-
Central Nervous System (CNS)
1. consists of brain and spinal cord
2. process information
3. reflexes processed in spinal cord
4. Spinal cord conducts info up and down through the cord.
-
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1. Conducts signals
2. Cranial Nerves (12 Pairs)
3. Spinal Nerves (31 pairs) in intervertebral foramen.
-
Somatic Nervous System
1. voluntary
-
Autonomic Nervous System
1. involuntary
a.) Sympathetic - exercise
b.) Parasympathetic - rest
-
Sensory neurons
conduct info towards CNS
-
Motor neurons
conduct info AWAY from CNS
-
Neuroglia
support nervous system
-
Neuroglia CNS
1. Ependymal cells- ciliated cells line the ventricles of brain and move CSF
2. Astrocytes - form blood-brain barrier
3. Microglia - phagocytes, devour foreign material in brain, dead cells injured cells.
4. Oligodendrocytes - cell web cover
-
Neuroglia PNS
1. Satellite Cells - provide physical support, stabilizing.
2. Schwann Cells - insulate nerve cell process, primarily axons, insulation is called myelin sheath. Insulation is discontinous, 10x
-
Nerve
neuron or nerve cell bundle
-
Tract
group of nerve cell processes in CNS
1. Spinal Cord
a.) Ascending Tracts (sensory)
b.) Descending Tracts (motor)
2. Brain
a.) Commissural Tracts - l/r hemispheres
b.) Projection Tracts - connect cerebrum w/ inferior parts of brain + primative parts of the brain.
c.) Association Tracts - connect different lobes of the brain
-
Nuclei vs Ganglia
These functional units are present in both central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The main difference between ganglia and nuclei is that ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies in the PNS whereas nuclei are clusters of nerve cell bodies in the CNS.
-
Plexus
network of nerves or vessels in body
-
Funiculus
a bundle of nerve fibers enclosed in a sheath of connective tissue, or forming one of the main tracts of white matter in the spinal cord.
-
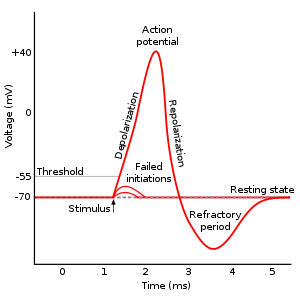
Action Potentials
flow of sodium ions
-
Action Potential
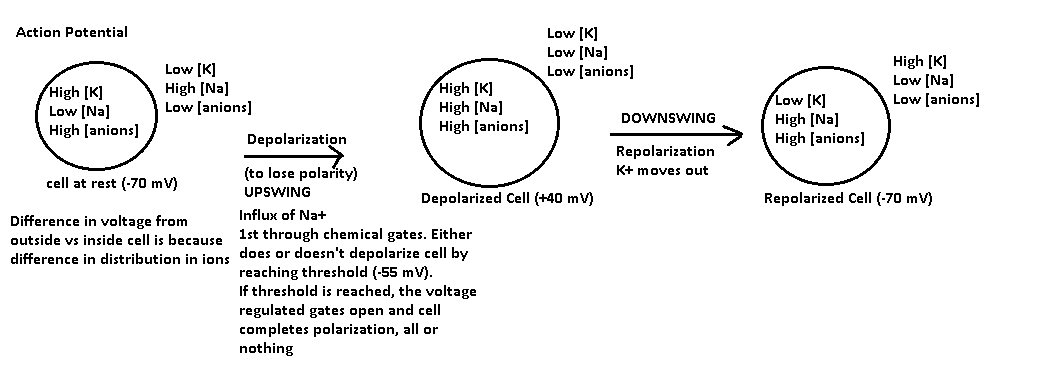
-
Energy Potential AP
1. Distribution of ions
2. Voltage differential (at equilibrium differential = 0).
These forces drive action potential.
Between each action potential the cell recovers.
-
Absolute Refactory
1. the cell is depolarizing, Na moving into the cell. It is impossible to begin another action potential.
-
Relative Refactory
1. Cell is repolarizing, it is possible to begin another action potential if there is some extracellular Na and stronger than usual stimulus.
