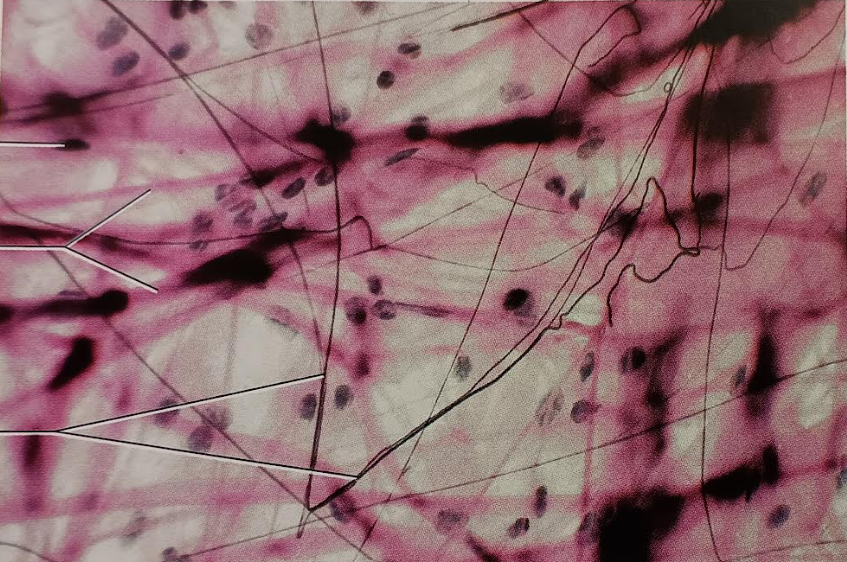
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper loose Areolar
-gel-like matrix with all three fiber types (collagen, elastic, reticular), fibroblasts (extracellular matrix component),
-macrophages (devour foreign material)
-mast cells (detect foreign microorganisms), and some white blood cells.
function is to wrap and cushion organs, hold and convey tissue fluid, phagocytize bacteria, and aid in inflammation for tissue repair.
found under the epithelium throughout the entire body.
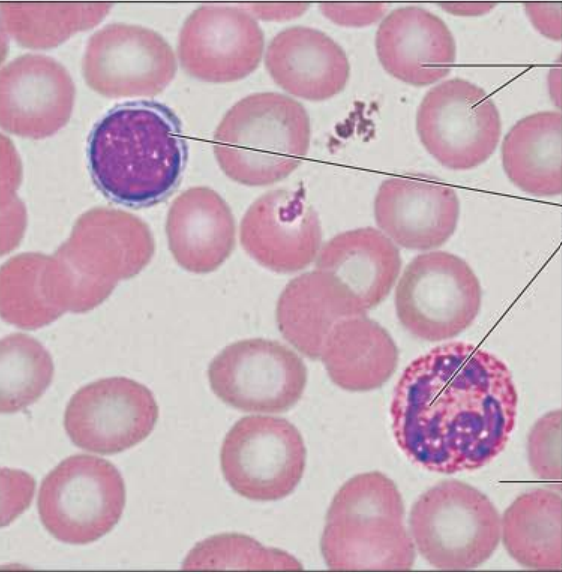
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue blood has red and white blood cells in a plasma matrix.
function is to transport respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
found within blood vessels.
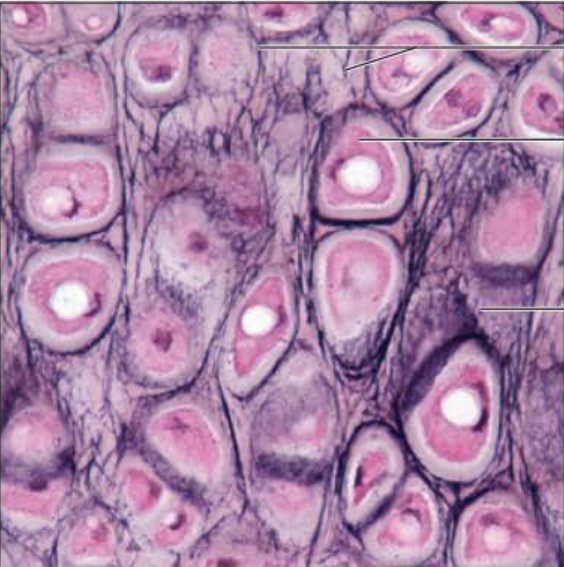
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
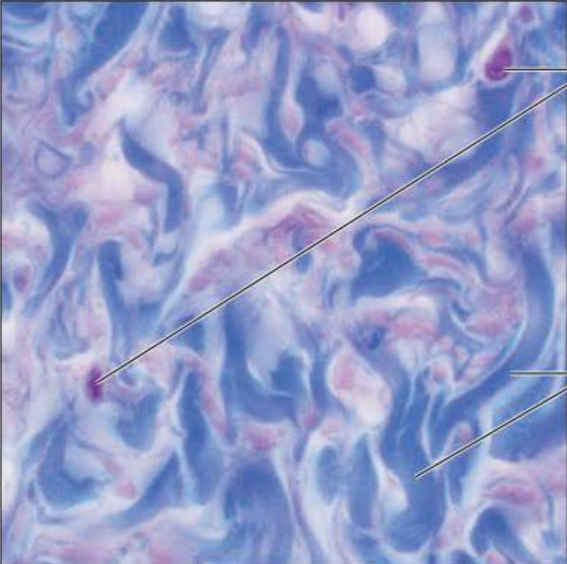
Connective tissue cartilage Elastic
-similar to the hyaline variant
-contains more elastic fibers in the matrix
function is to maintain the shape of a structure while allowing for great flexibility
found in the epiglottis.
