What were the health care responsibilities of the federal andprovincial governments outlined in the British North America Act?
Federal:
- Establishment and maintenance of marine hospitals
- Care of the Indigenous populations
- Management of quarantines (at the time; cholera, typhoid fever, tuberculosis and influenza)
Provincial:
- Establishment and maintenance of hospitals
- Establishment of charities
- Establishment of asylums
What were the first doctors of Canada?
A mix of civilian and military physicians that came with the settlers.
When was the first medical school in Montreal built?
1825
Early healthcare was primarily delivered by volunteer organizations. Name the ones responsible for healthcare of Canadians in the early 18th and 19th centuries.
The Order of St. John (1883): community-based first aid and support services.
Children's Aid Society (1891): provide help to the homeless and impoverished children in the city.
The Canadian Red Cross Society (1896): home care to keep families together in times of illness.
The Victorian Order of Nurses (1897): identified healthcare needs, particularly of women and children in remote locations.
What are three traditional health practices of Canada's Indigenous population? Briefly explain them.
The sweat lodge: person is placed in a hot dome building; the point was to weaken their physical self to allow their spiritual self to receive advice from spirits.
The healing circle: a circle which promotes open communication for people dealing with problems in life.
The medicine wheel: spiritual, physical, cognitive and emotional (NWES); person must acknowledge responsibility in all areas of the circle to gain total health.
When was health insurance first introduced in Canada?
In 1957, under John Diefenbaker passed the Hospital Insurance and Diagnostic Services Act.
What did the Hospital Insurance and Diagnostic Services Act detail?
It proposed that any province or territory willing to implement a comprehensive hospital insurance plan would receive federal assistance. The federal government would give 50 cents to every dollar the province spent on insured services. All residents of a province would be entitled to insured health services. Included full acute care and outpatient services.
When was the concept of prepaid hospital care first introduced introduced in Saskatchewan?
1939 – Sask. Gov. enacted the Municipal and Medical Hospital Services Act permitting charges either of land tax or a personal tax to finance hospital and medical services.
First mention in 1947 with the Hospital Insurance Act in SK by Tommy Douglas.
The full comprehensive publicly funded medical care in addition to hospital insurance was the Saskatchewan Medical Care Insurance Act in 1962 by PM Woodrow Lloyd.
When was the concept of prepaid hospital care first introduced introduced in Canada?
1966 Medical Care Act, (implemented in 1968) accepted by all provinces in 1972. Allowed all jurisdictions to administer their health plan as they saw fit so long as it fit the criteria of: universality, portability, comprehensive coverage, and public administration. This came after SK's implementation of its own act succeeded.
What are the 3 pieces of legislation leading up to the Canada Health Act?
1. The Hall Report (1960)
2. The Medical Care Act (1968)
3. The Established Programs Financing Act (1977)
Describe the details of the Hall Report (1960).
- supported the introduction of a national medicare
- recommended that private health insurance be replaced by ten provincial public health insurance plans
- required the fed. government to share the cost of health care plans implemented by jurisdictions
- recommended the fed. government to have strong control over health care financing, but the implementation of health services to be given to the provinces/territories
Describe the details of the Medical Care Act (1968).
- introduced in 1966, officially implemented in 1968
- allowed all jurisdictions to administer the plan as they saw fit as long as they adhered to the criteria of universality, portability, comprehensive coverage, and public administration - covered only in-hospital and physician services
- the need for community-based care and restructuring of the funding formula was recognized by all
Describe the details of the Established Programs Financing Act (1977).
- introduced a new funding formula to allocate money to health care
- replaced the previous 50/50 cost-sharing formula with a block transfer
- reduced restrictions on how jurisdictions could spend money, allowing them to fund community-based services - provided more transfer money for an extended health care services program
What are the criteria and conditions set up by the Canada Health Act?
Criteria:
1. Public administration
2. Comprehensive coverage
3. Universality
4. Portability
5. Accessibility
Conditions:
1. Information
2. Recognition
Why do the provinces/territories need to abide by the criteria and conditions proposed by the CHA?
So that they can qualify for federal payments by the government.
What does public administration and comprehensive coverage mean?
Public administration: the provincial health plan has to be managed by a public authority on a nonprofit basis. Meaning the plan can't be governed by a business, and can't make profit off of it. It's usually overseen by the Ministry of Health or the equivalent of the province.
Comprehensive coverage: The plan allows eligible persons with medical need access to prepaid, medically necessary services. Services included under the provincial/territorial plan must be equally available to all insured residents; there must be no barriers.
What does universality and portability mean?
