting tubes get smaller (2/3)
the _________ ____________ gets ________
Changes from ________________ __________ __________ to _______ _________ _________and then to _________ _________ ________ in the ________ _____________
Mucus-producing cells and cilia become _____ in bronchioles
bronchi
mucosal epithelium
thinner
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
simple columnar epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
terminal bronchioles
sparse
-
Main ________ have same tissue composition as trachea , but as conducting tubes get smaller (3/3)
the amount of _______ ________ ___________relative to _________ as passageways get ________
bronchi
smooth muscle increases
cartilage
smaller
-
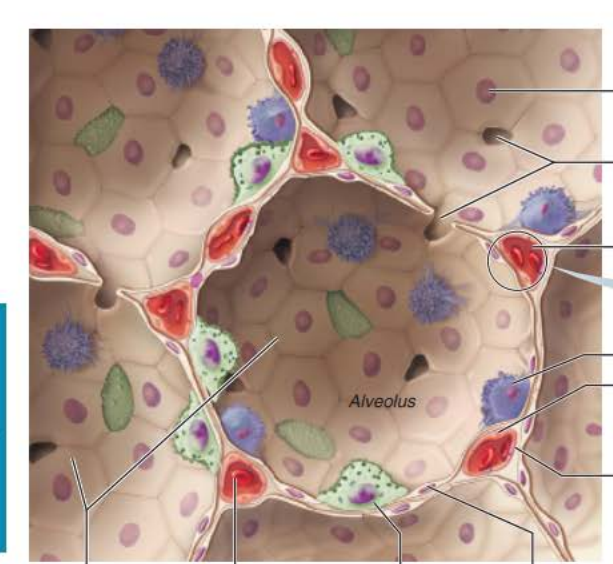
_______
Thin-walled air sacs extending from respiratory bronchioles
Surrounded by fine ______ _______
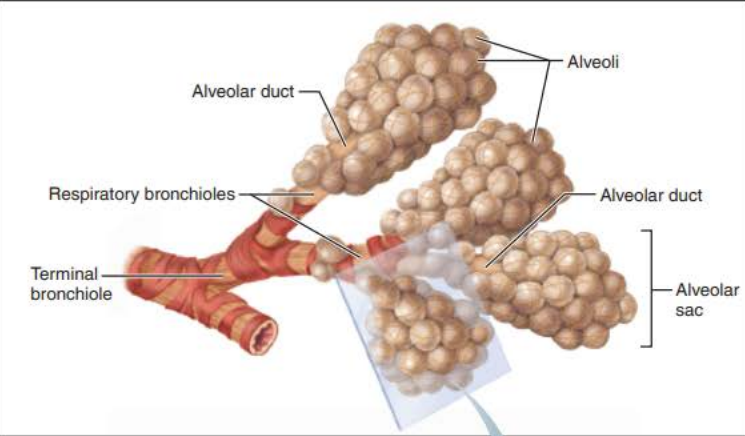
Alveoli
elastic fibers
-
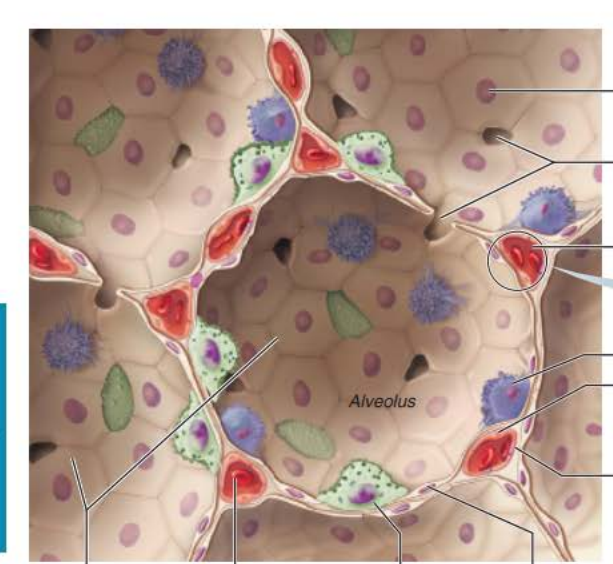
Alveoli
Respiratory Membrane component
Type 1 alveolar cells
_________ __________ cells compose the ______ of the alveoli
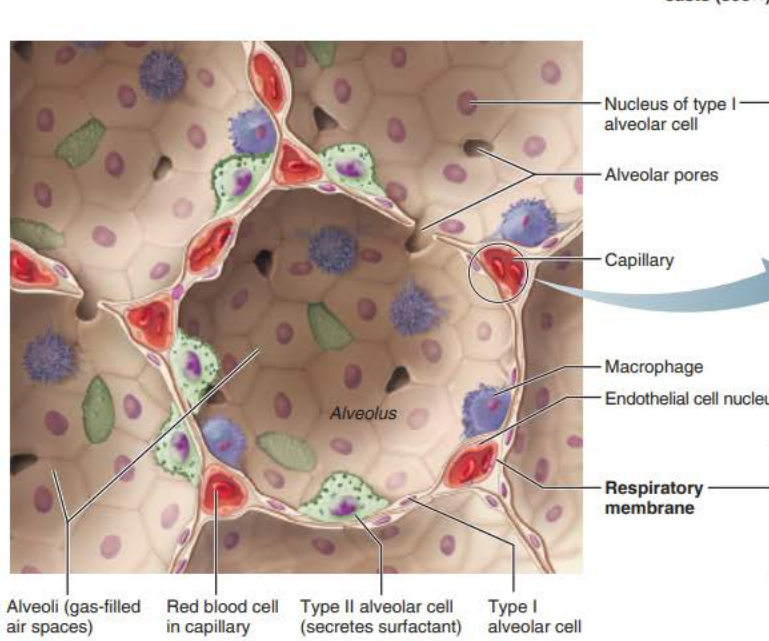
squamous epithelial
walls
-
Alveoli