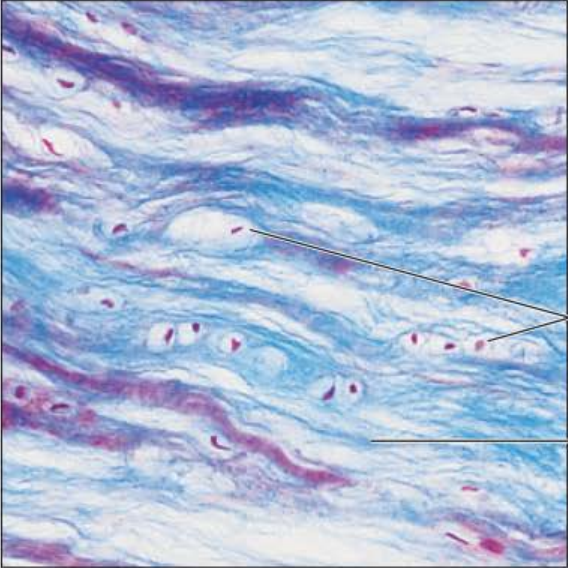
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue cartilage Fibrocartilage
-similar to the hyaline variant
-less firm with mostly thick collagen fibers.
function is the capacity for great tensile strength allowing for the absorption of compressive shock.
Found in intervertebral discs.
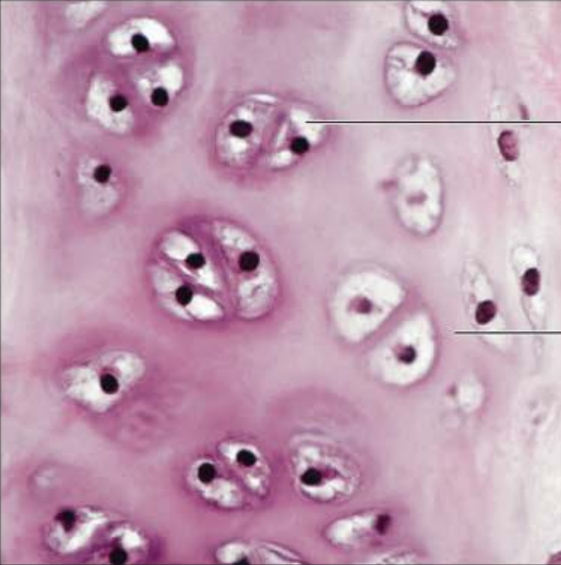
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue cartilage Hyaline
-amorphous but firm matrix.
-collagen fibers that form an imperceptible network
-chondroblasts that produce the matrix.
-When they become chondrocytes they lie in lacunae
function is to support and reinforce, they serve as a resilient cushion and resist compressive stress
Found in the costal cartilages of the ribs.
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
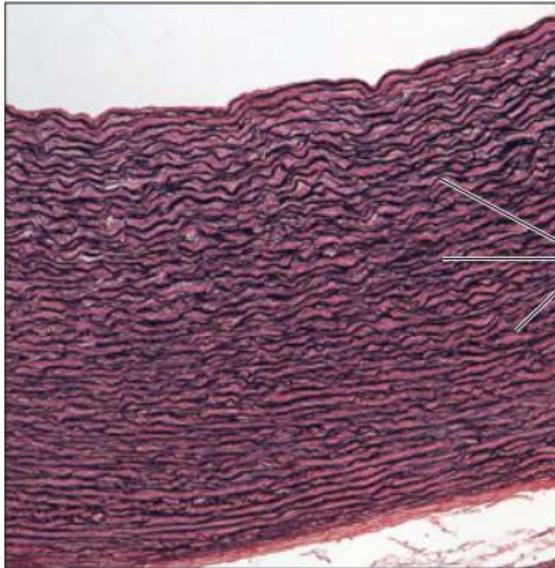
Connective tissue proper dense Elastic
-dense regular connective tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers
function is to allow the tissue to recoil after stretching, maintaining the pulsatile flow of blood through arteries, and aiding the passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
found in the walls of large arteries.
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper dense Irregular
-has mostly irregularly arranged collagen fibers
-some elastic fibers with fibroblasts being the major cell type.
function is to withstand tension exerted in many directions and to provide structural strength.
found in the dermis of the skin.
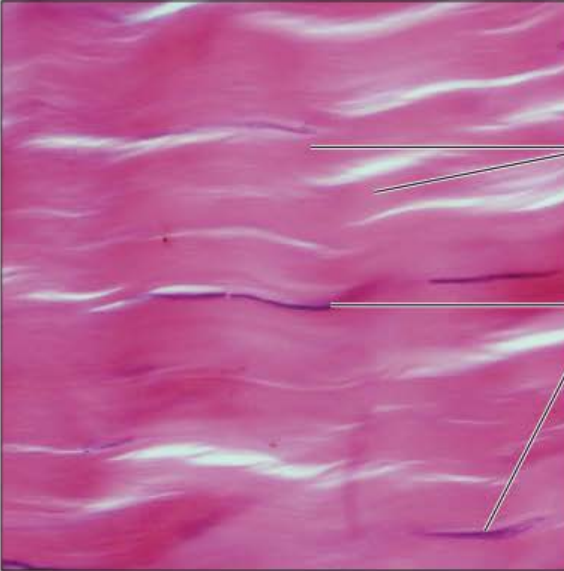
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper dense Regular
-primarily parallel collagen fibers (tensile strength)
-a few elastic fibers
-the major cell type is the fibroblast
function is attaching muscles to bones or to other muscles, attaching bones to bones, and withstanding great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
found in the tendons.
