b
When determining the terminal half-life for a two-compartment drug, which of the following must be assured?
A.The distribution phase has not started before drawing plasma levels
B.The distribution phase is completed before drawing plasma levels
C.The absorption phase is complete before drawing plasma levels
D.The absorption phase has not started before drawing plasma levels
c
Because the extraction ratio can maximally be 1, the maximum value that hepatic clearance can approach is that of ______.
A.Glomerular filtration
B.Biliary clearance
C.Hepatic blood flow
D.Intrinsic clearance
d
Which of the following is not a technique to slow down drug absorption?
A.Gel
B.Ion exchange resins
C.Esters of the parent drug
D.Microionization
d
When oral absorption is saturated as the oral dose increases, which of the following is false?
A.Limited solubility decreases oral bioavailability
B.Transport across the intestinal mucosa decreases oral bioavailability
C.First-pass metabolism in the intestinal epithelium increases oral bioavailability
D. Increase in dissolution decreases oral bioavailability
a,b
Which of the following increases oral bioavailability?
a) saturable first-pass metabolism
b) saturable transport across intestinal mucosa, as oral dose increases
c) limited dissolution/solubility as the oral dose increases
a
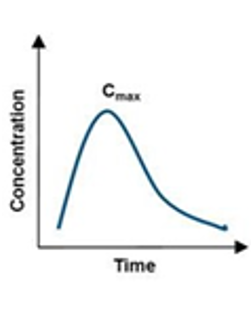
What kind of concentration vs time graph is this?
a) single oral absorption
b) nonlinear pk
c) 2 compartment model
d) 1-compartment model
b
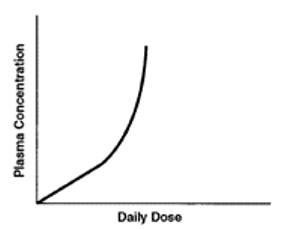
What kind of concentration vs time graph is this?
a) single oral absorption
b) nonlinear pk
c) 2 compartment model
d) 1-compartment model
d
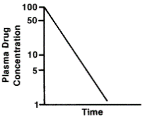
What kind of concentration vs time graph is this?
a) single oral absorption
b) nonlinear pk
c) 2 compartment model
d) 1-compartment model
c
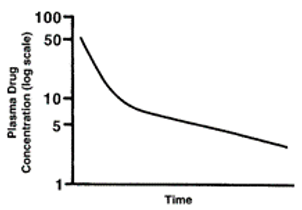
What kind of concentration vs time graph is this?
a) single oral absorption
b) nonlinear pk
c) 2 compartment model
d) 1-compartment model
a
EH > 0.8
a) proportional to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
b) somewhat affected by hepatic blood flow/QH
c) insensitive to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
c
EH<0.2
a) proportional to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
b) somewhat affected by hepatic blood flow/QH
c) insensitive to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
b
EH between 0.2-0.8
a) proportional to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
b) somewhat affected by hepatic blood flow/QH
c) insensitive to change in hepatic blood flow/QH
peripheral compartment
-organs that require more time for drug distribution to reach equilibrium
- not instantaneous
- fat, resting muscles
central compartment
-highly perfused organs that take little time for drug distribution to reach equilibrium
-instantaneous
- heart, liver, lungs, kidneys
a
Dose-independent describes ______.
a) Linear PK
b) Nonlinear PK
b
AUC is disproportional to the dose describes ______.
a) Linear PK
b) Nonlinear PK
a
PK parameters are constant describes _______.
a) Linear PK
b) Nonlinear PK
b
ADME is saturable.
a) Linear PK
b) Nonlinear PK
a
_______ obeys first order kinetics.
a) Linear PK
b) Nonlinear PK
saturable
Renal secretion and active renal reabsorption are _______ processes.
decreased
Saturated tubular secretion leads to _________ CLR.
increased
Saturated tubular reabsorption leads to ________ CLR.
true
Drug-plasma protein binding (Fp) can lead to an increase in hepatic clearance, renal clearance, and volume of distribution. T/F?
a
Filtration is a(n) __________ process.
a) passive
b) active
c) both
b
Secretion is a(n) _________ process.
a) passive
b) active
c) both
c
Reabsorption is a(n) ________ process.
a) passive
b) active
c) both
a
Where does filtration occur?
a) glomerulus
b) proximal tubule
c) distal tubule
d) loop of henle
b
Where does secretion occur?
a) glomerulus
b) proximal tubule
c) distal tubule
d) loop of henle
c
Where does reabsorption occur?
a) glomerulus
b) proximal tubule
c) distal tubule
d) loop of henle