What is the integumentary system?
The skin and its accessory structures.
What are its general functions?
- protects the body from surrounding environment
- maintains body temp.
- converts vit. D to its active form
What are the 2 parts of the skin?
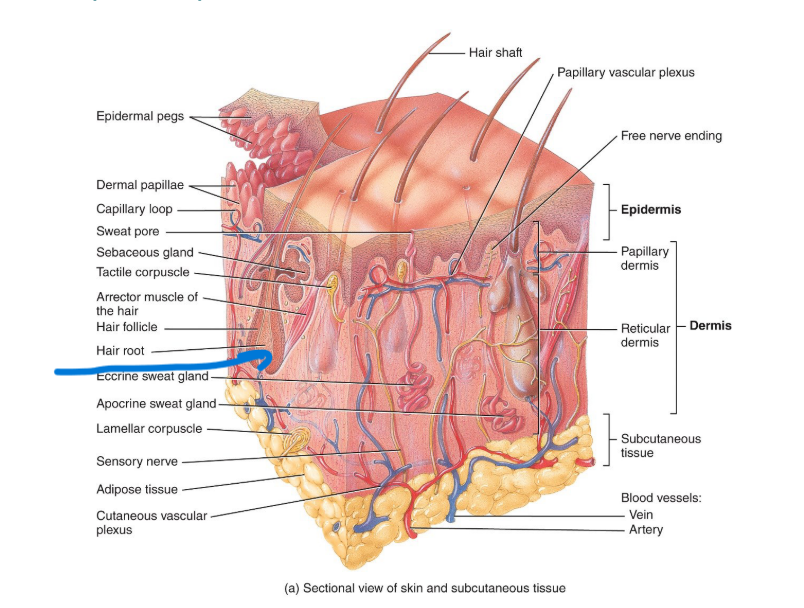
Epidermis - superficial portion
Dermis - deeper layer
What is the epidermis made of?
epithelium
What is the dermis made of?
connective tissue.
Where is the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) located?
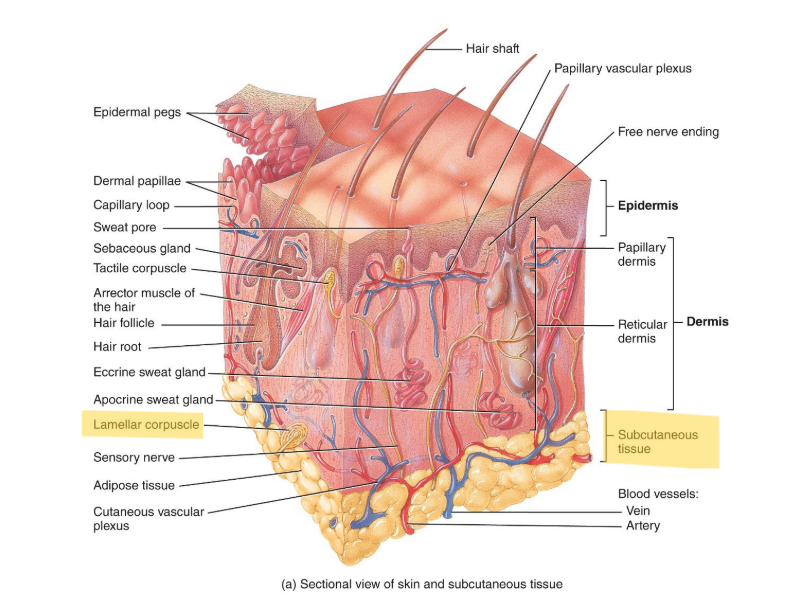
Deep in the dermis.
What is the subcutaneous layer made of?
areolar and adipose tissue
What are the functions of the subcutaneous layer?
Serves as a fat storage area, where blood vessels pass, provides shape and insulation.
Where are the pressure nerve endings (pacinian corpuscles or lamellar corpuscles) located?
subcutaneous layer
What are the 4 cells the epidermis is made of?