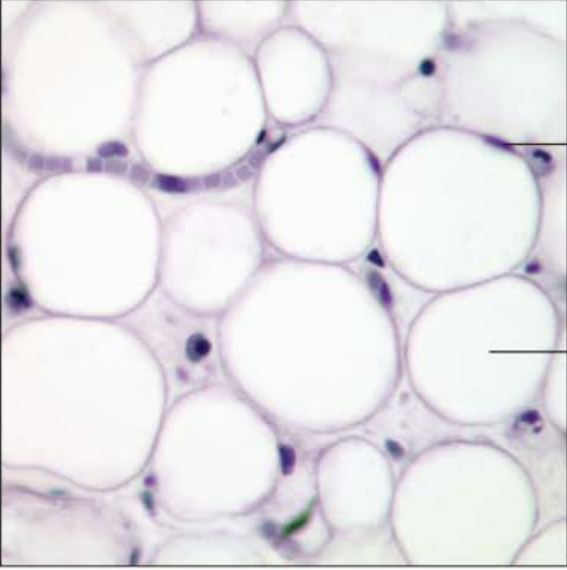
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper loose Adipose
-has a matrix that resembles the areolar subclass, but is very sparse.
-has very closely packed together adipocytes (fat cells) with their nucleus pushed to the side by a large fat droplet
function is to provide reserve food fuel, insulate against heat loss, and add support and protection to organs
found under skin in subcutaneous tissue.
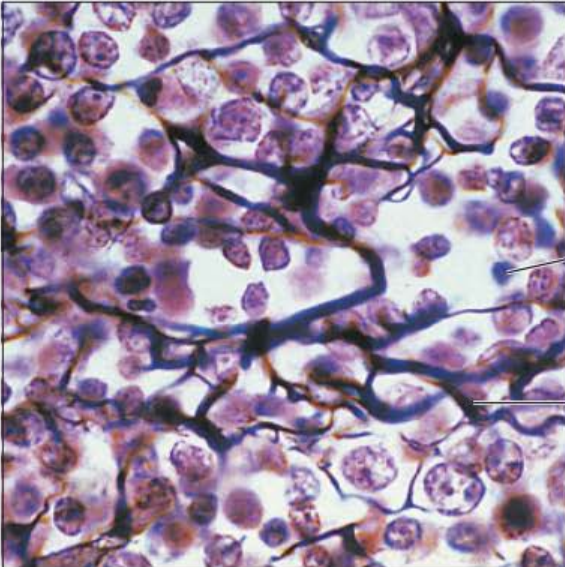
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper loose Reticular
-has a loose network of reticular fibers (made of collagen; surrounding small blood vessels)
-in a gel-like ground substance with reticular cells (fibroblasts) that lie on the fibers
function has their fibers form a stroma (soft internal skeleton) that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
found in the spleen.
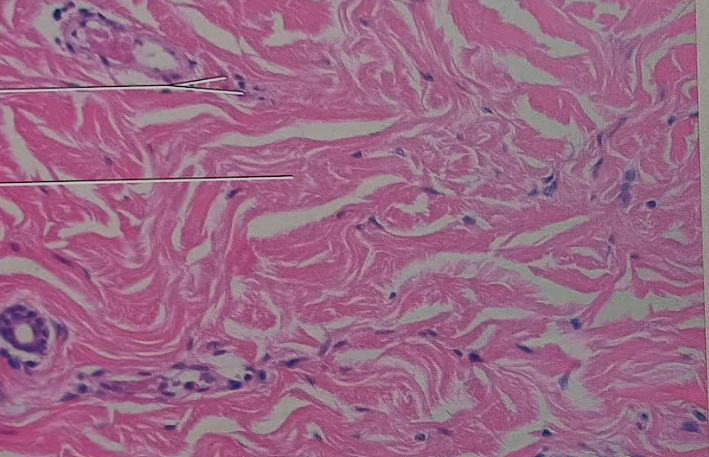
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper dense Irregular
-has mostly irregular arranged collagen fibers
-some elastic fibers with fibroblasts being the major cell type.
Their function is to withstand tension exerted in many directions and to provide structural strength.
They can be found in the dermis of the skin
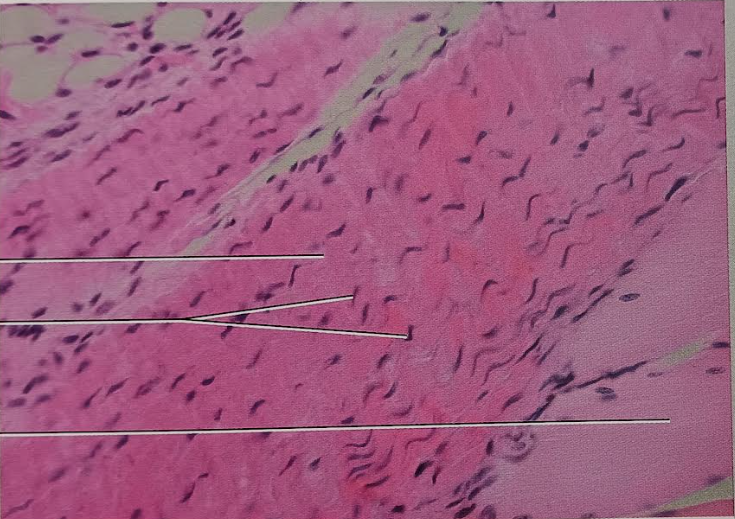
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue proper dense Regular
-has primarily parallel collagen fibers (tensile strength)
-a few elastic fibers
-the major cell type is the fibroblast.
Their function is attaching muscles to bones or to other muscles, attaching bones to bones, and withstanding great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction.
They can be found in the tendons.

Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue cartilage Elastic
-similar to the hyaline variant
-contains more elastic fibers in the matrix.
Their function is to maintain the shape of a structure while allowing for great flexibility.
They can be found in the epiglottis.
