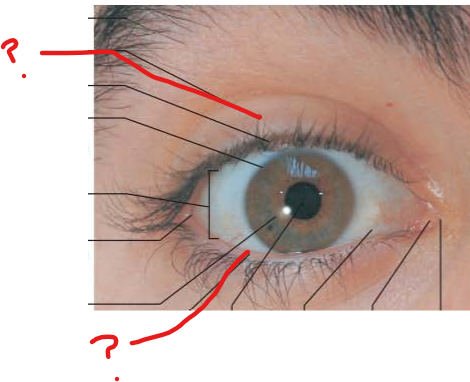
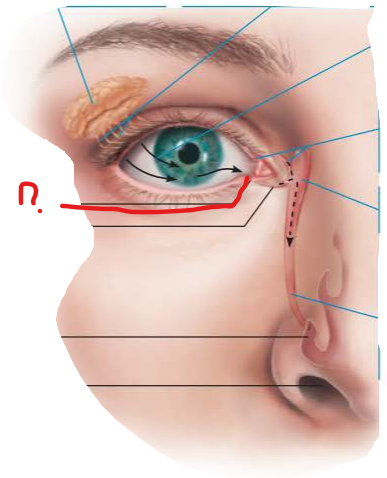
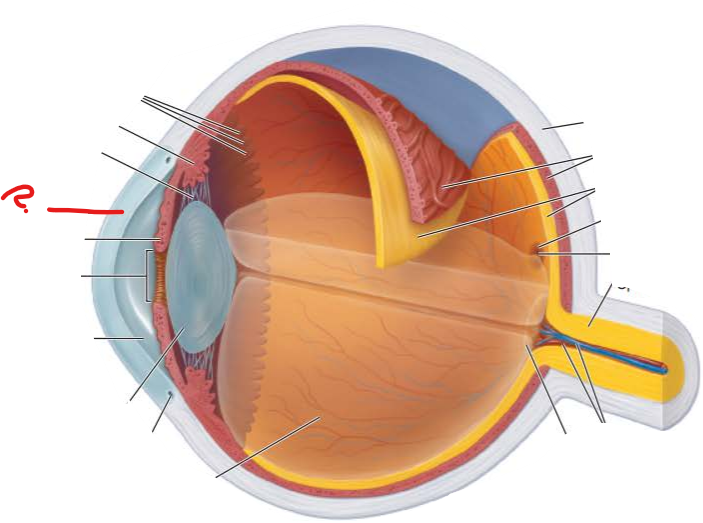
what is this and name a function
hair follicle receptors on eyelashes for reflexive blinking
eyelid muscles activated reflexively causing blinking every 3-7 seconds
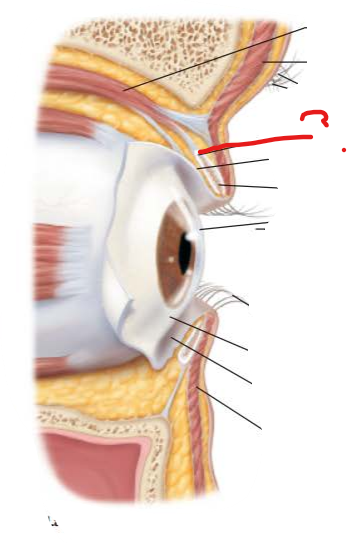
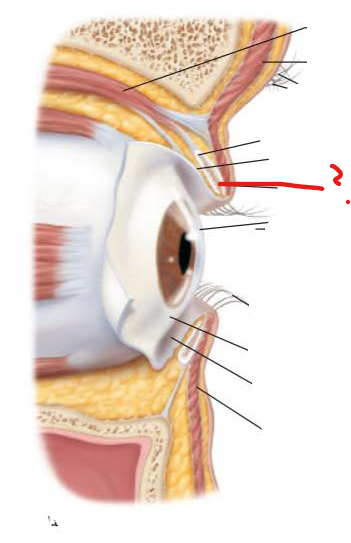
what is this and what is its function?
tarsal plates
supports internal structure of eyelids
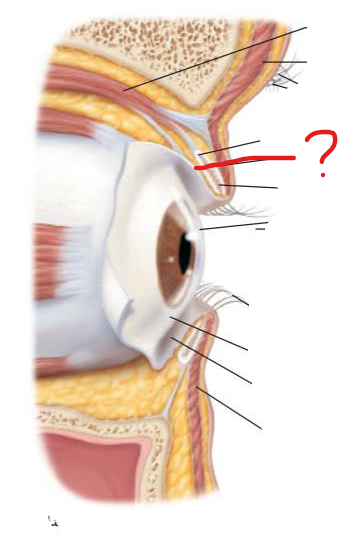
what are these? what do they secrete?
tarsal glands
oily secretion that lubricates eyelids
what 2 functions does blinking serve?