Universality: all eligible residents of a province are entitled to uniform terms to all insured health services. A citizen’s inability to pay shouldn’t prevent their access to appropriate medical care. Could not discriminate on any basis; due to previous health record, age, race or health status.
Portability: Canadians moving from one province to another are covered for insured health services by their province of origin. Canadians who leave the country will continue to be insured for health services for a prescribed period of time.
What does accessibility mean?
Accessibility: all eligible individuals have reasonable access to all insured health services. Reasonable access means access to services when/wherever they are available. For example: a person living in Winnipeg should have access to all services and hospitals in Winnipeg and nearby towns.
What does information and recognition mean?
Information: the provinces must provide the fed. government with information about their insured health services and extended health care services.
Recognition: the provincial/territorial governments must publicly recognize the fed. financial contributions to both insured and extended health care services.
What is extra billing?
Where the provider bills an eligible person for an insured health service. Ex. The public insurance plan pays $25 for a doctor's visit, the doctor then adds $10 for the patient to pay out-of-pocket.
What does medically necessary mean?
A clinical judgement made by a physician regarding the necessity of a service provided under a provincial or territorial health plan to maintain, restore, or palliate (i.e., ease symptoms, such as pain, without curing the underlying disease).
What does user charges mean?
A fee imposed for an insured health service that the provincial or territorial health care insurance plan does not cover.
How do medically necessary, extra billing and user charges relate to the CHA?
Extra billing and user charges are mentioned in the CHA as they are NOT allowed. They create a barrier to seeking medical care and thus render some of the CHA's criteria. If a province permits extra billing or user charges, the federal government will total the amount of money the province or territory has collected and will deduct that amount from the next transfer of funds. Medically necessary can be subjective and thus, may vary within each province/territory.
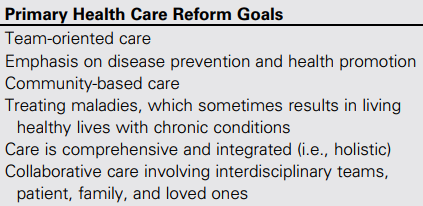
What were the goals of primary care reform?
Why was the Indigenous population by disease when non-Indigenous came to Canada?
Because the Europeans brought with them diseases that were unknown in NA. The Indigenous community had no natural immunity to them let alone traditional treatments. They were: smallpox, tuberculosis, influenza, whooping cough and measles.
What does aboriginal mean?
The people who were the earliest inhabitants of Canada. Later replaced by Indigenous.
What does Status Indian mean?
An Indian(Indigenous) who is registered as one with the federal government as is recognized as one in the Indian Act.
What are Treaty Indians?
Status Indians who belong to a community or bands (a governing unit of Indians under the act).
What is Treaty 6 and the medicine chest?
Treaty 6 was an agreement in 1876 between the Crown and numerous bands. It stipulated that the government move bands into reserves. And that a medicine chest (essentially a first aid kit) in the house of an Indian Agent (Indian government agent).
Describe the details of the Mazankowski Report (2001).
Purpose: to provide strategic advice to the premier on the preservation and future enhancement of quality health services for Albertans.
- supported private health care
- recommended the implementation of province-wide EHRs and electronic health cards
Describe the details of the Kirby Report (2002).
Purpose: to examine the state of the Canadian health care system and the role of the federal gov. in it.
- recommended the implementation of new taxes
- recommended setting limits to wait times
- recommended a gov.-funded assistance plan for medications under certain circumstances
- suggested gov. incentives encourage health care providers to return to Canada.
Describe the details of the Romanov Report (2002).
Purpose: to present recommendations to ensure the survival of Canada's health care system.
- believed that health care was sustainable but that immediate action was necessary
- opposed the privatization of health care
- recommended the creation of the Health Council of Canada to conduct regular review of the health care system
- recommended adding the criterion of accountability to the CHA
When was the Canada Health Transfer (CHT) and the Canada Social Transfer (CST) implemented?
April 1, 2004. A few years after the Romanov Report.
In 2000, what was the First Ministers' Meeting mission? And what were the key issues they identified?
To identify the significant issues facing health care in each province and territory, and to pledge to work collaboratively to address these concerns.
- wait times
- shortage of health professionals
- insufficient management of health records
- timely access to services
What was the key focuses on the First Ministers' Accord on Health Care Renewal in 2003?
The overriding commitment made was to preserve universal health care under the CHA. They wanted to establish standards of care for Canadians; including access to providers 24/7, and implementation of a national EHR system. They also addressed the unique needs of the Indigenous people.
What was the Indian Act (1876)?
A law passed to control the lives of the First Nations peoples and to legally identify them. Gave the government power over their land, education, culture and rights. But this did not apply to the Metis and Inuit peoples.