Aspirin is formed by reacting salicylic acid with ethanoic anhydride. Deduce the structural formula of the by-product of this reaction.
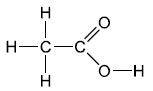
CH3COOH
Aspirin crystals are rinsed with water after recrystallization to remove impurities.Suggest why cold water is used.
to avoid dissolving the crystals/aspirin
The solubility of aspirin is increased by converting it to an ionic form. Draw the structure of the ionic form of aspirin.
Comment on the risk of overdose when taking aspirin as an analgesic, referring to the following values, for a person weighing 70 kg:
Minimum therapeutic dose = 0.5 g
Estimated minimum lethal dose = 15g
low/medium risk of overdosing and estimated lethal dose is 30 times/much larger than therapeutic dose
Explain how IR spectroscopy can be used to distinguish aspirin from salicylic acid.
salicylic acid contains absorption in the range 3200−3600 cm−1
due to phenol/hydroxyl/OH group not present in aspirin
Opiates are strong analgesics.
Explain why diamorphine (heroin) crosses the blood–brain barrier more easily than morphine .
blood-brain barrier is hydrophobic/non-polar/made of lipids
morphine has hydroxyl/OH groups /is more polar and diamorphine
Outline the meaning of the bioavailability of a drug.
fraction/proportion/percentage of administered dosage enters blood/plasma/circulation
This question is about antiviral drugs.
Oseltamivir, used for the treatment of severe flu, is inactive until converted in the liver to its active carboxylate form.
Draw a circle around the functional group that can be converted to the carboxylate by hydrolysis.
Anything that circles alkyl side chain
The resulting active metabolite of oseltamivir can be detected by mass spectrometry (MS) analysis.
Deduce the mass of the expected carboxylate ion.
Mr oseltamivir = 312
283
Suggest a reason for using a phosphate salt of oseltamivir in oral tablets.
More soluble in water
Anti-HIV drugs, such as zidovudine, often become less effective over time.
Explain the development of resistant virus strains in the presence of antiviral drugs.
viruses undergo rapid mutation
mutation causes a change in viral proteindrug no longer binds to virus
Medicines and drugs are tested for effectiveness and safety.
Distinguish between therapeutic window and therapeutic index in humans.
Therapeutic window:
Therapeutic index:
Therapeutic window:range of dosage over which a drug provides the therapeutic/desired effect without causing adverse/toxic effects
Therapeutic index:toxic dose of drug for 50 % of population divided by minimum effective dose for 50 % of population
Explain why diamorphine (heroin) is more potent than morphine using section 37 of the data booklet.
molecule of diamorphine is less polar than morphine
less polar molecules cross the blood–brain barrier faster/more easily
Codeine, morphine and diamorphine (heroin) are derived from opium.
Explain why diamorphine has greater potency than morphine.
morphine is more polar than diamorphine
diamorphine is more soluble in non-polar environment of CNS/central nervous system than morphine
diamorphine crosses the blood–brain barrier easily
Experimental research on both animals and humans contributes to the development ofpharmaceuticals.
State the meaning of the term therapeutic index in human studies.
toxic dose for 50% of population divided by minimum effective dose for 50 % of population
Excess stomach acid leads to medical conditions that affect many people worldwide. These conditions can be treated with several types of medical drugs.
Omeprazole exists as a racemic mixture whereas esomeprazole is a single enantiomer. Outline how, starting from a non-chiral molecule, esomeprazole but not omeprazole, could be synthesized. Details of chemicals and conditions are not required.
chiral molecule/auxiliary/optically active species is used/added/connected to the starting molecule to force reaction to follow a certain path
existing chiral centre affects configuration of new chiral centres
A polarimeter can be used to determine the optical rotation of an optically active substance.
Describe what happens to plane-polarized light when it passes through a solution of anoptically active compound
plane of polarization is rotated
A mixture of enantiomers shows optical rotation.