Protects the eye from foreign substances, oil, andmucus
saline solution spread across eyeball surface keeping it moist
what is the structure and function of conjunctiva?
transparent mucous membrane
produces lubricating mucous that prevents eyes from drying out
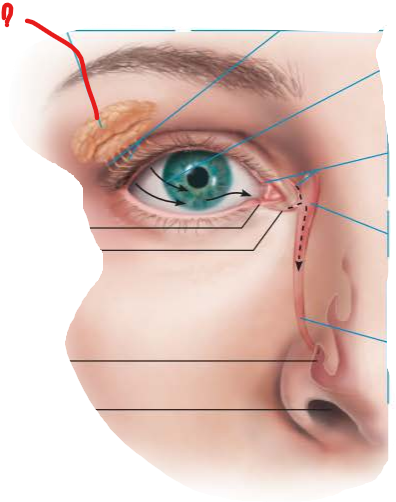
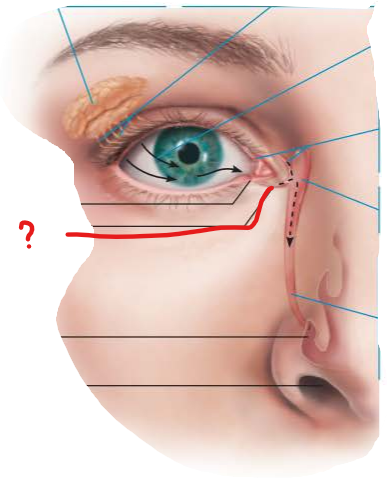
describe the flow of lacrimal secretion
secreted by lacrimal gland
reaches lacrimal puncta
enters lacrimal canaliculi
tears drained into lacrimal sac
nasolacrimal duct empties into nasal cavity at inferior nasal meatus
what is this?
palpebral conjunctiva
what is this and what does it contain?
bulbar conjunctiva
blood vessels
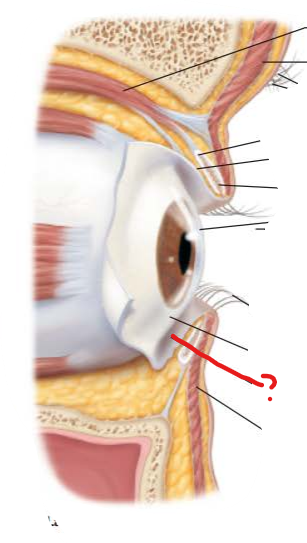
what is this?
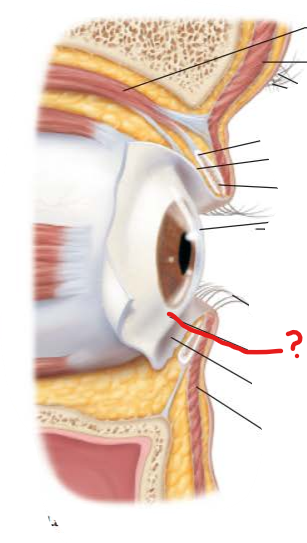
conjunctival sac
what is this and what does it secrete?
lacrimal gland
lacrimal secretion
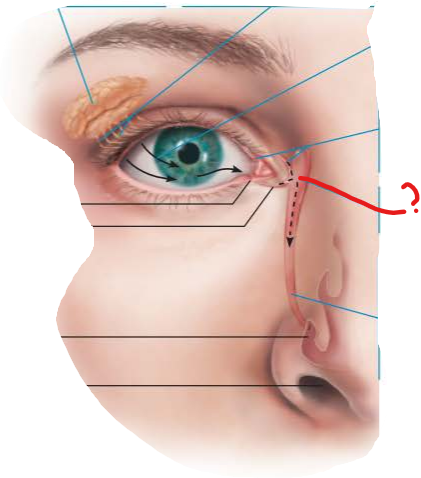
what is this?