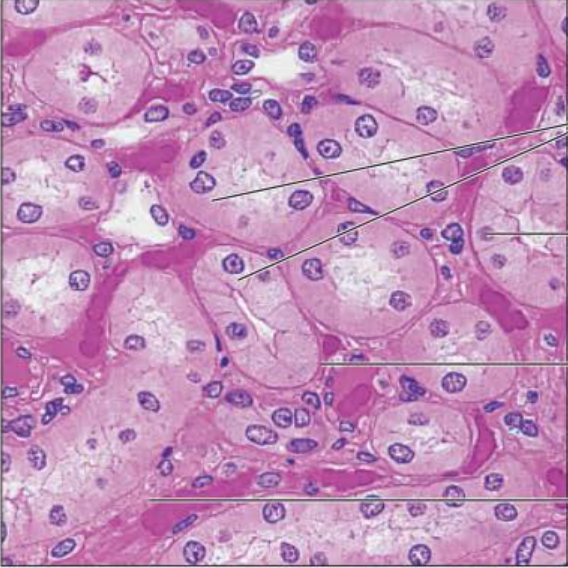
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Simple Cubodial Epithelium
-single layer of cubelike cells with large, spherical central nuclei
Their function is secretion and absorption
They can be found in kidney tubules.
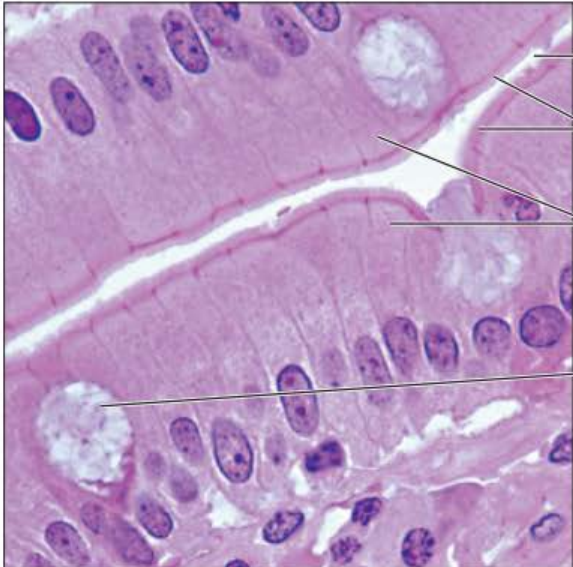
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Simple Columnar Epithelium
-single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei
-Many of the cells contain microvilli and some bear cilia
-They may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands called goblet cells.
Their function is absorption, secretion of mucus, and enzymes.
The nonciliated type lines most of the stomach and digestive tract, the ciliated version lines small bronchi.
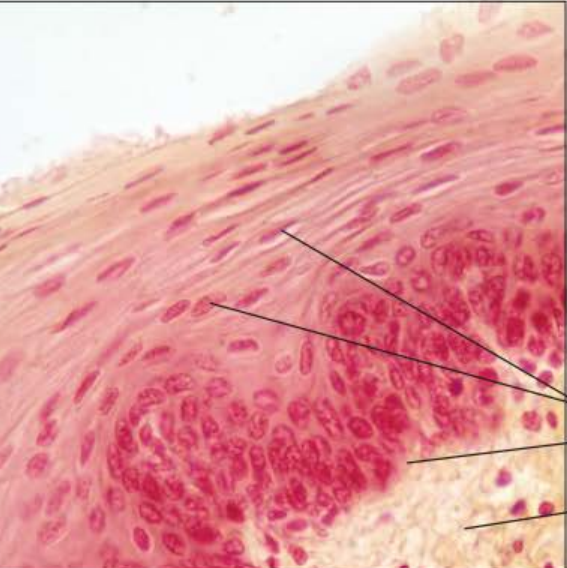
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
-thick epithelium composed of several cell layers
-the basal cells of this type are cubodial or columnar and metabolically active, they are also active in mitosis and produce the cells of the more superficial layers.
-surface cells are squamous, full of keratin and dead
The function of this epithelium is to protect underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
Nonkeratinized types are moist and found in the linings of the esophagus. The keratinized type can be found in the epidermis of the skin.
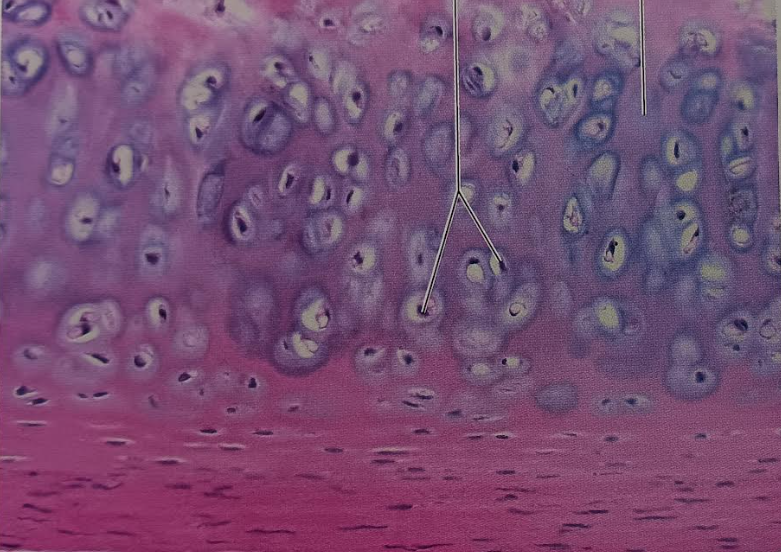
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue cartilage Hyaline
-has an amorphous but firm matrix.
-It has collagen fibers that form an imperceptible network and chondroblasts that
produce the matrix. When they become chondrocytes they lie in lacunae.
Their function is to support and reinforce, they serve as a resilient cushion and resist compressive stress.
They can be found in the costal cartilages of the ribs.
