What is abstinence and what are its benefits as a contraceptive method? (6)

100% Reliable
100% Safe
Non-user dependent
Unrelated to coitus
Visible to the woman
No ongoing medical input
What are the reversibility and discomfort aspects of abstinence as contraception? (2)

Completely reversible within 24 hours
No discomfort
What are the methods of contraception that require ongoing action by the individual? (6)
Oral contraception
Vaginal contraception
Barrier methods
Fertility awareness
Coitus interruptus
Oral emergency contraception
What are the methods of contraception that prevent conception by default? (4)
IUD (Intrauterine device)
Progesterone implant/IUS/injection
Male sterilisation
Female sterilisation
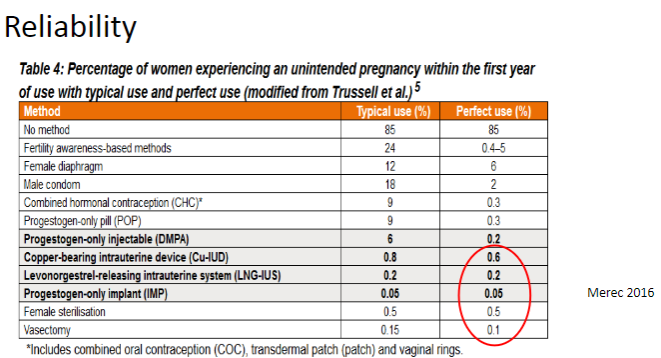
Picture demonstrating the reliability of different contraceptive methods:
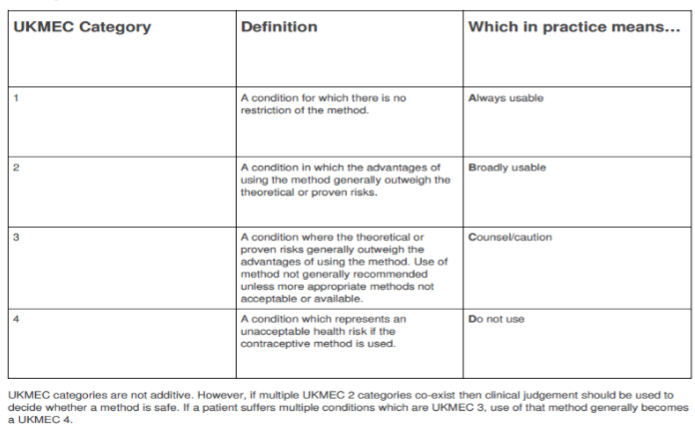
Picture demonstrating UK Medical Eligibility for Contraception 2016:
What are the components of combined oral contraception and their types? (5) Never Let Doctors Give New Nurturing Advice
Oestrogen: Ethinyl Oestradiol (20, 30, 35, 50 micrograms) - synthetic oestrogen
Progestogens:
Older (2nd generation): Norethisterone (Norethindrone) & Levonorgestrel
Newer (3rd generation): Desogestrel, Gestodene & Norgestimate (Noregestromin)
Latest (derived from Spironolactone): Drospirenone
"Never Let Doctors Give New Nurturing Advice"
Never → Norethisterone (2nd gen)
Let → Levonorgestrel (2nd gen)
Doctors → Desogestrel (3rd gen)
Give → Gestodene (3rd gen)
Nurturing → Norgestimate (3rd gen)
Advice → Drospirenone (latest)
What is the action of oestrogens in combined oral contraception? (3)
Act on the anterior pituitary & hypothalamus
Act on the endometrium
What is the action of progestogens in combined oral contraception? (4)
Act on the anterior pituitary & hypothalamus
Act on the endometrium
Act on the fallopian tubes
Act on cervical mucus
What are the basic principles of combined oral contraception? (6)
Supra-physiological levels (COc uses hormone levels that are higher than the normal physiological levels in the body, which are typically lower in a natural cycle.)
