State the full electron configuration of the chlorine atom.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
State, giving a reason, whether the chlorine atom or the chloride ion has a larger radius.
Cl- has a larger radius, more electron–electron repulsion
Outline why the chlorine atom has a smaller atomic radius than the sulfur atom.
Cl has a greater nuclear charge causing a stronger pull on the outer electrons
similar shielding
Explain the presence and relative abundance of the peak at m/z=74.
diatomic molecule composed of two chlorine-37 atoms
chlorine-37 is the least abundant isotope
Deduce, referring to oxidation states, whether MnO2 is an oxidizing or reducing agent.
oxidizing agent AND oxidation state of Mn changes from +4 to +2/decreases
Hypochlorous acid is considered a weak acid. Outline what is meant by the term weak acid.
partially dissociates/ionizes in water
State the formula of the conjugate base of hypochlorous acid.
ClO-
State the type of reaction occurring when ethane reacts with chlorine to produce chloroethane.
free radical substitution
Predict, giving a reason, whether ethane or chloroethane is more reactive.
chloroethane as it contains a polar bond
Calcium carbide, CaC2, is an ionic solid.
Describe the nature of ionic bonding.
electrostatic attraction AND oppositely charged ions
Describe how the relative atomic mass of a sample of calcium could be determined from its mass spectrum.
find the frequency of each isotope
sum of the values of products/multiplication from each isotope
When calcium compounds are introduced into a gas flame a red colour is seen; sodium compounds give a yellow flame. Outline the source of the colours and why they are different
promoted electrons fall back to lower energy level
energy difference between levels is different
Suggest two reasons why solid calcium has a greater density than solid potassium.
stronger metallic bonding
smaller ionic/atomic radius
Outline why solid calcium is a good conductor of electricity.
delocalized/mobile electrons free to move
Describe how sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are formed.
sigma (σ):
overlap of atomic orbitals along the axial/internuclear axispi (π):
overlap of p-orbitals above and below the internuclear axis
Deduce the number of σ and π bonds in a molecule of ethyne.
sigma (σ): 3
pi (π): 2
Subsequent experiments showed electrons existing in energy levels occupying various orbital shapes.
Sketch diagrams of 1s, 2s and 2p.
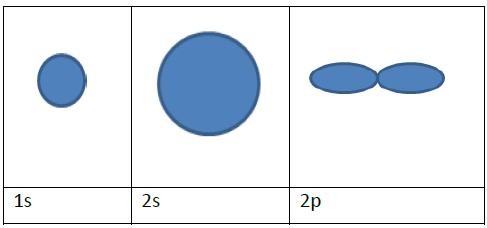
State the electron configuration of copper.
1s22s22p63s23p64s13d10OR[Ar] 4s13d10
Copper is a transition metal that forms different coloured complexes. A complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+ (aq) changes colour when excess Cl− (aq) is added.
Explain the cause of this colour change, using sections 3 and 15 from the data booklet.
chloride is lower in the spectrochemical series
ligand cause decreased/lesser splitting in d-orbitals compared to H2Ofrequency/energy of light absorbed is decreased
When are emission spectra produced
Emission spectra are produced when photons are emitted from atoms as excited electrons return to a lower energy level.
What does the line emission spectrum of hydrogen provide evidence for
The line emission spectrum of hydrogen provides evidence for the existence of electrons in discrete energy levels, which converge at higher energies.
What is a mass spectrometer
The mass spectrometer is used to determine the relative atomic mass of an element from its isotopic composition.
What does the limit of convergence correspond to
In an emission spectrum, the limit of convergence at higher frequency corresponds to the first ionization energy
What do trends in first ionisation energy account for?
Trends in first ionization energy across periods account for the existence of main energy levels and sub-levels in atoms.
What does successive ionisation energy data show for an element?
Successive ionization energy data for an element give information that shows relations to electron configurations.
Magnesium ions produce no emission or absorption lines in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Suggest why most magnesium compounds tested in a school laboratory show traces of yellow in the flame.
contamination with sodium/other compounds
Explain the convergence of lines in a hydrogen emission spectrum.
energy levels are closer together at high energy / high frequency / short wavelength
State what can be determined from the frequency of the convergence limit.
ionisation energy
Magnesium chloride can be electrolysed.
