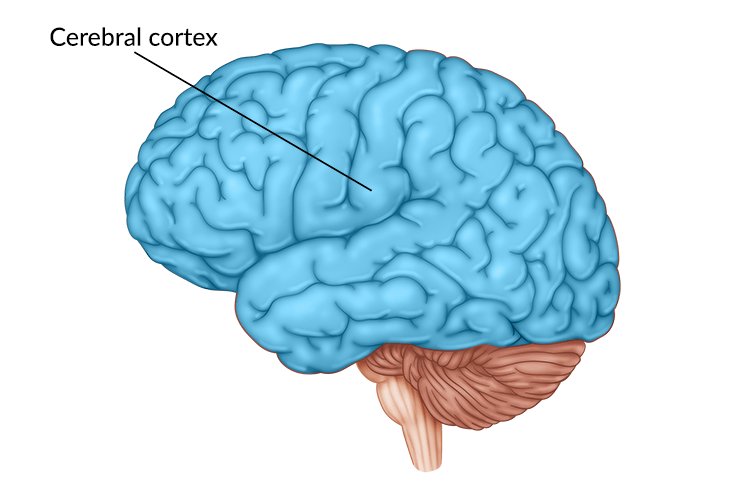
Cerebral Cortex - higher level processing memory/reasoning/emotion
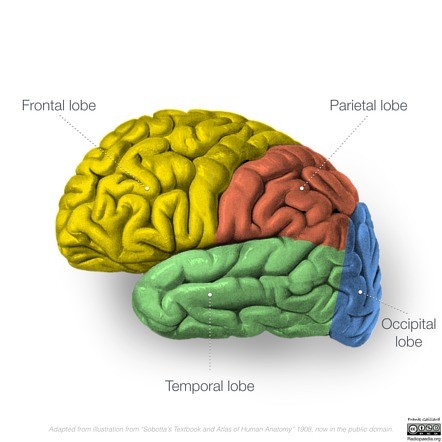
1. Frontal lobe - voluntary movement, high level cognitive skills planning, memory, language
2. Parietal lobe - somatosensory info such as touch, pain ,temp.
3. temporal lobe- hearing
4. occipital lobe - vision perception
5. insula lobe - links sensory experience and emotional valence
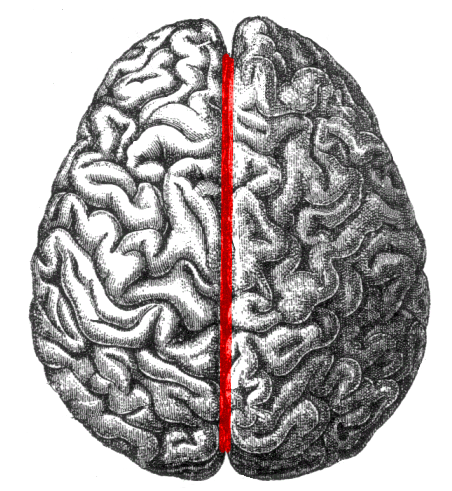
Longitudinal fissure - separates brain into two hemispheres
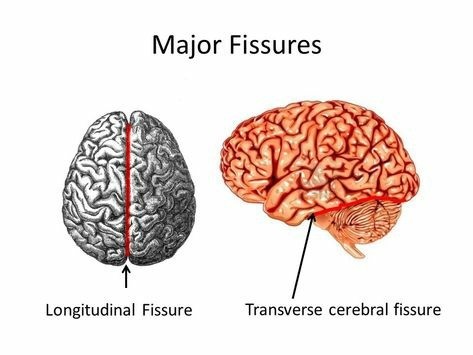
Transverse fissure - divides cerebrum from the cerebellum
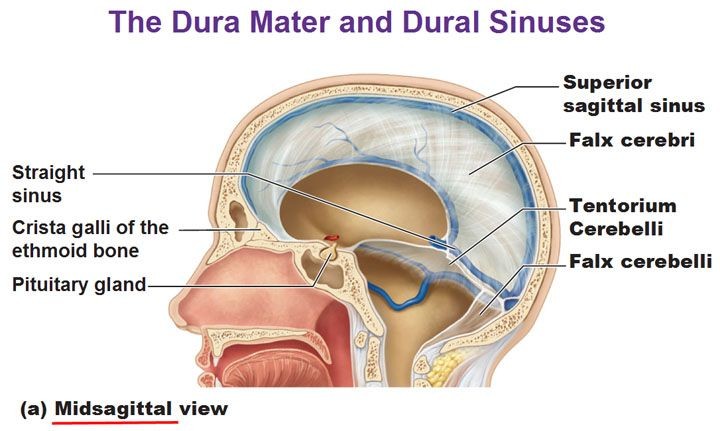
Falx cerebri - separates the cerebral hemispheres
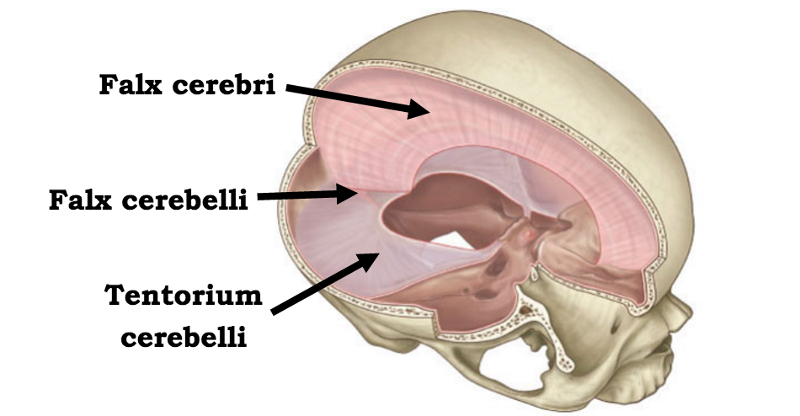
Tentorium Cerebelli - partition, dispelling burden of weight from supratentorial structures from inferior brain matter.
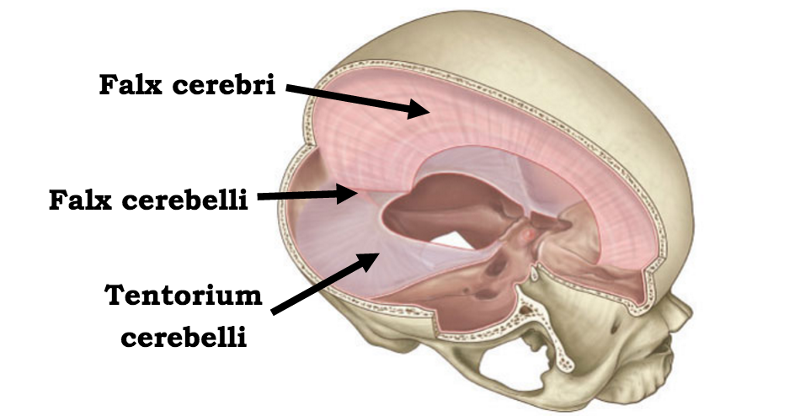
Falx Cerebelli - : the smaller of the two folds of dura mater separating the hemispheres of the brain that lies between the lateral lobes of the cerebellum.