"Pseudo-pregnancy" (causes changes in the body similar to those during pregnancy, tricking the body into thinking it’s pregnant, which prevents ovulation)
Suppression of the HPO (hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian) axis
Pharmacokinetics are highly variable (The way the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates the hormones in the COC can vary between individuals)
Individual serum levels vary (Each person's blood levels of the hormones may be different)
Suppression may not be absolute (Sometimes, the COC doesn’t fully prevent ovulation in every cycle, meaning ovulation could still occur)
What are the possible effects of combined oral contraception despite its principles? (2)
Follicular activity possible in some
Breakthrough bleeding in some
What are the benefits of combined oral contraception? (9)
Reliable
Safe
Unrelated to coitus
Woman in control
Rapidly reversible
Halves the risk of ovarian cancer
Halves the risk of endometrial cancer
Helps with endometriosis, premenstrual syndrome, dysmenorrhoea, and menorrhagia
Can stop periods if taken continuously
What are the cardiovascular risks associated with combined oral contraception? (2)
Arterial: Progestogen (mimics aldosterone), high blood pressure, smoking (age >35)
Venous: Oestrogen (increases synthesis of clotting factors in the liver Factor II (prothrombin), Factor VII, Factor X, and Factor XII), VTE (venous thromboembolism), clotting disorders (DVT, PE, migraine)
What are the neoplastic risks associated with combined oral contraception? (3)
Breast cancer: No significant risk
Cervical cancer: No significant risk
Liver cancer
What are the gastrointestinal and hepatic risks of combined oral contraception? (2)
Gastrointestinal: Effects on COH (Carbohydrate)/insulin metabolism, potential weight gain (Progestins/synthetic progestogens, can lead to insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood sugar. Progestogens can also cause appetite changes, stimulating hunger)
Hepatic: Hormone metabolism, congenital non-haemolytic jaundices (RARE), gallstones (COCs increase cholesterol content in bile, which may promote the formation of gallstones)
What are the dermatological and psychological risks of combined oral contraception? (2)
Dermatological: Chloasma (brownish or grayish-brown patches, due to increased melanin production, estrogen stimulates melanocytes), acne, erythema multiforme (target-like lesions)
Psychological: Mood swings, depression, changes in libido
What are drugs that induce liver metabolism and reduce hormone levels in combined oral contraception? (11)
Griseofulvin
Barbiturates
Lamotrigine
Topiramate
Carbamazepine
Oxcarbazepine
Phenytoin
Primidone
Rifampicin
Modafinil
Certain antiretrovirals
What should you do if taking any of these drugs while on COCP? (1)
Always check any new drug if on COCP!
What are the pill rules for combined oral contraception (COCP)? (5)
Start the 1st packet on the 1st day of a menstrual period
Take 21 pills and stop for a 7-day break (PFI)
Restart each new packet on the 8th day (same)
Do not start new packets late
If pills are missed in the 1st 7 days, use condoms
What should be done if pills are missed in the last 7 days of the COCP? (1)
No PFI (period free interval)
What is the procedure for annual BMI and BP monitoring in COCP users? (1)
Annual BMI and BP checks are recommended
What are the characteristics of the combined vaginal contraceptive method? (4)
Same as COCP except vaginal delivery (ring) for 21 days
Remove for 7 days
Advantage: Don’t have to take it every day
Disadvantage: Don’t have to take it every day!
Releases Hormones: The ring contains ethinyl estradiol (a form of estrogen) and etonogestrel (a form of progestogen). These hormones work together to prevent pregnancy by:
Preventing ovulation: The hormones stop the ovaries from releasing eggs (ovulation).
Thickening cervical mucus: The progestogen thickens the mucus in the cervix, making it more difficult for sperm to enter the uterus.
Thinning the endometrium: The estrogen and progestogen alter the lining of the uterus, making it less suitable for implantation in case fertilization occurs.
