What is another term for micturition?
urination, voidin
What are the functions of the urinary system?
- Removal of metabolic wastes (nitrogenous and acidic).
- Removal of hormones, drugs, and other foreign material.
- Secretion of erythropoietin.
- Activation of Vit. D.
- Regulation of blood pressure through the renin-angiotensin--aldosterone system.
What does "normal urine" look like?
Straw colored with a mild odour.
What does cloudy urine indicate?
May indicate the presence of large amounts of protein, blood, bacteria and pus.
What does a dark colour of the urine indicate?
Hematuria, excessive bilirubin, or highly concentrated urine.
Old urine specimens still contain accurate information. True or false?
False; old specimens will not provide accurate information.
If your urine has an unpleasant or unusual odor, what can that indicate?
An infection or from certain dietary components or medication.
What do small and large amounts of blood in the urine indicate?
Small: infection, inflammation or tumors in urinary tract.
Large: increased glomerular permeability or hemorrhage.
What are urinary casts?
Microscopic-sized molds of the tubules, they indicate inflammation of the kidney tubules.
Specific gravity indicates ability of tubules to concentrate urine. What does a low and high specific gravity indicate?
Low: dilute urine (with normal hydration)
High: concentrated urine (with normal hydration)
Very high and low specific gravities are likely related to renal failure.
What does an elevated serum urea and serum creatinine levels indicate?
Indicate failure to excrete nitrogen wastes (from protein metabolism) attributed to decreased GFR.
Culture and sensitivity studies on urine specimens identify what?
Identification of causative organism of infection and help select appropriate drug treatment.
What does a cystoscopy do?
Visualizes the lower urinary tract and may be used to perform biopsies and remove kidney stones.
What is incontinence?
Loss of voluntary control of the bladder. Can be due to:
- DM
- pregnancy/childbirth
- enlarged prostate
- weak sphincter/bladder muscles
- UTIs
- severe constipation
- injuries to the spinal cord
What is enuresis?
Involuntary urination by a child beyond the age of 4-5 yrs (when bladder control becomes expected).
Stress incontinence is more common in ___.
women.
Overflow incontinence is due to an ___ and is usually associated to ___ because of a weakened detrusor muscle.
incompetent bladder sphincter, older adults.
What is retention?
The inability to empty the bladder. May be accompanied by overflow incontinence.
What are the lower urinary tract infections?
- cystitis
- urethritis
What are the upper urinary tract infections?
- pyelonephritis
What is cystitis and urethritis? Name some of its symptoms.
Cystitis: bladder wall is inflamed. Most likely from a bacterial infection or potential irritants.
Urethritis: urethra is inflamed. Usually caused by an STI.
Pain is common in the pelvic area.
- dysuria
- urgency
- frequency
- nocturia
- urine cloudy, with unusual odor.
- systemic signs
What is pyelonephritis?
Infection of one or both kidneys. The infection extends from the ureter into the kidney. Purulent exudate fills the pelvis and calyces.
What can happen if the infection in pyelonephritis is severe or long term?
If severe it can obstruct urine flow to the ureter which can lead to chronic renal failure.
If recurrent or chronic it can lead to the formation of fibrous scar tissue over the calyx --> loss of tubule function and hydronephrosis.
What are the signs and symptoms of pyelonephritis?
- signs of cystitis + pain (in lower back or flank)
- systemic signs (high temp.)
What are the signs and symptoms of pyelonephritis that indicate that infection is present and that kidney involvement exists?
Infection: fever, pain, malaise
Kidney involvement: urinary casts, obstruction
What is the sequence that follows nephrotic syndrome?
1. Increased permeability in glomerular capillaries --> plasma protein to escape into the filtrate.
2. Hypoalbuminenia, resulting in decreased plasma osmotic pressure and generalized edema.
3. BP may remain low or normal.
4. Decreased blood volume increases aldosterone --> more severe edema.
5. High levels of blood and lipoprotein in the urine, likely as a response of the liver to heavy protein loss.
What is urolithiasis?
Stones in the urinary tract.
Calculi tend to form with:
- excessive amounts of solutes in filtrate
- insufficient fluid intake
Manifestations of calculi tend to only occur with obstruction of urine flow. Name some possible.
- infection (stasis in the urine, builds up bacteria, and irritates tissue)
- hydrophresosis with dilation of the calyces
- atrophy of renal tissue
How are calculi treated?
- extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL)- lithotripsy
- drugs
- surgery
Hydronephrosis is a secondary problem caused by:
- calculi
- tumors, scar tissue
- urine flow obstruction
Where do most bladder tumors arise from?
The transitional epithelium of the bladder.
Name and list some congenital kidney disorders.
- vesicoureteral reflux
- agenesis
- hypoplasia
- ectopic kidney
- "horsehoe" kidney
What is vesicoureteral reflux and agenesis?
Vesicoureteral reflux is the backward flow of urine from the bladder into the kidneys.
Agenesis is the failure of one kidney to develop.
What is hypoplasia, ectopic kidney and "horseshoe" kidney?
Hypoplasia is the failure of the kidney to develop to normal size. An ectopic kidney is a kidney and ureter displaced out of normal position. Horseshoe kidney is when the kidney are fused together.
What is the main characteristic of chronic renal failure?
The gradual irreversible destruction of the kidney over a long period of time. Once advanced, it can't be stopped.
What are the three As of end-stage CRF?
- azotemia/uremia (^ waste products in blood)
- anemia
- acidosis
What is adult polycystic kidney?
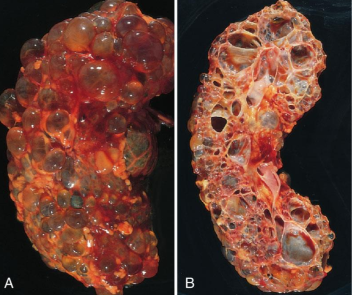
A genetic condition where cysts develop and enlarge overtime in the kidneys. Manifestations occur in adulthood and develops into chronic renal failure.
What is nephrosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis of the renal arteries and arterioles. This reduces blood supply to the kidneys and may lead to ischemia and atrophy if untreated. Continued ischemia leads to necrosis which leads CRF.