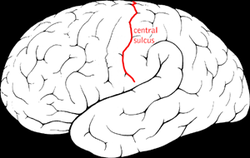
Central sulcus - divides pre/post central gyri which all motor and sensory functions are organized
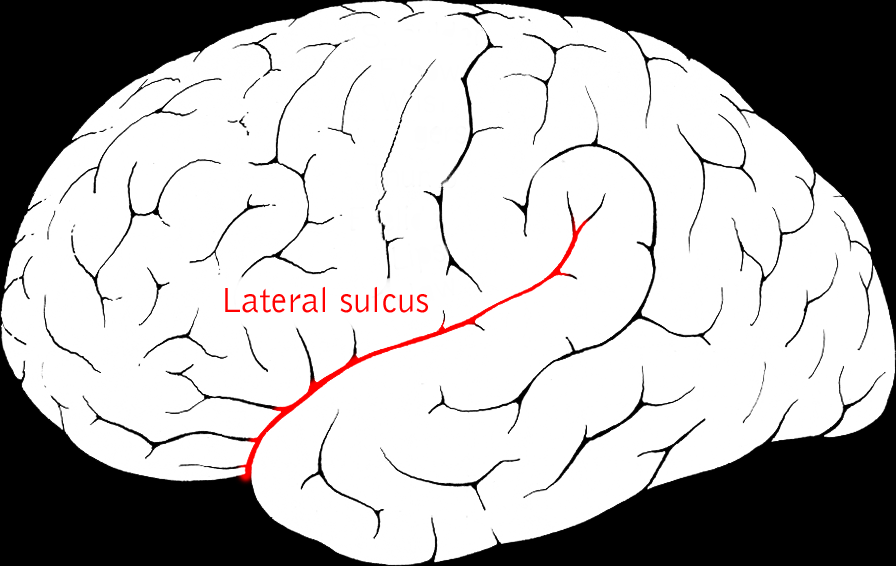
Lateral sulcus - separate the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
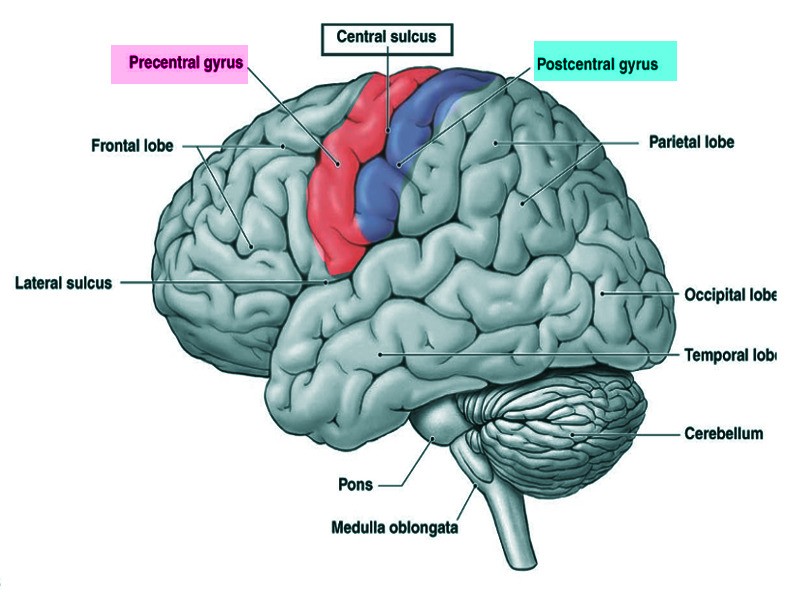
1. Precentral - voluntary motor movements
2. Postcentral - involuntary functions, somatic sensory cortex
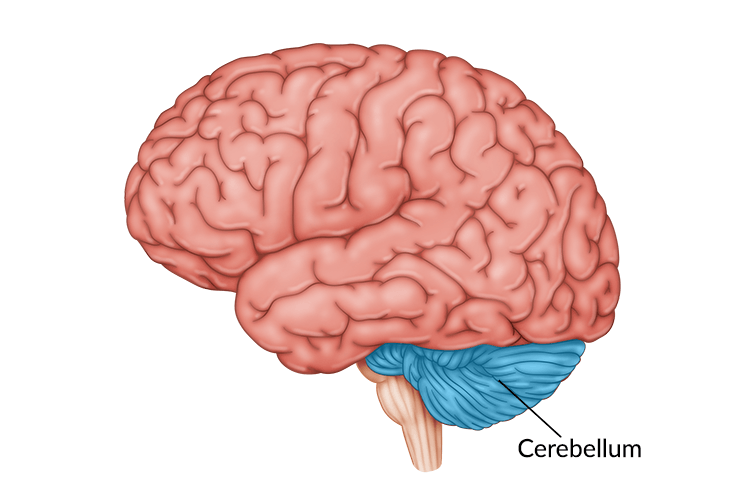
Cerebellum - balance, coordinates movement, vision, motor learning
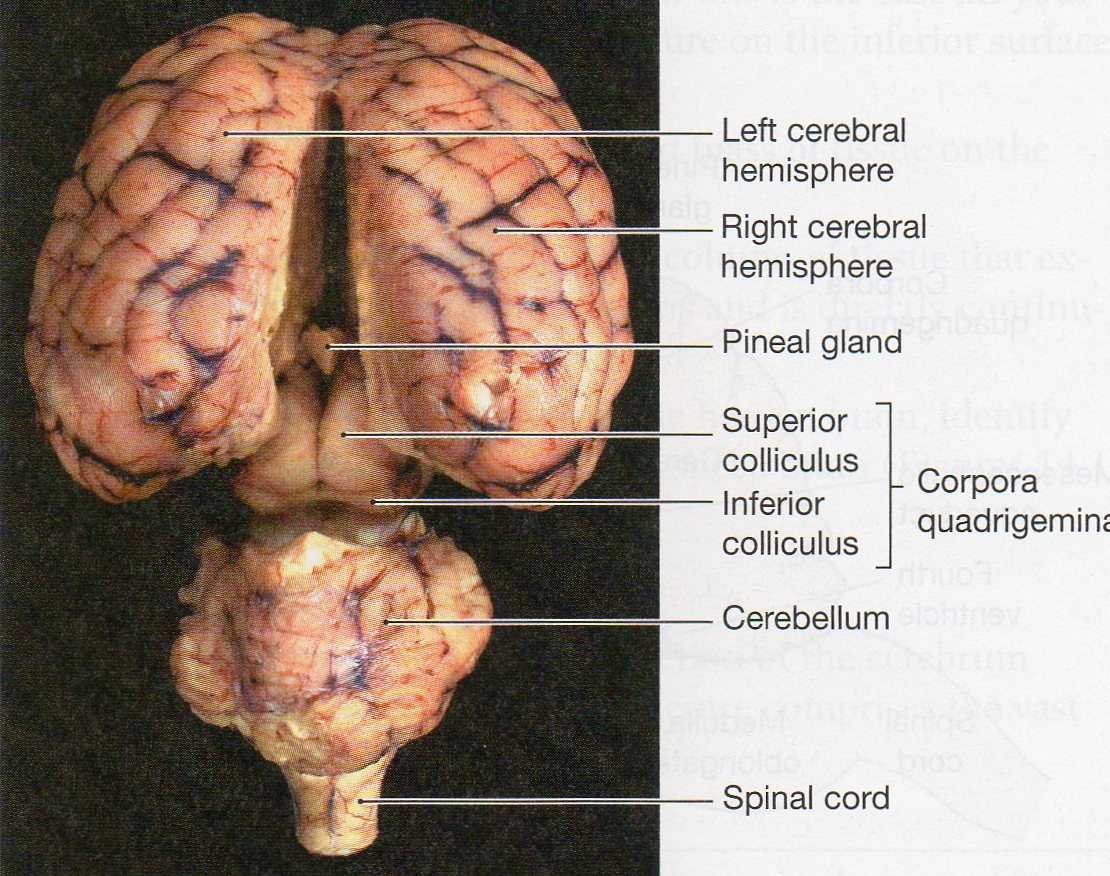
Corpora quadrigemina - controls position of head and eyes in response to visual auditory and somatic stimuli.
