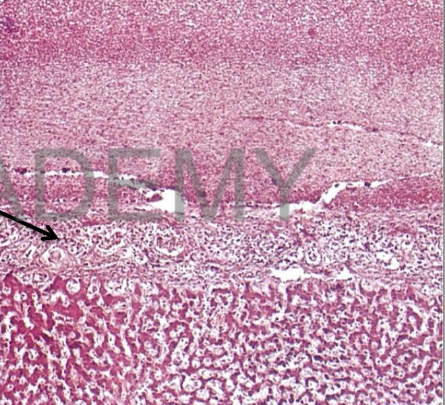
Diagnosis: Lobar
pneumonia, Red
hepatization
Describe:
Section in the lung shows:
All the alveolar spaces:
contain a network of
fibrin entangling many
intact red blood cells
and some intact
polymorphs &
macrophages.
The alveolar walls:
edema and congested
capillaries.
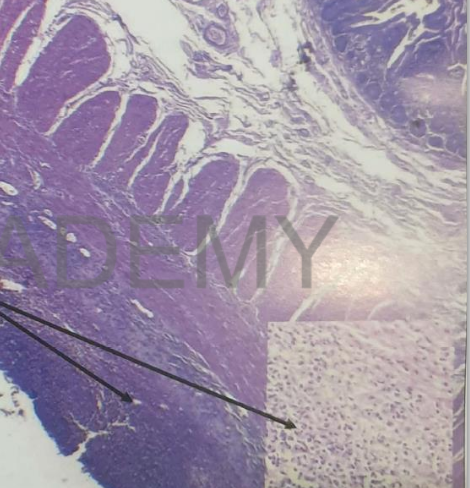
Diagnosis: Fibrinous peritonitis,
intestine
Describe: Section in small intestine
shows:
covering peritoneum: shedded
serosal cells. Covered by
network of fibrin entangling
acute inflammatory cellular
infiltrate (exudate)
Sub serosal connective tissue:
edema, congested capillaries,
formed of acute inflammatory
cellular infiltrate = many
polymorphs and few
macrophages.
Intestinal mucosa and
submucosa are normal
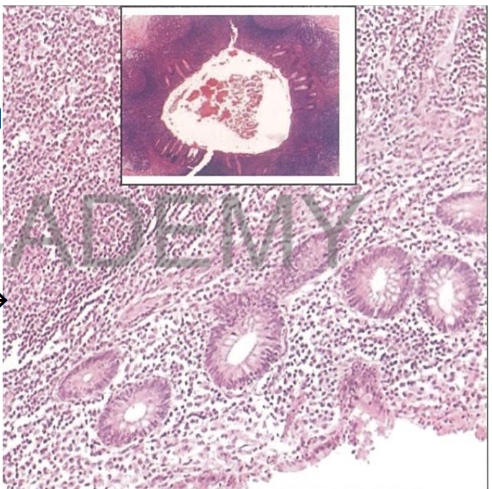
Diagnosis: Acute suppurative
appendicitis
Describe:
Transverse section in the
appendix shows:
mucosal glands: partly sheded
ulcerated.
mucosa, submucosa,
musculosa, Serosa: edema,
congested capillaries, dense
acute inflammatory exudate
infiltration by PMNs, pus cells,
macrophages
Lumen: of the appendix
contains a fibrin network +
necrotic sheded mucosal cells
+ PMNs + pus cells
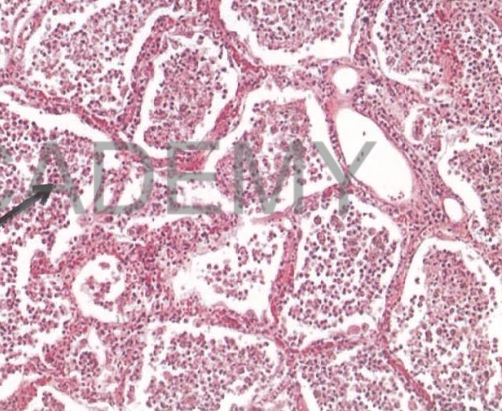
Diagnosis: Lobar
pneumonia, Red
hepatization
Describe:
Section in the lung shows:
All the alveolar spaces:
contain a network of
fibrin entangling many
intact red blood cells
and some intact
polymorphs &
macrophages.
The alveolar walls:
edema and congested
capillaries.