Suggest a conclusion you can draw from this data.
mixture contains optically active impurity
Taxol is produced using a chiral auxiliary. Describe how the chiral auxiliary functions to produce the desired product.
chiral molecule/auxiliary/optically active species added/connected/attached to non-chiral starting molecule to force reaction to follow a certain path
chiral auxiliary creates stereochemical condition necessary to follow a certain pathway
after new chiral centre created chiral auxiliary removed to obtain desired product
Explain how zanamivir works as a preventative agent against flu viruses.
drug blocks/inhibits viral enzyme activity
Explain, with reference to the action of penicillin, why new penicillins with different side-chains need to be produced.
bacterial resistance to older penicillins/antibiotics
prevent penicillinase in bacterium to deactivate
State and explain the relative solubility of codeine in water compared to morphine and diamorphine.
codeine less soluble in water than morphine more soluble than diamorphine
State the natural source from which codeine, morphine and diamorphine are obtained.
opium poppy
Explain the role of the chiral auxiliary in the synthesis of Taxol.
chiral auxiliary is optically active
is attached to non-optically active/non-chiral substrate
creates stereochemical condition necessary to follow a certain pathway
Taxol was originally obtained from the bark of the Pacific yew tree.
Outline how Green Chemistry has improved the process of obtaining Taxol.
Taxol produced semi-synthetically
uses renewable resources
Many drugs are chiral. Explain how a polarimeter can be used to determine the relative proportion of two enantiomers.
pure enantiomers rotate the plane of plane-polarised light by equal angles in opposite directions
find angle of rotation of pure enantiomers
measure angle of rotation of mixture
Outline how chiral auxiliaries are used to synthesize the desired enantiomer.
chiral auxiliary creates stereochemical condition necessary to follow a certain pathway
chiral molecule is used to the starting molecule to force reaction to follow a certain path
Explain the process of solvent extraction by which Taxol is isolated.
immiscible solvents
partitioning of Taxol between the two solvents
shaking/stirring the mixture
Enantiomers can be identified using a polarimeter. Outline how this instrument differentiates the enantiomers.
plane-polarised light passed through sample
analyser/second polarizer determines angle of rotation of plane of plane-polarized light
Examine the synthesis of taxol in terms of green chemistry criteria
sustainable because synthesised and not obtained from yew trees
one enantiomer produced
Outline the operation of a polarimeter used to distinguish between enantiomers
light passes through polariser/polarising filter
measure angle/direction of rotation
State the feature of Taxol that is a major challenge in its synthesis
numerous stereoisomers
Describe how the challenge of numerous stereoisomers was resolved by pharmaceutical companies
chiral auxiliaries/molecule binds to reactant blocking one reaction site by steric hindrance
Technetium-99m is the most widely used medical radioisotope. It is usually made on-site in medical facilities from isotopes of molybdenum.
Deduce equations for the following nuclear reactions:
(i) Molybdenum-98 absorbs a neutron.
(ii) The isotope produced in (a) (i) decays into technetium-99m.
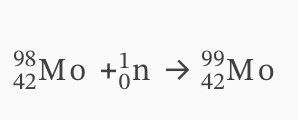
i)
Molybdenum-99 has a half-life of 66 hours, while technetium-99m has a half-life of 6 hours. Outline why technetium-99m is made on-site.
molybdenum-99 can be easily transported before it decays/more stable
Outline two reasons, other than its half-life, why technetium-99m is so useful in medical diagnosis.
emits gamma rays
Outline the nature of the radioactive waste that is generated by the use of technetium-99m in medical diagnosis.
small amounts of ionizing radiation for short time
Yttrium-90 is used in treating certain cancers.
Formulate a nuclear equation for the beta decay of yttrium-90.
90Y → 90Zr +β–
Lutetium-177 is a common isotope used for internal radiation therapy.
Suggest why lutetium-177 is an ideal isotope for the treatment of certain cancers based on the type of radiation emitted.
beta-radiation/emission and targets tumour/cancer cells
A breathalyser measures the blood alcohol content from a breath sample.Formulate half-equations for the reactions at the anode (negative electrode) and thecathode (positive electrode) in a fuel cell breathalyser.
Anode (negative electrode): C2H5OH +H2O → CH3COOH +4H++ 4e–
Cathode (positive electrode): O2 +4H++ 4e–→ 2H2O
Explain why alpha-radiation is particularly suitable for this treatment
more damaging than other radiation types
causes little damage to surrounding tissues
Outline how the alpha-radiation in TAT is directed to cancer cells
radioactive isotope/radionuclide/alpha-emitter administered using carrier drug /protein/antibodies
Identify the type of radiation emitted by these two radioisotopes
beta
State an equation for the one-step decay of yttrium-90.
