outside of the peritoneal cavity; retroperitoneal
Where is the kidney located?
Glomerulus Capillary system
- a high-pressure capillary filtration system located between the afferent and efferent arterioles
Peritubular Capillary System
- a low-pressure reabsorptive system that originates from the efferent arteriole
b
Moving two ions in the same direction.
a) antiport
b) sypmort
c) Exchange
a
Moving two or more ions in opposite directions.
a) antiport
b) sypmort
c) Exchange
the cells exchange 3 sodium ions for 2 potassium ions
What does "exchange" mean?
increase; increase
Vasodilation of the afferent arteriole will lead to a _______ in blood flow and
______ in glomerular blood pressure.
decrease; increase
Vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole will lead to a _________ in blood flow and ___________ in glomerular blood pressure.
f; cortical
The majority of nephrons are juxtamedullary. T/F?
erythropoietin regulates the differentiation of RBC's in bone marrow
What is the function of EPO?
increases ca2+ reabsorption from GI; regulates ca2+ deposition in bone
What is the function of Vitamin D? (2)
b
These cells are involved in Na+ & water reabsorption.
a) Intercalated Cells
b) Principal cells
a
These cells secrete acids & transport HCO3 (bicarb).
a) Intercalated Cells
b) Principal cells
b
These cells are more in number in the nephron.
a) Intercalated Cells
b) Principal cells
renal corpuscle; renal tubule
The nephron is composed of ______ & _______.
bowman's capsule; glomerular capillaries
The renal corpuscle consists of _______ & _______.
it is located by the area where afferent arteriole and DCT are in close proximity to one another; senses changes in NaCl concentration and changes in BP
Explain the Juxtaglomerular Complex.
EPO, calcitriol, Renin production
What are the endocrine functions of the kidney? (3)
myogenic response, RAAS, tubuloglomerular feedback
What are the mechanisms for monitoring GFR? (3)
b
A negative feed-back system that stabilizes renal blood flow.
a) myogenic response
b) tubuloglomerular feedback
c) RAAS
d) adenosine
d
Causes vasoconstriction and lowers blood flow & GFR.
a) myogenic response
b) tubuloglomerular feedback
c) RAAS
d) adenosine
a
Responds to stretches in blood vessels and decreases lumen vessel size.
a) myogenic response
b) tubuloglomerular feedback
c) RAAS
d) adenosine
renal pelvis, ureter, urethra, cortex, papilla, calyx, medulla + renal pyramid, renal pelvis, ureter
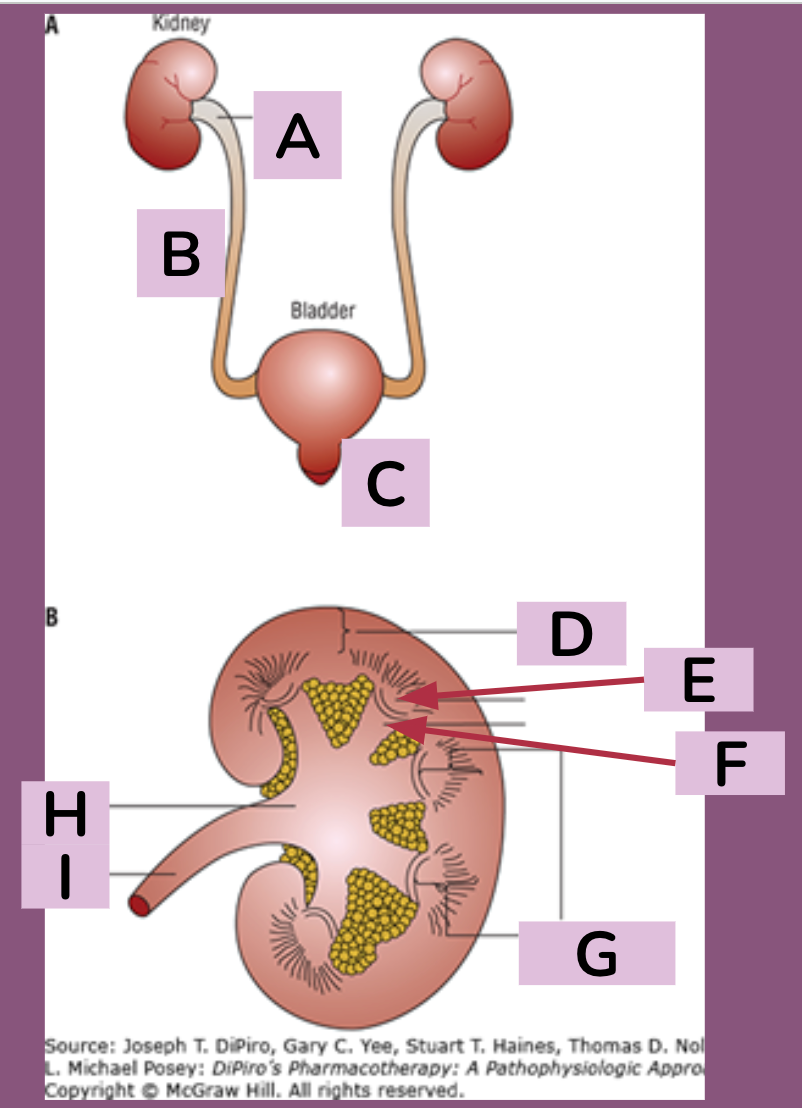
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
urinalysis, BUN, creatinine, GFR, inulin
What are tests to measure renal function? (5)