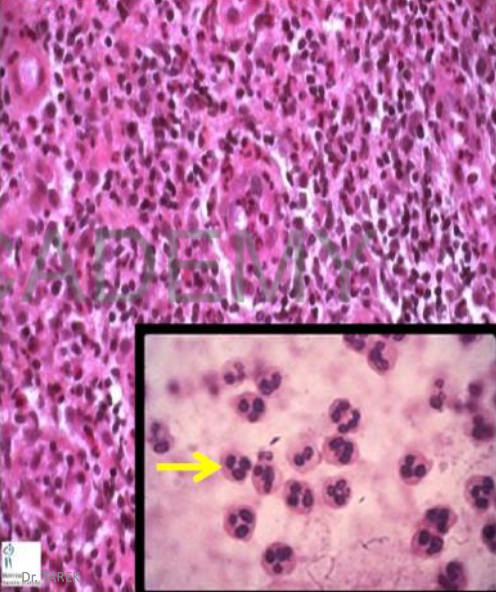
Acute inflammatory cells:
Section at acute
inflammation:
Congested capillaries,
dense acute inflammatory
cellular infiltrate (exudate)
formed of:
• many PNMLs
(segmented nucleus)
• few macrophages
(larger cells with ovoid
indented nucleus)
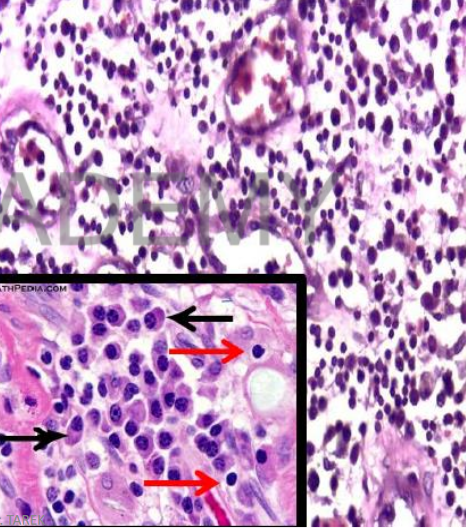
Chronic inflammation:
Chronic inflammatory cells:
• Lymphocytes (small
rounded cells with small
rounded dark nuclei,
inconspicuous
cytoplasm)
• Plasma cells (eccenteric
nucleus)
• Macrophages (larger
than lymphocytes with
abundant cytoplasm and
ovoid indented nuclei)
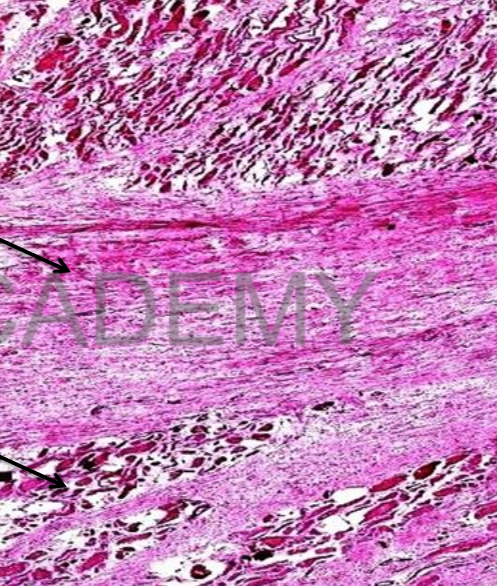
Diagnosis: myocardial
scar (healed MI)
Section in the
myocardium (cardiac
muscle) showing:
• Areas of scar tissue.
• The scar tissue is
homogenous pink with
dilated capillaries and
some fibroblasts.
• The adjacent cardiac
muscle fibers: red and
slightly atrophic with
pyknotic nuclei.
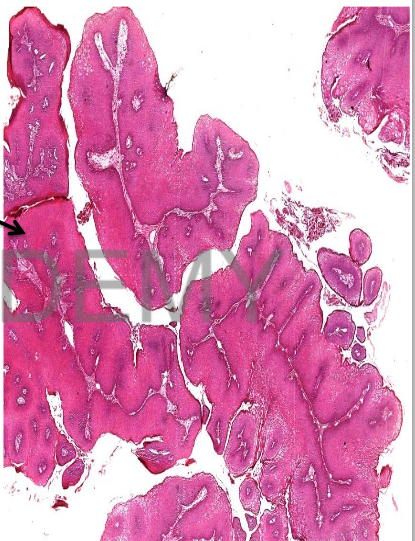
Diagnosis: squamous cell
papilloma
section in a non-capsulated
benign tumor formed of:
• Papilla with Branching core
of connective tissue covered
by a thick hyperplastic
stratified squamous
epithelium.
N.B:
• acanthiosis (increase prickle cell
layer), parakeratosis (nucleated
surface keratin), hyperkeratosis
(excessive keratin)
• The core shows blood vessels.
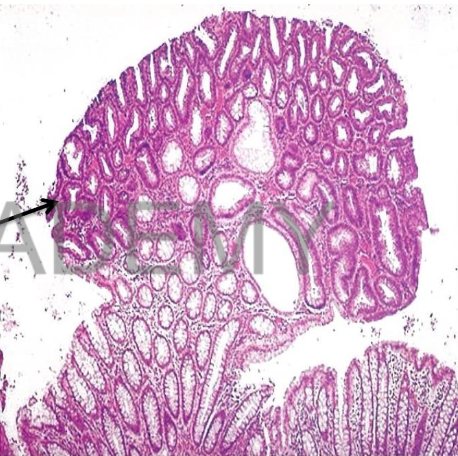
Diagnosis: Adenomatous polyp
(adenoma), intestine
Describe:
benign tumor formed of :
Proliferated acini (glands)
variable in size and shape
lined by one layer of columnar
mucin secreting cells with basal
nuclei.
