why is the embryo skeleton made of cartilage?
flexible cartilage matrix allows for mitosis and growth
high water content that resumes original shape after compression
what is the perichondrium
dense irregular CT that surrounds cartilage
vascular and diffuses nutrients to cartilage
what are the cells of the cartilage? what are they encased in?
chondrocytes
lacunae
what are the functions of bones?
support
protection
movement
mineral & growth factor storage
hematopoiesis
what is compact bone?
external layer
what is spongy bone?
internal layer of bone made of trabeculae
what is the outer layer of the periosteum made of?
the inner layer?
what is its function?
dense irregular connective tissue
osteoblasts, osteoclasts
provides anchor for ligaments and tendons
what are bone-forming cells?
osteoblasts
what are bone-destroying cells?
osteoclasts
where is endosteum found?
what is it made of?
the inner layer?
covers trabeculae and lines canals through compact bone
connective tissue
osteoblast, osteoclasts
where is the red marrow in bone?
where is it in childhood?
in adulthood?
trabecular cavities of spongy bone
in childhood the central medullary cavity
in adulthood only the epiphysis
what are osteogenic cells?
mitotic stem cells in periosteum & endosteum
become osteoblasts or stay as stem cells
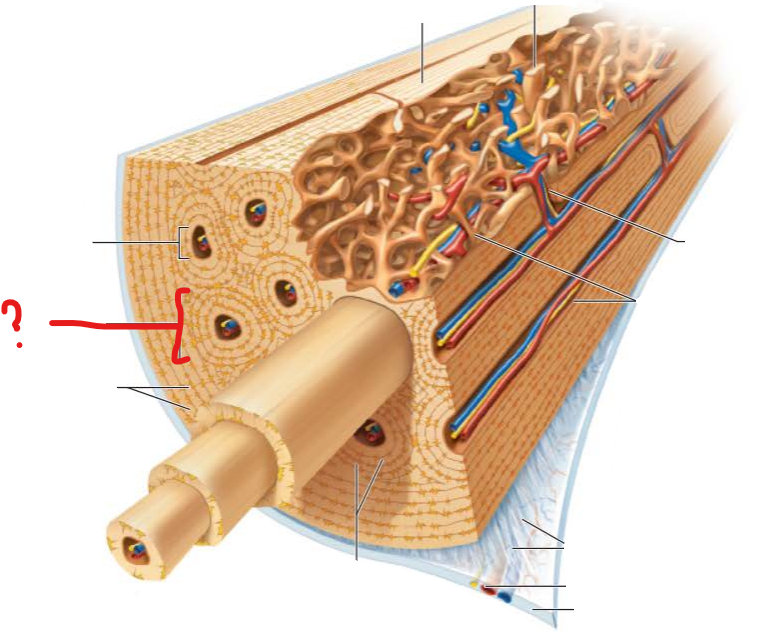
what is this?
osteon
elongated cylinder or group of hollow tubes one inside the other
what is this?
lamella
hollow tubes inside the osteon
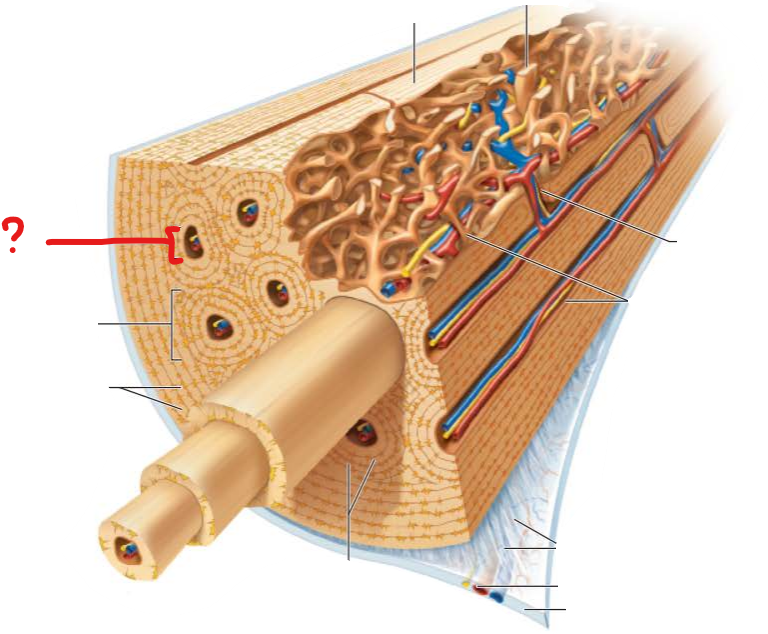
what is this?
central canal
hollow tube through the middle of the osteon containing blood vessels and nerves
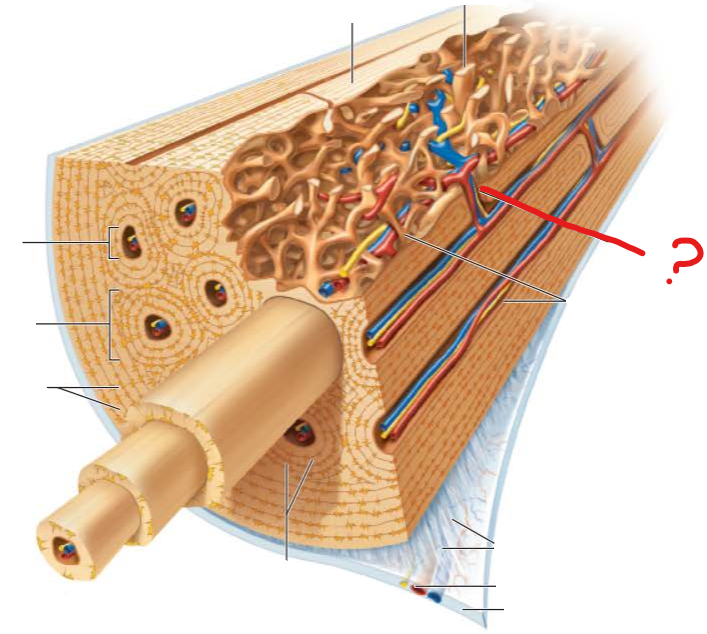
what is this?
