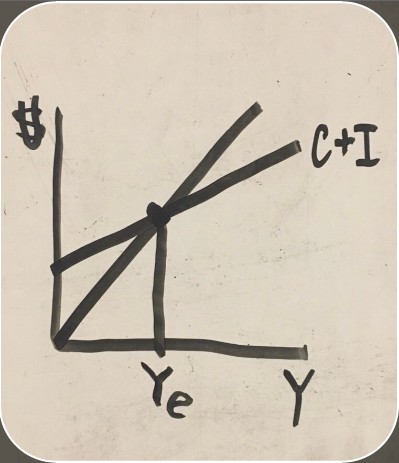
non-descriptive aggregate spending graph
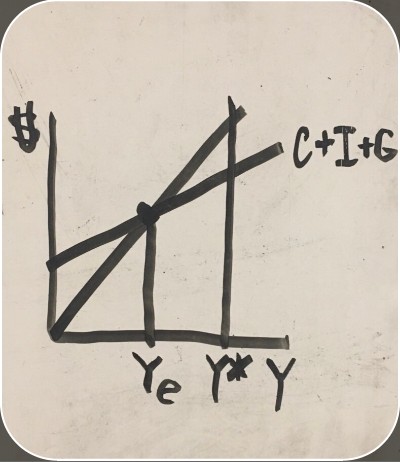
recession on an aggregate spending graph
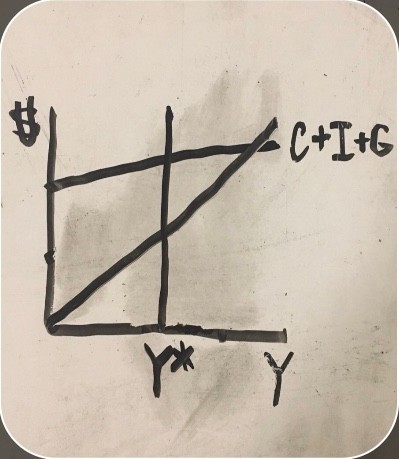
inflation on an aggregate spending graph
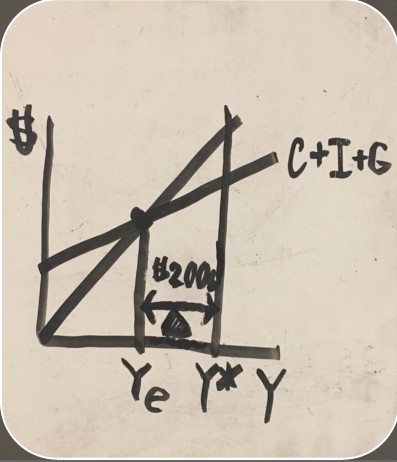
size of a recession on an aggregate spending graph

potential GDP (aggregate spending graph)

equilibrium (aggregate spending graph)
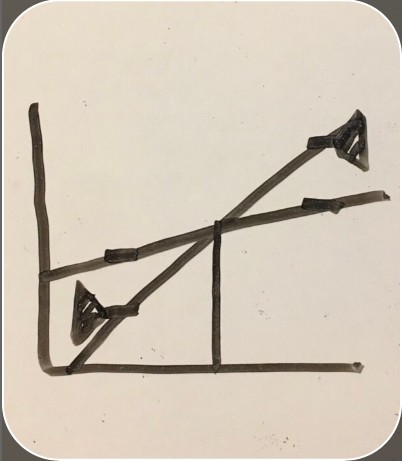
amount of goods being produced
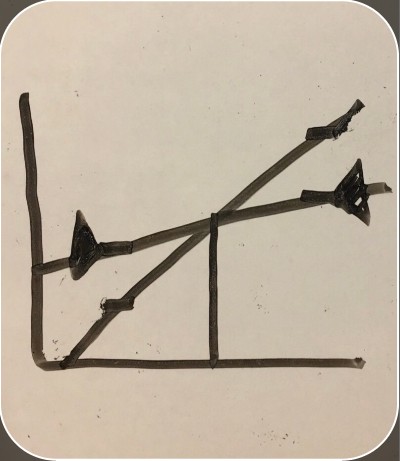
amount of goods being consumed
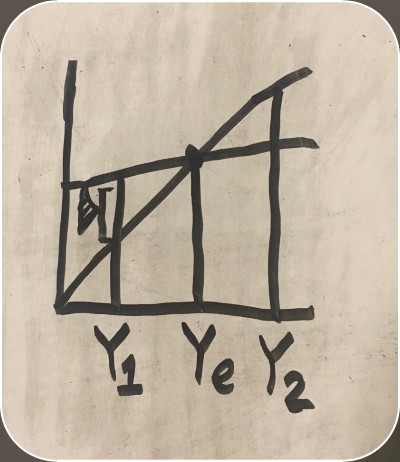
decreasing inventory