__________ _______
Connects adjacent alveoli to allow ___ _______throughout the lung to be __________
Provides _________ ______ to any _________ alveoli
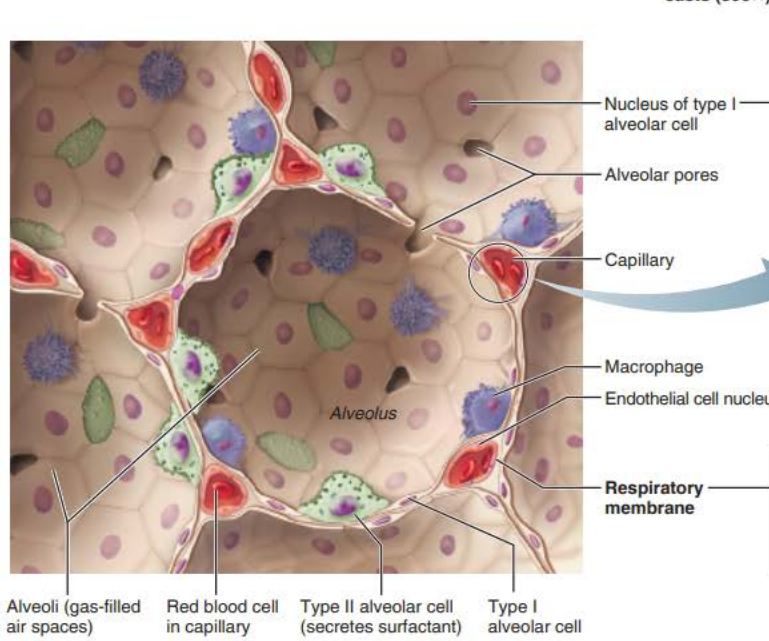
alveolar pores
air pressure
equalized
alternate routes
collapsed
-
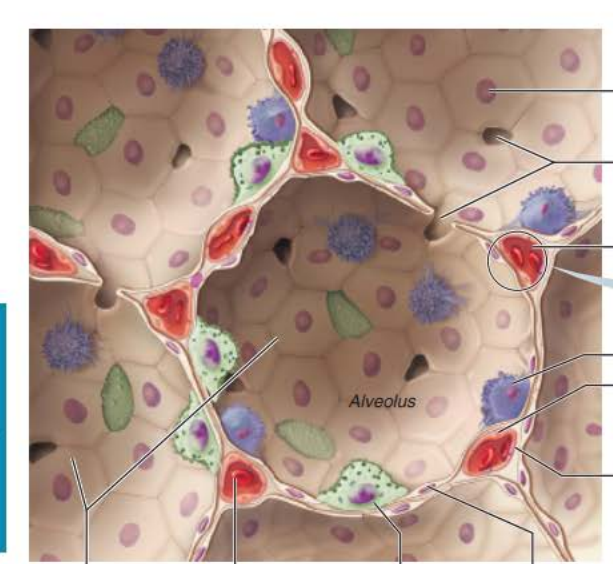
Alveoli
Type 2 alveolar cells
__________ _______ cells scattered amongst type 1 cells
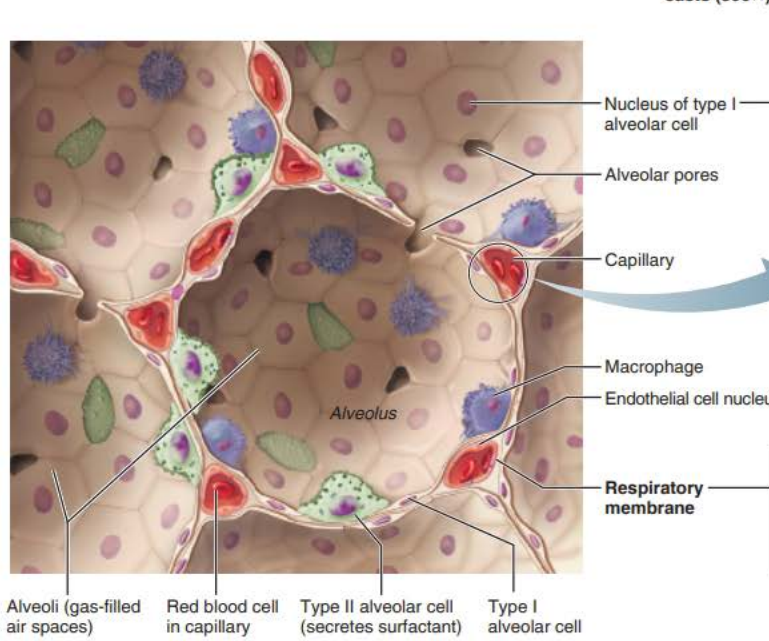
cuboidal epithelial
-
Alveoli
Respiratory Membrane component
External surfaces
Cobweb of _________ _______________
pulmonary capillaries
-
