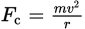Objects can undergo only two types of motion—that which is _____ or that which is _____.
constant (with no acceleration)
changing (with acceleration)
In linear motion, the object’s velocity and acceleration are _____.
along the line of motion, so the pathway of the moving object continues along a straight line.
Kinematic equations
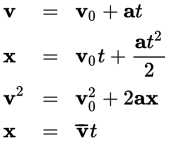
Acceleration due to gravity
9.8 m/s2
free fall
Motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it
terminal velocity
The maximum velocity attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid
Air resistance _____ the motion of an object.
opposes
An object in free fall will experience a growing _____ as the magnitude of its velocity increases.
drag force
Projectile motion is motion that follows a path along _____.
two dimensions
Inclined planes equations for gravity
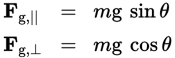
Circular motion occurs when forces cause an object to move in a _____.
circular pathway
In uniform circular motion, the instantaneous velocity vector is always _____.
tangent to the circular path
A centripetal force is a force that makes a body _____.
follow a curved path.
In what direction does centripetal force point?
perpendicular to the instantaneous velocity vector
In what direction does an object accelerate when travelling in a circle? What is this type of acceleration called?
towards the center of the circle
centripetal acceleration
Equation for circular motion