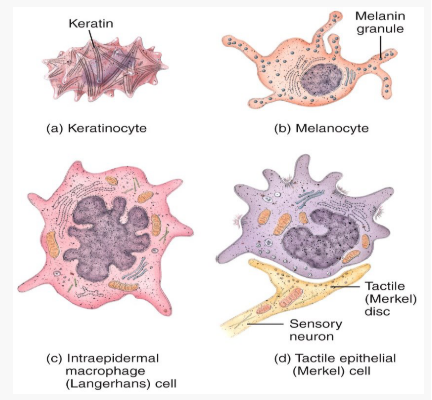
keratinocytes, melanocytes, langerhans cells, and merkel cells
Function of keratin?
Protects skin and underlying tissue from heat, microbes and chemicals.
What do keratinocytes produce?
Keratin and lamellar granules.
What -cyte produces melanin?
melanocyte
Function of melanin?
Contributes to skin colour and absorbs UV light.
What do langherans do?
They participate in immune responses.
Function of merkel cells?
Help in the sensation of touch.
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis.
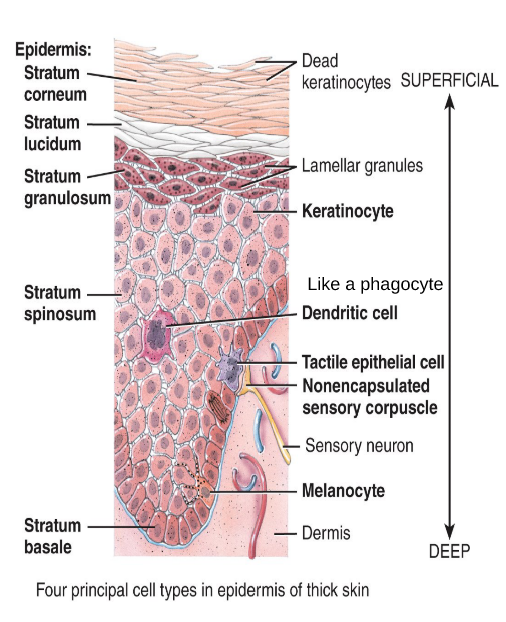
1. Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granolusom 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum
Where is the stratum basale located?
The deepest layer of the epidermis.
What is the stratum basale made of?
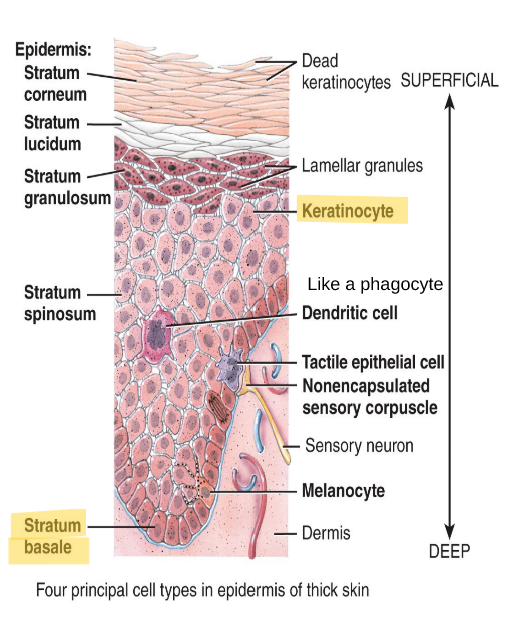
A single row of cuboidal or columnar keratinocytes
Which layer of the epidermis is capable of undergoing mitosis?
The stratum basale
How many layers does the stratum spinosum have?
8-10
What is the function of the stratum spinosum?
Provides strength and flexibility to the skin.
The stratum granulosum has ___ rows of ___ undergoing ___.
The stratum granulosum 3-5 rows of keratinocytes undergoing apoptosis.
Which layer acts as a gateway betwen metabolically active strata and dead cells?
The stratum granulosum
Which layer are keratins being manufactured in?
The stratum granulosum
Where is stratum lucidum located?
Only in the palms, fingers and soles.
What makes the stratum corneum water-repellant?
The lamellar granules
What layer are calluses formed and how?
In the stratum corneum, when it is exposed to constant friction.
What is the dermis made of?
CT with collagen and elastic fibers/
What are the 2 regions of the dermis?
The papillary and the reticular.