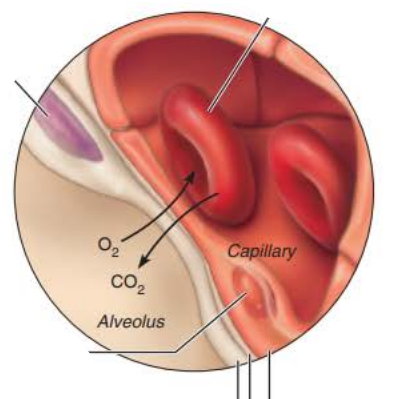
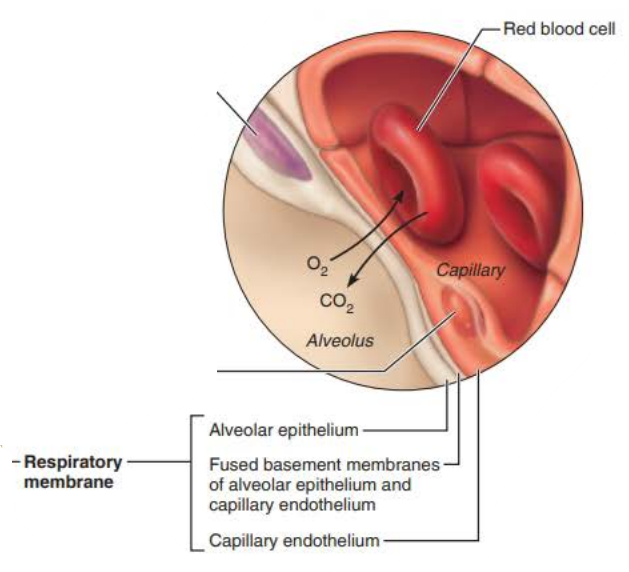
Alveoli
the ______________ ____________ is composed of the ______, _______ _______, and _________ __________
0.5-µm-thick ______ ___ _______
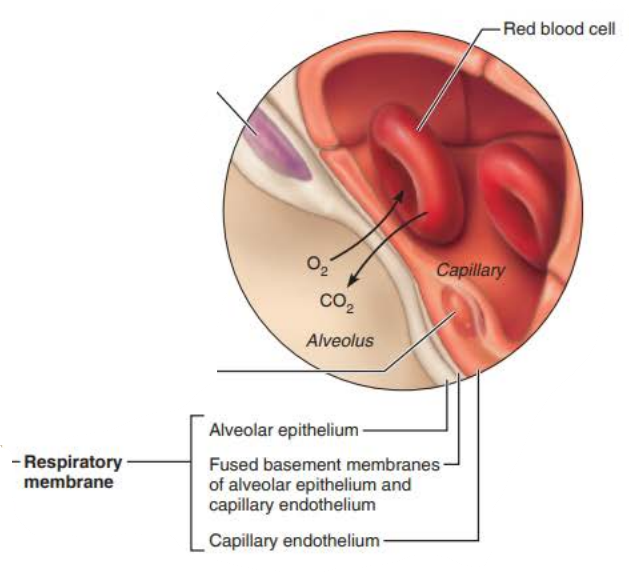
respiratory membrane
capillaries
alveolar walls
basement membrane
blood air barrier
-
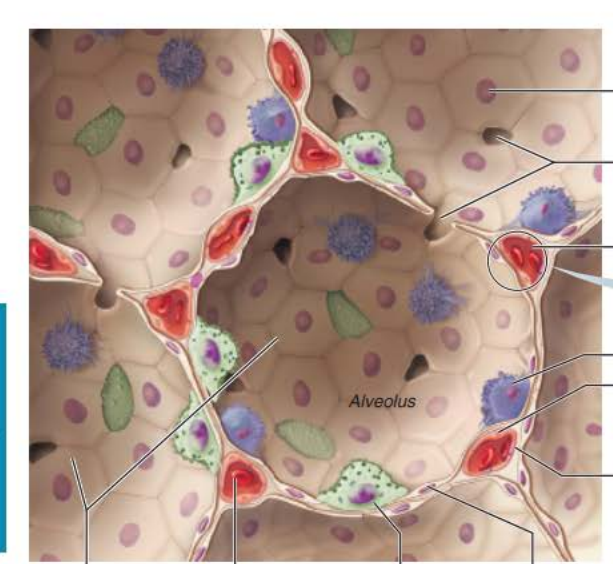
Alveoli
___________ ______________
Roam interior alveolar surfaces consuming bacteria, dust and other debris
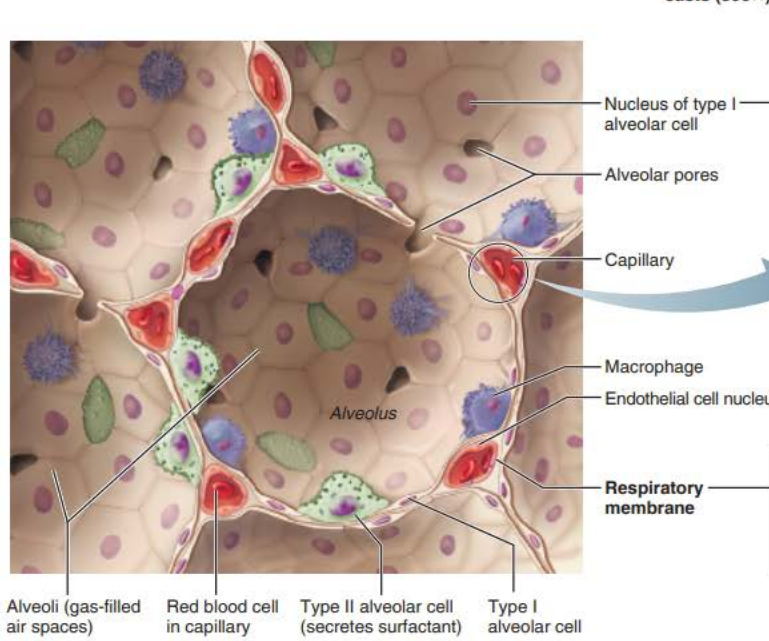
alveolar macrophages
-
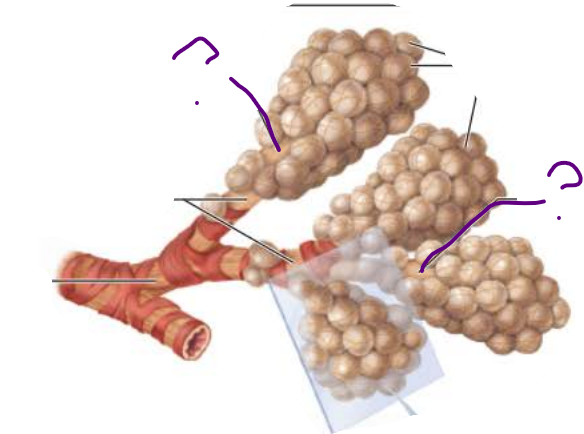