Superior = optic
inferior = auditory
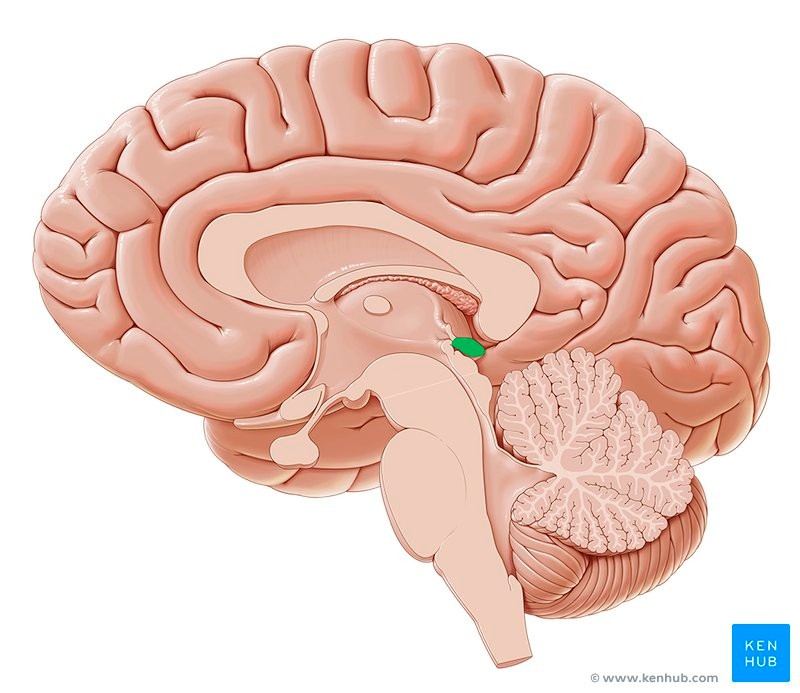
Pineal Gland - The main function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and convey this information to produce and secrete the hormone melatonin.
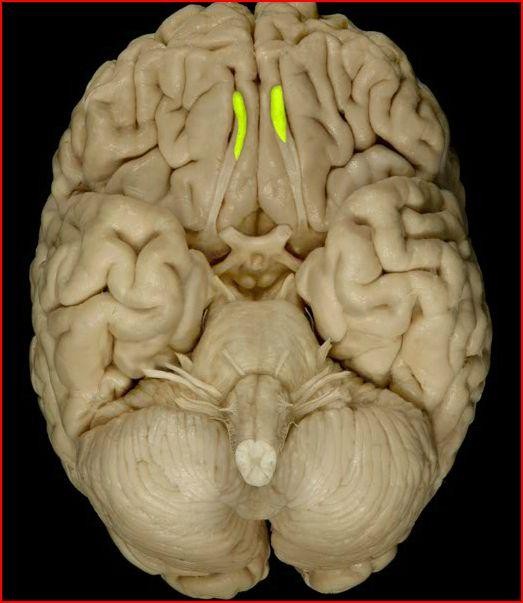
Olfactory bulb - receive info about smells from the nose and send it to the brain by ways of olfactory tracts.
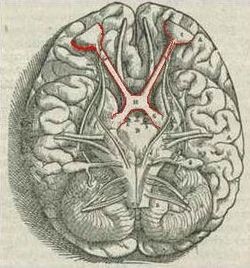
Optic chiasm - where optic nerves cross and primary importance of visual pathway
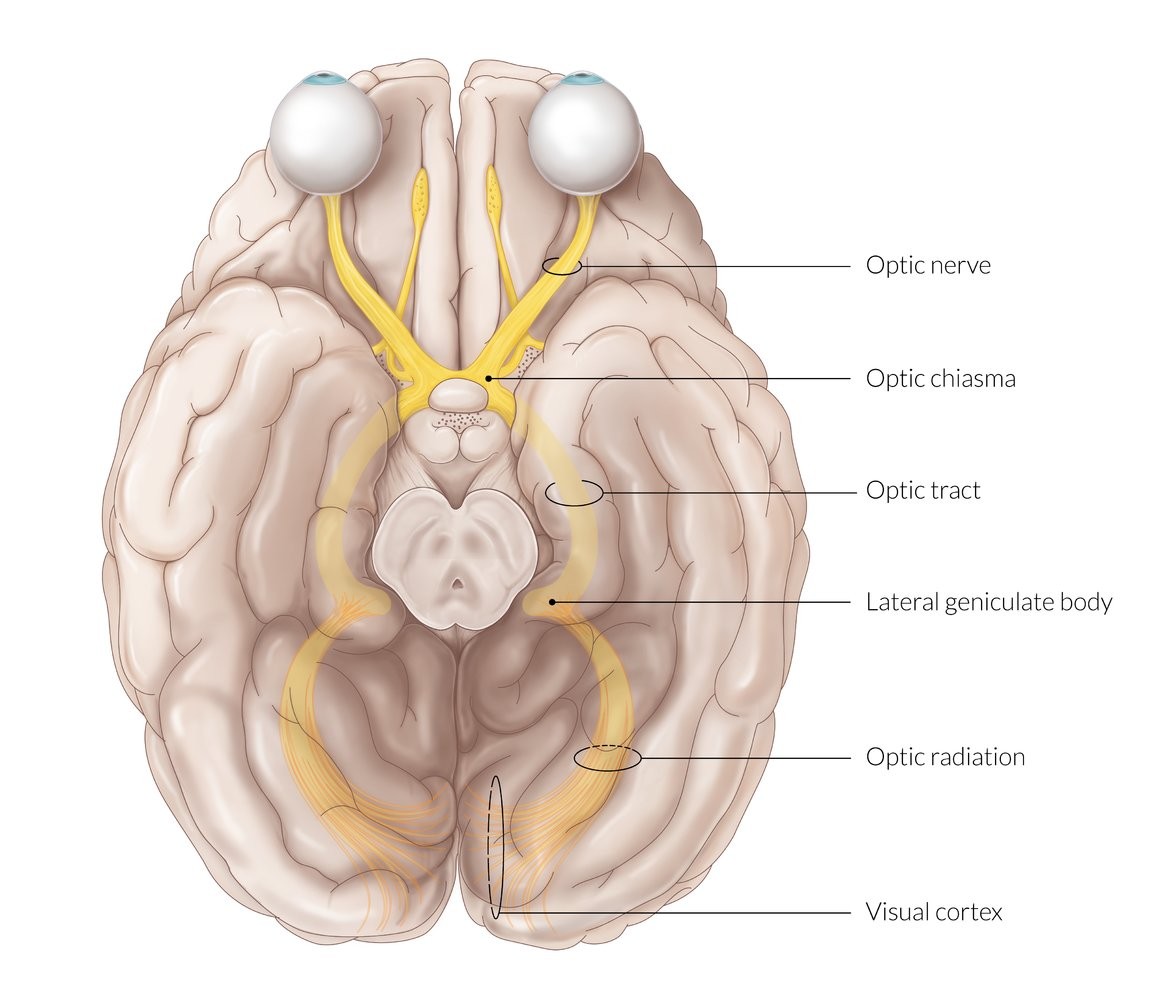
Optic nerves - transmits impulses from eyes to brain, light reflex/accomodation reflex.