lacrimal puncta
tiny openings
name this
lacrimal canaliculus
name this
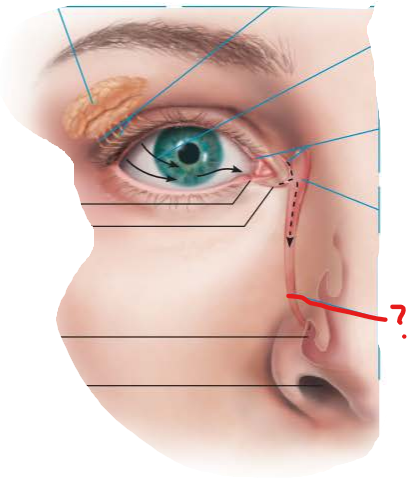
what is drained into here?
lacrimal sac
tears
name this
nasolacrimal duct
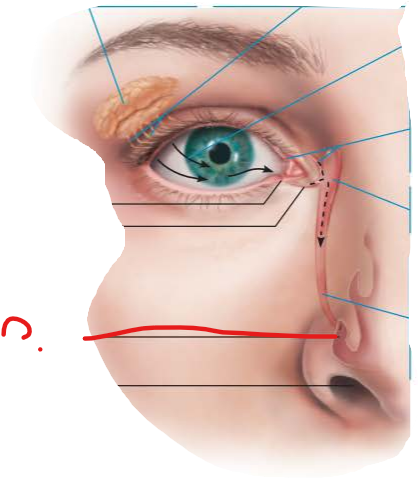
name this
inferior meatus of the nasal cavity
describe the function of lacrimal secretion, what enzyme does it contain?
-dilute saline solution
-contains lysozyme, destroys bacteria
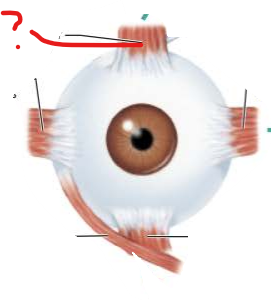
What is this?
What is its function?
Superior Rectus Muscle
Elevates eye and turns it medially
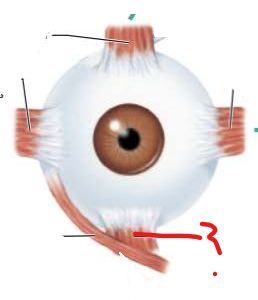
What is this?
What is its function?
Inferior Rectus Muscle
Depresses eye and turns it medially
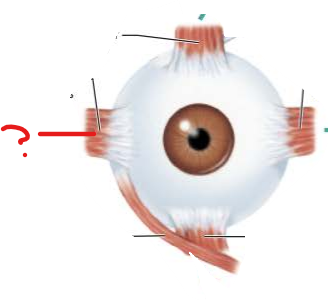
What is this?
What is its function?
Lateral Rectus Muscle
Moves eye laterally
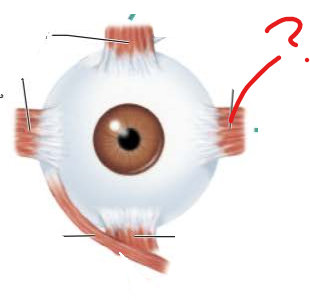
What is this?
What is its function?
Medial Rectus Muscle
Moves eye medially
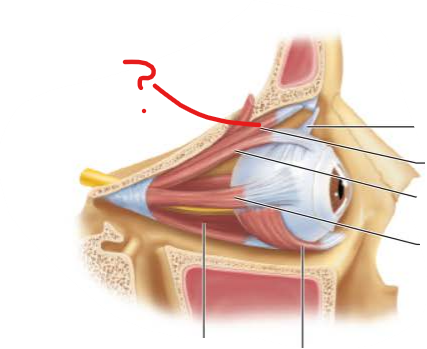
What is this?
What is its function?
