Inertial observers (must or must not) have acceleration
Must not
True or False: A person who is doing a uniform circular motion is an inertial observer.
False, changing direction therefore changing velocity which means they have acceleration.
T/F: Speed of light is constant and it is equal to 'c', regardless of who is measuring it.
True
What is the speed of light?
3 × 10^8 m/s
True or False: The order of the events also depends on the observer.
True
What time is the shortest to happen between events?
Proper time
=Distance traveled/speed
True or False: As a consequence of constancy of speed of light, being simultaneous is relative motion.
True
The ______length is the longest length measured by an observer.
proper
True or False, People traveling near the speed of light relative to Earth would measure their lifespans and find them, on the average, longer than the average human lifespan as measured on Earth.
False
You observe a rocket moving away from you. Compared to the passage of time measured by the watch on your wrist, the passage of time on the rocket's clock is
slower
What is the rest energy?
Er=mc^2
If object with mass wants to go the speed of light, it requires...
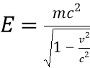
Infinite energy impossible
see formula
Total energy is equal to...
Kinetic energy plus rest energy
Length contraction formula
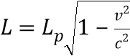
True or False: You cannot measure position and momentum of an object with 100% certainty simultaneously.
TRUE
By increasing the accuracy in measuring position, accuracy in measuring momentum will be.
Reduced
True or False: The effects of uncertainty principles are significant for moving large obiects.
False only very very small objects
Position-momentum principle relation ship
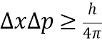
As one increases
must decrease (like delta x or delta p)
What is the uncertainty principle for energy and time?
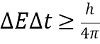
The uncertainty principle for energy and time states that the product of the uncertainty in an energy measurement and the uncertainty in the time interval during which the measurement is made is equal to or greater than a constant value, which is h / (4π) or more, where h is the Planck constant.
Experiments showed that light incident on certain metallic surfaces caused
the emission of electrons from the surfaces.Aka the photoelectric effect.Emitted electrons are photoelectrons
In the photoelectric effect, to get an electron you must...
Overcome the energy that keeps the electron in the metal (binding energy)
In the photoelectric effect, what is the minimum energy required to ejected electron known as?
Work function
Note: Max kinetic energy
If an electron releases more energy than binding energy, it will ejected and difference is the...
Kinetic energy
The electron with the smallest binding energy has...
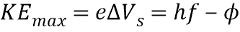
Maximum kinetic energy
Dual nature of light
Particles and waves
Light is made of tiny particles, called photons traveling at the speed of
light
. Energy of each photon is proportional to
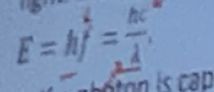
The frequency of light
How can you find the cut off wavelength?

what is frequency
also equal to?

If the frequency is less than the cuttoff frequency...
No photoelectron
is emitted.
If the wavelength is greater than the cut off frequency..
No photoelectron is emitted.
How can you find
the cut off frequency?

Which has more
energy, a photon of: red, yellow, green,
blue light?
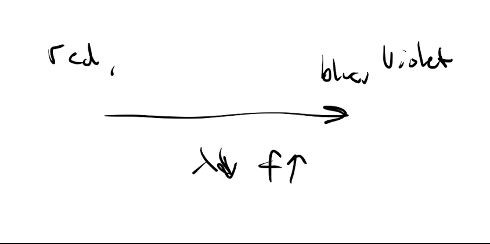
Blue light sinceE=hf and blue has
the highest frequency
If the cutoff frequency for light in the photoelectric effect for metal b is greater than that of metal A, which metal has a greater work function?