Optic tracts - bundle of nerve fibers that carry visual info from the optic chiasm to brain.
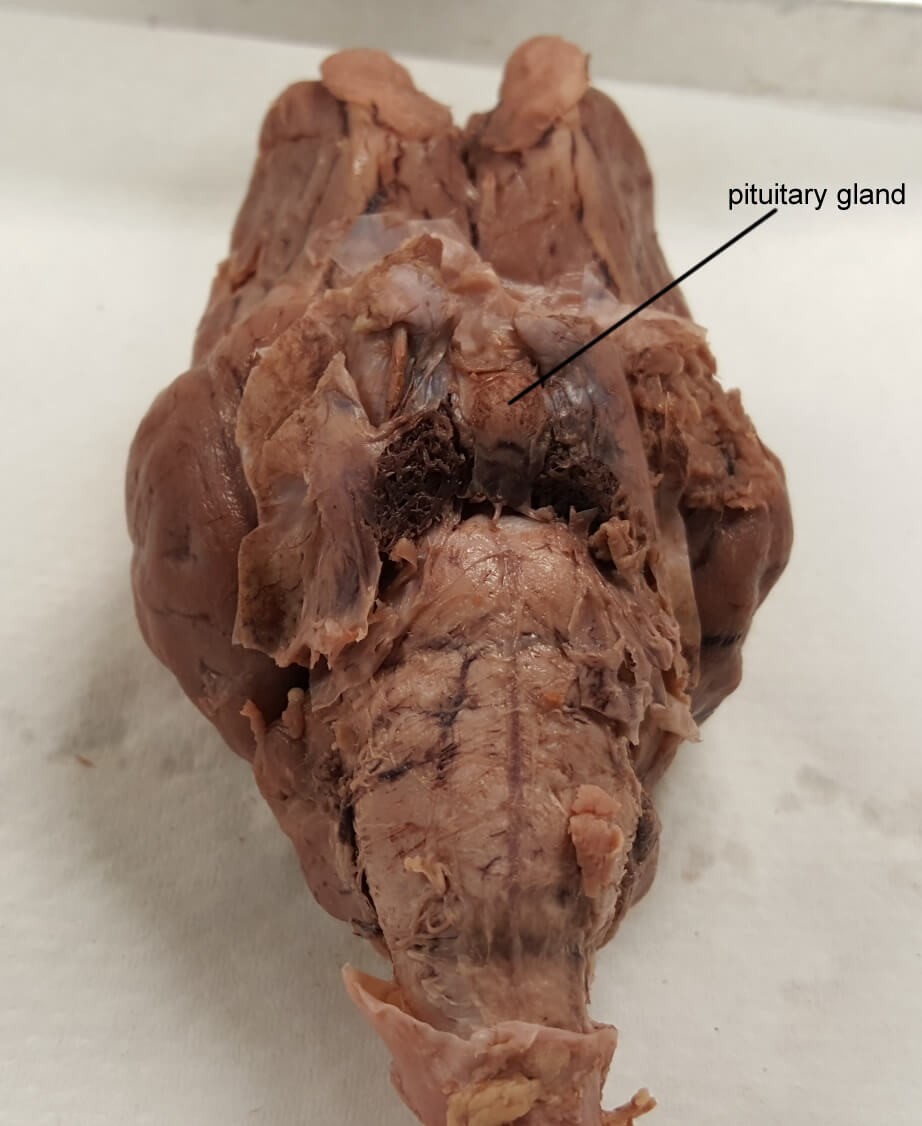
Pituitary gland - produce and release several hormones that carry out important bodily functions such as growth and metabolism.
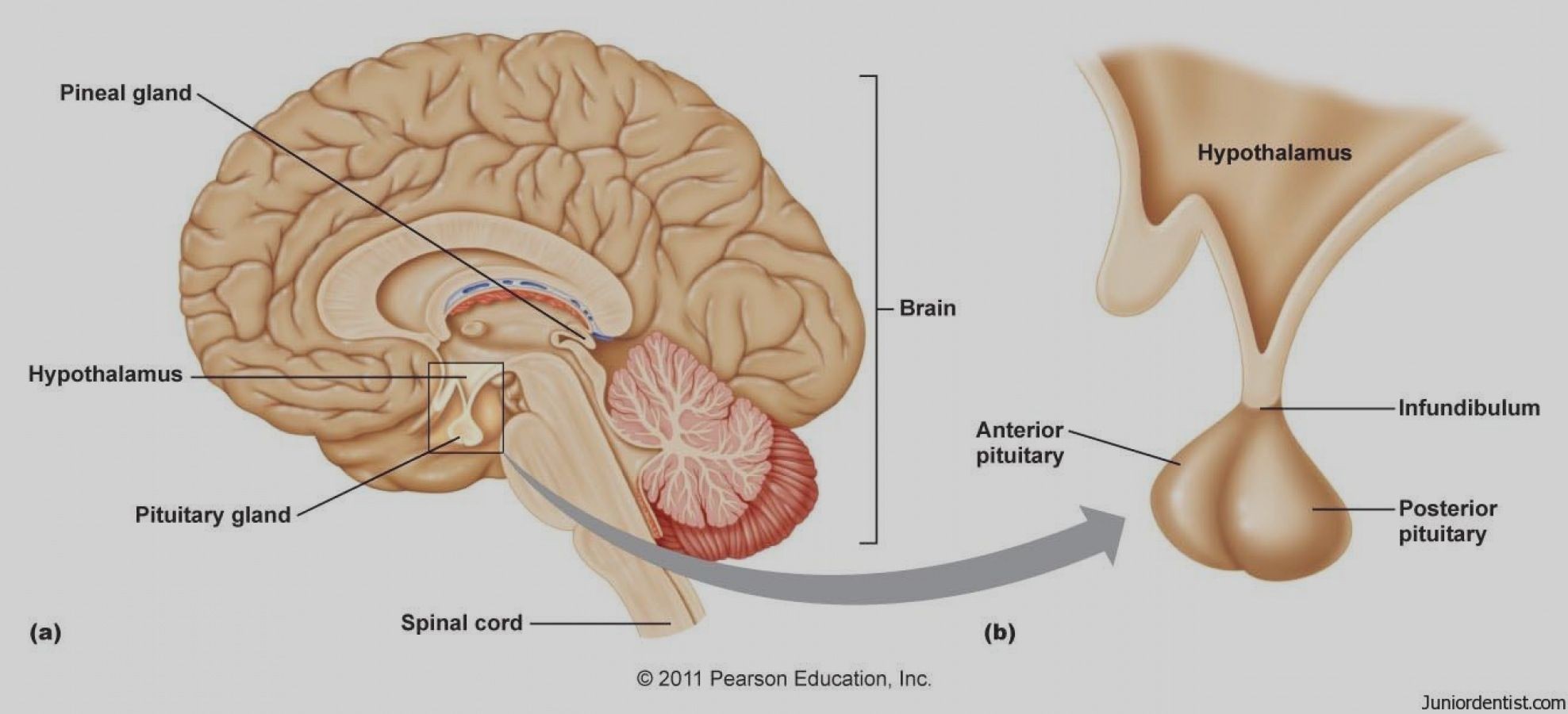
Infundibulum - connects pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
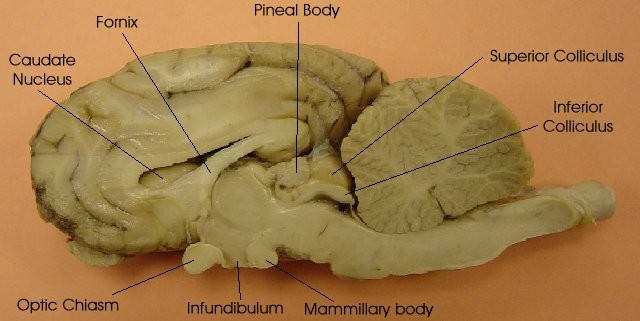
Mammillary body - part of limbic system (emotions) relay station in olfactory pathway and control motor reflexes associated with eating.
