what does the lymphatic system consist of?
- lymph nodes along the vessel network cleanse lymph as it passes through them (contain T & B lymphocytes that clean)
- one way network of lymphatic vessels (which collect 10% of the extracellular fluid the leaked out from cardriovascular capillaries and returns this fluid (called lymph) to venous blood)
What does extracellular fluid conatin of?
- its a fluid found outside of cells
- blood plasma (5% body weight), fluid in blood, sometimes leave capillaries to form ISF
- ISF (interstitial fluid, 15% body weight) fluid between cells within the body (except blood cells, that's plasma between), some moves into lymphatic capillaries to form lymph
- lymph (1% body weight), fluid inside lymphatic vessels, returned to blood plasma
What is ICF
- intracellular fluid (found within cells, 40% of body weight)
What is the lymphatic circulation summary?
lymphatic capillaries -> lymphatic collecting vessels (with valves) -> lymphatic ducts -> subclavian veins
What is the lymphatic circulation summary? (visual)
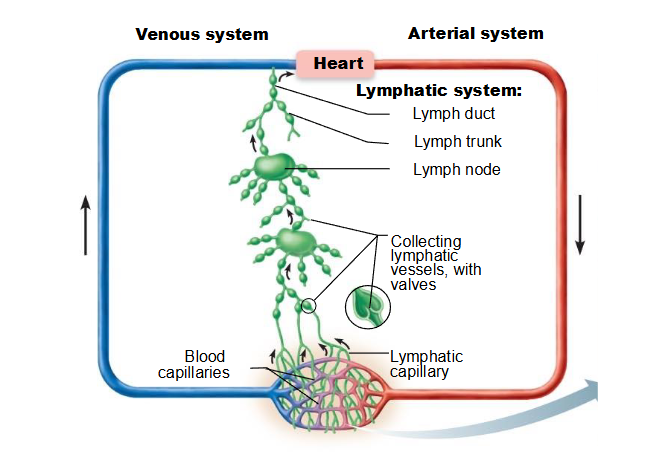
What is step one in lymphatic circulation?
- lymph enters lymphatic capillaries (closed ended vessels that project into cardiovascular capillary beds)
- lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine also play a role in fat absorption
What is step two in lymphatic circulation?
- lymphatic capillaries connect to larger lymphatic collecting vessels that have one-way valves
- lymph nodes along collecting vessels filter lymph for bacteria & debris
- transports lymph fluid away from tissues towards either:
right lymphatic duct or thoracic duct
What is the right lymphatic duct?
- lymph from right side of the head, chest and arm
- drains into right subclavian vein to re-enter blood circulation
What is the thoracic duct?
- lymph from below the ribs and the entire left side of body
- collecting vessels from below the ribs converge to an enlarged lymph vessel (cisterna chyli, most inferior portion of thoracic duct)
- thoracic duct drains into the left subclavian vein to re-enter blood circulation
Why does fluid flow through lymphatic? Where does it go?
- fluid flows through lymphatic collecting vessels mostly because of body movements that move fluid towards the heart
- one-way valves in the collecting vessels prevent back flow of blood
What are lymphoid tissues & organs? what do they do?
- contain many lymphocytes and play a key role in the body's immune system
- primary lymphoid organs and tissues (mature lymphocytes leave here and move into the blood to migrate towards secondary)
- secondary lymphoid organs and tissues
What are the primary lymphoid organs and tissues?
- locations where lymphoid stem cells divide and mature (become immunocompetent) which includes:
- red bone marrow: all lymphocyte stem cells arise here, site of B lymphocyte proliferation (mitosis) maturation
- thymus gland (early in dev (fetal stage) lymphocyte stem cells migrate here, site of T lymphocyte proliferation (mitosis) maturation
What are the secondary lymphoid organs and tissues?
- where lymphocytes detect and remove pathogens
- locations where lymphocytes are activated and proliferated further
- includes: lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
What are lymph nodes?
- small masses of lymphoid tissue along the lymphatic collecting vessels
- high concentrations of lymph nodes are located in: cervical (neck), axillary (armpit), inguinal (groin), intestinal, pelvic regions
What is the spleen?
- located in the left side of abdominal cavity, just below diaphragm next to stomach
- filters (cleans) blood by removing pathogens (organisms that can cause disease like bacteria or viruses), old and defective blood, and cellular debris
What is Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)? What does it do?
- traps and removes pathogens at points of entry into the body
- includes tonsils, appendix, and other lymphoid tissues on mucous membranes
Where are some MALTs?
- lingual (1) bumpy nodules on posterior part of tongue
- palatine (2) in oropharynx, these are you tonsils
- pharyngeal (1) in posterior nasopharynx (refered to adenoids when swollen)