Some are lined by dysplastic
epithelium shows mucin
depletion, hyperchromatic,
elongated pseudostratified
nuclei.
vascular connective tissue
stroma
between the glands with few
inflammatory cells.
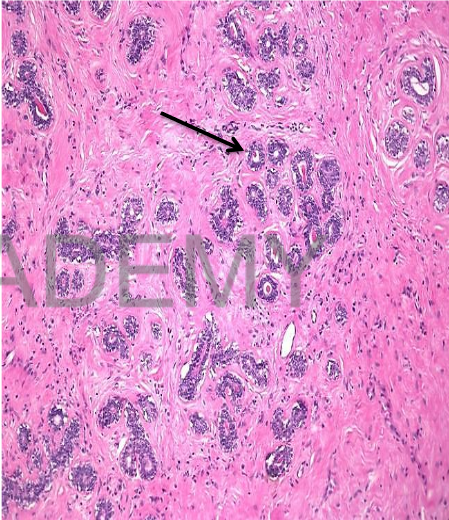
Diagnosis: Fibroadenoma
pericanalicular
Section in a benign tumor
formed of:
• Proliferated glands (ducts),
rounded or oval in cut
section with patent lumen.
• lined by two layers of cells,
outer flattened and inner
cubical.
• The ducts are separated by
delicate fibrous tissue
containing blood vessels and
few lymphocytes.
• The tumor is surrounded by
a fibrous capsule.
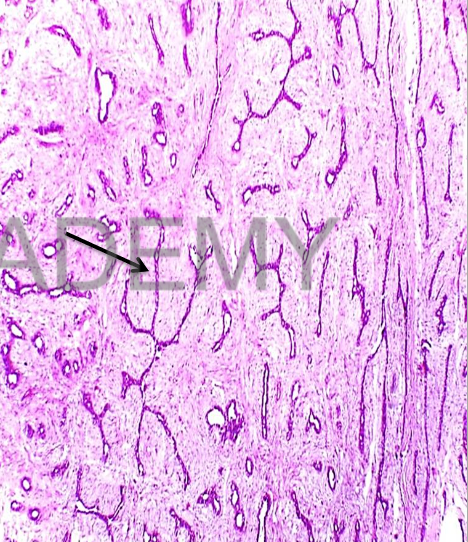
Diagnosis:
Fibroadenoma Intracanalicular
Section in a capsulated benign
tumor formed of:
• Proliferated ducts,
compressed (obliterated
lumen)
• lined by two layers of cells,
outer flattened and inner
cubical.
• ducts are invaginated by
Excess fibrous tissue giving
the false impression that the
epithelium surround the
fibrous tissue in some areas
(intracanalicular).
• Tumor is surrounded by
fibrous capsule
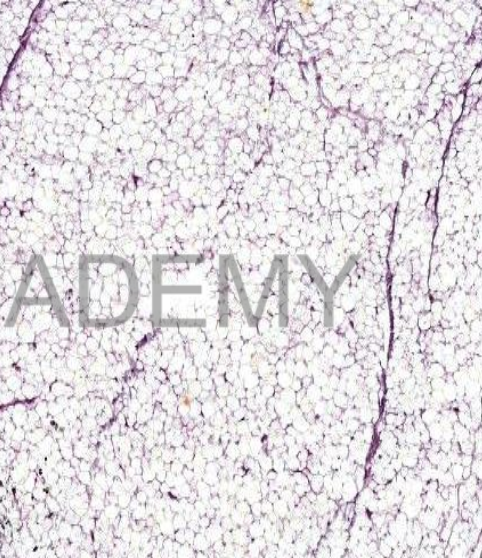
Diagnosis: lipoma
Section from a benign
tumor shows:
A fibrous capsule
surrounds the tumor
and sends fibrovascular septa dividing
the tumor into lobules.
The lobules are formed
of *mature fat cells:
large, polygonal and
vacuolated. *nuclei:
flattened, compressed
against cell membrane
(signet ring
appearance).