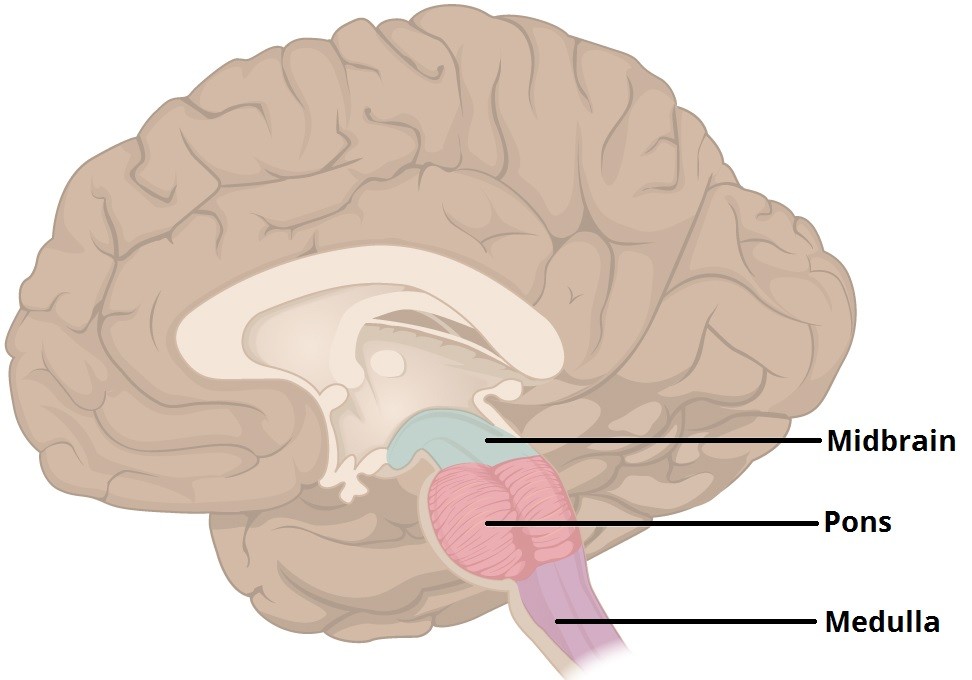
Pons - the part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus. handles unconscious processes and jobs, such as your sleep-wake cycle and breathing
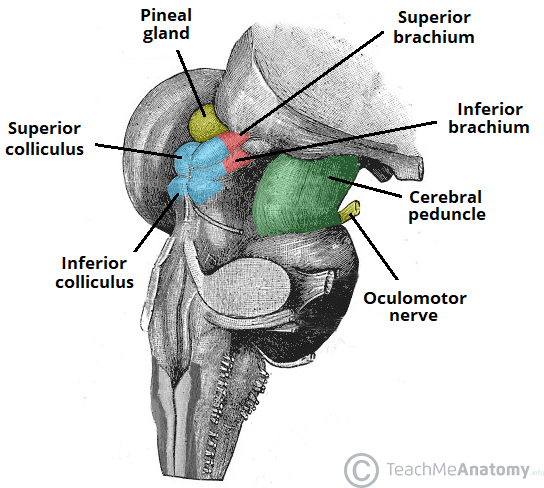
Cerebral Peduncles - assist refining motor movements, learning new motor skills, converting proprioceptive info into balance and posture maintenance.
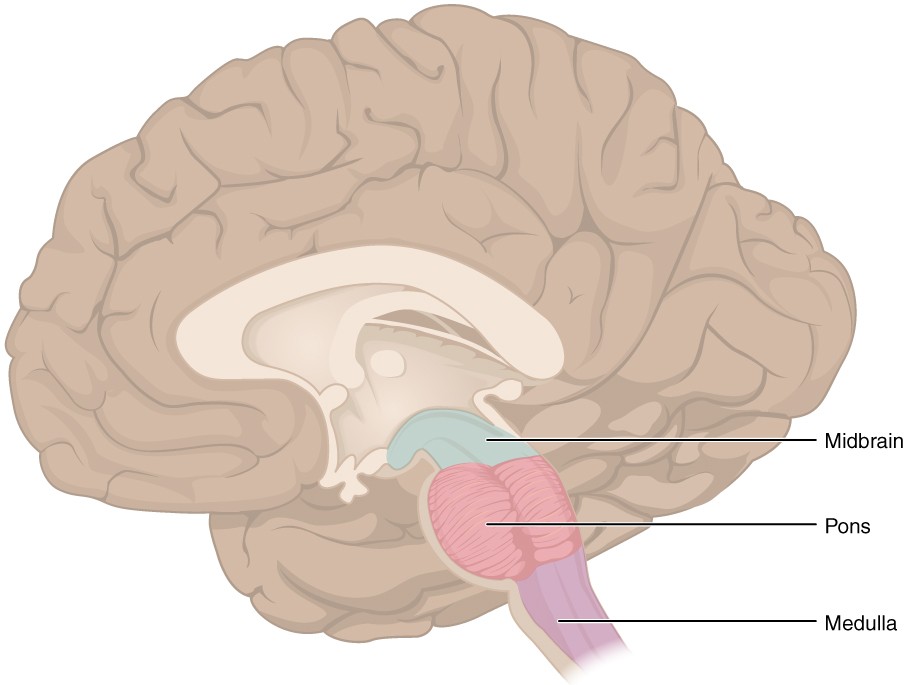
Medulla oblongata - bottom most part of brain, where brain and spinal cord connect. Controls vital process such as HR, BP and breathing.