Superior Oblique Muscle
depresses eye and turns it laterally
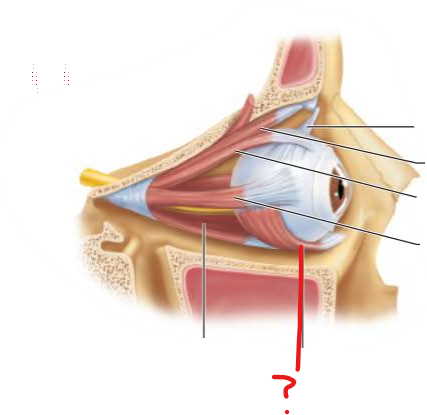
What is this?
What is its function?
Inferior Oblique Muscle
Elevates eye and turns it laterally
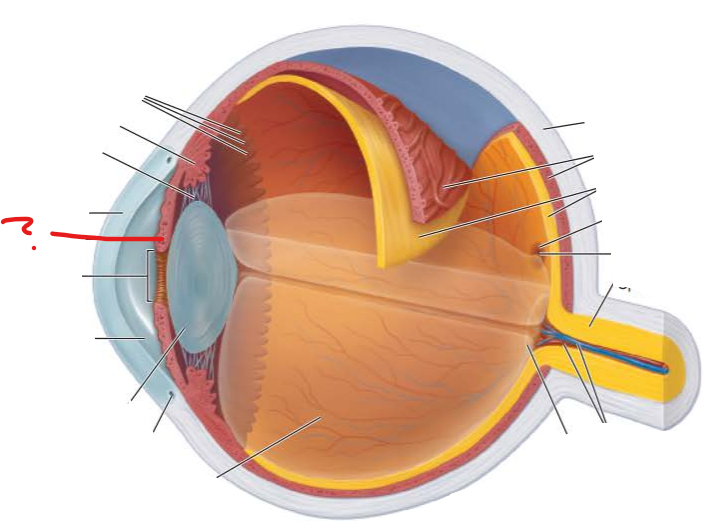
What structures form the fibrous layer of the eye?
What type of tissue is it?
sclera and cornea
dense avascular connective tissue
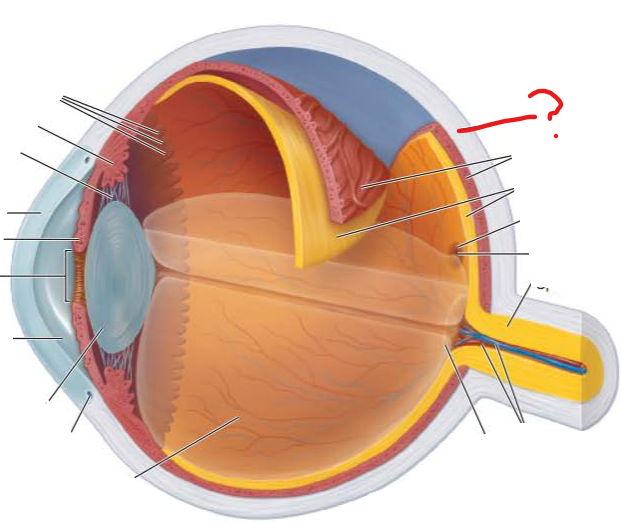
What is this?
What is its function?
Sclera
protects and shapes eyeball
provides anchoring site for extrinsic eye muscles
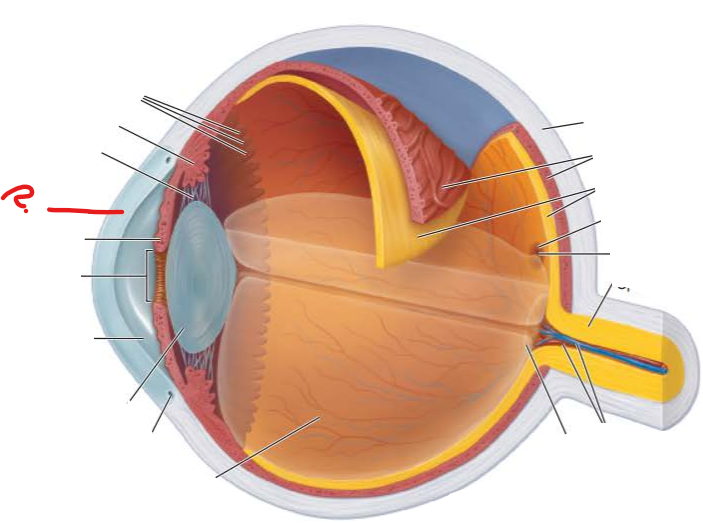
What is this?