90Y→90,40Zr+β
State the type of radiation technetium-99m emits.
gamma
Discuss the properties that make a radioisotope suitable for diagnosis.
easily detected/traced
short/intermediate half-life hence does not remain in body for long time
energy of photons is low
excreted quickly From body
Describe the proper disposal of low-level radioactive waste in hospitals
store until material becomes inactive/radiation levels drop
dispose with other waste
Describe how ionizing radiation destroys cancer cells.
radiation causes breaks in DNA chains
radiation causes errors in DNA sequences
Outline how Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) is used for treating cancers that havespread throughout the body.
radiation source delivered directly to targeted cancer cells
by a carrier drug/protein/antibody
several sites in body can be targeted at same time
Explain the targeted alpha therapy (TAT) technique and why it is useful.
alpha-emitting isotopes attached to drugs
absorbed by cancer/growing cells
short-range of emission of alpha-particles
Explain how TAT is relatively safe to use in the treatment of dispersed cancers.
alpha emitter carried to/selectively absorbed by cancer cells by antibodies,carrier drug, protein
Suggest why the percentage of technetium-99m remaining in the human body two days after injection will be lower than that calculated
removed by excretion
Outline what is meant by low-level waste.
small/low amounts of radiation and for a short time
Outline the disposal of LLW.
stored in shielded containers until radiation level drops to a safe level
Suggest why MRI is much less dangerous than imaging techniques such as X-rays and radiotracers
lower frequency/longer wavelength/lower energy
does not use ionizing radiation/radionuclides
State two common side effects of radiotherapy
hair lossfatigue
Explain why technetium-99m is the most common radioisotope used in nuclear medicine.
half-life is 6 hours/long enough for a scan to occur
gamma rays less likely to be absorbed by cells
The use of performance-enhancing drugs presents a challenge in the world of competitive sports. New regulations have lowered the acceptable concentrations of certain drugs in athletes’ bodies.
Suggest what may have led to these changes in acceptable concentrations.
improvements in technology
Suggest why lutetium-177 is an ideal isotope for the treatment of certain cancers basedon the type of radiation emitted.
beta-radiation/emission and targets tumour/cancer cells
A breathalyser measures the blood alcohol content from a breath sample.Formulate half-equations for the reactions at the anode (negative electrode) and the cathode (positive electrode) in a fuel cell breathalyser.
Anode (negative electrode): C2H5OH +H2O → CH3COOH +4H++ 4e–
Cathode (positive electrode): O2 +4H++ 4e–→ 2H2O
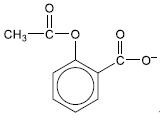
Suggest why aspirin is slightly soluble in water
presence of large benzene/arene ring and non-polar/hydrophobic
contain COOH and ester group and polar/hydrophilic
A student prepares aspirin from salicylic acid in the laboratory, extracts it from thereaction mixture, ensures the sample is dry and determines its melting point.
Suggest why the melting point of the student’s sample is lower and not sharp compared to that of pure aspirin.
Students sample impure
fewer intermolecular forces due to presence of impurities
Discuss how acid-base properties and the process of solvent extraction can be used to separate aspirin from the mixture.
dissolve compounds in an organic solvent
add NaOH(aq)/OH–(aq) to the mixture to convert aspirin to its water soluble salt
separate the two immiscible layers
convert salt in aqueous layer back to aspirin by reacting with acid/H+
evaporate solvents and dry
State a green solution to the problem of organic solvent waste.
catalysis that leads to better/higher yield
reducing number of steps
Describe how mild analgesics function.
prevents/interferes with the production of prostaglandins
Explain how the concentration of ethanol in a sample of breath can be determined using a fuel cell breathalyser
ethanol is oxidised to ethanoic acid
electrons are released
current compared to a reference to determine concentration
Explain how hexane and propanone may be separated by fractional distillation.
different molar masses
different strength of intermolecular forces
component with lower boiling point leaves column first
Fuel cells use an electrochemical process to determine the concentration of ethanol.
Formulate the overall equation for this process.
C2H5OH(g) +O2(g) → CH3COOH(aq) +H2O(l)
State an analytical technique used to separate anabolic steroids from other compounds in an athlete’s urine or blood.
gas chromatography
Ethanol in breath can be detected by a redox reaction. Outline this method of detection.
oxygen reduced to water
ethanol oxidized to ethanoic/acetic acid
current measured
Describe how a fuel cell breathalyser works.
ethanol in breath is oxidised to ethanoic acid
electrons pass through external circuit to cathode where O2 is reduced
current is proportional to alcohol concentration
Alcohol levels in the breath can also be determined using IR spectroscopy.