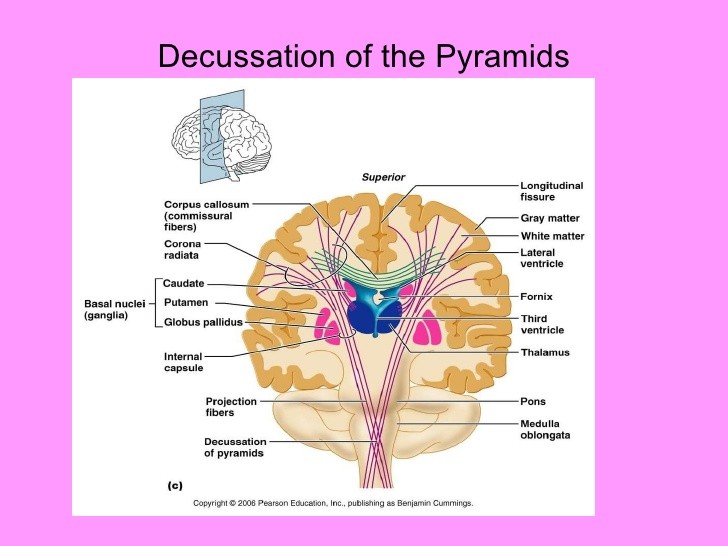
Pyramids (decussation) - Section of the medulla oblongata at the level of the decussation of the pyramids. The two pyramids contain the motor fibers that pass from the brain to the medulla oblongata and spinal cord. These are the corticobulbar and corticospinal fibers that make up the pyramidal.
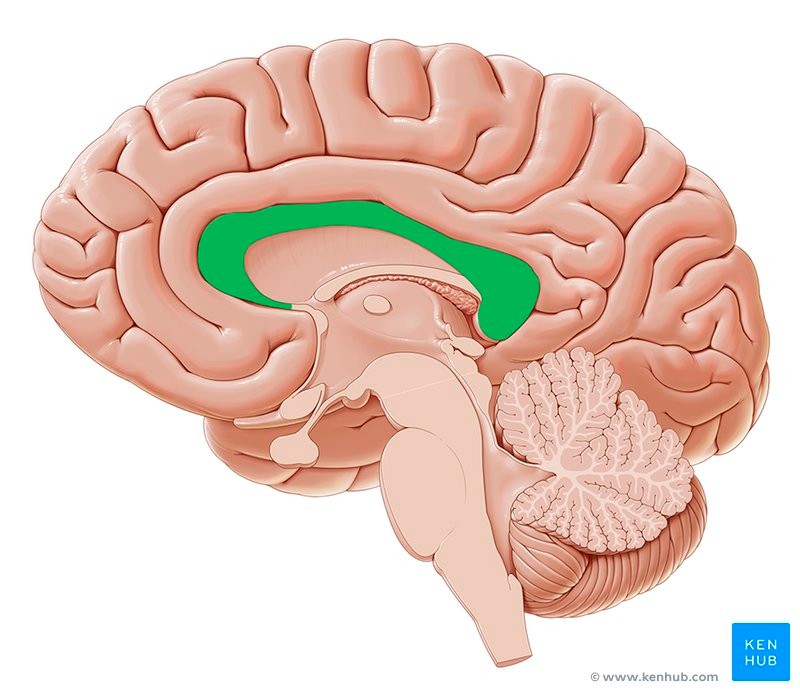
Corpus callosum - ensures both sides of the brain can communicates and send signals to one another.
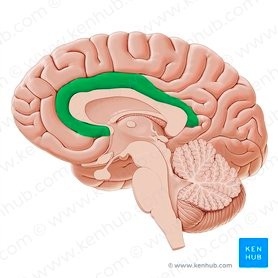
Fornix -white matter bundle connect various nodes of limbic circuitry play a key role in cognition and episodic memory recall.
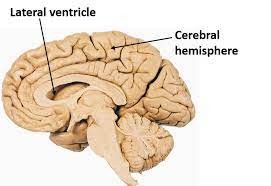
Lateral ventricle - contain CSF that provides cushioning for the brain while also helping circulate nutrients and remove waste.
Septum pellucidum - acts as a partition between a portion of the lateral ventricles.
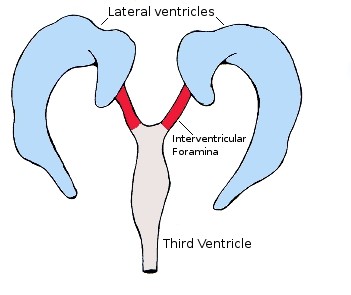
Interventricular foramen - connects lateral ventricles and third ventricle. Allows CSF to pass through them.
Third Ventricle - produce, secrete, and convey CSF
Choroid plexus - major site of CSF production
Thalamus - Your thalamus is your body's information relay station. All information from your body's senses (except smell) must be processed through your thalamus before being sent to your brain's cerebral cortex for interpretation. Your thalamus also plays a role in sleep, wakefulness, consciousness, learning and memory
Hypothalamus - Its main function is to keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis. It does its job by directly influencing your autonomic nervous system or by managing hormones
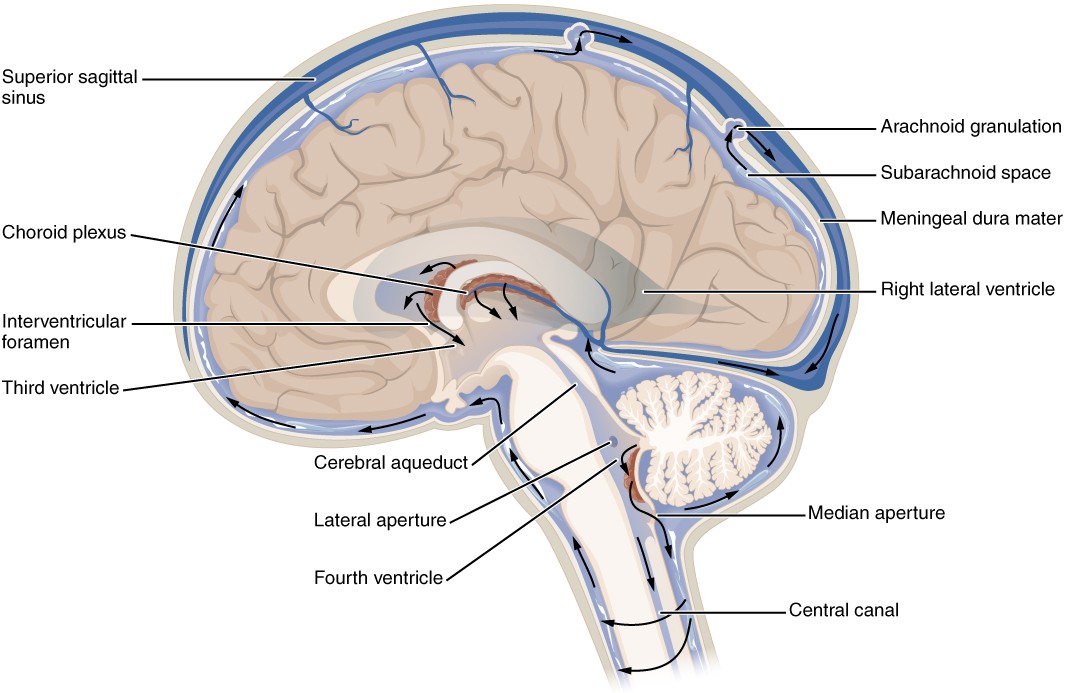
Cerebral aqueduct - allows CSF to flow from 3rd to 4th ventricle
Fourth ventricle - The main function of this ventricle is to protect the human brain from trauma (via a cushioning effect) and to help form the central canal, which runs the length of the spinal cord. This ventricle has a roof and a floor.