What is its function?
Cornea
forms a window that lets light enter the eye
What covers the cornea Externally?
what is its function?
what covers the cornea internally?
External sheet stratified squamous epithelium that protects the cornea from abrasion
Corneal endothelium simple squamous epithelium
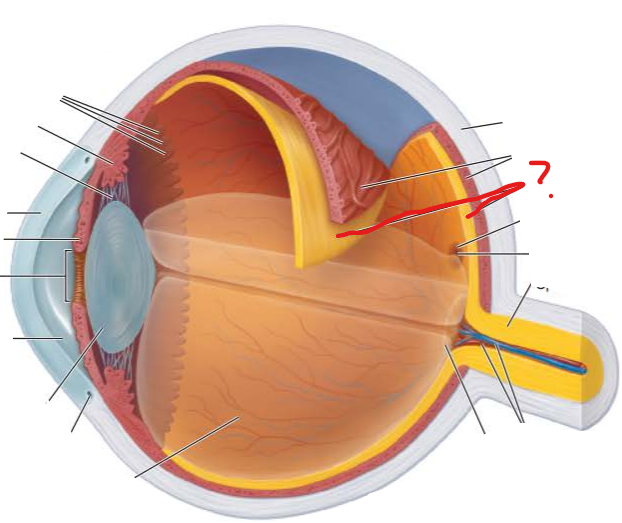
what three structures compose the vascular layer?
choroid
ciliary body
iris
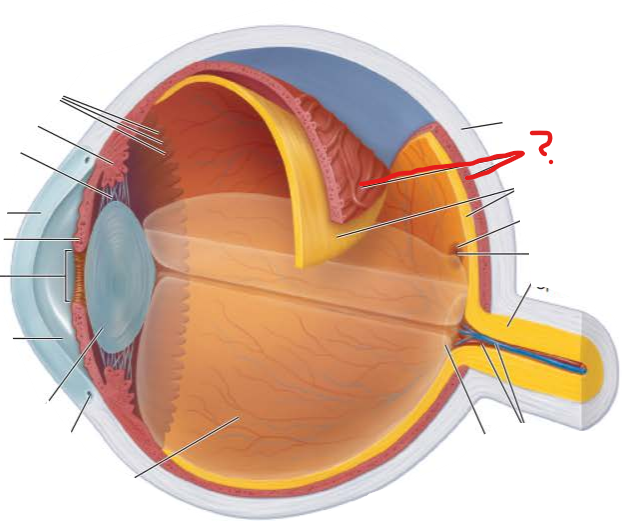
What is this?
What is its function?
what opening does it contain?
choroid
blood vessels nourish all layers
brown pigment produced by melanocytes
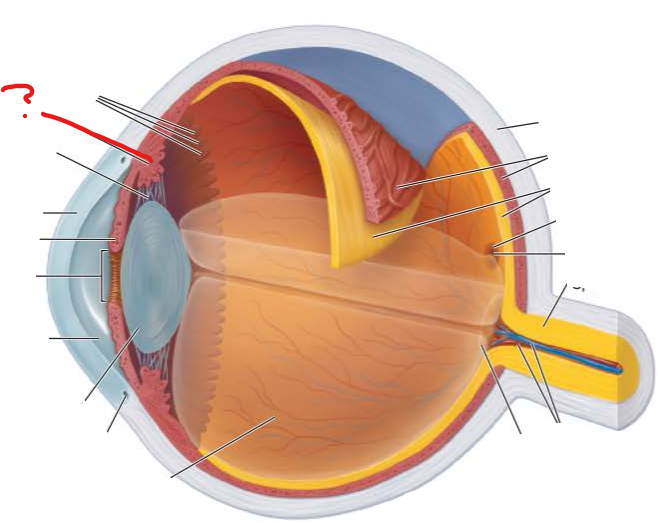
What is this?
what three parts make it?