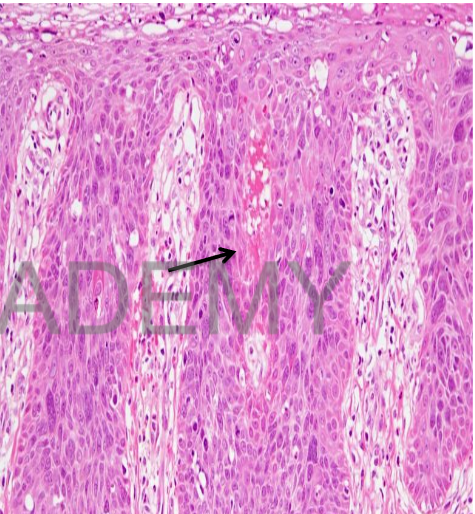
Diagnosis: Squamous cell
carcinoma insitu:
Section in uterine cervix
• Squamous metaplasia +
full thickness high grade
dysplastic changes
• Cells:
loss of orientation, large
hyperchromatic
pleomorphic nuclei + high
nucleocytoplasmic ratio
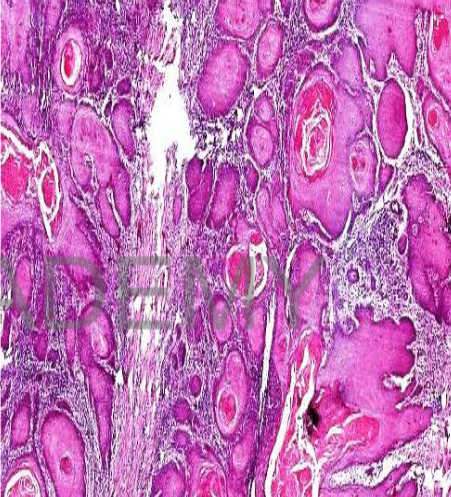
Diagnosis: squamous cell carinoma
section in skin shows:
• Sheets of malignant epithelial
cells infiltrating the dermis
• focal ulcerated epidermis.
• tumor masses variable in size
and shape
• Their periphery: layer of dark
stained small basal like cells,
inner to this are polyhedral cells
and the central cells show a red
stained keratin pearls (cell nest).
• The malignant cells: variable in
size and shape with abundant
pink cytoplasm, and large
hyperchromatic nuclei showing
prominent nucleoli.
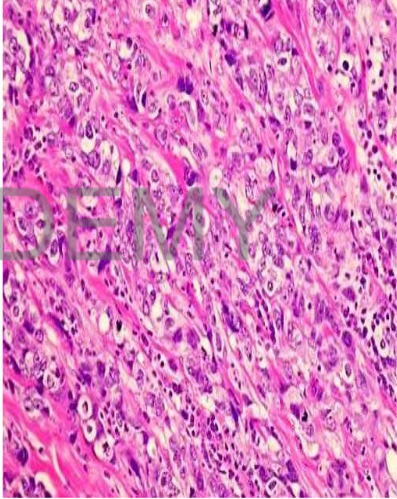
Diagnosis: Infiltrating duct
carcinoma, breast.
Section in breast showing:
Infiltrating sheets of
malignant epithelial cells
separated by excessive dense
fibrous tissue
• malignant cells: Rounded to
polyhedral, variable in size
• Nuclei: large pleomorphic
hyperchromatic,
• prominent nucleoli
• mitotic figures.
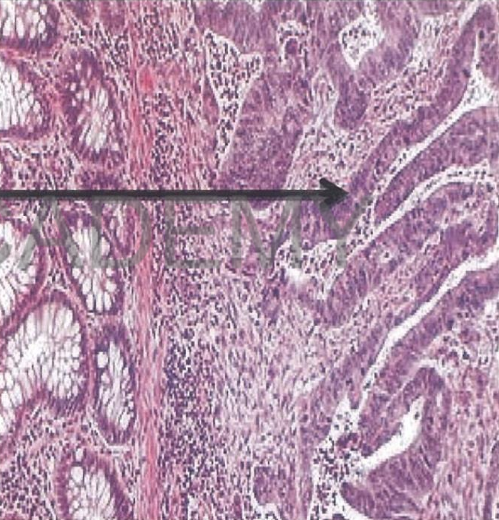
Diagnosis: Adenocarcinoma,
colon
Describe:
Section in colonic wall shows:
* malignant tumor:
irregular acini
infiltrating submucosa and
muscle layer (musculosa).
acini vary in size and shape
lined by one or more layers
of malignant cells (loss of
polarity)
malignant cells vary in size
and shape.