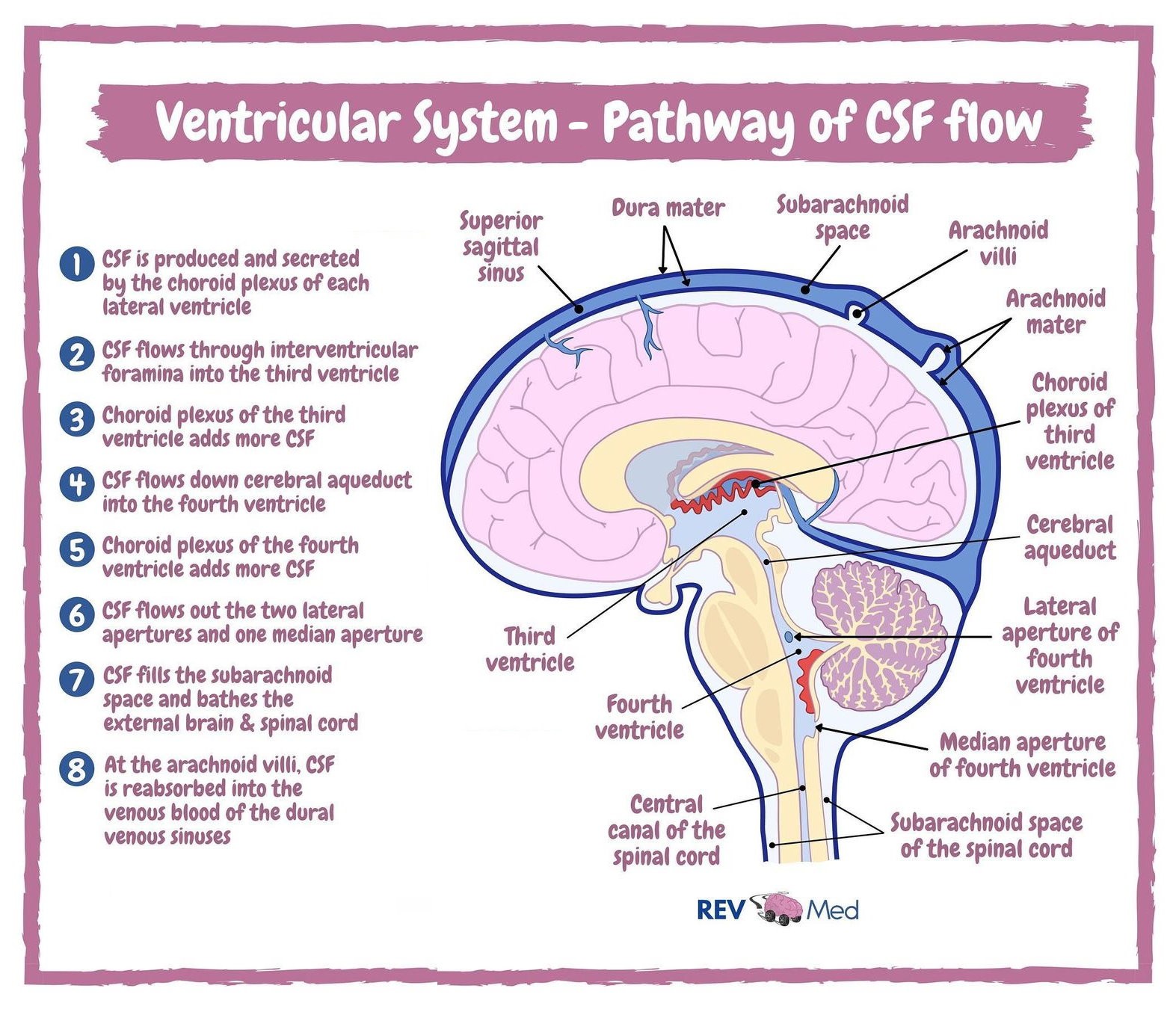
Flow of CSF
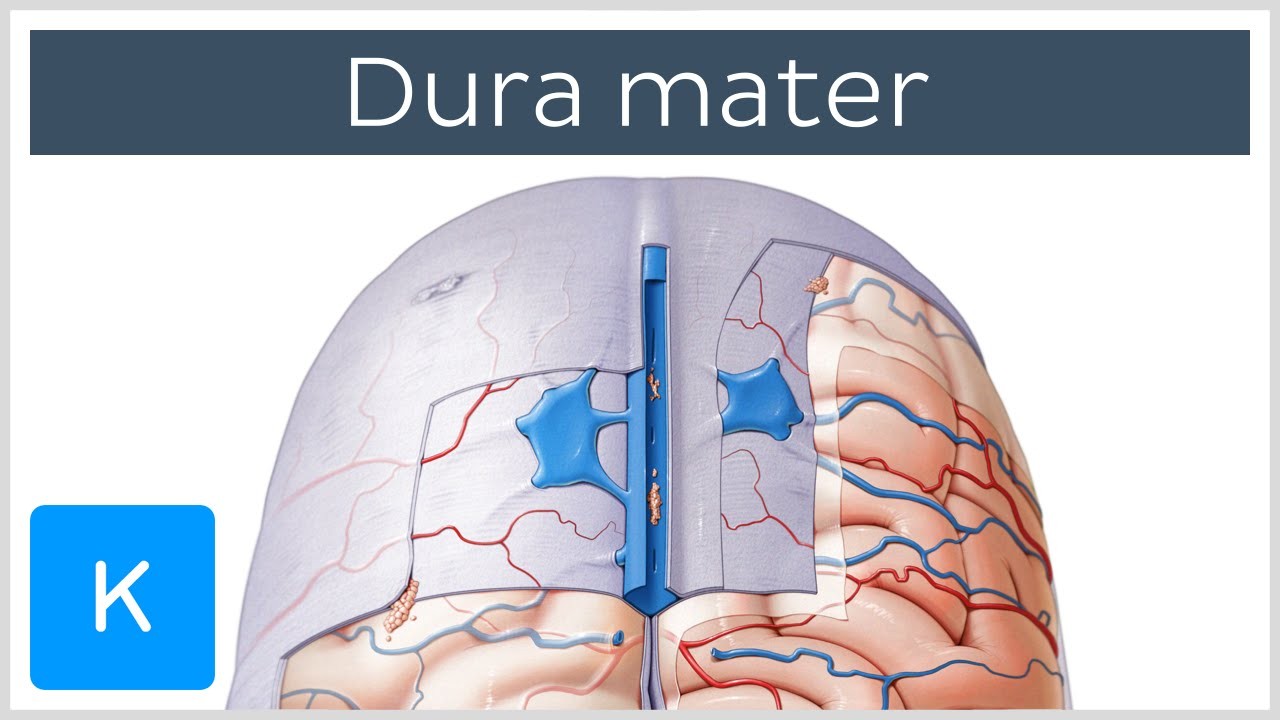
Dura mater - protect brain, Your dura mater contains a drainage system, called the dural venous sinuses, which allows blood to leave your brain and allows cerebrospinal fluid to re-enter the circulation. Your dura mater receives its blood supply from your middle meningeal artery and vein, and your trigeminal nerve runs through it.