(i) Deduce the half-equations for the reactions at each electrode when molten magnesium chloride is electrolysed, showing the state symbols of the products. The melting points of magnesium and magnesium chloride are 922K and 987K respectively.
Anode (positive electrode):
2Cl–→ Cl2 (g) + 2e–
Cathode (negative electrode):
Mg2+ + 2e–→ Mg (l)
Magnesium chloride can be electrolysed.
Identify the type of reaction occurring at the cathode (negative electrode).
reduction
Magnesium chloride can be electrolysed.
State the products when a very dilute Aqueous solution of magnesium chloride is electrolysed.
Anode (positive electrode):oxygen/O2
Cathode (negative electrode):hydrogen/H2
Describe the bonding in metals.
electrostatic attraction
between a lattice of metal/positive ions/cations AND a sea of delocalised electrons
Explain why an aluminium-titanium alloy is harder than pure aluminium.
titanium atoms/ions distort the regular arrangement of atoms/ions
prevent layers sliding over each other
Describe, in terms of the electrons involved, how the bond between a ligand and a central metal ion is formed.
pair of electrons provided by the ligand
Outline why transition metals form coloured compounds.
partially filled d-orbitals
ligands cause d-orbitals to split
light is absorbed as electrons transit to a higher energy level in d–d transitions
energy gap corresponds to light in the visible region of the spectrum
colour observed is the complementary colour
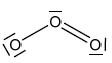
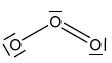
Discuss the bonding in the resonance structures of ozone.
lone pair on p orbital of O atom overlaps/delocalizes with pi electrons from double bond
both O–O bonds have equal bond length
Deduce one resonance structure of ozone and the corresponding formal chargeson each oxygen atom.
The first six ionization energies, in kJ mol–1, of an element are given below.
Explain the large increase in ionization energy from IE3 to IE4.
IE4: electron closer to nucleus
IE4: electron more tightly held by nucleus
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal.
Explain why a copper(II) solution is blue
orange light is absorbed and the complementary colour is observed
light is absorbed as electrons move to a higher energy orbital in d–d transitions
light is absorbed as electrons are promoted
The electron configuration of copper makes it a useful metal.
Copper plating can be used to improve the conductivity of an object.
State, giving your reason, at which electrode the object being electroplated should be placed.
cathode/negative electrode AND Cu2+reduced at that electrode
Justify why sulfur is classified as a non-metal by giving two of its chemical properties.
forms acidic oxides rather than basic oxides
forms covalent/bonds compounds with other non-metals
State a technique that could be used to determine the crystal structure of the solid compound.
X-ray crystallography
Outline, in terms of their electronic structures, why the ionic radius of the sulfide ion is greater than that of the oxide ion.
valence electrons further from nucleus/extra electron shell/ electrons in third/3s/3p level not second/2s/2p
Suggest why chemists find it convenient to classify bonding into ionic, covalent and metallic.
allows them to explain the properties of different compounds
Explain why the addition of small amounts of carbon to iron makes the metal harder.
disrupts the regular arrangement of iron atoms/ions
Explain why Si has a smaller atomic radius than Al
nuclear charge/number of protons increases causing a stronger pull on the outer electrons
same number of shells/outer energy level/shielding
Explain why the first ionization energy of sulfur is lower than that of phosphorus.
P has three unpaired electrons in 3p sub-level AND S has one full 3p orbital and two 3p orbitals with unpaired electrons
Describe metallic bonding and how it contributes to electrical conductivity.
electrostatic attraction
between a lattice of cations/positive metal ions AND a sea of delocalized electrons
mobile electrons responsible for conductivity
Suggest, giving reasons, the relative volatilities of SCl2 and H2O.
H2O forms hydrogen bonding while SCl2 does not
SCl2 much stronger London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces
Describe the nature of ionic bonding.
electrostatic attraction AND oppositely charged ions