2. Na gates are closed. K gates open.
-
Cable Properties
diffusion of Na+
-
Saltatory Conduction
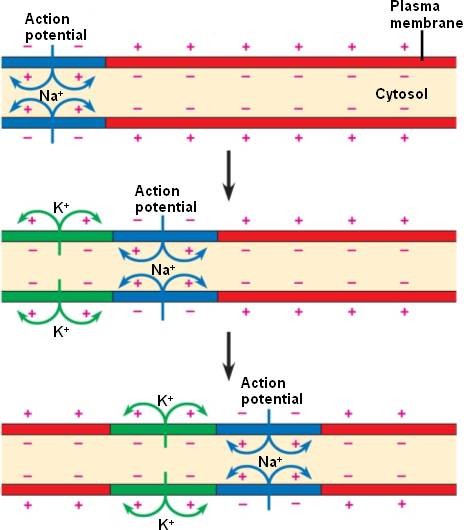
1. AP occurs at the nodes, jumps node to node
2. Each AP stimulates the next AP.
-
Spatial Summation
1. simultaneously +5 from different neurons.
(can combine temporal and spatial summation)
-
Temporal Summation
1. summation overtime from one neuron source
-
Synaptic Potential
1. signal travel through axons @ 100m/s
2. Synapse = junction, Synaptic cleft = physical space
-
Synapse AP
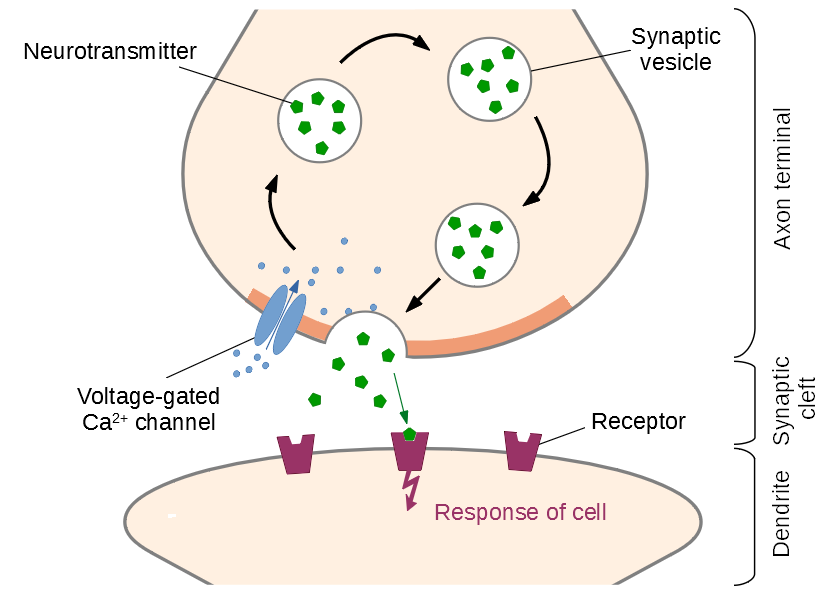
1. AP reduces axon terminus.
2. Influx of Ca
3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane.
4. Exocytotic release of acetylcholine
5. Acetylcholine fills the synapse.
6. Ach binds the receptors, on post synaptic membrane.
7. This binding opens chemical gates.
8. Influx of Na into 2nd cell.
9. If downstream reaches threshold, the voltage regulated gates open, and the signal is conducted to the 2nd cell.
10. As fast as Ach binds the receptors, achase breaks it down.
-
Myasthenia Gravis
1. People see receptors for Ach on skeletal myo as non-self.
2. Produce anti-bodies that bind receptors, paralysis results.
Ach = most common NTS.
-
Order of Brain Regions
RMP becomes:
My Mz Ms D T
1. <---- Complexity
-
Matter in CNS
1. Cerebral Cortex (gray matter), nerve cell bodies (nuclei) processing centers.
2. Cerebral Medulla (white matter), nerve cells processes (tracts)
-
Brain Lobes
1. Frontal - movement, complex processes, decision making
2. Parietal - sensory, interpreting speech.
3. Temporal- hearing
4. Occipital - vision
5. Insula - memory, helping other lobes work together.
-
Functional Areas of Cerebral Cortex
1. Primary Motor Area: in precentral gyrus, relatively small, simple movements
2. Pre Motor Area: anterior to primary motor area, much larger, responsible for complex movements. (Any movement requires muscles to work in synchronized fashion).
