What is funding and delivery?
Funding: refers to how health care is paid for.
Delivery: is how health care services are managed, structured and distributed.
All medically necessary health care services are publicly funded but are mostly delivered by private businesses. True or false?
True.
Name some ways health care is funded.
- federal, provincial/territorial governments through taxes
- raised funds
What are the four main transfer models?
1. Canada Health Transfer (CHT): largest annual cash transfer from the Federal government. Can't fall below 3% of the GDP and must be used on health care.
2. The Canada Social Transfer (CST): provides funding to the jurisdictions through cash and tax points for social programs. Money must be applied to these areas.
3. The Territorial Formula Financing (TFF): calculates money given to the territorial governments for health care and public services. Funding is provided through taxes from all across Canada.
4. Equalization Payments: made to provinces and territories with less money.
In the 2016 Health Accord, what was agreed on?
That additional funding needed to go into areas of home care and mental health for each province and territory.
The Federal Government is responsible for the health care of:
- Indigenous populations
- Serving Canadian Forces personnel
- Inmates
- Refugees
A number of factors influence the per capital spending of health care among provinces/territories. Name some of them.
- differences in services offered
- population distribution and geograpy
- age and health of a population
What is the most effective way to reduce health care costs while still providing high-quality health care?
By implementing disease prevention and health promotion, early diagnosis, prompt intervention and spending more on social programs.
What is the main source of revenue for hospitals?
The province/territory.
What is the leading health care expenditure in Canada?
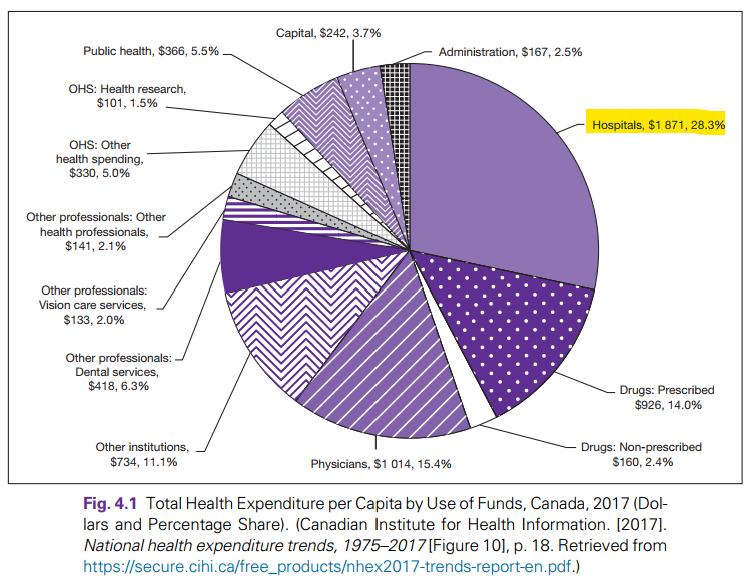
Hospitals
What are some problems hospitals are facing?
- cuts to services
- reduction in hospital beds
- closures/merging of hospitals
- rationalization of services (catering to the specific needs of the community)
- insufficient and demoralized staff
- long wait lists
Describe the block/global funding model, the health-bases allocation model and the line-by-line funding model.
Block/global funding model: funding is determined by its previous year's expenditures and is given an annual lump sum.
Health-bases allocation model: money is based on its expected expenses from the demographic profile of the community.
Line-by-line funding model: itemizes the costs of specific services and equipment. Referred to as line items or inputs, gets funding for each service.
Name an advantage and disadvantage of block/global funding model.
Advantage: Encourages administrators to implement protocols to discharge patients early to control costs.
Disadvantage: No consideration of the population the hospital serves, or their specific health care needs.
Describe the quality-based procedures model, patient-based funding model and service-based funding/case-mix approach.
Quality-based procedures model: focused on the number of patients treated and the procedures performed which looks at efficiency and a "best practices" approach.
Patient-based funding model: monetary incentives are provided to the hospital (by reaching targeted goals) to maximize the quality of care delivered in the most cost-effective manner.
Service-based funding/case-mix approach: identifies the types of cases treated and the volume of patients. Funding is related to many patients it treats requiring each combination of services.
Describe the activity-based funding and population-based funding model/capitated funding.
Activity-based funding: pays hospitals in accordance with the number and types of services the facility provides to each patient. The goal is to make the facility more efficient and reduce wait times.
Population-based funding model/capitated funding: grants money based on the demographics. With varying amounts rewarded depending on the location and how many patients fall into certain categories. Ex. a hospital in an area with a large population of older adults may receive more funding than one with a mainly younger population,
A hospital in the red must look for ways to ___.
A hospital in the red must look for ways to reduce costs or to be approved for extra funding.
Name some factors that affect hospital costs.
- size & location
- ^teaching hospitals
- cost of wages and cost of living
- drug costs
- hospitals with rehab facilities see a cost reduction
What is the most commonly applied strategy to reduce hospital costs?
Decreasing length of stay; the longer a patient stays in the hospital, the higher the cost.
Name some strategies that reduce the length of stay.
- same-day admissions
- day surgery
- deliveries (most new mothers are discharged within 24 hours)
- bed management
What are the two ways hospital mergers can occur?
1. Horizontal model: merges several hospitals under one administration.
2. Vertical model: merges specific programs within a single organization, but not necessarily one board.
What are the advantages of merging?
- reduced duplication of services
- ^ efficiency
- lower admin. and management costs
- offers more services for better results
Mergers of smaller hospitals appear to be more successful because the resulting facility broadens its service base while retaining staff and improving care. True or false?
True.
Rationalization involves delivering the ___.
Rationalization involves delivering the right kind of care at the right level to the right person.
What are some options for continuing care?
- home care
- residential care
- private residences
- long-term care facilities (nursing homes)
What are some factors that drive drug expenditure in Canada?
- ^usage
- ^costs
- aging population
- introduction of new drugs
What is the difference between brand name drugs and generic drugs?
Brand name: owned and sold by a company, typically costs more than generic. They're always capitalized (Advil).
Generic: contain the same active ingredients as brand name drugs, but are cheaper.
What is the Patented Medicine Prices Review Board responsible for?
Regulates the price that pharmaceutical companies sell their patented medications. But can't control what retailers charge.
What does health human resources (HHR) mean?
Refers to all people who work in the health care field.
How are most physicians being paid. Define it.
Mostly being paid by the fee-for-service method. This means that doctors charge the provincial/territorial plan for every service they perform.
Summarize capitation-based funding.

Doctor is paid for each rostered patient in his practice.