Nuclei: large,
hyperchromatic
Mitotic figures
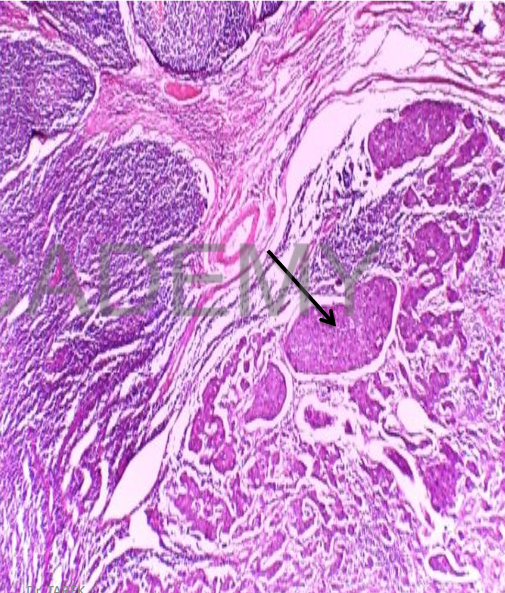
Diagnosis: Metastatic
carcinoma at lymph node
Section in enlarged lymph
node:
• Partial replacement of
nodal tissue by
malignant tumor
deposits
• Tumor: solid masses of
malignant cells variable
at size and shape
• Hyperchromatic nuclei
• Abundant mitosis
• Tumor emboli at
lymphatics
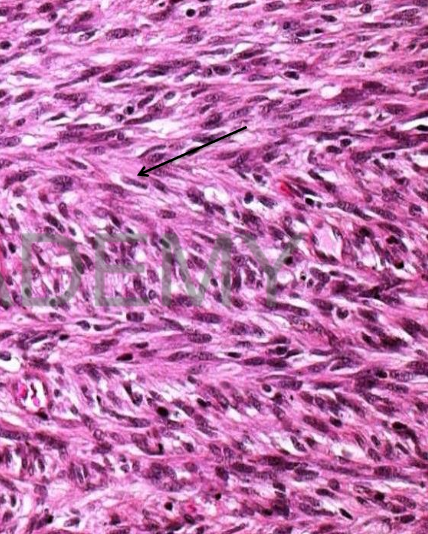
Diagnosis: Spindle cell
sarcoma (Fibrosarcoma)
Section in a malignant
tumor showing:
Proliferated spindle cells
arranged in fascicles
herring bone pattern. The
cells have dark elongated
nuclei high nucleocytoplasmic ratio and
mitotic figures.
The background shows
little amount of collagen
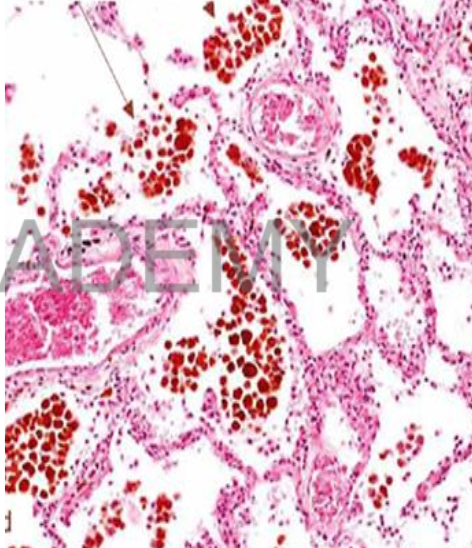
Diagnosis: Chronic venous
congestion, Lung
Describe:
Section in lung shows:
The alveolar walls: thickened
interstitial edema and
congested capillaries.
alveolar spaces: homogenous
pink transudate entangling
red cells, hemosiderin
granules, and heart failure
cells.
HEART FAILURE CELLS: large
rounded phagocytic cells
engulfing brown hemosiderin
granules.
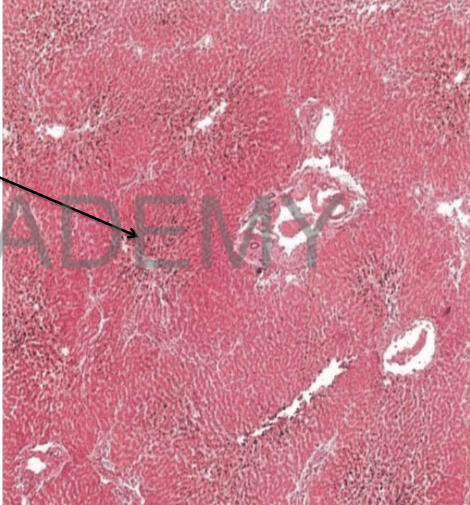
Diagnosis: Chronic venous
congestion, liver
Describe:
Section in liver shows:
• central veins and
sinusoids: dilated and
congested.
• liver cells in the center of
lobules: atrophic.
• liver cells in the
periphery of lobules:
cloudy swelling and fatty
degeneration.
• Kupffer cells are
distended with brown
hemosiderin granules
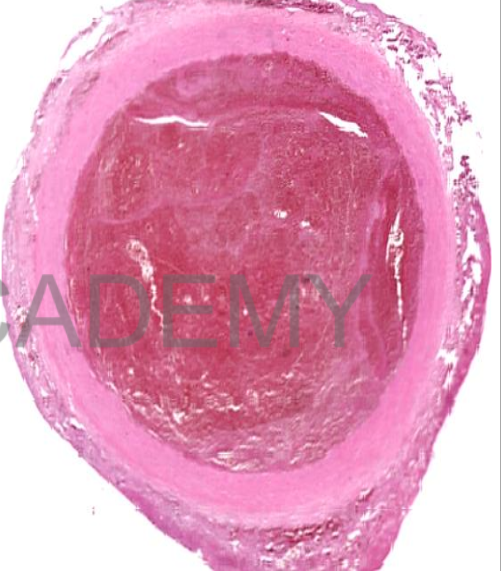
Diagnosis: recent
thrombus
Transverse section in a
blood vessel:
• The lumen is occluded
by a thrombus:
• red mass transversed
by pale structurless
lines formed of fused
platelets (lines of
zahn)
• In between lines of
zahn: network of fibrin
entangling red and
white blood cells.