3. Primary Sensory Area: Post central gyrus, responsible for somatesthetic proprioception (temp, texture, position)
-
Special Sensory Areas
1. Visual area
2. Auditory Area
3. Olfactory Area
4. Taste Area
-
Association Areas
Association areas process what is actually sensed.
1. Frontal Association Area - consciousness, awareness, sense of self, personality, logic, raising, judgement, appropriate behavior for ones environment, right vs wrong.
-
Basal Nuclei
groups of nerve bodies in the cerebral medulla, inhibit movement. NTS = dopamine
-
Dicencephalon
Limbic system - love/hate/emotions, fornix
1. Pineal 2 hormones
a.) Serotonin - stimulated by sunlight, levels are higher in daytime that at night + summer, happiness.
b.) Melatonin - inhibited by sun, levels higher at night, and winter, associated with sleep and depression.
-
Hypothalamus
Mamillary bodies - small, licking, sucking
-
Pituitary Gland
Infundibulum-stalk that connect the pit gland to the hypothalamus.
-
Hypothalamus-Hypophyseal Axis
1. Hypothalamus is the master gland of the endocrine system.
2. Pit gland is the 2nd in command.
3. Virtually all endocrine glands are controlled by the hypothalamus and pit gland
-
Hypothalmus-hypophyseal flow
Hypothalamus -> Hormone1 -> Anterior Pit Gland -> Hormone2 -> End Gland -> Hormone3 -> physiological change
1. inc metabolic rate, inc heat production, inc bgl
-
Anterior Pituitary
(Adenohypophysis)
-
Posterior Pituitary
Neurohypophysis
1. Neurosecretory Cells - nuclei produce hormones.
2. Hormones travel through hollow axons to be stored in, and released from the post pit.
-
Portal System
vascular system
1. Ant pit makes hormones
2. Post pit does NOT make hormones
-
Hypothalamo-hypopseal portal system
1. Hypothalamus master gland
2. Pituitary gland 2nd in command
3. Hypothalamus is part of limbic system (love/hate/ emotions)
4. Both control Water, salt balance, thirst, hunger, cycles of sleeping/waking, and body temp.
-
Mesencephalon
1. Contains: corpora quadrigemina Cerebral Pedicles,
2. Superior colliculi - visual reflex center
3. Inferior colliculi - auditory reflex center
4. Cerebral peduncles - projection tracts
5. Cerebral aqueduct - connects 3rd ventricle to 4th ventricle
-
Metencephalon
Contains: cerebellum, pons + 4th ventricle
1. Cerebellum - balance, posture, equilibrium
2. Pons - balance, posture, equilibrium, eye movement, taste, two respiratory centers (inhale vs exhale)
-
Myencephalon
Contains: Medulla Oblongata(brain stem)
1. Contains 1 respiratory center
2. Cough center
3. Decussation (crossing) of the pyramids
a.) Primary motor sensory = pyramidal tracts l/r cross in the medulla oblongata
b.) Pre motor area = extrapyramidal tracts l/r cross in the medualla oblongata
4. 2 Cardiac Centers
5. Vasomotor Center, introduces hemodynamics, stimulates them causing vasoconstriction.
-
Ventricles (4)
1. Pathway of CSF: Lateral Ventricles -> Interventricular foramen (IVF) -> 3rd Ventricle -> Cerebral Aqueduct -> 4th Ventricle -> Apertures -> subarachnoid space
-
Choroid plexus
Choroid plexus in each ventricle, and epidermal cells, produce CSF
-
Meninges
A. Dura Mater
1. Periosteal Dura - forms sinus (space) 1. superior sagittal sinus in longitudinal fissure
2. Meningeal Dura - transverse sinus in transverse fissure.
-
Arachnoid Mater
deep to the dura mater, 2nd layer
2. arachnoid villi absorb the CSF from the subarachnoid space into the superior sagittal sinus.
3. Transverse sinus, drained by internal jugular veins.
-
Pia Mater
deep to arachnoid mater, 3rd layer
1. space between is called the subarachnoid space (CSF is here)
DAP - dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
-
Lumbar Puncture
1. removes CSF