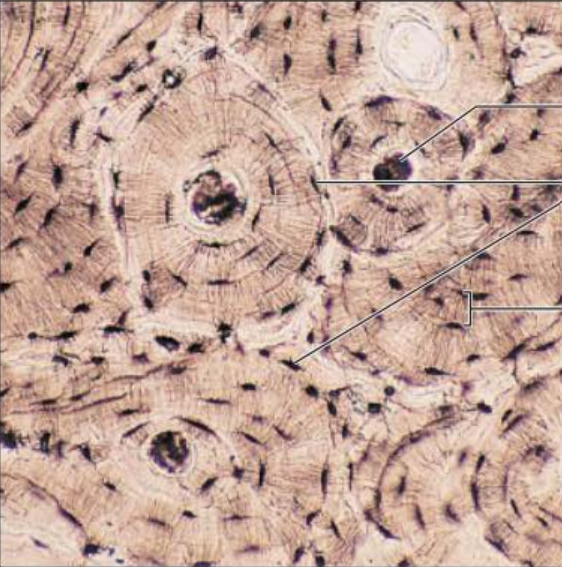
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Connective tissue bone
-hard and has a calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers
-Osteocytes lie in lacunae and this tissue is very well vascularized.
Its function is to support and protect by enclosing. It provides levers for the muscles to act on. The storage of calcium, other minerals, and fat. The marrow inside bones is the site for hematopoiesis (blood cell formation).
They can be found in the bones.
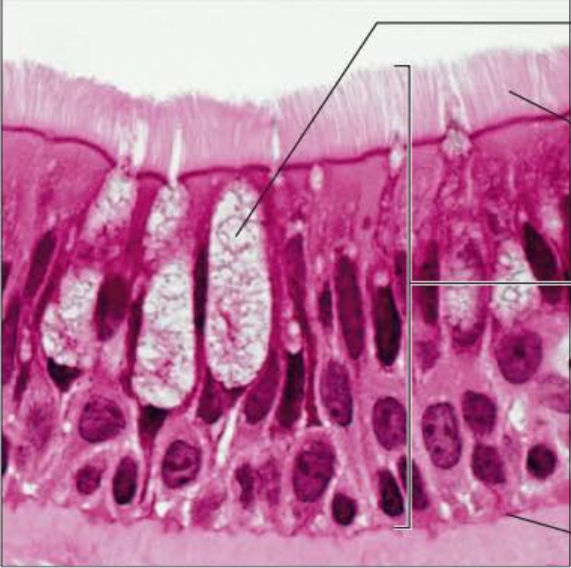
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
-a single layer of cells of differing heights, with nuclei seen at different levels.
-May contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia.
Their function is to secret substances, particularly mucus.
The ciliated variety lines the trachea and nonciliated types can be found in the ducts of large glands.
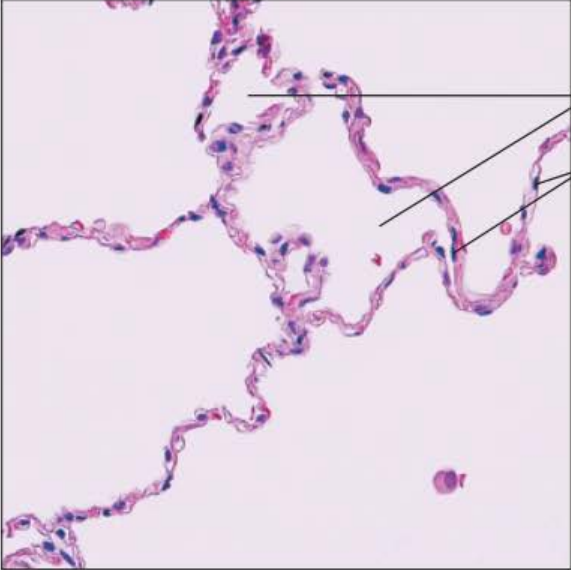
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Simple Squamous Epithelium is flattened laterally with sparse amounts of cytoplasm
.
It can be found in the walls of the alveoli contained within the lungs for the function of gas exchange.
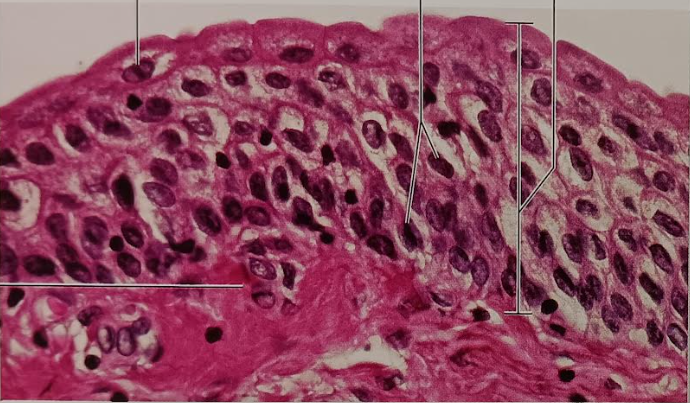
Identify this tissue
Name a function
Name a specific place where it is found
Transitional Epithelium
-resemble both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal.
-Basal cells of this variety are cuboidal or columnar.
-Apical cells are squamous-like depending on the degree of organ stretch.
Their function is to stretch readily and to permit stored urine to distend the urinary organs.
They can be found in the lining of the bladder.
what is the epidermis?
outer protective layer of skin made from epithelial cells
what is the dermis?
tough leathery layer that makes the bulk of the skin, made of connective tissue
which part of the skin is vascularized?
only the dermis
what is the papillary layer?
-areolar connective tissue
-fine interlacing collagen and elastic fibers that form a loosely woven mat with many small blood vessels
what is the reticular layer?
dense irregular connective tissue that nourishes
where is the hypodermis? what is its structure and function?
under the dermis
its structure is adipose tissue
its function is the storage of nutrients, shock absorber, and insulator
what are eccrine sweat glands?
most abundant exocrine gland located everywhere especially on the palms and feet
its function is temperature control
what are sebaceous glands?
found everywhere except palms and soles
secretes on the upper part of the hair follicle
contains oily sebum meant to lubricate, prevent water loss, and antibacterial
what is a Pacinian corpuscle?
a cutaneous sensory receptor found in the deeper dermis
alerts us to bumps or contacts involving deep pressure
what are dermal papillae?