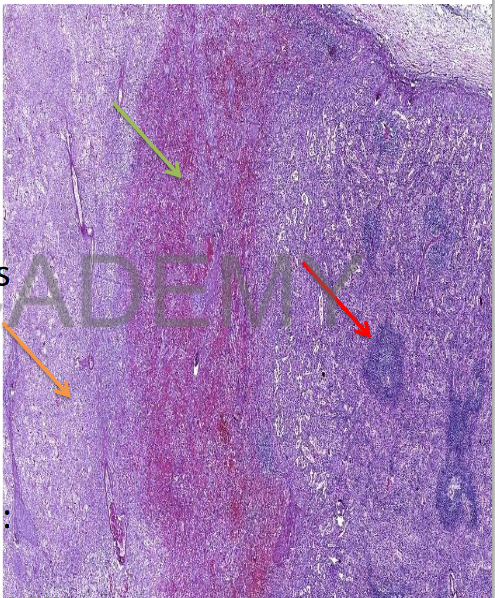
Diagnosis: Infarction,
spleen:
Section in spleen
showing two zones:
• Zone of infarction:
structurless pink area
of coagulative necrosis
• Red and white pulp:
ghosts
• The adjacent spleen is
normal
• In-between two zones:
zone of congestion
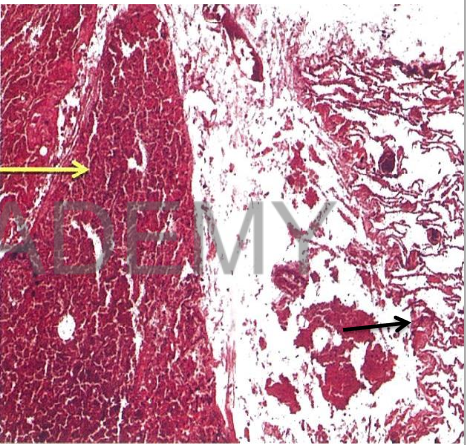
Diagnosis: Infarction, lung
Describe:
Section in lung shows two zones:
The infarct:
atrophic alveolar walls thin
fibrous septa
alveolar spaces: many intact
and haemolysed red blood cells
and SHADOWS of heart failure
cells.
The rest of the lung:
picture of chronic venous
congestion (describe).
Pleura opposite the infarct:
fibrinous pleurisy (describe)
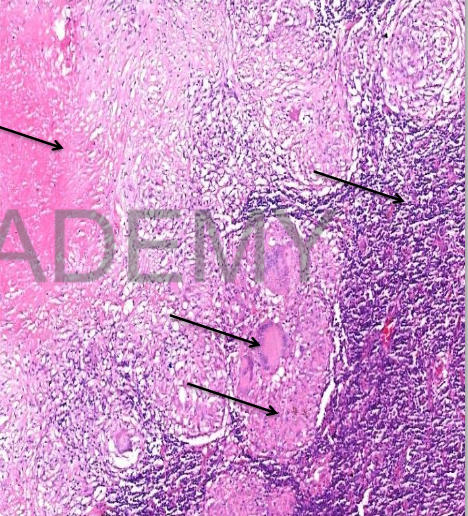
Diagnosis: Caseating tuberculosis,
lymph node:
Section in enlarged lymph node:
• Lymph node structure is partially
effaced and replaced by
homogenous pink caseous
material entangling blue nuclear
fragments
• Multiple tubercles surrounding
the caseation
• Tubercle: the microscopic unit of
TB = large pink epitheloid cells,
langhan’s giant cells (peripheral
horse shoe arrangement of
nuclei) and lymphocytes
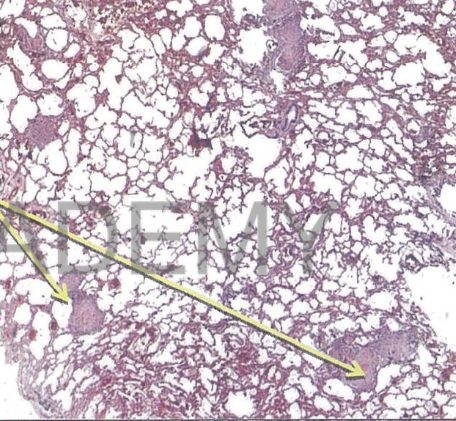
Diagnosis: Miliray
tuberculosis, lung
Describe:
Section in the lung shows:
Small many miliary
tubercles scattered in the
interstitial lung tissue
perivascular.
tubercle is formed of
epithelioid cells, langhan's
giant cells and
lymphocytes.