Suggest, giving a reason, which bond’s absorbance is most useful for detecting ethanol in breath.
Bond:
Reason:
Bond: C-O
Reason: cannot use O–H bonds as in water found in breath
Describe a technique for the detection of steroids in blood and urine.
sample/liquids vaporised in oven/at high temperature
stationary phase consists of a packed column
components separated by partition between mobile phase and stationary phase
detector/mass spectrometer/MS at end of column
Explain how redox chemistry is used to measure the ethanol concentration in a breathalyser.
ethanol is oxidised to ethanoic acid at anode and oxygen is reduced to water at cathodecurrent/voltage/potential is measured by computer
What are the main steps in the development of synthetic drugs?
The main steps in the development of synthetic drugs include identifying the need and structure, synthesis, yield and extraction.
What are drug-receptor interactions based on?
Drug-receptor interactions are based on the structure of the drug and the site of activity.
How does aspirin function as a mild analgesic?
Mild analgesics function by intercepting the pain stimulus at the source, often by interfering with the production of substances that cause pain, swelling or fever.
What is aspirin prepared from?
Aspirin is prepared from salicylic acid.
What are the medical uses of aspirin?
Aspirin can be used as an anticoagulant, in prevention of the recurrence of heart attacks and strokes and as a prophylactic.
What are penicillins?
Penicillins are antibiotics produced by fungi.
What is the beta-lactam ring?
A beta-lactam ring is a part of the core structure of penicillins.
How do some antibiotics work?
Some antibiotics work by preventing cross-linking of the bacterial cell walls.
What results in penicillins that are more resistant to the penicillinase enzyme?
Modifying the side-chain results in penicillins that are more resistant to the penicillinase enzyme.
What determines a drug's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier?
The ability of a drug to cross the blood-brain barrier depends on its chemical structure and solubility in water and lipids.
What are opiates?
Opiates are natural narcotic analgesics that are derived from the opium poppy.
What are some medical uses of morphine and codeine?
Morphine and codeine are used as strong analgesics.
How do strong analgesics work?
Strong analgesics work by temporarily bonding to receptor sites in the brain, preventing the transmission of pain impulses without depressing the central nervous system.
What are non-specific reactions?
Non-specific reactions, such as the use of antacids, are those that work to reduce the excess stomach acid.
What are active metabolites?
Active metabolites are the active forms of a drug after it has been processed by the body.
Why are viruses more difficult to target with drugs than bacteria?
Viruses lack a cell structure and so are more difficult to target with drugs than bacteria.
How do antiviral drugs work?
Antiviral drugs may work by altering the cell's genetic material so that the virus cannot use it to multiply. Alternatively, they may prevent the viruses from multiplying by blocking enzyme activity within the host cell.
What is high-level waste (HLW)?
High-level waste (HLW) is waste that gives off large amounts of ionizing radiation for a long time.
What is low-level waste (LLW)?
Low-level waste (LLW) is waste that gives off small amounts of ionizing radiation for a short time.
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when micro-organisms become resistant to antibacterials.
What is Taxol and what is it commonly used for?
Taxol is a drug that is commonly used to treat several different forms of cancer.
Where does Taxol naturally occur and how is it produced now?
Taxol naturally occurs in yew trees but is now commonly synthetically produced.
What is a chiral auxiliary?
A chiral auxiliary is an optically active substance that is temporarily incorporated into an organic synthesis so that it can be carried out asymmetrically with the selective formation of a single enantiomer.
What types of emissions are used for medical treatment?
Alpha, beta, gamma, proton, neutron and positron emissions are all used for medical treatment
What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an application of NMR technology.
What are the two types of radiotherapy?
Radiotherapy can be internal and/or external.
What are Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT)?
Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) are two methods which are used in cancer treatment
What techniques can be used to analyse and identify organic structures?
Organic structures can be analysed and identified through the use of infrared spectroscopy, mass spectroscopy and proton NMR.
How can the presence of alcohol in a sample of breath be detected?
The presence of alcohol in a sample of breath can be detected through the use of either a redox reaction or a fuel cell type of breathalyser.