Metal B since they are proportional:
A metal surface with a work function of phi= hc/550 m is struck with blue light and electrons are released. If the blue light is replaced by red light of the same(intensity What is the result?
NO ELECTRONS ARE
EMITTED Rearranging, the
cut off wavelength is 550 nm. The wavelength of red light is 700 nm.Since the wavelength
is greater than the cut off wavelength: no photoelectrons emitted.
A metal surface is struck with light of λ= 400 m, releasing a stream of electrons. If the 400 m light is replaced by λ= 370 nm light of the same intensity, what is the result?
Emitted electrons are more energetic since as wavelength decreases frequency increases and E=hf so energy increases.
A metal surface is struck with light of ^ = 400 m, releasing a stream of electrons. If the light intensity is increased (without changing ^), what is the result?
More electrons are emitted in a given time interval.As light intensity increases, the number of photons increases so more electrons have to be emitted.
Spectrum of the emitted light from different atoms are ...
different
True or False: Comparing the line emission and line absorption spectra, one can observe that the same lines missing in the absorption spectrum are present in the emission one
True
Photons do NOT have
Rest mass
How can you find deBroglie's wavelength? (use if momentum is known)
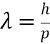
Mass of electron:
9.11 x 10^-31 kg
The speed of proton A is larger than the speed of proton B. Which one has the longer wavelength?
PROTON B
Since proton A
has more momentum (mv) since it has more speed it has a smaller wavelength
because it is inversely proportional.
An electron and a proton have the same speed. Which has the longer wavelength?
Longer wavelength
for electron
Electrons has
less mass than proton
b.
An electron and a proton have the same momentum. Which has the longer wavelength?
Same wavelength
What is the wavelength of the emitted photon if the electron in the hydrogen atom jumps from the fifth state into the second state?
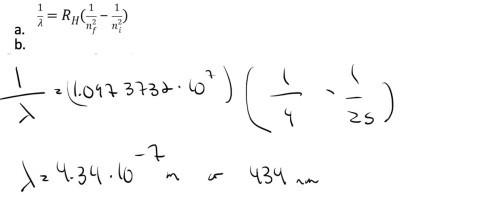
The Balmer series for hydrogen can be observed in the visible part of the spectrum. Which transition leads to the reddest line in the spectrum?
3 -> 2
4 -> 2
5->2
6-> 2
3 -> 2
reddest means lowest energy jump?
. Find radius give orbit for bor model
a.
A0=0.0529 nm memorize
How can you find energy given energy level n.
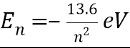
How to convert eV
to joules?
Multiply the eV value by 1.60217662 × 10^-19 J/eV
For balmer series what is n final?
2
For lyman series what is n final
1
For Paschen series what is n final?
3
What series is in the visible spectrum?
Balmer
What is the wavelength of the emitted photon if the electron in the hydrogen atom jumps from the fifth state into the second state??
Suppose there is
an atom that contains exactly five energy levels. How many different transitions
are possible? (Count only one direction!)
10 Since
How much energy is needed to jump from n=1 to n=2?
10.2 eV
Absorbed
Use formula and calculate difference
When the principal quantum number is n = 5, how many different values of I are possible?
A.) 1
B.) 5
C.) 9
D.) 25
C.) 9
Use n-1 and that l
includes 0.
Therefore B.) 5
possible values
OR you can just
look at n
When the principal quantum number is n = 5, how many different values of mi, are possible for the largest value of I?
A.) 1
B.) 5
C.) 9
D.) 25
2*l+1
2(4) + 1=9
OR find each number 4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,4 so 9 possible values
S orbitals are what shape
sphere
P orbital is shaped like a what
dumbbell
Atomic number, the number on the top, is the...
Number of protons
which gives identity to the element
Mass number, the number on the bottom, is the...
number of nucleons
. Isotopes of an element have different number of
neutrons
N denotes
Number of radioactive nuclei
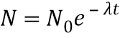
where N is the number
of
Remaining active
nuclei
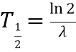
relates
a.
Half life (t ½)
to decay rate
To find how many half live have passed (n)
N=t/T1/2
To find the number
of remaining active nuclei given n and N0
N=N0(1/2)n
Activity of a radioactive substance reduces from 6.12×106 atoms per day into 1.72×10 atoms per day, after seven days. What is the half life for this substance? (practice this question)
Activity is (R)
so find that R=R0e-7λ
True or False: A radioactive atom always decays after two half-lives have elapsed.
False
What fraction of a radioactive sample has decaved after two half-lives have elapsed?
3/4
Suppose the decay constant of radioactive substance A is twice the decay constant of radioactive substance B. If substance B has a half-life of 4 h, what's the half-life of substance A?
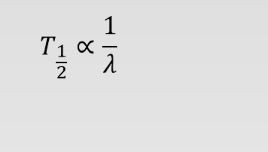
Half live is inversely proportional to decay constant (lambda)
i.