The papillary layer is the most ___.
superficial layer
The papillary layer contains the dermal papillae, which houses:
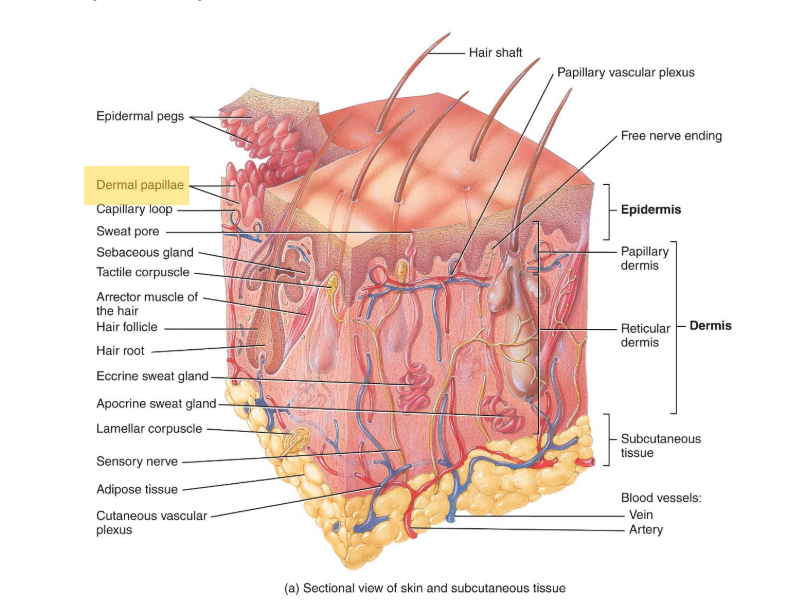
blood vesels, corpuscles of touch and free nerve endings for temp., pain etc.
What are the corpuscles of touch (meissner's corpuscle)?
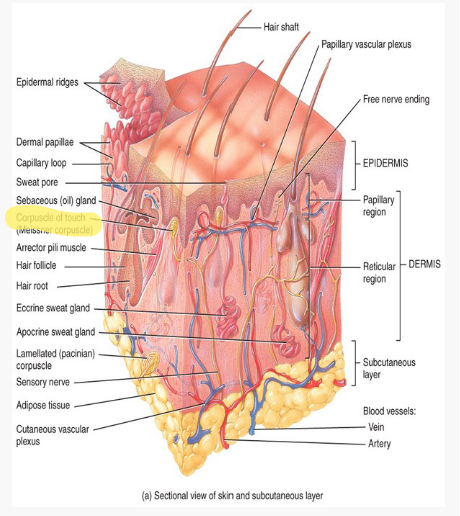
They are nerves that are responsible for detecting touch and vibration on skin.
How are our finger/footprints formed?
The projections of the dermal papillae into the epidermis making epidermal ridges form our finger/footprints.
What gives your skin strength and elasticity?
Collagen and elastic fibers.
Where is the reticular region located?
The deeper part of the dermis; below the papillary.
What is the reticular region made of?
Dense, irregular CT which has collagen and some elastic fibers. You want it to stretch in multiple directions.
What do collagen and elastic fibers provide?
Strength, extensibility and elasticity
Spaces between collagen and elastic fibers may contain:
adipose cells, hair follices and sudoriferous (sweat) glands
What 3 pigments help determine skin colour?
Melanin, carotene (vit. A) and hemoglobin
What tones does hemoglobin contribute to?
Pink
Hair, glands and nails are:
accessory skin structures
How are new hairs developed?
