___ compounds completely dissociate into ___ to create ___ solutions that ___
- Ionic
- Single ions
- Electrolyte
- Can conduct electricity
___ do not dissociate, instead they dissolve as ___ in water to create ___ solutions that ___
- Molecular compounds
- Intact molecules
- Non-electrolyte
- Do not conduct electricity
In a solution, ___ is the smaller amount and ___ is the larger amount
- Solute (minor)
- Solvent (major)
A common way to express solution concentration is
Molarity (M) = amount of solute in mol. ÷ volume of solution in L
Dilution formula
M1V1 = M2V2
How do you determine moles of solute using molarity and volume
Mol. = M · V
Use concentration and volume to find moles of 2nd substance
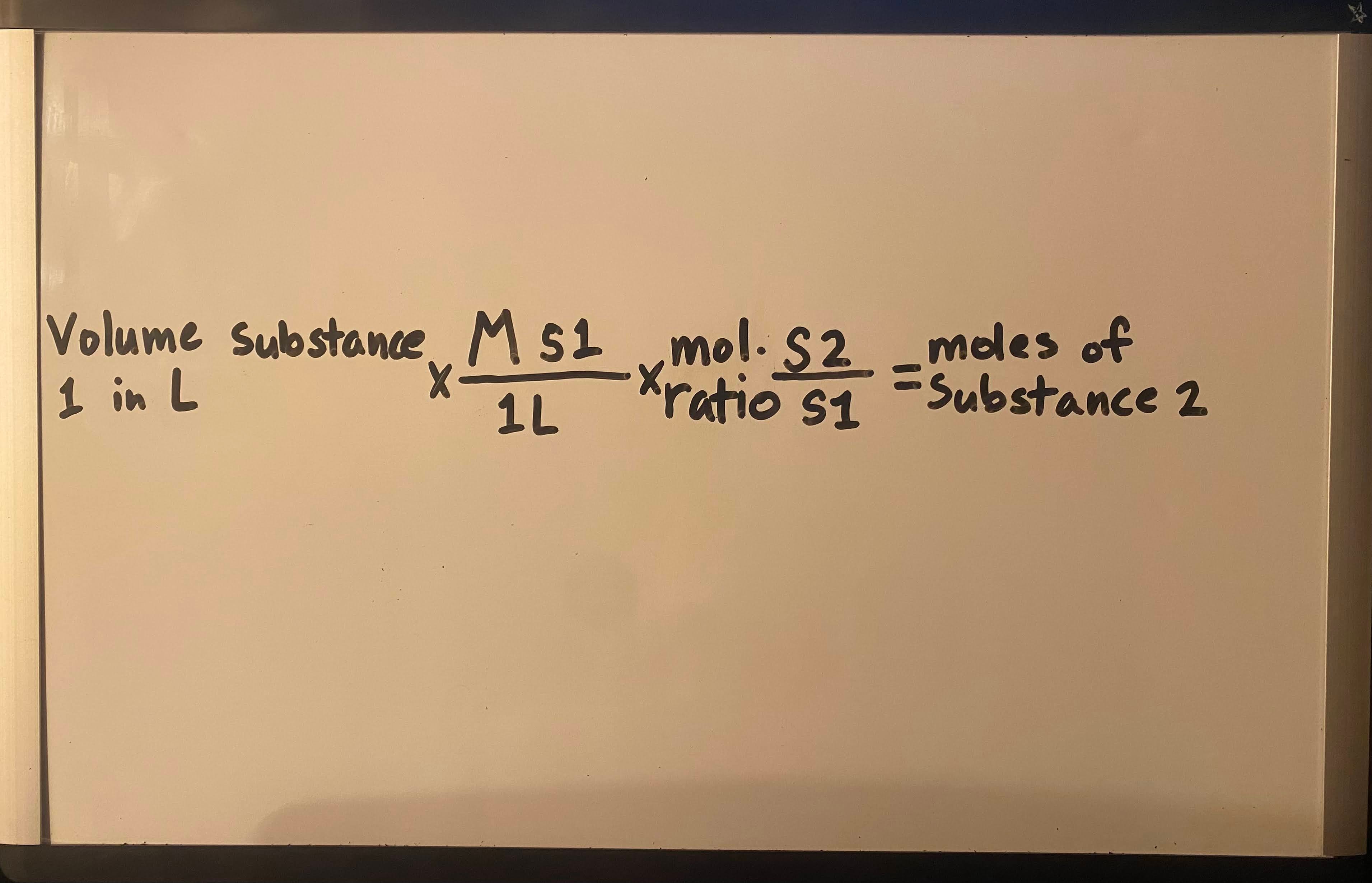
Moles = M · V
Substances that completely dissociate when dissolved in water are ___
Strong electrolytes
Substances that only partially dissociate when dissolved in water are ___
Weak electrolytes
What are acids
Molecular compounds that ionize to form (release) H+ ions when they dissolve in the water
The total molarity of a solution
When given a molarity (M), apply that value to each atom/molecule/element and add the total together
What does soluble mean
A compound that dissolves in water
What does insoluble mean
A compound that does not dissolve in water
What is solubility (partially) dependent on