What are the default methods of Progestogen-Only contraception? (2)
Implants: Nexplanon (ETN), Norplant (LNG)
Hormone-releasing IUCD: Mirena IUS (LNG), Jaydess IUS (3 years), Kyleena IUS (4 years)
What are the user-dependent methods of Progestogen-Only contraception? (2)
POPs (Progestogen Only Pills):
Desogestrel (Cerazette)
Norethisterone
Ethynodiol diacetate
Levonorgestrel
Norgestrel
What are the injectable methods of Progestogen-Only contraception? (2)
Depo Provera (MPA) (12-weekly)
Noristerat (NET)
How do Progestogens act in contraception? (5)
On the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus
On the endometrium
On the fallopian tubes
On cervical mucus
On the HPO axis (hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis)
What are the basic principles of Progestogen-Only Methods? (5)
Delivery method is user choice
Systemic side effects (e.g., headache, bloating, acne) depend upon systemic absorption
Effect on cervical mucus and endometrium is highly reliable
Effect on HPO (Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian axis) suppression is less reliable—some women may still ovulate
Irregular bleeding is a potential issue for all methods
Why is Desogestrel becoming widely used in Progestogen-Only Methods? (5)
As effective as combined oral contraception (COCP)
No oestrogen—suitable for contraindicated groups (e.g., breastfeeding women)
More favorable side effect profile compared to older POPs
Bleeding is as predictable as COCP, though probably not quite as good
12-hour window for pill-taking
How do Copper-bearing IUCDs work? (2)
Destroy spermatozoa
Prevent implantation by causing an inflammatory reaction and prostaglandin secretion, as well as a mechanical effect
What are the types of Copper-bearing IUCDs and their duration of use? (5)
Ortho T 380 – 8-12 years
Multiload 375 – 5 years
Multiload 250 – 5 years (Standard & Short)
Nova T 380 – 5 years
Nova T 200 – 5 years
GyneFix (IUI) – 5 years
What are the types of Hormone-bearing IUCDs and their duration of use? (3)
Mirena (IUS) – 8 years
Jaydess – 3 years
Kyleena IUS – 4 years
What are the benefits of IUCDs? (6)
Non-user dependent
Immediately and retrospectively effective
Immediately reversible
Can be used long-term
Extremely reliable
Unrelated to coitus and free from serious medical dangers
What are the disadvantages of IUCDs? (5)
Requires fitting by trained medical personnel
Fitting may cause pain or discomfort
Periods may become heavier and more painful
Does not offer protection against infection
Threads may be felt by the male during intercourse
What are the risks associated with IUCDs? (4)
May be expelled due to contraction of the uterus
Uterus may be perforated (very rare) through incorrect insertion
Miscarriage if a pregnancy occurs with the IUCD in place, IUCD may interfere with the fertilised egg
Potential for ectopic pregnancy
What are the absolute contraindications for using an IUCD? (4)
Current pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Suspected or known pregnancy
Unexplained vaginal bleeding
Abnormalities of the uterine cavity
What are the relative contraindications for using an IUCD? (6)
Nulliparity (no children)
Past history of pelvic inflammatory disease
Not in a mutually monogamous relationship
Menorrhagia (heavy periods) / Dysmenorrhoea (painful periods)
Small uterine fibroids
Not recommended in certain cases
What are the advantages of male condoms? (5)
Man in control
Protects against STIs
No serious health risks
Easily available (e.g., free at Family Planning clinics)
Does not require medical supervision
What are the advantages of female condoms? (5)
Woman in control
Protects against STIs
Can be inserted in advance and left inside after erection is lost
Not dependent on male erection to work
Gives the woman more control over contraception
What are the disadvantages of male condoms? (7)
Last-minute use
Needs to be taught (proper usage)
May cause allergies
May cause psychosexual difficulties
Higher failure rate among some couples
Oily preparations can damage rubber
Not always reliable if used incorrectly
What are the disadvantages of female condoms? (5)
Obtrusive and uncomfortable for some users
Expensive compared to other options
Can be messy
May rustle during sex, causing discomfort
Uncertain failure rate
What are the characteristics of diaphragm caps? (5)
Made of latex
Fit across the vagina
Available in sizes 55 – 95mm in 5mm increments
Must be used with spermicide
Should be left in for at least 6 hours after sexual intercourse
What are the characteristics of suction (cervical) caps? (4)
Made of plastic
Suction to cervix or vaginal vault
Available in different sizes
Must be used with spermicide and left in for 6 hours or more
What are the advantages of diaphragm caps? (4)

Woman in control
Can be inserted in advance
Offers protection against cervical dysplasias
