Diffusion
movement of solutes from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Simple Diffusion
(passive movement no ATP)
Simple diffusion carries things across the membrane and does not require help or ATP (pumps), it uses kinetic energy, the energy of movement
Facilitated Diffusion
(passive movement no ATP)
is diffusion that requires help through the use of enzymes
Osmosis
the movement of h2o from an area of low concentration of solutes to high concentration of solutes
Filtration
The separation of molecules across a filter using hydrostatic pressure
Semi-permeable
certain factors allow things inside a membrane
Factors that affect diffusion
Permeability goes up and the rate of diffusion increases
Temperature goes up and the rate of diffusion increases
Size/Mass affects the rate of diffusion (inverse relationship)
Concentration gradient affects the rate high to low is faster, low to high is slower
Steepness of gradient increases the rate
Carrier mediated facilitate diffusion
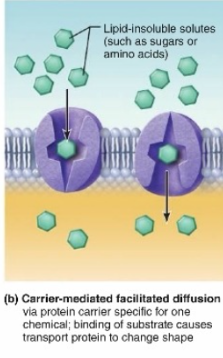
(passive movement no ATP)
Requires the right size, shape, charge -> comes in contact with the protein (enzyme) -> binding/bonding -> shape is changed (conformational change) -> enzyme flops over and closes the outside and opens the inside > allows it in the membrane
Channel mediated facilitated diffusion
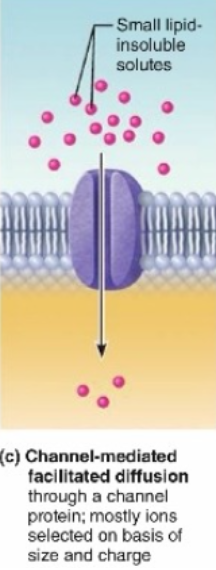
(passive movement no ATP)
Enzyme does not change shape and is always open, but only allows ions based on size and charge
Describe how molecular size can affect diffusion through a semipermeable membrane
Larger molecules move more slowly than smaller molecules due to their greater size and weight
This is an inverse relationship
State the forces that drive the process of filtration
Hydrostatic pressure
Identify the factors that determine the amount of filtrate that will be formed
The separation of molecules across a filter using hydrostatic pressure depends on the relative size of the particle and the hole
isotonic
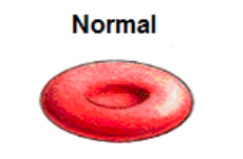
no net movement of water, equal amount of solutes inside and outside the cell
hypertonic

high amount of solutes outside the cell and low amount of solutes inside the cell
hypotonic

water enters the cell because of the low amount of solutes outside of the cell
hypertonic