Alveoli
________ ________
Continues from _________ _____________
Contains diffusely arranged rings of smooth muscle cells
__________ ________ fibers
Outpocketing Alveoli
alveolar ducts
respiratory bronchioles
connective tissue
-
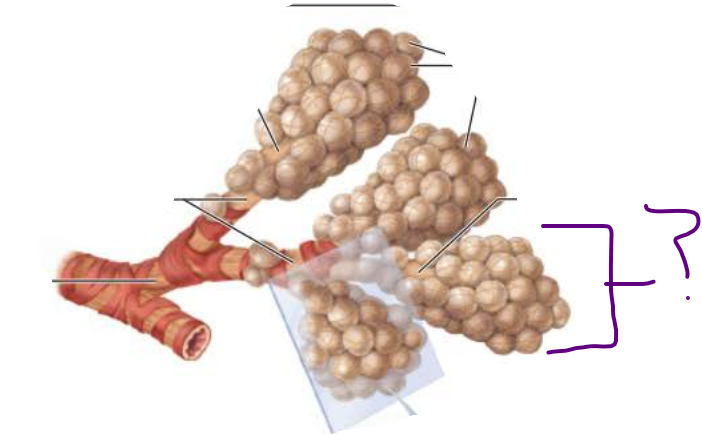
Alveoli
__________ ____
Continues from alveolar ducts
alveolar sacs
-
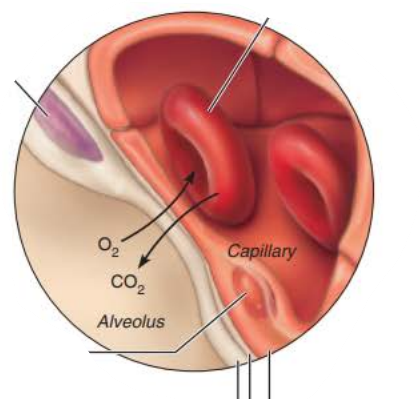
Alveoli
the ____________ ___________ site of gas exchange through the process of _______ __________
___ passes from _______ into _______
____ leaves ______ to enter gas filled _______
respiratory membrane