-areolar connective tissue
-interlacing collagen and elastic fibers form a loosely woven mat with many small blood vessels
-allows phagocytes and other defensive cells to patrol the area for bacteria
-houses Meissner's corpuscle
what are arrector pili muscles?
-smooth muscle cells
-pulls follicles into an upright position which produces goosebumps
-propels sebum to the skin surface when contracts
what are hair follicles?
-an inner epithelial root sheath and an outer peripheral connective tissue sheath derived from the dermis
-base of the hair follicle produces hair
-richly vascularized
what is the hair follicle receptor?
the root hair plexus
-free nerve endings that wrap around the hair follicle
-touch receptors
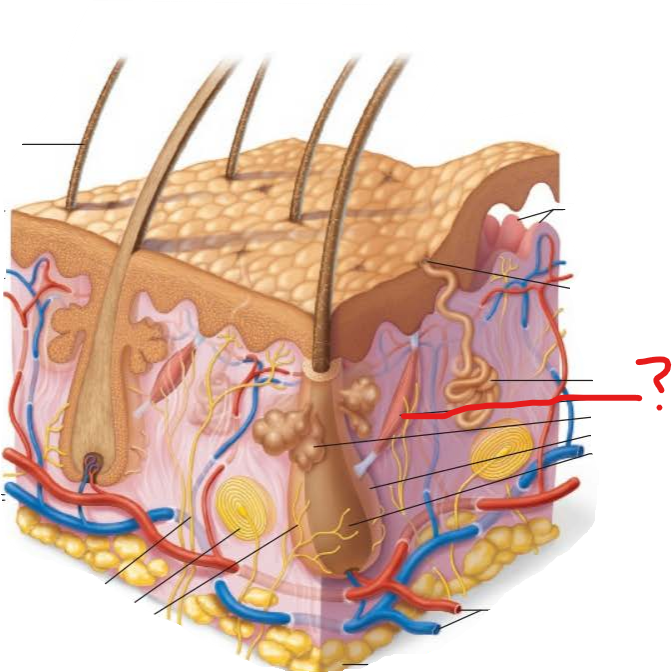
arrector pili muscle
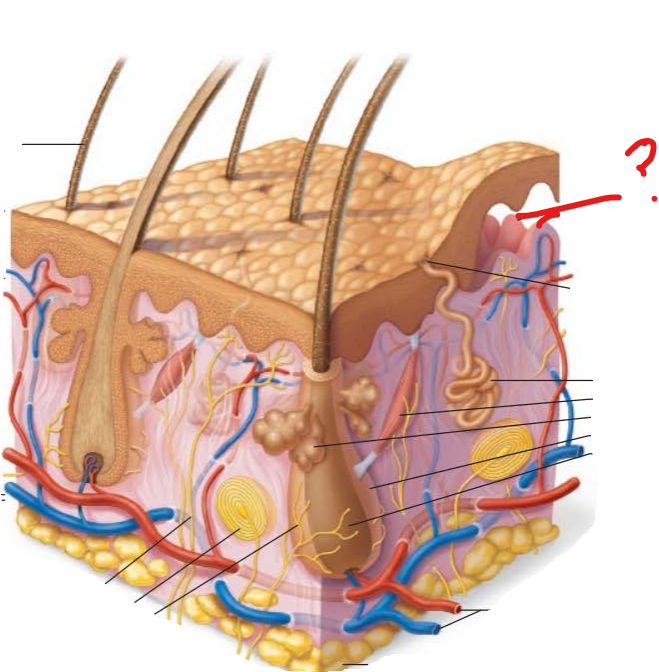
dermal papillae
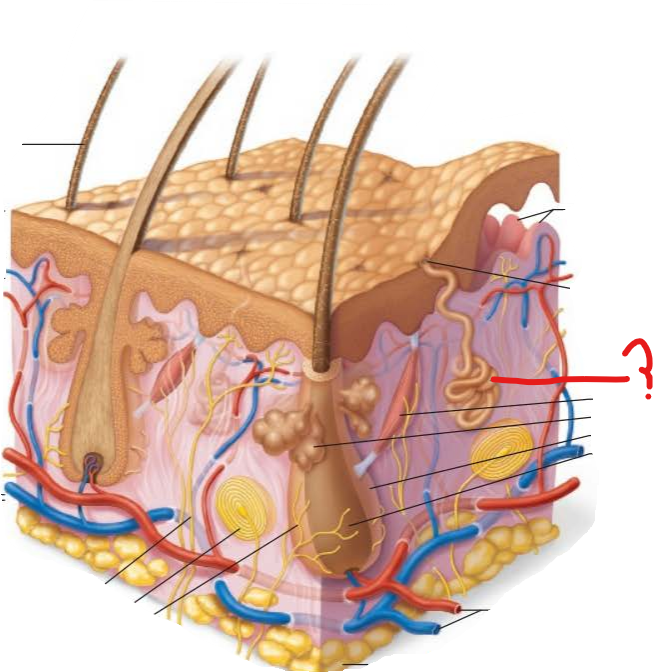
eccrine sweat gland