From cell division of the matrix in the bulb
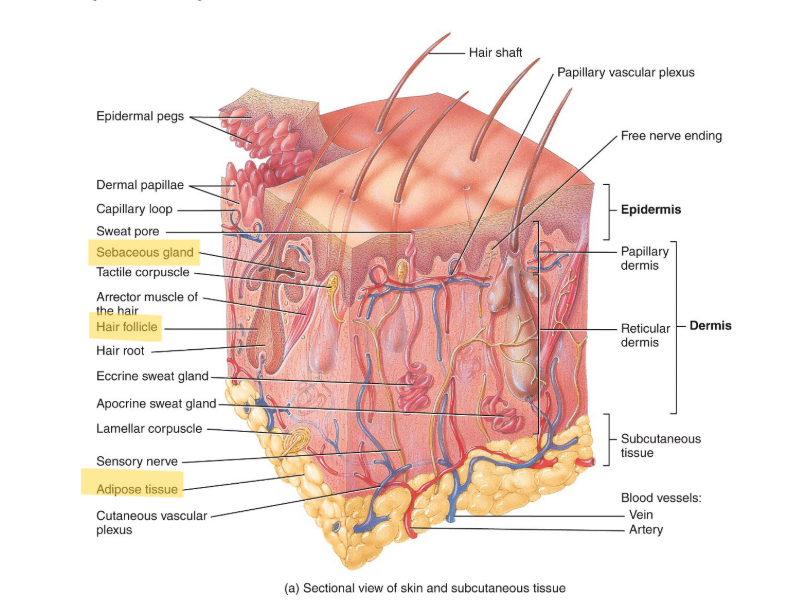
Oil in hair comes from:
the sebaceous glands.
What is the purpose of hair?
Protection, decrease in heat loss, sensing light touch.
Hormones influence the growth and loss of hair. True or false.
True
What are the 3 types of skin glands?
Sebaceous (oil) glands, sudoriferous (sweat) glands and ceruminous (wax) glands
What does sebum do?
Moistens hairs, waterproofs and softens skin and where bacteria can grow.
Sudoriferous glands are divided into:
eccrine and apocrine types.
Where are apocrine sweat glands distributed?
pubis, areolae; their ducts open into hair follicles.
When are apocrine sweat glands stimulated?
During emotional stress and/or sexual excitement.
Regulates body temp. through evaporation. Eccrine or apocrine?
Eccrine
Ceruminous glands produce___.
cerumen
What are nails?
They are hard, keratinized epidermal cells.
What are nails made of?
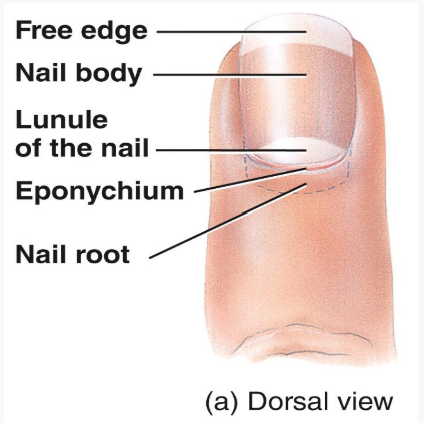
Free edge, nail body, lunula, eponychium, nail root and matrix.
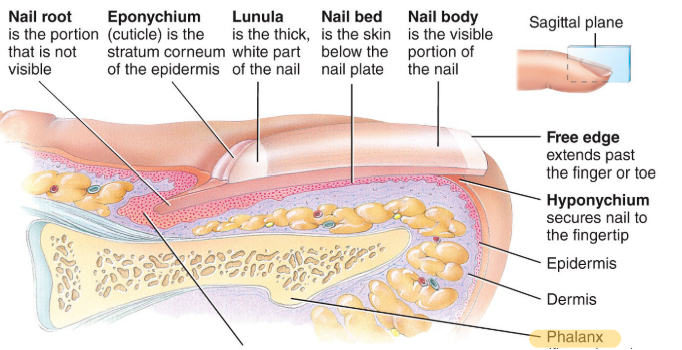
Label this unnamed area and what is it's purpose?
The nail matrix: where mitosis occurs and produce new nail cells.
What is the function of nails?
- Help in grasping and manipulating small objects.
- Provides protection against trauma to the ends of the digits.
What does thin skin NOT cover?
palms, palmar, surfaces of the digits and the soles
Which type of skin has more sensory receptors?
Thick skin
What does thick skin lack?
Lacks hair follicles, arrector pili muscles, and sebaceous
glands, and has more sweat glands than thin skin.
What are the functions of skin?
- thermoregulation
- protection
-vit. D synthesis
- cutaneous sensation
Cutaneous sensation include:
- touch
- pressure
- vibration
- itch
- temp.
- pain
What does skin excrete?
Salt and water
Skin absorbs by ___.
allowing the passge of materials from the outside into body cells (transdermal absorption).
What is the most active form of vit. D?
calcitriol