increasing inventory
fiscal policy
when the government changes spending, taxes, and/or transfer payments
G (fiscal policy)
government spending
T (fiscal policy)
taxes
TR (fiscal policy)
transfer payments
fiscal policy actions that can end a recession
increasing government spending, decreasing taxes, and increasing transfer payments
government spending multiplier formula

tax multiplier formula

transfer payments multiplier formula

how to calculate the fix for a recession
Use one of the formulas to calculate the multiplier, then divide the monetary amount of the recession by the multiplier.
how to use two policies to fix a recession
split the GDP distance so that half can be fixed with one policy and half can be fixed with the other, then proceed as normal
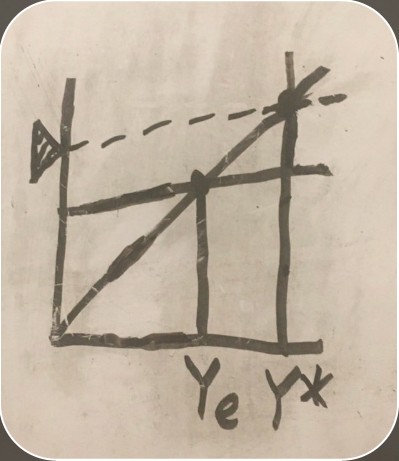
economic growth from fiscal policy

new equilibrium created by fiscal policy
example of a regressive tax
sales tax
example of a progressive tax
income tax
main issue of a recession
unemployment
unemployment rate definition
percentage of labor force (aged 16 or older) who want to work, but are without jobs
full employment rate of employment
4%-5%, not 0%
situation if unemployment is equal to job vacancies
the unemployment rate is still the amount of the labor force aged 16 and older who want to work but do not have jobs
effect on model if unemployment is equal to job vacancies
the model is at full employment, so nothing needs to be done to stimulate the economy
frictional unemployment
percentage of people in-between jobs
structural unemployment
longer-term frictional unemployment due to having to move or train for the new job
problems with unemployment
financial hurt of the unemployed, social ills with unemployment, in a recession, everyone’s income grows more slowly and lost production is permanent
inflation
a general increase in prices
price index
index used to measure inflation
C.P.I.—Consumer Price Index
price index that measures the change in prices in goods and services that consumers consume
P.P.I.—Producer Price Index
price index that measures the change in prices in goods and services that producers consume; also influences C.P.I.
GDP deflator
used to calculate real GDP
problems with inflation
fixed incomes’ purchasing power decreases, it destroys price information, and it affects lending and borrowing (making lending riskier)
ideal inflation rate
1.5%-2%
one thing that resists price reductions
wages
effect of wage raises not being given during inflation
real wages decrease
automatic stabilizers
unemployment compensation, graduated income tax, and spending rigidities
fiscal drag
stabilizers when preventing the eradication of inflation or a recession by reducing the size of the multiplier
deficit
this year’s debt or surplus number
debt
total debt
surplus
a negative deficit that makes debt decrease
surplus equation
T>G+TR
deficit equation
T<G+TR
balanced budget equation
T=G+TR
budget philosophies
annually balanced budget, full employment balanced budget, and discretionary fiscal policy
annually balanced budget effect
causes destabilization by stimulating inflated economies and increases deficit
full employment balanced budget effect
balances the economy only if it is at full employment and has a neutral impact on the economy
discretionary fiscal policy effect
stabilizes the economy while making surpluses and deficits worse
investment multiplier formula
same as the government spending multiplier
how to calculate an equilibrium output increase
Use the investment multiplier formula to calculate the multiplier, then multiply the amount of the investment by the multiplier."