simple diffusion
O2
alveoli
blood
CO2
blood
alveoli
-
Alveoli
_____ _ ________ ____
Secretes __________ _______ for innate immunity and secretes __________ a fluid containing a detergent-like substance that _____ _______ _________ ________
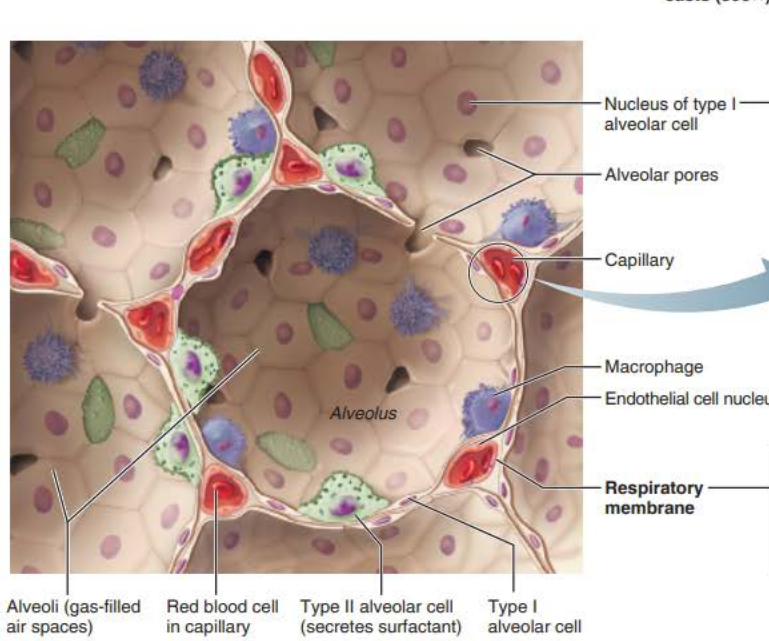
type 2 alveolar cells
antimicrobial proteins
surfactant
coats gas exposed alveolar surfaces
-
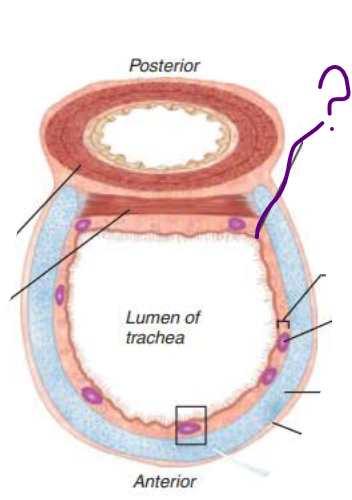
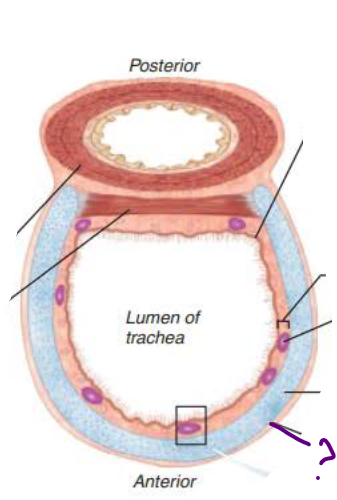
Trachea
the ________ is composed of __________ _______ ___________
Rests on lamina propria
Elastic fibers