- The intermolecular forces of the solute and solvent molecules
- in general, a solute with dissolve in a solvent if they have like intermolecular forces
Polar molecules are more soluble in ___ solvents
Nonpolar molecules are more soluble in ___ solvents
Polar molecules = polar solvents
Nonpolar molecules = nonpolar solvents
Immiscibility
When 2 liquids can't combine to form a homogeneous mixture
miscibility
The ability of 2 liquids to combine and form a homogeneous mixture
Hydrophobic vs hydrophilic
Hydrophobic = nonpolar molecules that do not mix with water
Hydrophilic = polar molecules that do mix with water
What is precipitate
The insoluble compound that forms when 2 aqueous ionic solutions are mixed and produce a solid ionic compound
What are the steps for predicting a precipitation reaction
1) Break down the ions in the reactants and determine their charges
2) switch the cations and anions of the reactants
3) Use the solubility table to determine if the new ionic compounds will form a solid product
4) Denote any solid products as (s) and any aqueous products as (aq)
5) balance the equation if needed
Use concentration and moles to find volume of 2nd substance
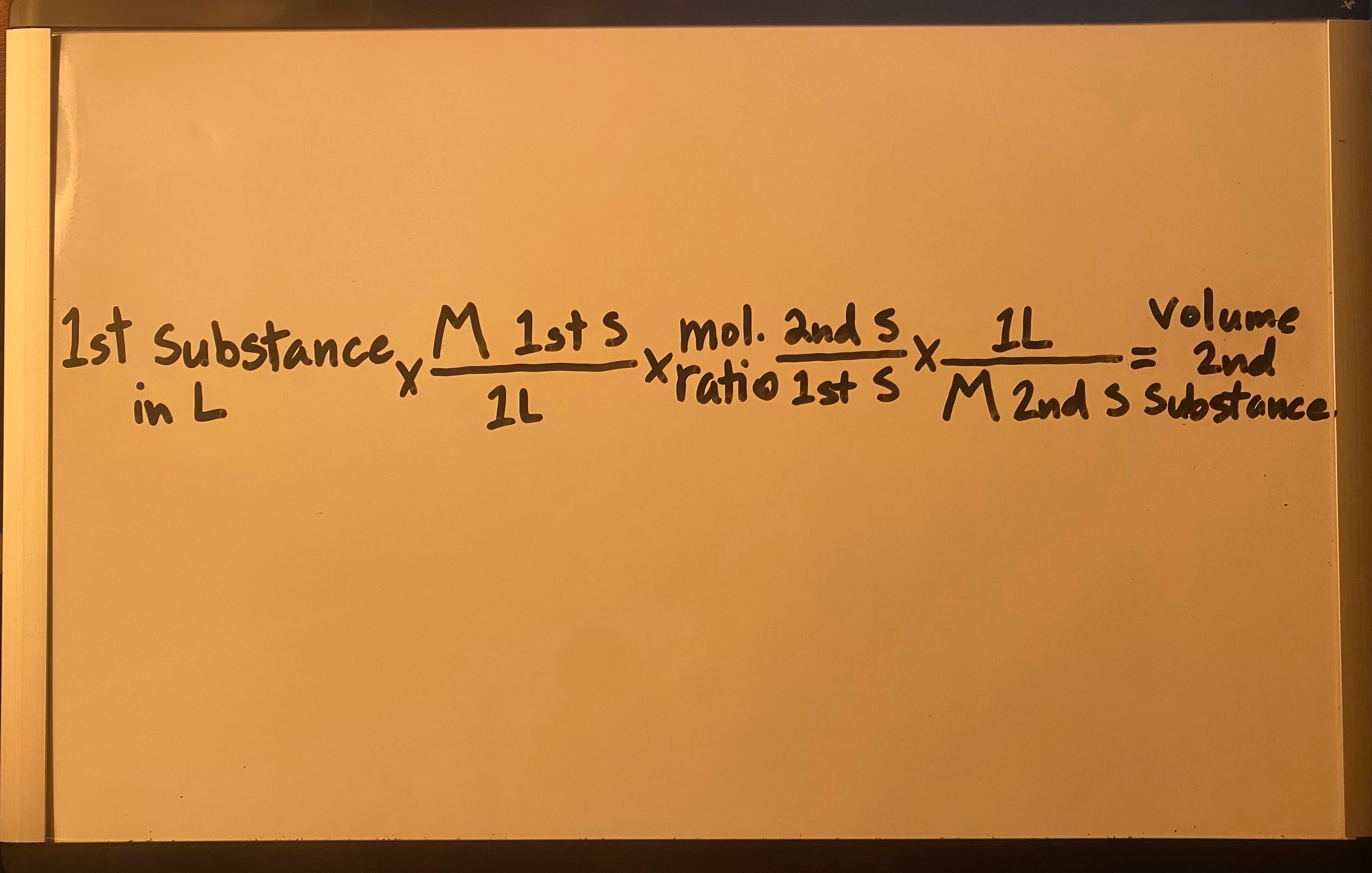
Moles ÷ M = V
Use moles and volume to find concentration of 2nd substance
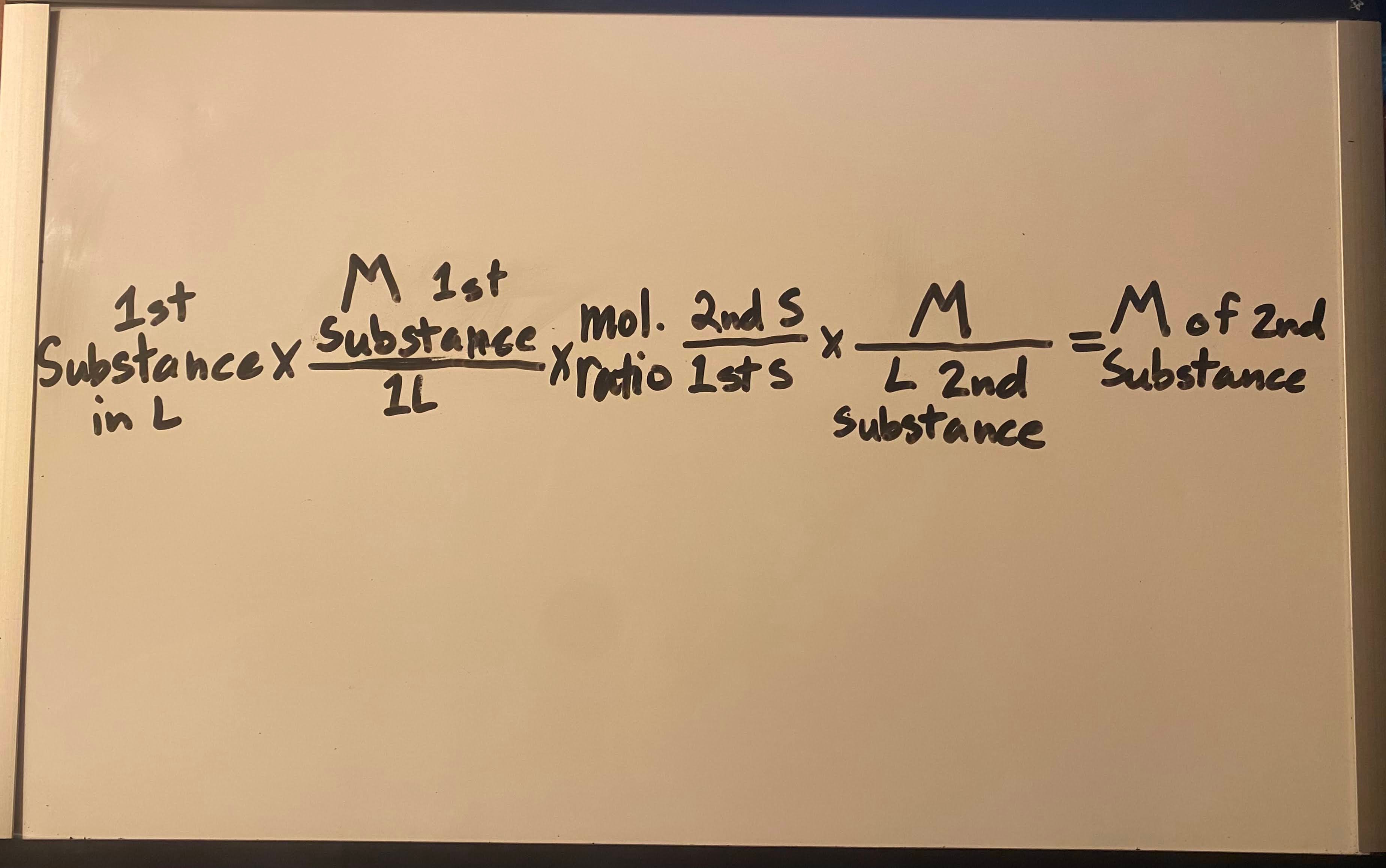