more tonicity, more solutes outside the cell, water moves out of the cell causing the cell to shrink
isotonic
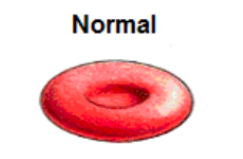
no net movement of water, an equal amount of solutes inside and outside the cell
plasma membrane
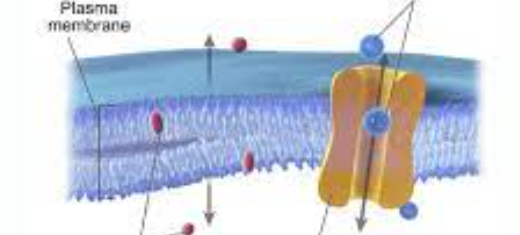
function : allows for selective permeability in and out of the cell
nucleus
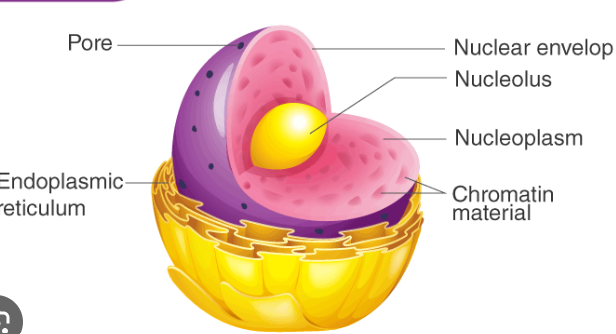
function : cell's control center and creates DNA
nucleolus
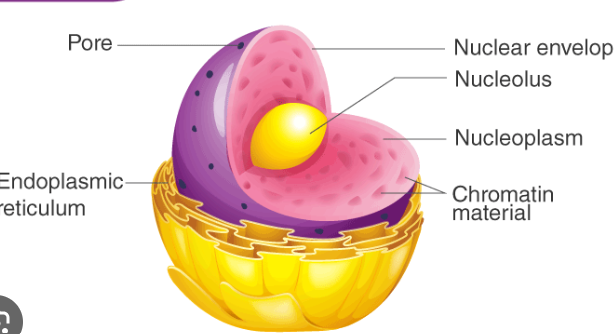
function : creates RNA and ribosomes
Nuclear envelope
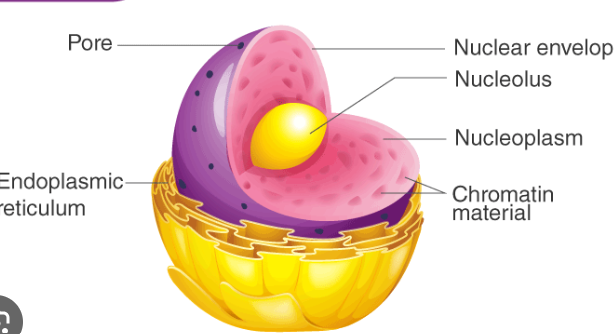
function : outer boundary of the nucleus that separates it from the cytoplasm outside the nucleus
Nuclear Pores
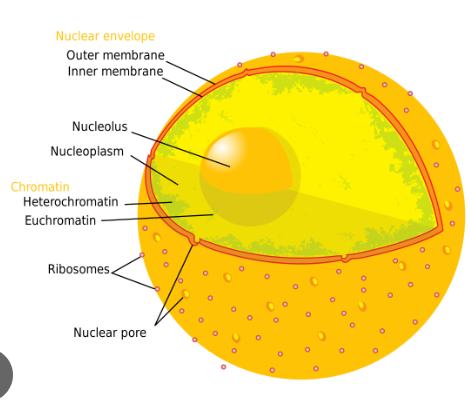
allows small molecules like proteins and RNA in and out of the nucleus
Centrioles
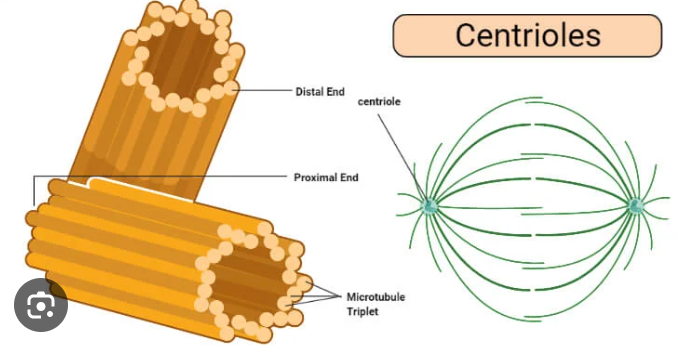
ensures the correct amount of DNA goes to each cell after mitosis as well as the organization of microtubules
Rough endoplasmic Reticulum
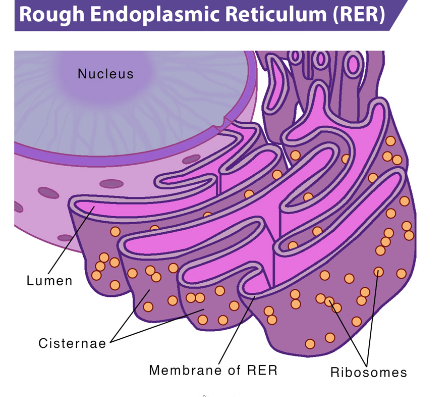
membranous organelle that is responsible for storing ribosomes as well as transporting the ribosomes to the Golgi apparatus
ribosomes
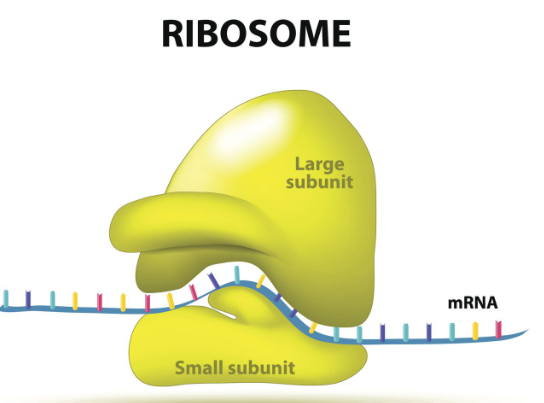
site of protein synthesis reads the mRNA sequence and turns it into proteins
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
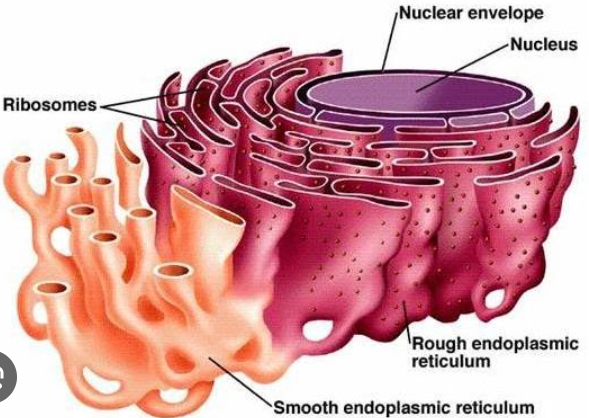
site of steroid (cholesterol) and lipid synthesis
Golgi apparatus
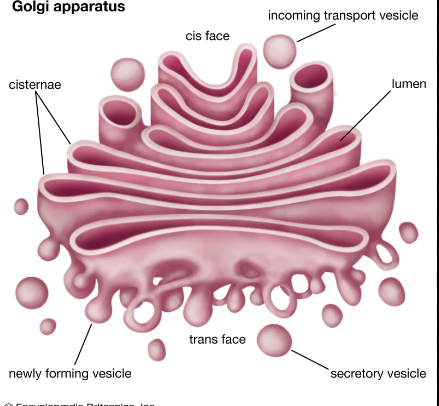
packages, modifies and sorts proteins for exocytosis
mitochondria
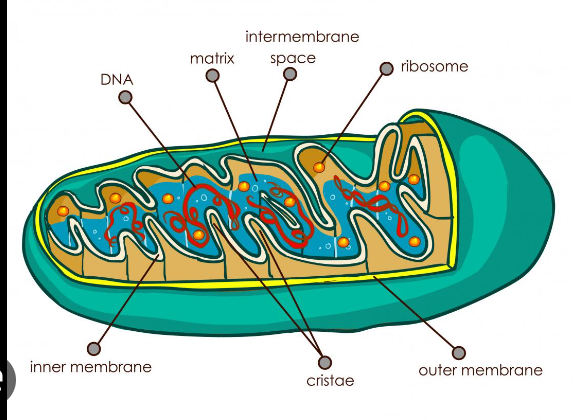
site of ATP synthesis contains folds of cristae that increase surface area to maximize ATP synthesis