Minimal casation & absent
fibrosis
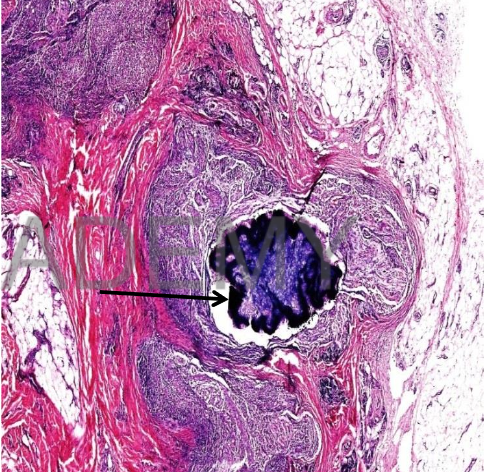
Diagnssis: Madura foot,
actinomycosis
Section from skin showing:
Many abscesses
surrounded by fibrosis.
• Each abscess consists of
blue fungal colonies
surrounded by
neutrophils and
macrophages.
• The fungal colonies: dark
blue hyphae attached to
pink stained club
shaped peripheral
structures.
D
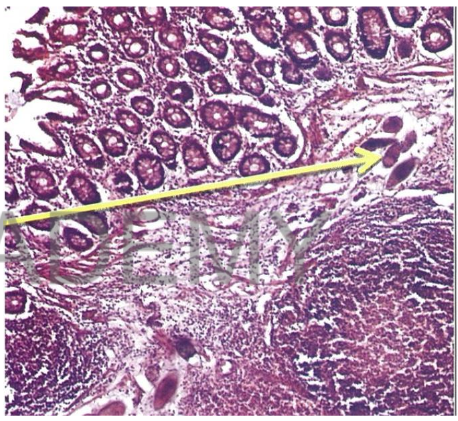
Diagnosis: Bilharziasis, colon
Describe:
Section in Colonic Mucosa
shows:
Many bilharzia ova in
submucosa with yellowish
refractile shell.
Some are fresh showing
pink miracidia and others
are calcified(dark blue).
Ova are surrounded by
bilharzial reaction
(lymphocytes, plasma cells
macrophages, eosinophils,
fibrosis)
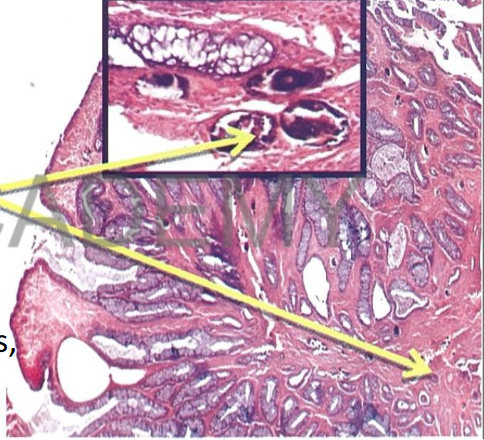
Diagnosis: Bilharzialpolyp,
colon
Describe:
Section in a polyp shows:
central core of vascular
connective tissue
fresh, degenerated and
calcified ova (describe)
surrounded by bilharzial
reaction (lymphocytes,
plasma cells, macrophages,
eosinophils, fibrosis)
Hyperplastic covering
mucosa (increased number
of mucosal glands)
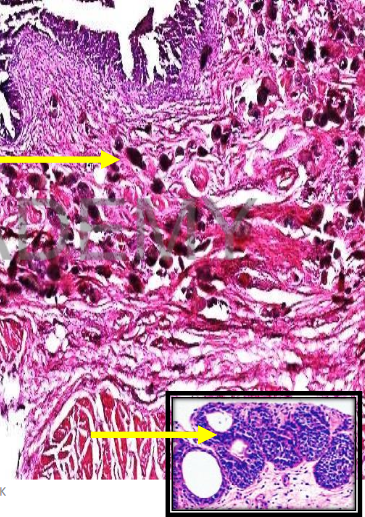
Diagnosis: section from the urinary
bladder wall shows:
Bilharzia ova are deposited mainly in
the submucosa and less in the other
layers.
• The ova are surrounded by
lymphocytes plasma cells,
eosinophils. Old lesions show
fibrosis.
• The mucosa: hyperplasia, atrophy,
ulceration or squamous
metaplasia
• The hyperplastic epithelium dips
down into the submucosa
epithelial nests (Brunn's nests),
Some nests show central
degeneration cyst formation
(cystitis cystica).