Moles ÷ V = M
Acids are ___ that form ___ when dissolved in water
- Molecular compounds
- H+ ions
Bases are ___ OR ___ that form ___ when dissolved in water
- Molecular compounds
- Ionic compounds
- OH- ions
Neutralization reaction (is complete when ___)
In a solution H+ combines with OH- to make water
- Is complete when moles of acid = moles of base
Molecular equation shows the ___
Complete neutral formula for each compound in a reaction
Complete ionic equation shows ___
All ions present in a reaction
Net ionic equation shows ___
Only the species that actually change in a reaction
Titration reaction (allows us to find ___)
A substance of known concentration is reacted with a substance of unknown concentration
- Allows us to find the unknown concentration of the 2nd substance)
Equivalence point
The point in titration when the moles of H+ = moles of OH-
What is a binary acid and how do you name one
Hydrogen and a nonmetal
Hydro + Base name of nonmetal - ic acid
What is an oxyacid
Hydrogen and an oxyanion (anion of nonmetal + oxygen)
How do you name an oxyanion that ends with 'ate'
Base name of oxyanion - ic acid
How do you name an oxyanion that ends with 'ite'
Base name of oxyanion - ous acid
Redox reaction
When electrons transfer from one reactant to another in a chemical reaction
Oxidation is the ___ of electrons
Loss of electrons
Reduction is the ___ of electrons
Gain of electrons
The ___ agent causes the oxidation of the other substance and is the agent that is ___
- Oxidizing agent
- The oxidizing agent is reduced
The ___ agent causes the reduction of the other substance and is the agent that is ___
- reducing agent
- The reducing agent is oxidized
The oxidation state of free elements are ___
zero
The oxidation state of monoatomic ions is ___
equal to its usual ionic charge
The sum of oxidation states in a neutral molecular compound is ___
zero
The sum of oxidation states in an ionic compound is ___
Equal to its usual ionic charge
In compounds, metals have positive oxidation states that are ___
equal to their usual ionic charge
- Group 1A = +1
- Group 2A = +2
In compounds, nonmetals have oxidation states based on ___
Table 8.3
When assigning oxidation states to nonmetals, what do you do for the separate elements in the compound
- Only use the oxidation state table for the element highest up the table
- Assign an oxidation state of 0 to the element lowest on the table
Steps for identifying an redox reaction
1) Identify the ox state of free elements (reactant side)
2) Identify the ox state of compounds (product side)
3) Identify and label which elements are oxidized/reduced and which are the oxidizing/reducing agent