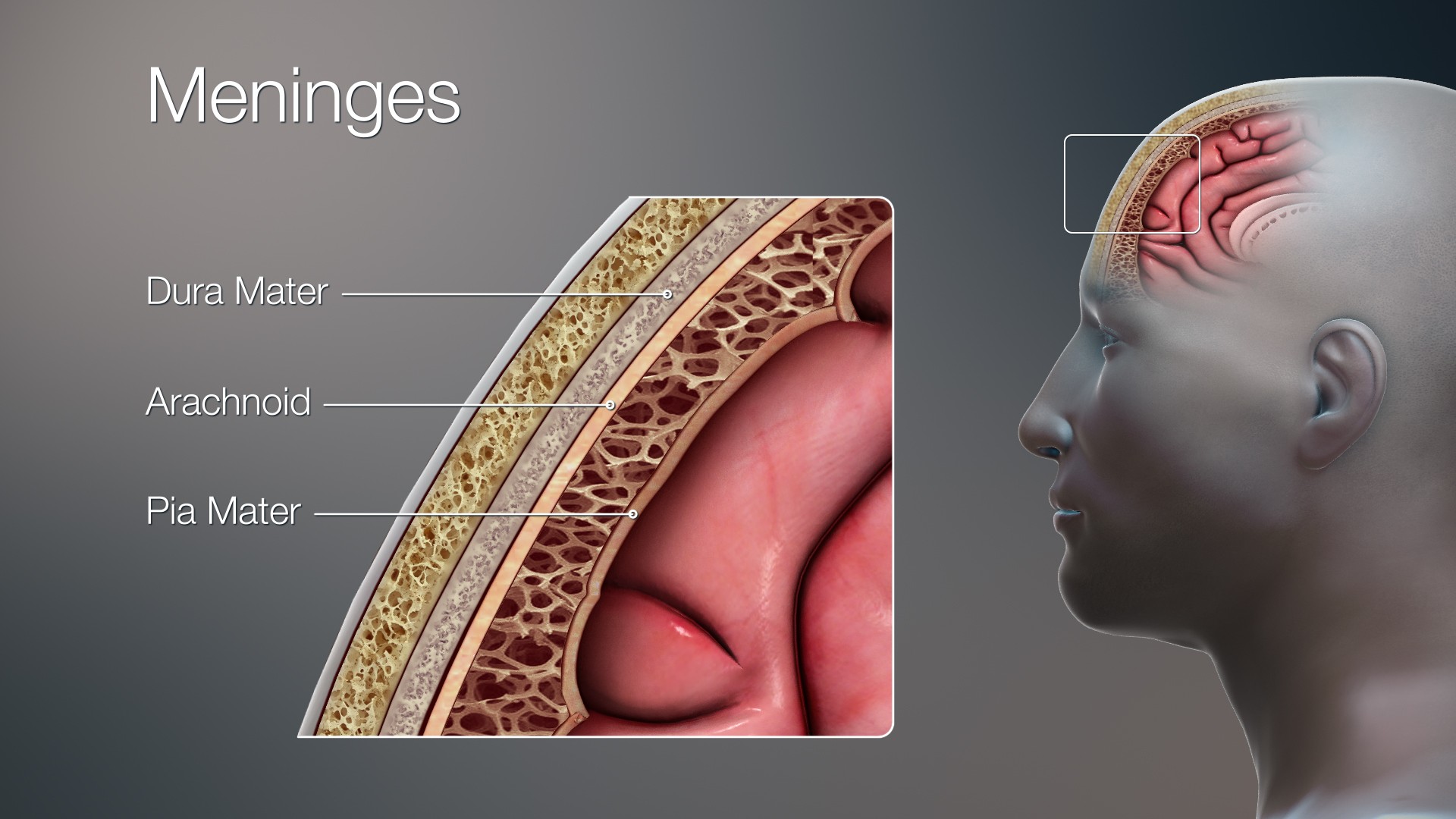
Arachnoid mater - acts as barrier and aids in production of CSF
Pia mater - provides stability
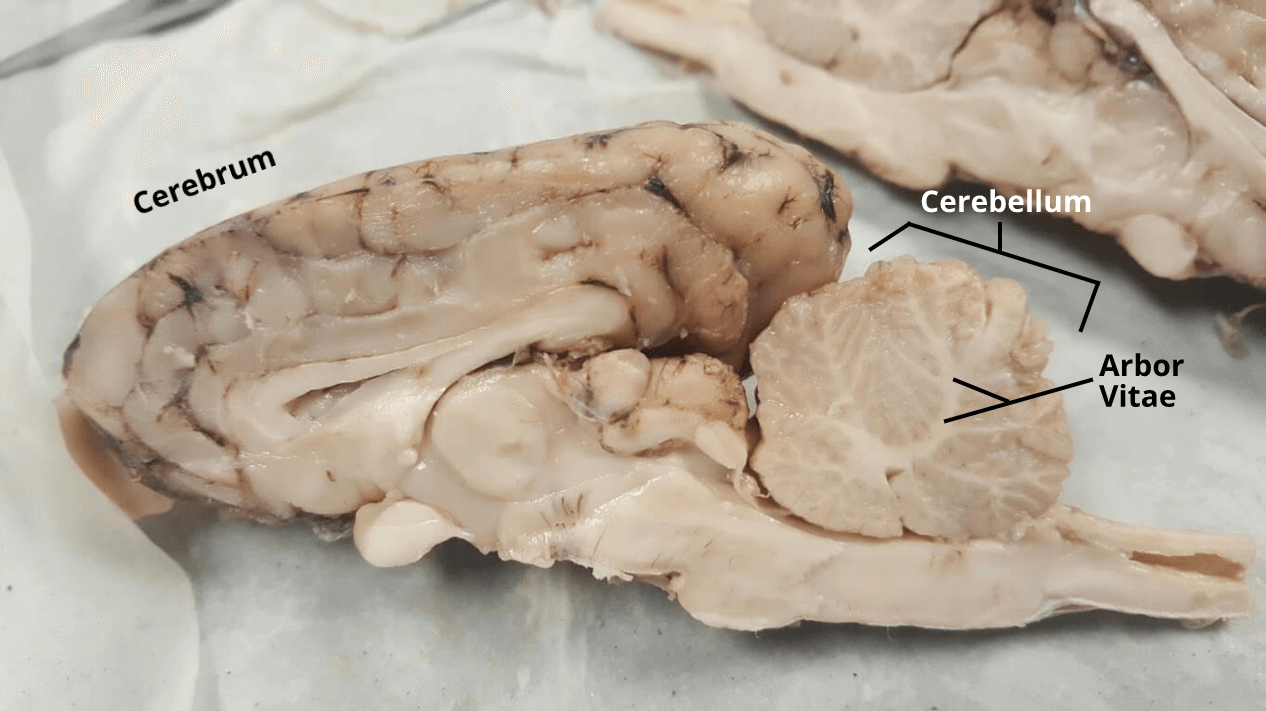
Arbor vitae - Brings sensory/motor function info to and from cerebellum.