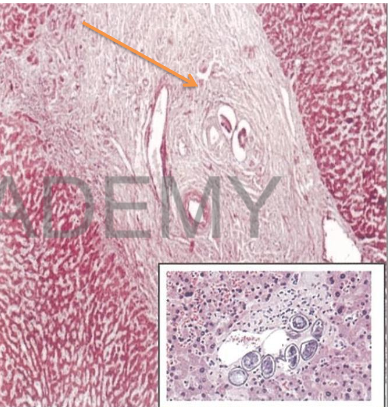
Diagnosis: Bilharzial
periportalfibrosis
Describe:
Section in the liver shows:
portal tracts: wide fibrous
expansion + Bilharzial ova
surrounded by bilharzial
reaction(lymphocytes, plasma
cells, macrophages,
eosinophils and fibrosis)
newly formed capillaries,
some of them are dilated
(angiomatoid), newly formed
bile ducts
Brown bilharzial pigments
within kupffer cells
liver lobules are normal.
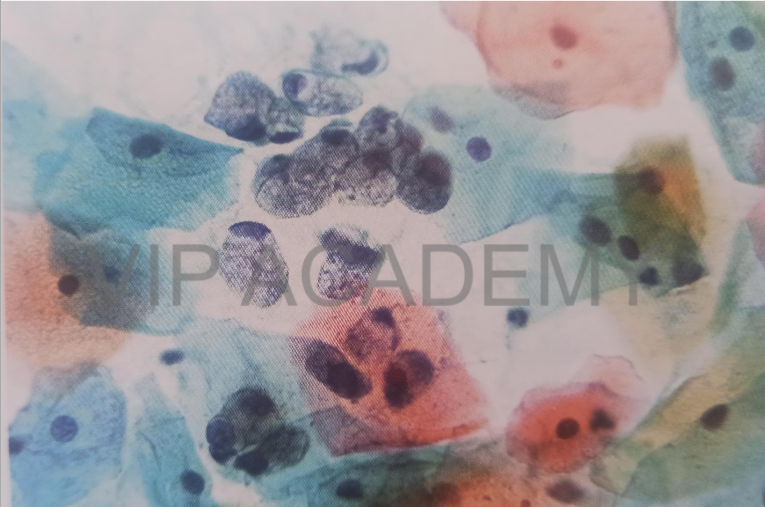
Cytology film
Cervical smear stained by PAP
stain
Cytology PAP smear
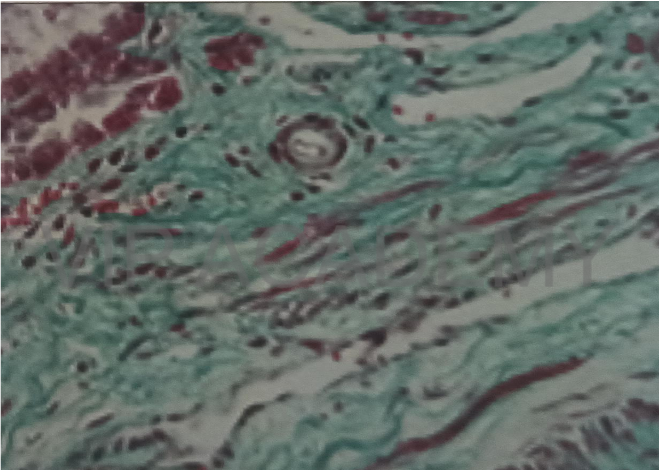
Masson trichom special stain
Section in fibrous tissue
Masson trichom stains the
collagen bundles green

Prussian blue special stain
Section in liver hemochromatosis
Cells show blue hemosedrin
pigment
Appears brown in H&E section
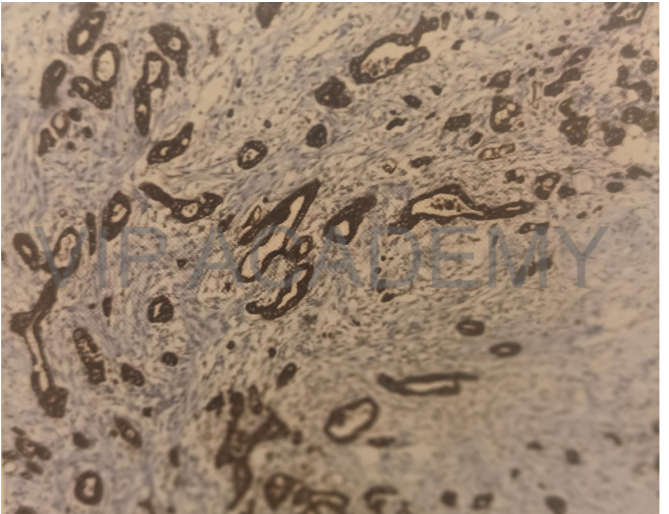
Immune histochemical stain by
Cytokeratin
Section at adenocarcinoma
Cytoplasmic brown staining by
cytokeratin antibody

Immunehistochemical stain by CD 20
Section at large B cell lymphoma
Membranous brown stain by CD 20
(pan B antibody)