Fluids
Fluids are characterized by their ability to flow and conform to the shapes of their containers.
Solids
Solids do not flow and are rigid enough to retain a shape independent of their containers.
Both liquids and gases are _____.
fluids
Both fluids and solids can _____, although only solids can _____.
exert forces perpendicular to their surface
withstand shear (tangential) forces.
Density
The ratio of an object's mass to its volume
Density is a _____ quantity.
scalar
Equation for density
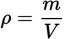
SI units for density
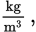
Alternative units for density
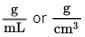
Density of water
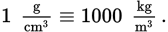
Conversion between mL and cm3
1 mL = 1 cm3
Conversion between L and m3
1000 L = 1 m3
Weight equation
Fg = ρVg
Specific gravity
The density of a fluid compared to that of pure water at 1 atm and 4°C
Specific gravity formula (with units)
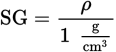
unitless
When an object's density is given in g/cm3, the specific gravity is simply ...
... the density as a dimensionless number.
Pressure
Pressure is a ratio of the force per unit area.
Equation for pressure
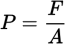
P = pressure
F = magnitude of the force vector
A = area
SI unit for pressure
pascal (Pa)
Pascal in base SI units
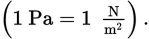
3 other common units of pressure
mercury (mmHg)
torr
atmosphere (atm)
Conversion between the four common units of pressure
1.013 × 105 Pa = 760 mmHg ≡ 760 torr = 1 atm
Pressure is a _____ quantity because ...
scalar
... pressure is calculated from the magnitude of the force vector.
No matter where one positions a given surface, the pressure exerted on that surface within a closed container will be _____, neglecting gravity.
the same
Pressure is the same at all points along the walls of a container and within the space of the container itself; therefore, pressure applies _____ and, therefore, is a _____.
in all directions at any point
scalar
When unequal pressures are exerted against objects, the forces acting on the object will add _____, possibly resulting in _____.
in vectors
acceleration
Atmospheric pressure
The pressure within the atmosphere of Earth
Why don't we feel atmospheric pressure?
Our internal organs exert a pressure that perfectly balances it.
Atmospheric pressure changes with _____.
altitude
Atmospheric pressure impacts a number of processes, including _____ (biological) and _____ (physical, think camping).
hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen
the boiling of liquids.
Absolute (hydrostatic) pressure
Absolute (hydrostatic) pressure is the total pressure that is exerted on an object that is submerged in a fluid.
Equation for absolute pressure
P = P0 + ρgz
P = absolute pressure
P0 = incident or ambient pressure
ρ = density of the fluid
g = acceleration due to gravity
z = depth of the object
Incident or ambient pressure
The pressure at the surface
Do not make the mistake of assuming that P0 always stands for _____.
atmospheric pressure
Think of absolute pressure like diving in a pool:
At the surface of the water, the absolute pressure is usually equal to the atmospheric pressure (P0). But if you dive into the pool, the water exerts an extra pressure on you (ρgz), in addition to the surface pressure. You feel this extra pressure on your eardrums.
Gauge pressure
Gauge pressure is the amount of pressure in a closed space above and beyond atmospheric pressure.
Equation for gauge pressure
Pgauge = P – Patm = (P0 + ρgz) – Patm
Note that when P0 = Patm, then Pgauge = P – P0 = ρgz at a depth z.