Perceived as "natural"
What are the advantages of suction caps? (4)
Suitable for women with poor pelvic muscles
No issues with rubber allergies
Very unobtrusive
Woman in control
What are the disadvantages of diaphragm caps? (5)
Needs to be taught (proper usage)
Messy to use
Higher failure rate than most other methods
Higher risk of UTIs
Higher risk of candidiasis (yeast infections)
What are the disadvantages of suction caps? (4)

Needs an accessible and suitable cervix
Higher failure rate than diaphragm caps
Not easy to find an experienced teacher
Requires proper fit and use
What is the basis of fertility awareness in predicting ovulation? (3)
Ovulation typically occurs 14 days before the start of the next period
Sperm can survive for 5 days in the female reproductive tract
The ovum can survive for 24 hours after ovulation
What is the journey of an ovum after fertilization? (3)
The ovum is fertilized in the fallopian tube
It takes 4 days to reach the uterus
The fertilized ovum implants in the uterus
What changes in the body are related to fertility around ovulation? (2)
Cervical mucus becomes more receptive to sperm around ovulation
Intercourse should be timed to the pre-ovulatory phase to conceive
What are the methods used in natural family planning? (6)
Temperature tracking
Rhythm method
Cervix position
Cervical mucus observation
Persona method (device for fertility tracking)
Lactational amenorrhoea (LAM)
What are the advantages of fertility awareness? (5)
Non-medical method
Can be used in low-resource settings (e.g., third-world countries)
Allowed by the Catholic Church
Can strengthen the bond between partners through understanding
Requires no medication or devices
What are the disadvantages of fertility awareness? (5)
Failure rate is heavily user-dependent
Requires skilled teaching to be effective
May require cooperation and communication between partners
Can limit sexual activity
Can cause strain in relationships due to restricted sexual activity
What is the mechanism of action of postcoital pills in emergency contraception? (4)
Postpones ovulation during the first part of the cycle
May act by preventing implantation during the second part of the cycle
Prevents 3 out of 4 pregnancies with Schering PC4
Prevents 7 out of 8 pregnancies with Levonelle
What are the types of postcoital pills used for emergency contraception? (3)
Schering PC4 – prevents 3 out of 4 pregnancies
Levonelle – prevents 7 out of 8 pregnancies
ellaOne (ulipristal) – similar to Levonelle in efficacy
How effective is the copper-bearing IUCD for emergency contraception? (2)
Can be used up to 5 days after unprotected sexual intercourse (UPSI) or presumed ovulation
Failure is extremely rare
What are the mechanisms of action of the copper-bearing IUCD in emergency contraception? (3)
Kills sperm during the first part of the cycle
Prevents implantation during the second part of the cycle
Highly effective in preventing pregnancy when used after UPSI
What is the composition of Levonelle 2 for emergency contraception? (2)
Consists of 2 tablets, each containing 750 micrograms of Levonorgestrel
One dose is 1.5mg
What are the key points about the PC4 postcoital pill for emergency contraception? (4)
No longer available, but some people self-administer it
Lower failure rate if taken within the first 24 hours
Causes nausea and vomiting in many women
Contraindicated during a focal migraine attack
How does Levonelle 2 compare to PC4 for emergency contraception? (3)
Levonelle 2 has a lower failure rate in the first 24 hours
Very little nausea compared to PC4
Only contraindicated in women taking potent liver enzyme medications (e.g., anti-TB drugs)
What is the mechanism and effectiveness of ellaOne for emergency contraception? (4)
Contains Ulipristal acetate, a selective progestagen receptor modulator (SPeRM)
Can be used up to 120 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse (UPSI)
Has similar pregnancy prevention rates as Levonelle
May have a slightly higher side effect profile, mainly gastrointestinal symptoms
What is the effectiveness of Levonelle 2 for emergency contraception at different time intervals? (3)
Up to 24 hours: 95% effective
25 to 48 hours: 85% effective
49 to 72 hours: 58% effective
What is the effectiveness of Schering PC4 for emergency contraception at different time intervals? (3)
Up to 24 hours: 77% effective
25 to 48 hours: 36% effective
49 to 72 hours: 31% effective
What are the key points regarding the choice and use of contraceptives? (5)
There are many contraceptive choices available
The best choice depends on age, future pregnancy wishes, and medical history
All contraceptives have pros and cons
The real failure rates differ from perfect use rates
Contraception is one of the most important pillars of women’s health provision worldwide