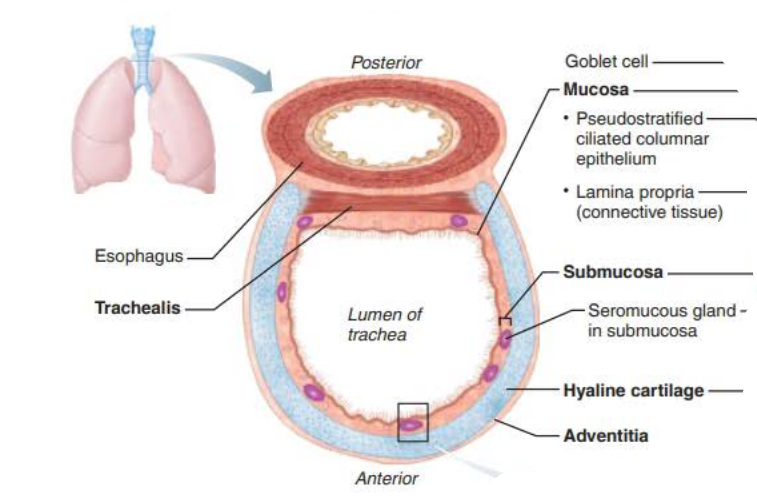
mucosa
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
-
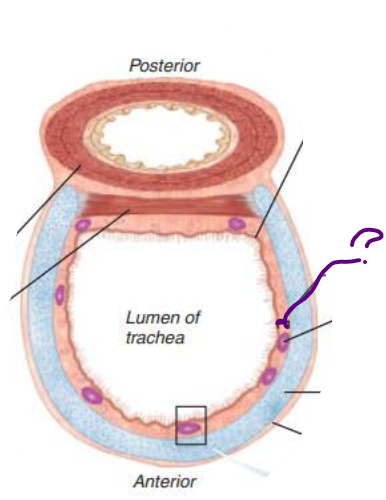
Trachea
the ___________ is deep to the _______
Connective tissue
Seromucous glands
Supported by 16-20 C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
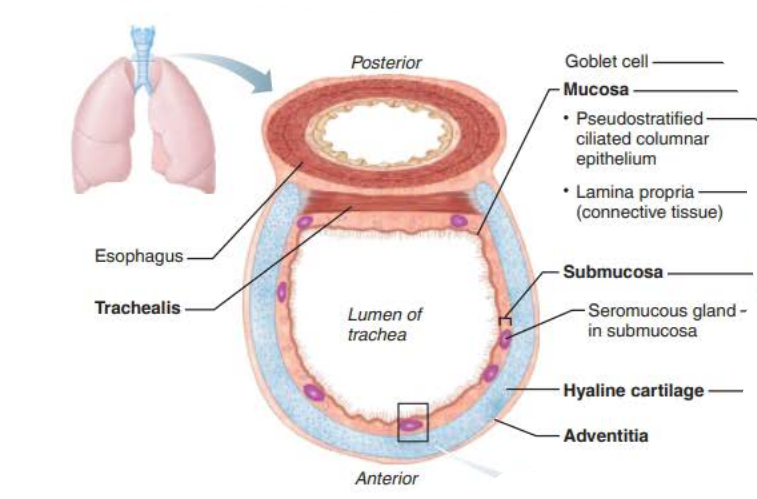
submucosa
mucosa
-
Trachea
___________
Encases ________ cartilage
_______ _________ ______ of _________ tissue
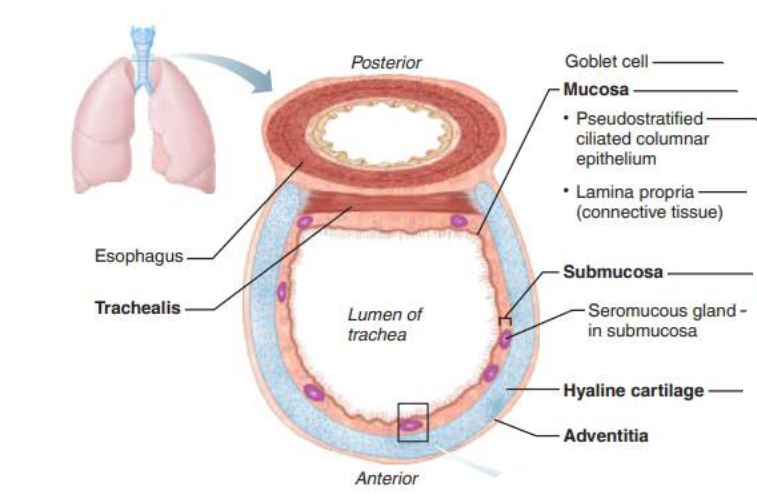
adventitia
hyaline
outer protective layer
connective
-
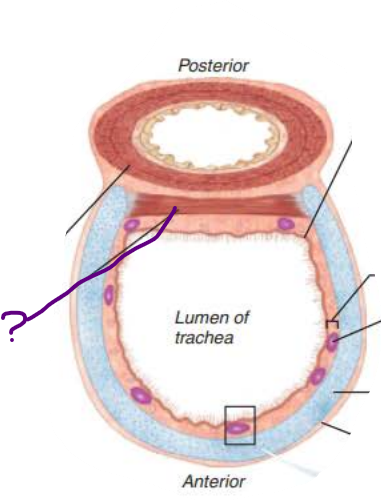
