What is our nervous system composed of?
10 billion nerve cells and has external and internal receptors.
What is the function of nerve cells (neurons)?
Carries electrical messages all over the body.
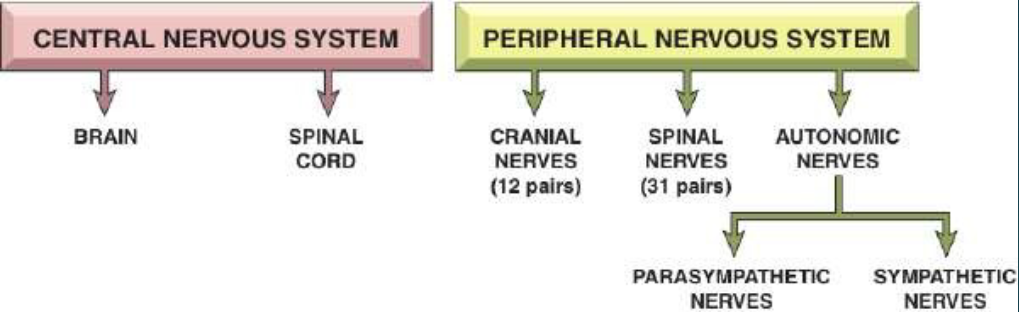
What are the 2 divisions of our nervous system?
1. Central nervous system (CNS), 2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What is in the CNS?
Brain and spinal cord
What is in the PNS?
Cranial, spinal nerves, plexuses and peripheral nerves
What do cranial nerves do?
They carry impulses between the brain and the head and neck.
What do the spinal nerves do?
They carry messages between the spinal cord and the chest, abdomen and extremities.
Spinal and cranial nerves detect and respond to changes in the outside world. True or false.
True
Where do sensory (afferent) nerves carry messages to?
Spinal cord and brain
Where do motor (efferent) nerves travel to?
To the muscles of the body, giving them instruction.
Where does autonomic nervous system carry impulses to?
CNS to organs
What nerves stimulate our FIGHT OR FLIGHT/stress?
Sympathetic nerves
Parasympathetic nerves balance ___.
sympathetic nerves
How do the parasympathetic nerves balance the sympathetic nerves?
- Slowing heart rate
- Lowers blood pressure
What are the divisions of the CNS and PNS?
What are the parts of a neuron?
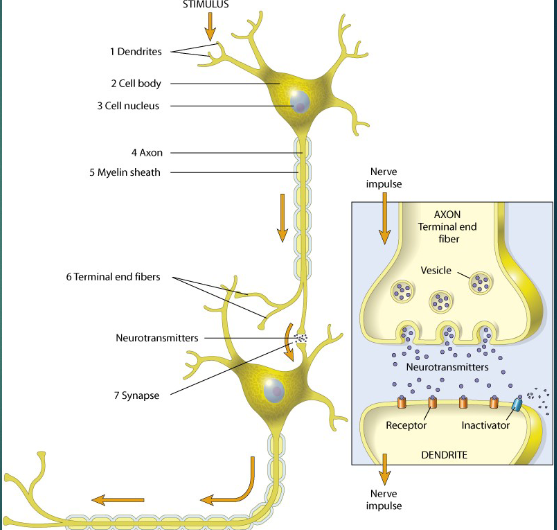
-dendrites
-cell body
-cell nucleus
-axon
-myelin sheath
-terminal end fibers
-synapse
What are the cerebrum's surface nerve cells?
cerebral cortex
What is the cerebrum responsible for?
speech, vision, speech, smell, movement, hearing and thought
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
coordinates voluntary movements and maintains balance
What does the hypothalamus do?
- It controls temp., sleep, appetite and emotions.
- Regulates hormones from pituatary gland
- Monitors par/sympathetc nervous systems
What are the meninges?
Layers that protect the brain.
What are the layers of the meninges?
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid membrane
3. Pia mater
What is the chemical released at the ends of nerve cells?
acetylcholine
Where do afferent nerves send messages to?
Towards the brain and the spinal cord.
What is the middle layer that surrounds the brain and spinal cord?
Arachnoid membrane
What does the axon do?
Carries impulse along a nerve cell.
Where is the brainstem and what does it do?
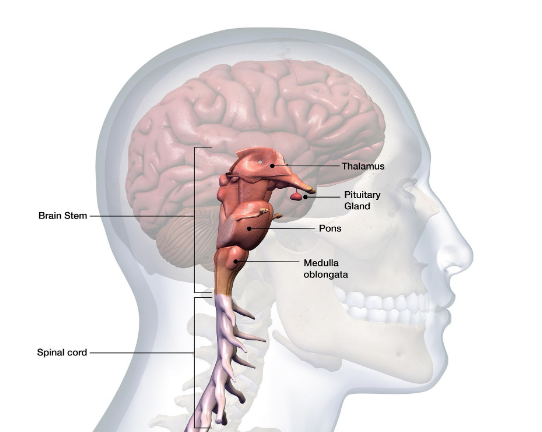
Posterior side of the brain; connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord.
What moves throughout the brain and spinal cord?
cerebrospinal fluid
What is the largest part of our brain?
The cerebrum
In a nerve cell, what part of its structure receives the impulse first?
Dendrites
Where does the efferent nerve send the messages?
Away from the brain, towards the body.
What does the myelin sheaths do?
Speeds impulse conduction.
The thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges is the:
pia mater
What is the combining form of cerebellum?
cerebell/o
What is the combining form of cerebrum?
cerebr/o
What is the combining form of dura mater?
dur/o
What is the combining form of brain?
encephal/o
What is the combining form of membranes/meninges?
mening/o or meningi/o
What is the combining form of muscle?
my/o
What is the combining form of spinal cord?
myel/p
What is the combining form of excessive sensitivity to pain?
alges/o or -algesia
What is the suffix for pain?
-algia
What is the combining form of burning?
caus/o
What is the combining form of deep sleep?
comat/o
What is the combining form of feeling or nervous sensation?
ethesi/o or -esthesia
What is the combining form of movement?
kines/o, -kinesia, -kinesis, kinetic
What is the combining form of word, phrase?
lex/o
What is the suffix for seizure?
-lepsy
What is the suffix for paralysis?
-plegia
What is the suffix for speech?
-phasia
Which term means nerve pain?
Neuralgia
Which type of hematoma occurs between the skull and the dura as a result of a ruptured meningeal artery, usually after a fracture of the skull?
epidura