ciliary body
thickened ring of tissue that circles the lens
ciliary muscles
ciliary processes
ciliary zonule
describe the structure and function of the ciliary muscles
makes up most of the ciliary body
smooth muscle bundles that controls lens shape
describe the structure and function of ciliary processes
radiating folds on the posterior surface of ciliary body near lens
secretes aqueous humor
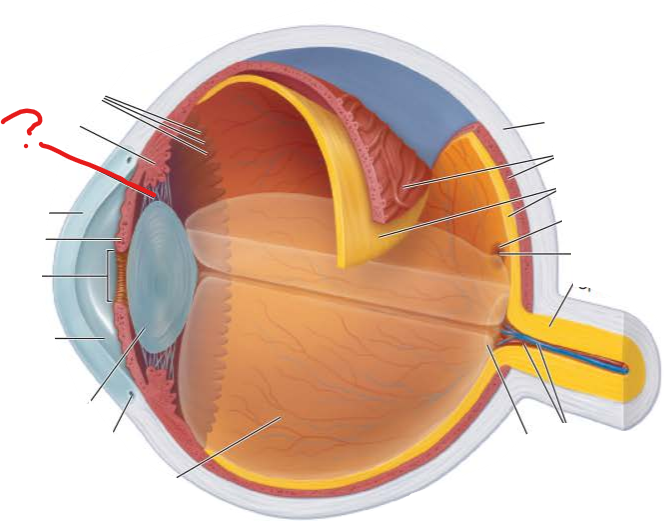
What is this?
What is its function?
ciliary zonule
helps hold the lens upright
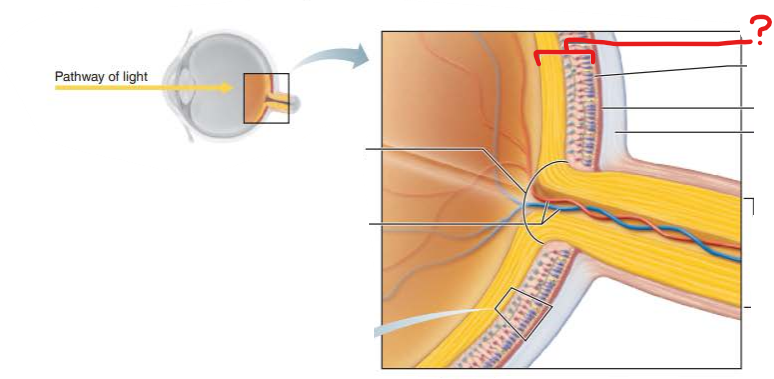
What is this?
What is its function?
what are the two smooth muscle layers that make it?
Iris
round central opening allows light to enter eye
sphincter pupillae
dilator pupillae
Explain the function of sphincter pupillae
what fibers control it?
In close vision and bright light, sphincter pupillae contract and the pupil constricts
parasympathetic fibers
explain the function of dilator pupillae
what fibers control it?
In distant vision and dim light, the dilator pupillae contract and the pupil dilates allowing more light to enter
sympathetic fibers
What is this?
What is its function?
what two layers make it?
Retina
transduce light energy
outer pigmented layer
inner neural layer
What is this?
What are the 3 main cells of this layer?
Neural layer
photoreceptors
bipolar cells
ganglion cells
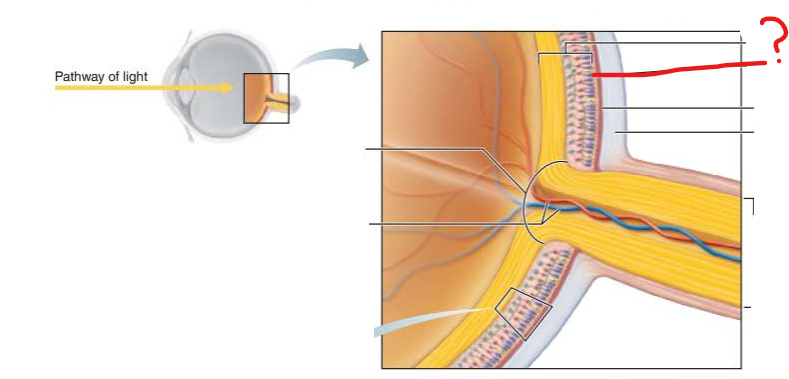
What is this?
What is its function?