perforating canals
runs perpendicular to central canal
connects blood vessels and nerves of periosteum, central canals, and medullary cavity
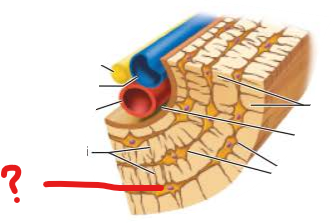
what is this?
osteocytes in lacunae
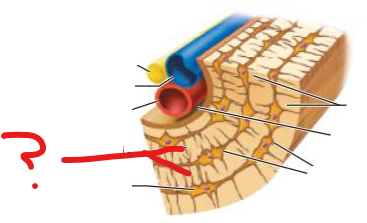
what is this?
canaliculi
tiny canals connect lacunae and central canal
links all osteocytes in osteon
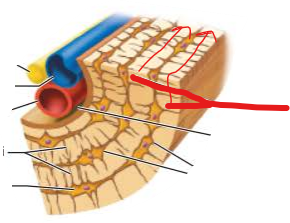
are there osteons in spongy bone? how do osteocytes inside spongy bone receive nutrients?
no
from capillaries in endosteum covering trabeculae
what % of bone is organic? what are the organic components?
35%
osteogenic cells, osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
osteoid
ground substance
collagen fibers
what are sacrificial bonds?
collagen fibers forming crosshatch patterns on the layers of lamellae
bonds between collagen break on impact dissipating energy to resist fracture
what & of bone is inorganic? what are the inorganic components?
65%
calcium
phosphate
crystals packed around collagen
explain why bone is durable and strong but not brittle.
the combination of organic and inorganic elements
in human embryo, before 8 weeks, what does the human skeleton consist of?
fibrous membrane
hyaline cartilage
what is intramembranous ossification? what does it form?
bone from fibrous membrane
forms skull bones and clavicle
what is endochondral ossification
bone from hyaline cartilage
forms all bones except skull bones and clavicle
how do long bones grow in length?
interstitial growth of epiphyseal plate cartilage and its replacement by bone
what is interstitial growth?
growth from inside cartilage tissue
responsible for the lengthening of bones
how do long bones grow in thickness?
appositional growth
what is appositional growth?
growth from outside
responsible for the thickening of bones
what is bone remodeling? what does it maintain? what is it controlled by?
simultaneous bone deposition and resorption
maintains appropriate proportions between diaphysis and epiphysis
controlled by mechanical forces and hormones
what regulates bone growth in children?
in puberty?
growth hormone modulated by thyroid hormone
estrogen or testosterone
what does bone homeostasis involve?
remodeling and repair
what is the bone's response to stress?
thicken
develop thicker prominences
rearrange trabeculae
what is osteomalacia?
bones not adequately mineralized
calcium salts not deposited
bones soft and weak
causes pain with weight bearing
what is rickets?
osteomalacia but in children
what is osteoporosis?
bone reabsorbs more than it deposits
causes extreme fragility in the bone
caused by endocrine disorders
not enough calcium in the diet
where can you find osteogenic cells?
what do they become?
periosteum and endosteum
osteoblasts or osteogenic cells
are there osteons in spongy bone? what do the canaliculi connect?
no
osteocytes
how does spongy bone receive nutrients?
capillaries in the endosteum covering trabeculae
when do we form the bony skeleton?
when do we have bone growth?
when does bone remodeling take place?
-in embryo
-birth to early adulthood
-adulthood
describe the formation of the bony skeleton
-pre 8 weeks in embryo skeleton is fibrous membrane and hyaline cartilage
-post 8 weeks
-intramembranous ossification
-endochondral ossification
describe postnatal bone growth
long bones increase length due to interstitial growth from epiphyseal plate
long bones grow in diameter by appositional growth
what is bone remodeling? what two cells perform this?
deposit and resorption of bone
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
why is bone remodeling important?
allows our bones to grow and repair
plays an important role in blood calcium hemostasis
why is blood calcium hemostasis important?
calcium used to transport nerve impulses
calcium used in cell division
calcium used in muscle contraction
calcium used in blood coagulation
what range does calcium blood levels need to be maintained in?
9~11 mg/dl blood
what are the homeostatic consequences of abnormal blood calcium?
neurologic non-responsiveness or hyperexcitability
what are the four classifications of bones?
long bones
short bones
flat bones
irregular bones
what is a sesamoid bone?
give an example
short bone formed in a tendon
patella
what is the diaphysis?
tubular shaft
thick outer layer of compact bone
central medullary cavity
what is the epiphysis?
bone ends
outer compact bone
inner spongey bone
joint surface covered with articular cartilage
epiphyseal line
what is the epiphyseal plate made of?
hyaline cartilage disc
describe the general structure of short, irregular, and flat bones
thin plates of compact bone outside and spongey bone inside
define "diploe"
spongey bone of flat bone
___ of body ________ stores located in ______
99%
calcium
bone