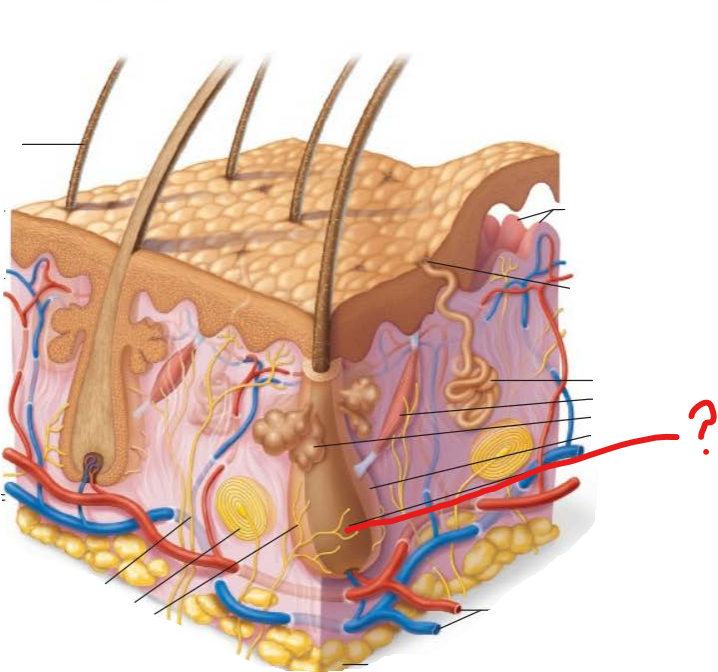
hair root
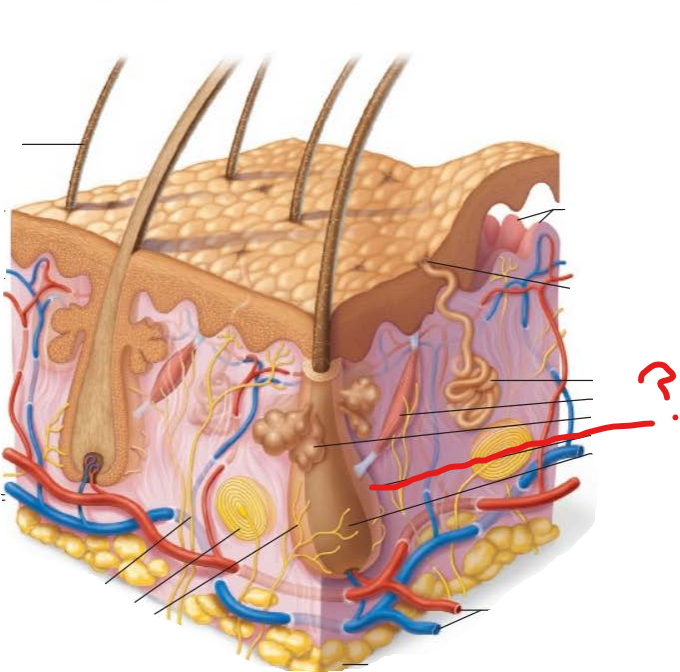
hair follicle
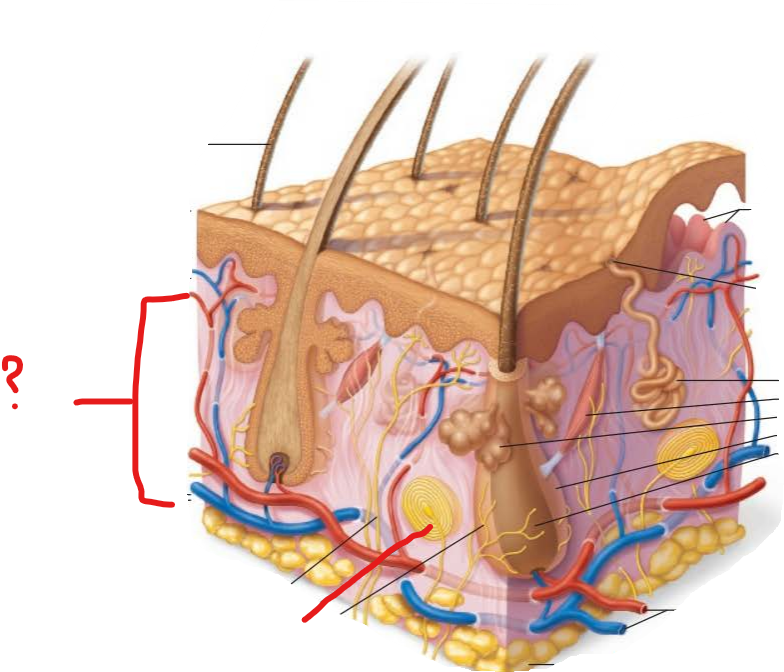
Pacinian corpuscle
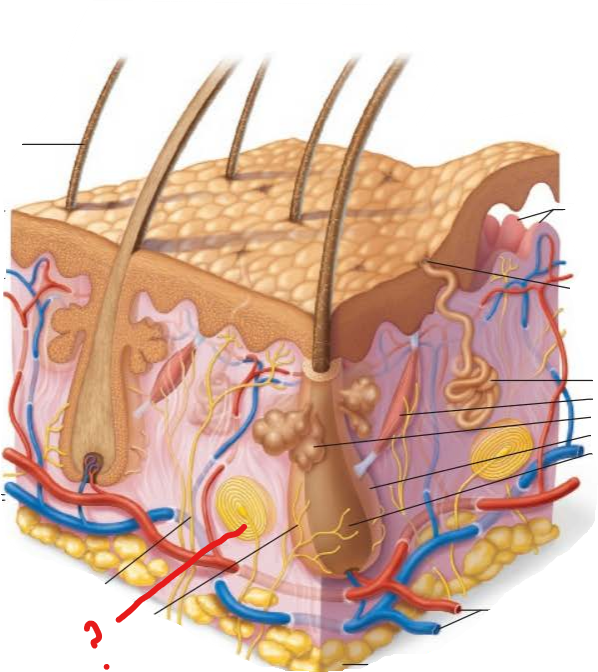
papillary layer
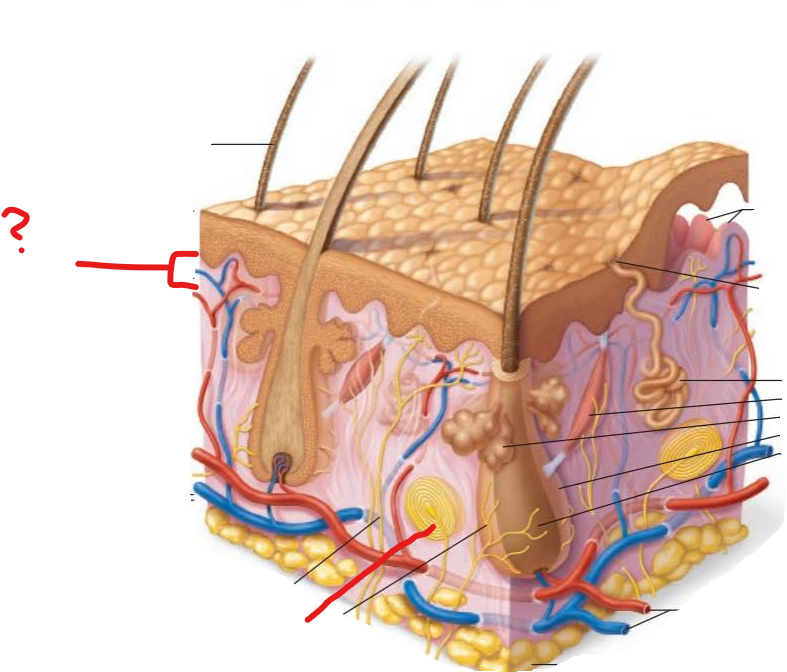
reticular layer
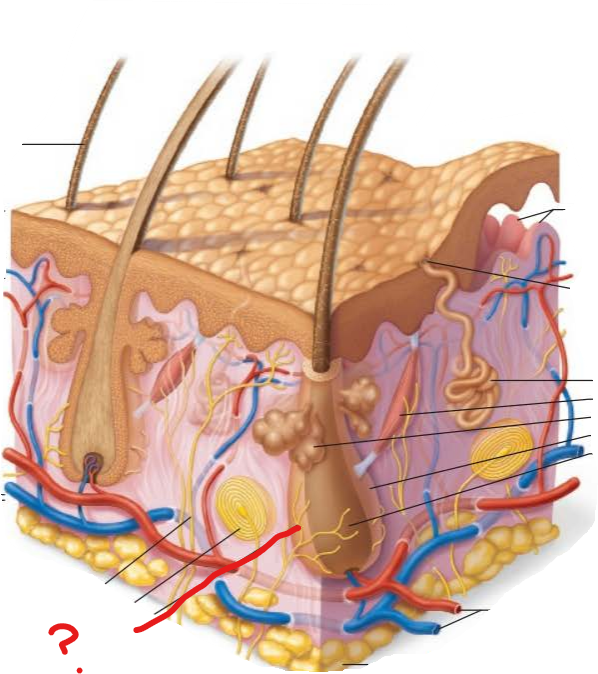
root hair plexus
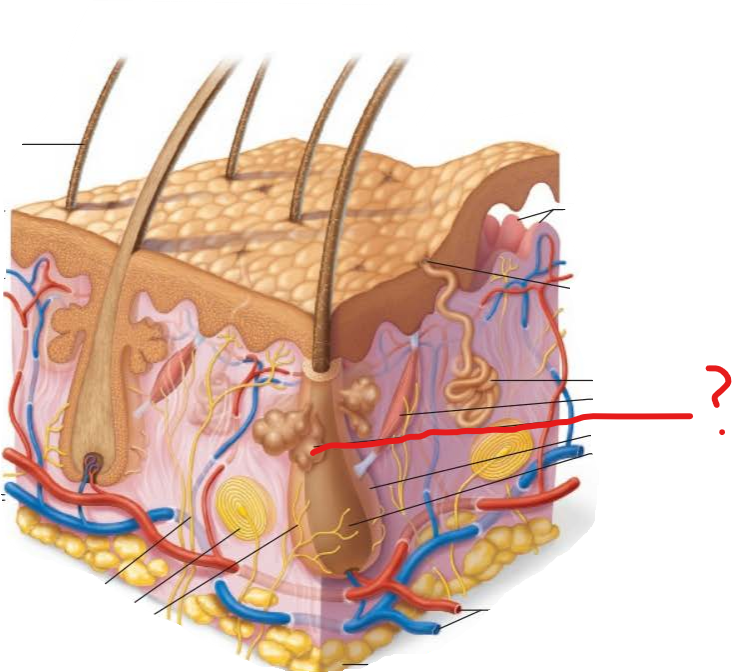
sebaceous gland
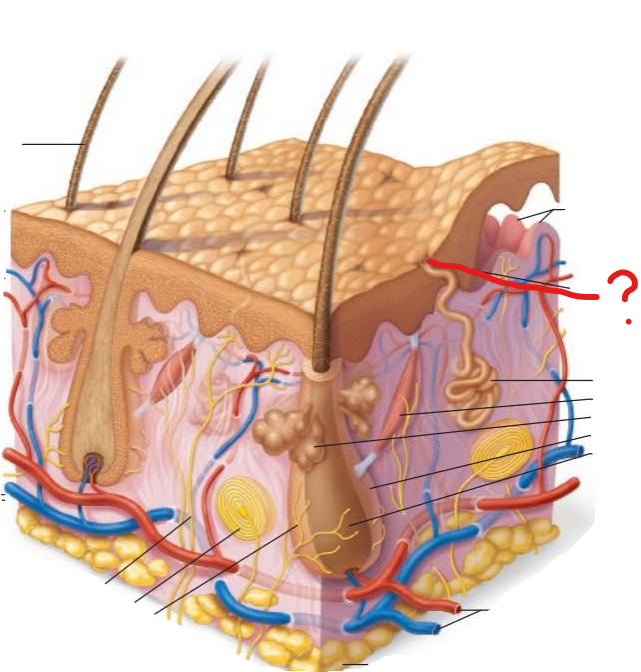
sweat pore