Pigmented Layer
pigment cells absorb light and prevent it from scattering in the eye
stores vitamin A
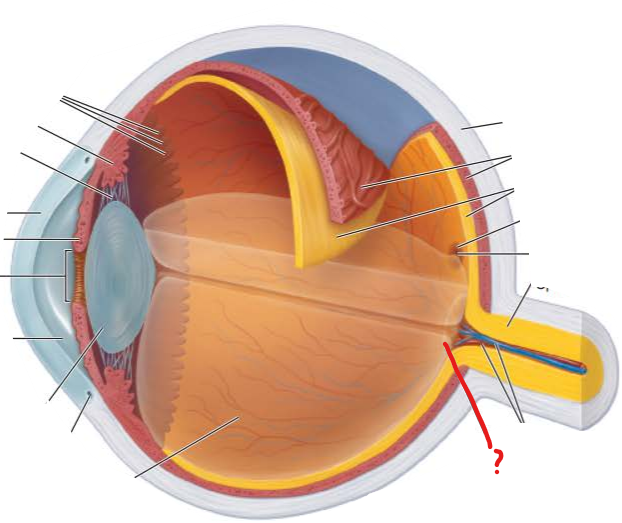
What is this?
What is its function?
what is it also called and why?
optic disc
where optic nerve leaves eye
blind spot because it lacks photoreceptors
what are the two types of photoreceptors found in the neural layer?
rods
cones
describe the function of rods
dimlight and peripheral vision receptors
more numerous and sensitive to light than cones
do not produce sharp images or color vision
describe the function of cones
vision receptors for bright light
high-resolution color vision
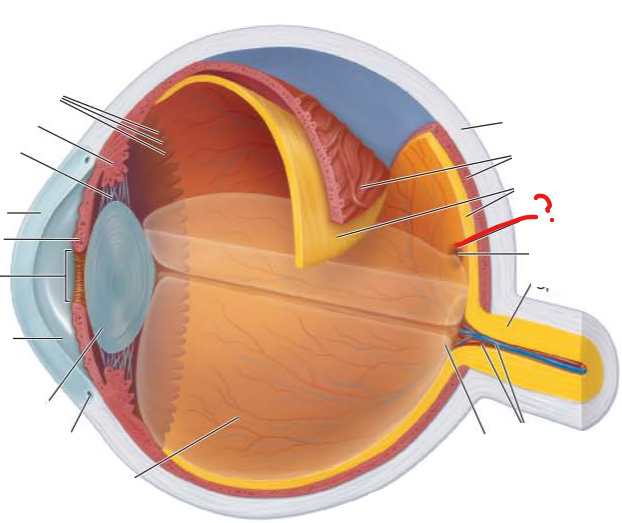
What is this?
What is its function?
what does photoreceptor does it contain?
Macula Lutea
Retinal structures in macula lutea are displaced to sides allowing light to pass almost directly to photoreceptors rather than several retinal layers greatly enhancing visual acuity
contains mostly cones
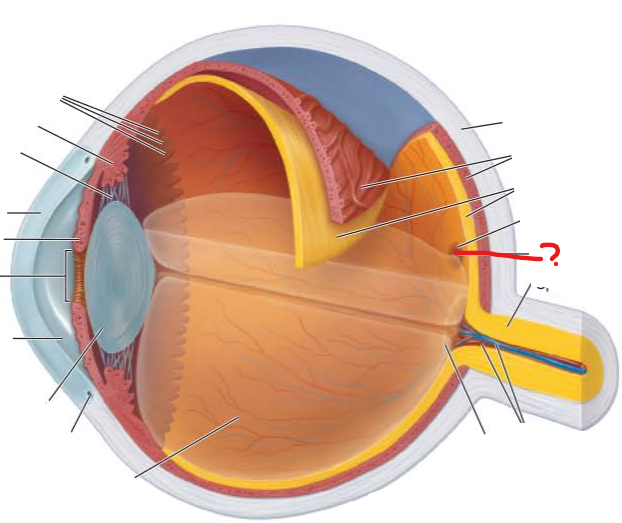
What is this?
what photoreceptor does it contain?
Fovea Centralis
tiny pit in center of macula lutea
contains only cones
what is the edge of macula lutea called?
what photoreceptor does it contain?
retina periphery
contains mostly rods
the anterior chamber contains what?
what is its function?
aqueous humor
maintains intraocular eye pressure
when is light bent entering the eye?
entering cornea
entering lens
leaving lens