Trachea
__________
smooth muscle fibers
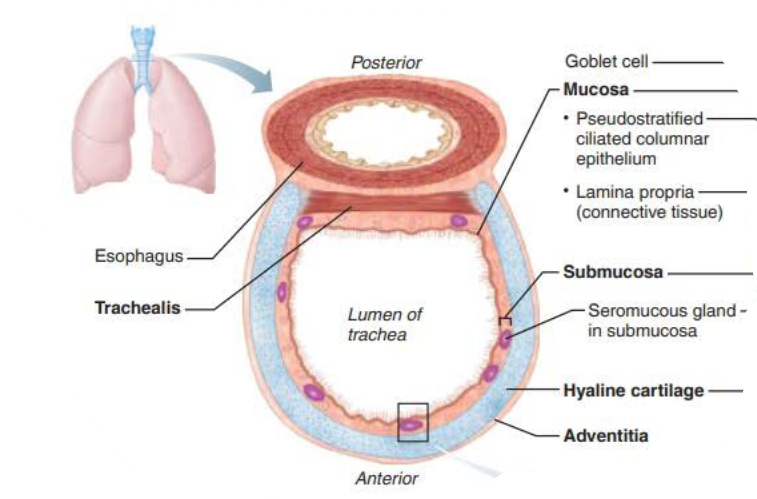
trachealis
-
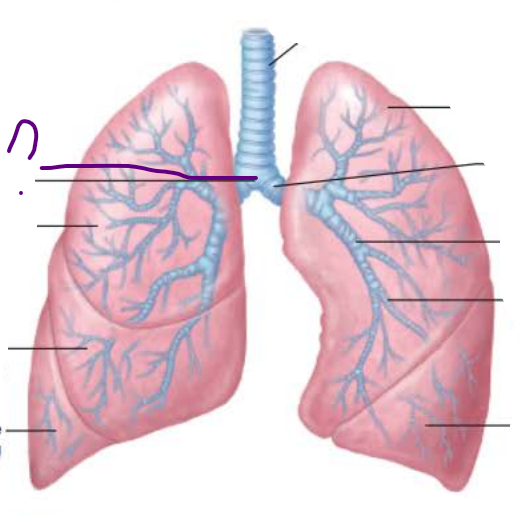
Trachea
_________
_____ tracheal ________
Branches into two ______ ________
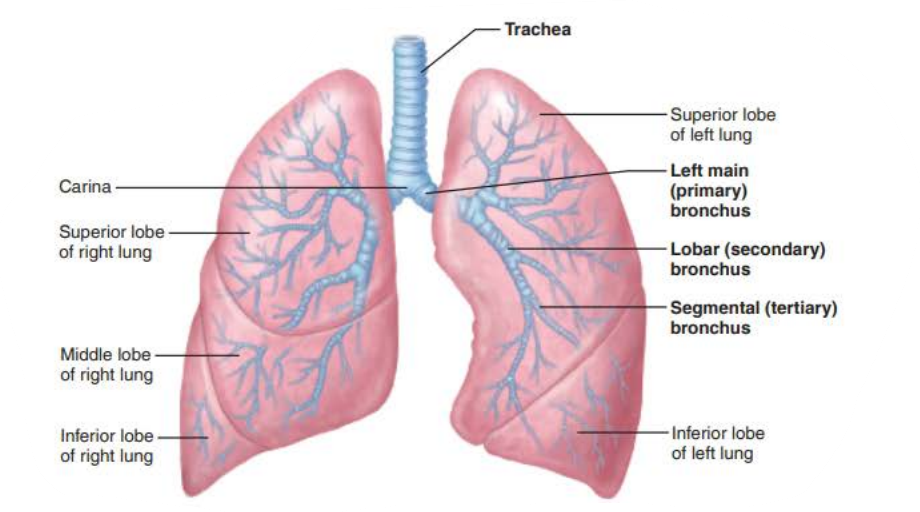
carina
last
cartilage
main bronchi
-
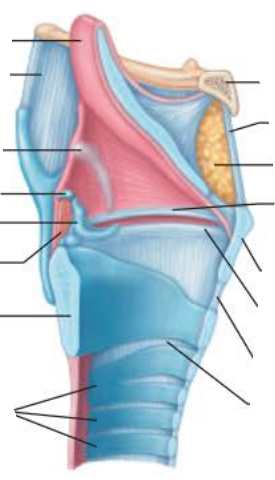
Larynx
Function
Provides an ____ _______
Acts as a __________ _____________ to route __ and ______ into the proper channels
______ production
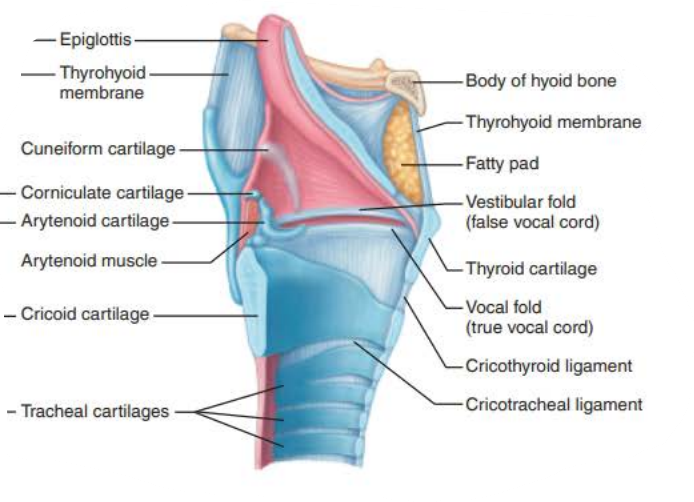
open airway
switching mechanism
route air
food
voice

